Energy priority routing method based on extended transmission distance and retransmission
A technology of transmission distance and energy, applied in the field of wireless networks, can solve the problem of inability to accurately simulate the working conditions of the physical layer, and achieve the effect of increasing paths, dense topology structures, and increasing transmission distances.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
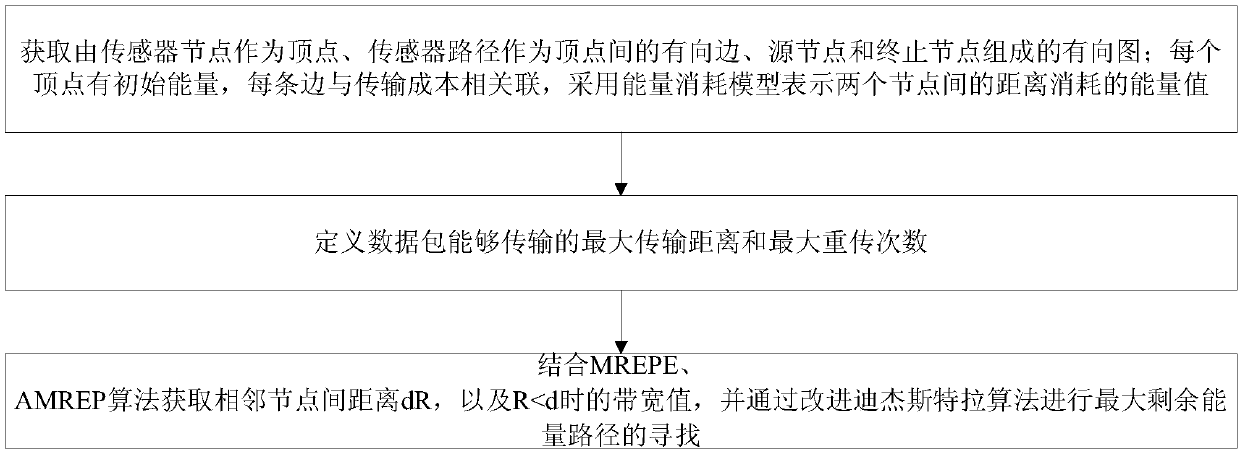
[0046] The embodiment of the present invention proposes a set of low-complexity design schemes, the MREPE algorithm does not increase the complexity of the MREP algorithm, and the AMREP algorithm hardly increases. It is generally considered that a wireless sensor network includes a series of static nodes randomly distributed in a square. Assume that each node knows the distance from itself to other nodes, and in the sensor network, there is a source node and a sink node, except these two nodes are supported by sufficient energy, other nodes are supported by a limited energy Batteries provide energy.
[0047] Each node participating in message forwarding will consume a certain amount of energy. The energy consumption value depends on the number of transmitted packets and the distance transmitted. Before sending a packet, based on the modified MERP algorithm, the source node chooses a reasonable path that can maximize the lifetime of the system. This method converts the maxim...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Combined with the specific calculation formula, Figure 2-Figure 5 1. Examples further introduce the scheme in Example 1, see the following description for details:
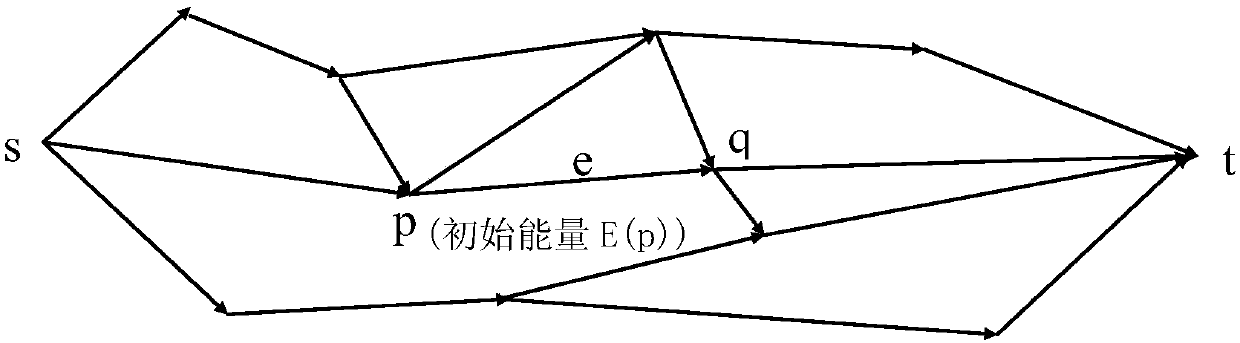
[0066] 201: node definition;
[0067] see figure 2 , the routing problem can be regarded as a directed graph G(N, A) model, N is all the vertices (sensor nodes) in the graph, A is the directed edge (sensor path) between the vertices in the graph, such as (p,q) means from vertex p to vertex q. Two special vertices s and t represent the source node and the destination node, respectively. Each vertex p has an initial energy E(p) ≥ 0, where E(p) is the energy available to the current node p before sending a packet.
[0068] Each edge, such as e=(p,q) and transmission cost S e (S p,q ) contact, S e Indicates the energy consumed by transmitting a packet from vertex p to vertex q along edge e. Thus transmitting a packet along edge e, the node energy E(p) of vertex p will be reduced by S e . Let d repre...
Embodiment 3
[0115] The embodiment of the present invention takes wireless network-based data packet transmission as an example to give a specific implementation mode. Figure 3 to Figure 5 The functions and effects in the embodiments of the present invention are demonstrated, and the specific steps are as follows:
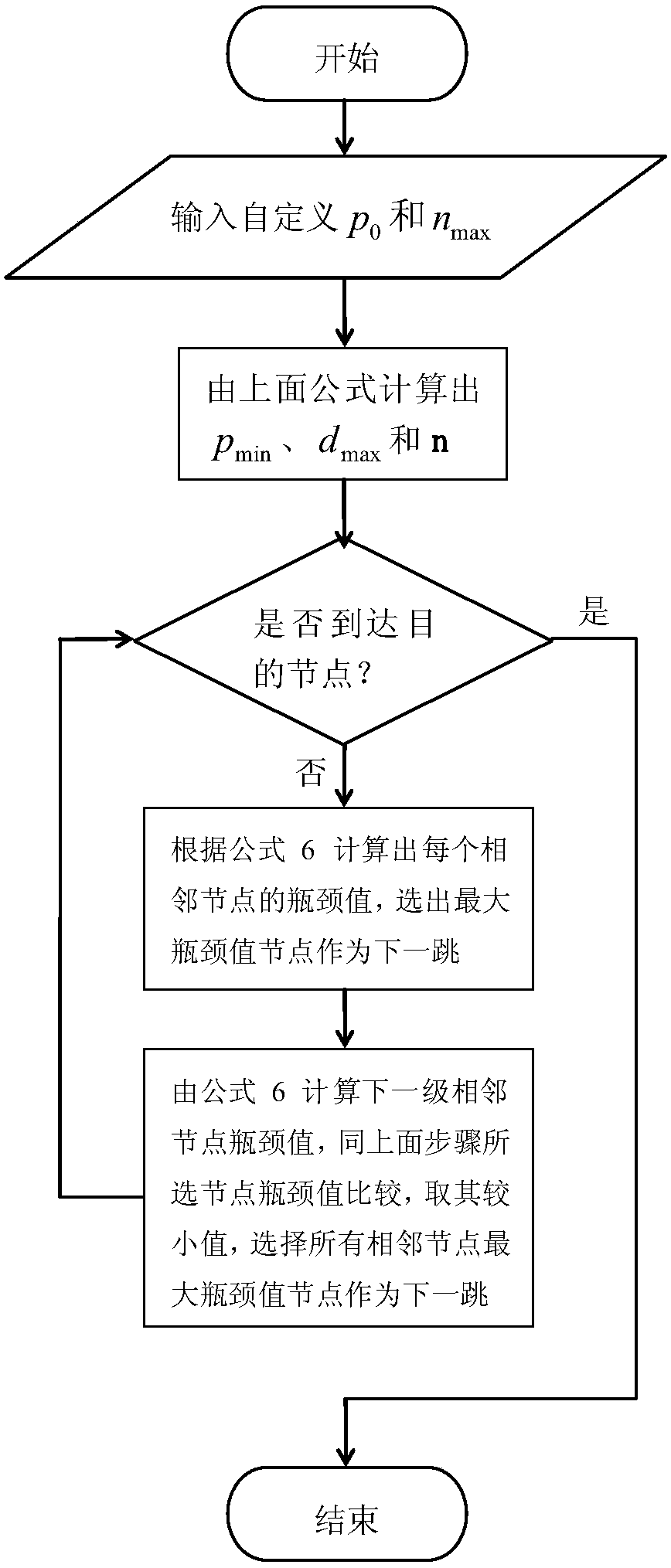
[0116] (1) Maximum transmission distance d max and the determination of the number of retransmissions n;
[0117] Assume that each node knows the distance from itself to other nodes. And in the sensor network, there is a source node and a sink node, except that these two nodes are supported by sufficient energy, and the other nodes are powered by a battery with limited energy. custom p 0 and n max The value of d can be obtained respectively according to the above formula max and n. In subsequent steps, the number of transmission times and the transmission distance of the same data packet on a pair of nodes shall not be greater than n max and d max .
[0118] (2) Combi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com