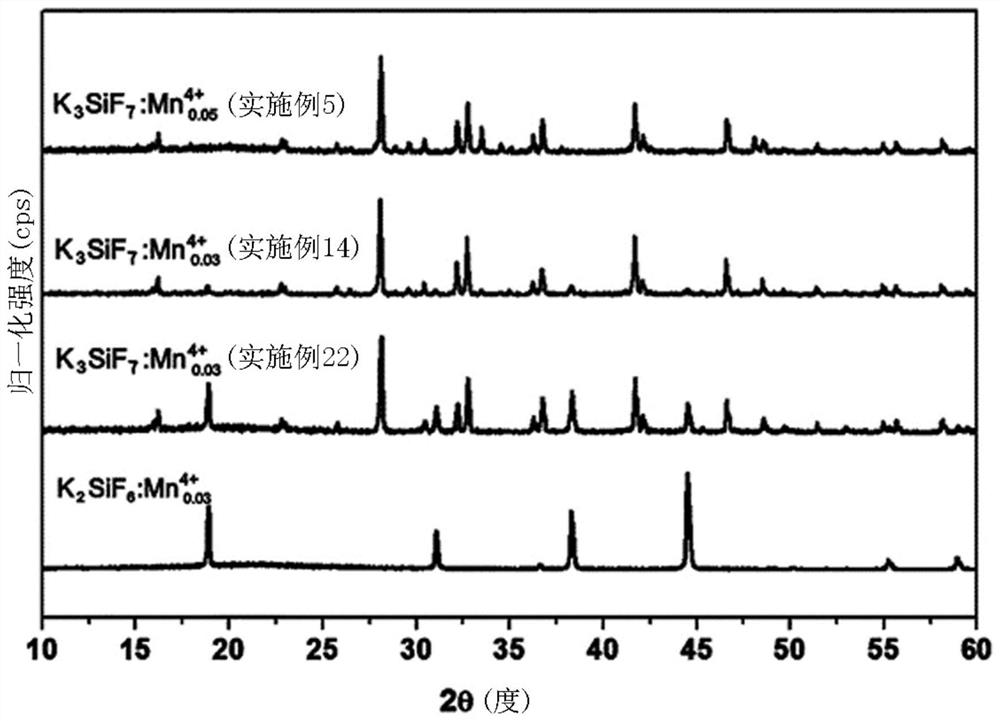
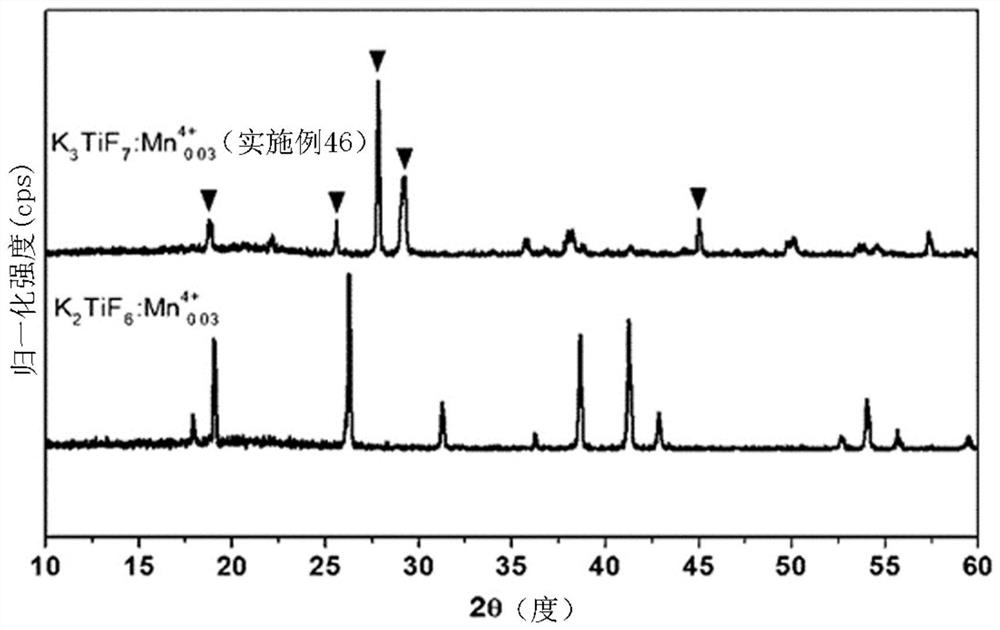
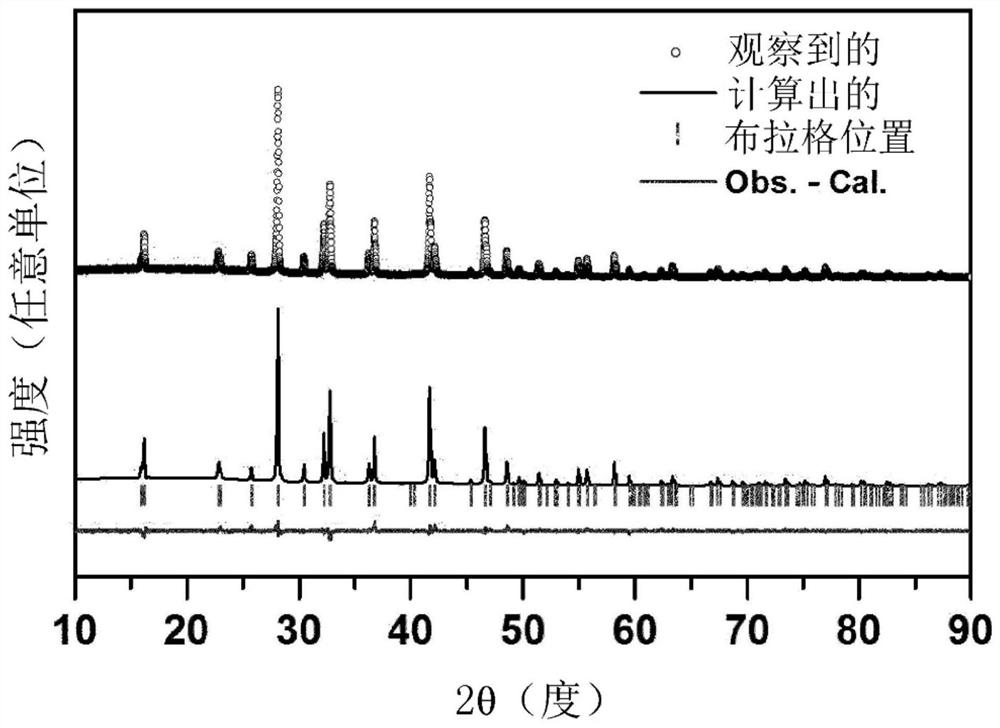
Metal fluoride red phosphor and light emitting element using same
A red phosphorescence and fluoride technology, applied in luminescent materials, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems that have not been proposed, are not suitable for lighting sources and LED color background light sources, and cannot provide color rendering performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0082] As a first preparation method according to the present invention, a method for preparing a metal fluoride red phosphor by solid-state reaction includes:
[0083] (step 1) weighing raw materials containing A precursor, M precursor and manganese (Mn) precursor, and physically mixing the materials;
[0084] (step 2) drying the raw material mixture in an oven at 80 to 150° C.; and
[0085] (Step 3) The dried mixture is heat-treated at 100 to 500° C. under hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas or a gas mixture thereof, thereby preparing a metal fluoride red phosphor having a composition ratio represented by Formula 1.
[0086] The method of preparing phosphor by solid-state reaction can use a phosphor matrix of metal fluoride or a metal fluoride phosphor containing a manganese (Mn) lubricant disclosed in Patent Document 3 as a raw material, and includes physically mixing the raw materials and reacting in hydrogen, The material is heat treated under nitrogen or a gas mixture thereof to...
Embodiment 1 to 50
[0113] Examples 1 to 50: Preparation of Phosphors by Solid State Reaction
[0114] Under the content conditions shown in Table 1 or Table 2 below, the raw materials each containing the A precursor, the M precursor and the manganese (Mn) precursor were respectively weighed and put into a mortar and pestle, to which 5 mL of ethanol and physically mixed for 10 minutes. The raw material mixture was dried in an oven at a constant temperature of 100° C. for 1 hour to completely remove ethanol. The dried raw material mixture was subjected to heat treatment at 400° C. for 30 minutes in a platinum and boron nitride crucible under a reducing atmosphere. At this time, a reducing atmosphere was generated and maintained by supplying a gas mixture of hydrogen (150 mL / min) and nitrogen (450 mL / min). The phosphor obtained by the heat treatment was ground to a particle diameter of 20 μm or less, thereby obtaining phosphor powder.
[0115] Table 1
[0116]
[0117]
[0118]
[0119...
Embodiment 51 to 62
[0121] Examples 51 to 62: Preparation of Phosphors by Liquid Reactions
[0122] The raw materials each containing the A precursor, the M precursor, and the manganese (Mn) precursor were weighed under the content conditions shown in the following Table 3 or Table 4, and dissolved in 100 mL of hydrofluoric acid while stirring (HF). The solution containing the raw materials was stirred well until completely dissolved, and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain a solid. The resulting solid was dried in an oven at a constant temperature of 100° C. for 1 hour to completely remove the remaining hydrofluoric acid. The dried solid was subjected to heat treatment at 400° C. for 30 minutes in a platinum and boron nitride crucible under a reducing atmosphere. At this time, a reducing atmosphere was generated and maintained by supplying a gas mixture of hydrogen (150 mL / min) and nitrogen (450 mL / min). The phosphor obtained by the heat treatment was ground to a particle diameter...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com