Method and device for wireless communication
A wireless communication and soft information technology, applied in the field of communication, which can solve the problems of strict delay requirements and inability to wait for the completion of eMBB service data transmission.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
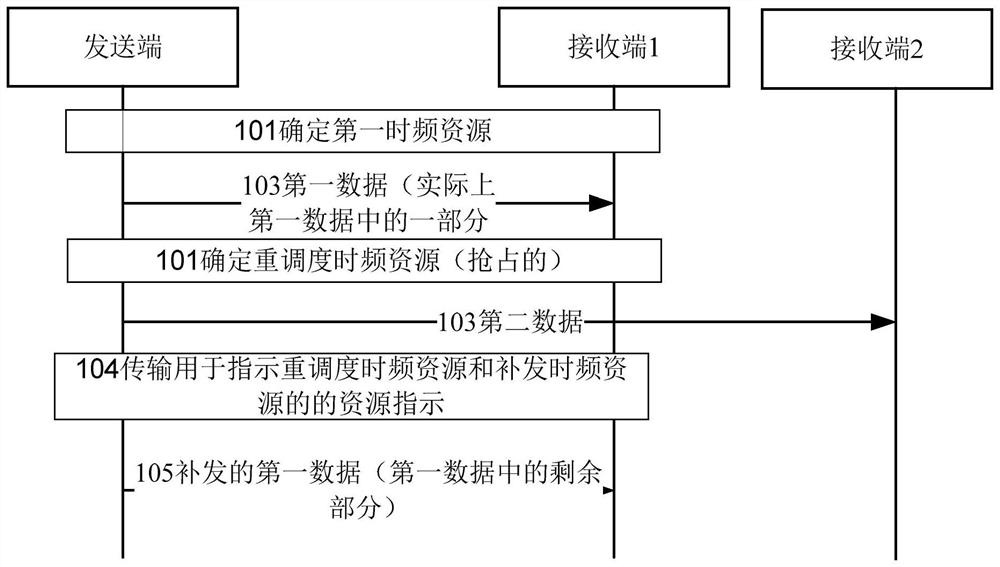
[0076] The mode of embedding the reissued data into the data of the next scheduling unit at the receiving end
[0077] Such as Figures 2A-2E In the schematic diagram of the data structure, an eMBB time slot (for example, the sth slot) sent to the common terminal 102 includes an eMBB control field (eMBB control), an eMBB data field (eMBB data), URLLC mini-slot (URLLC mini-slot). The URLLC mini-slot further includes a URLLC control domain (URLLC control) and a URLLC data domain (URLLC data). Certainly, the URLLC control domain may also be called the PDCCH corresponding to the mini-slot, or mini-PDCCH for short.
[0078] An eMBB control field (eMBB control) and an eMBB data field (eMBB data) are included in a subsequent eMBB time slot (for example, the s+t slot) sent to the common terminal 102 . Wherein, in the eMBBdata in the s+t slot, on the time-frequency resources that are at the same relative position or related (or the same relative shape) as the URLLC mini-slot in the ...
example 2
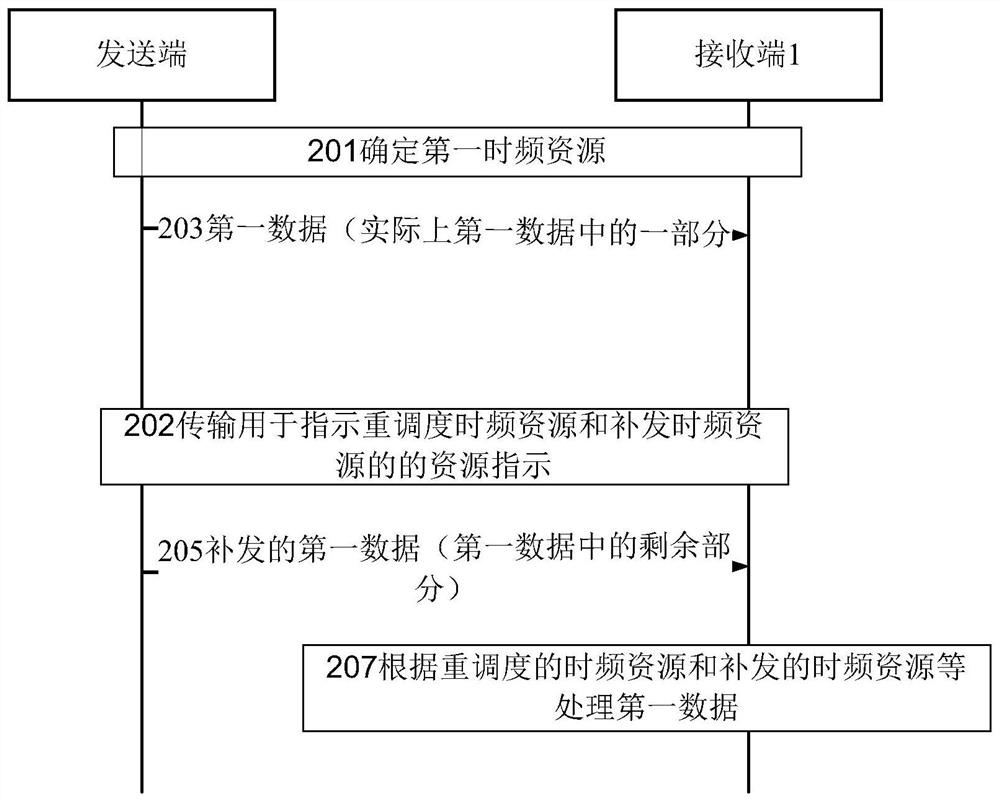
[0088] Example 2. Reference Figure 2B , eMBB frequency selection scheduling
[0089] In the eMBB frequency selection scheduling method, the transmission data for a terminal device (or user) can be scheduled on different frequency domain resources in different slots, such as Figure 2B As shown, the frequency domain resource of slot s+t is different from that of slot s. In the embodiment of the present invention, the relative time-frequency position of the eMBB reissue (retransmission) data in the normally scheduled eMBB slot is the same (or has the same shape) as the relative time-frequency position of the previously punctured URLLC mini-slot. For its content, please refer to Figure 2B And the aforementioned descriptions about the same or related positions.
example 3
[0090] Example 3. Reference Figure 2C , eMBB adaptive scheduling
[0091] In the eMBB adaptive scheduling mode, for different eMBB transmission times, the size of frequency domain resources to be scheduled may be different. Even for reissued (retransmitted) data in a certain eMBB process, if adaptive HARQ is used, the size of the frequency domain resource during retransmission may be different. In this case, starting from the frequency domain start position of the eMBB service, the relative time domain position can also be kept the same.
[0092] exist Figure 2C In the manner shown, the eMBB control channel part in the eMBB slot s+t indicates the time-frequency resource where the reissued (retransmitted) data is located.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com