Call profile adjusting method, application server and storage medium
A technology of application server and scene mode, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of inflexible adjustment of call scene mode, and achieve the effect of improving user experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
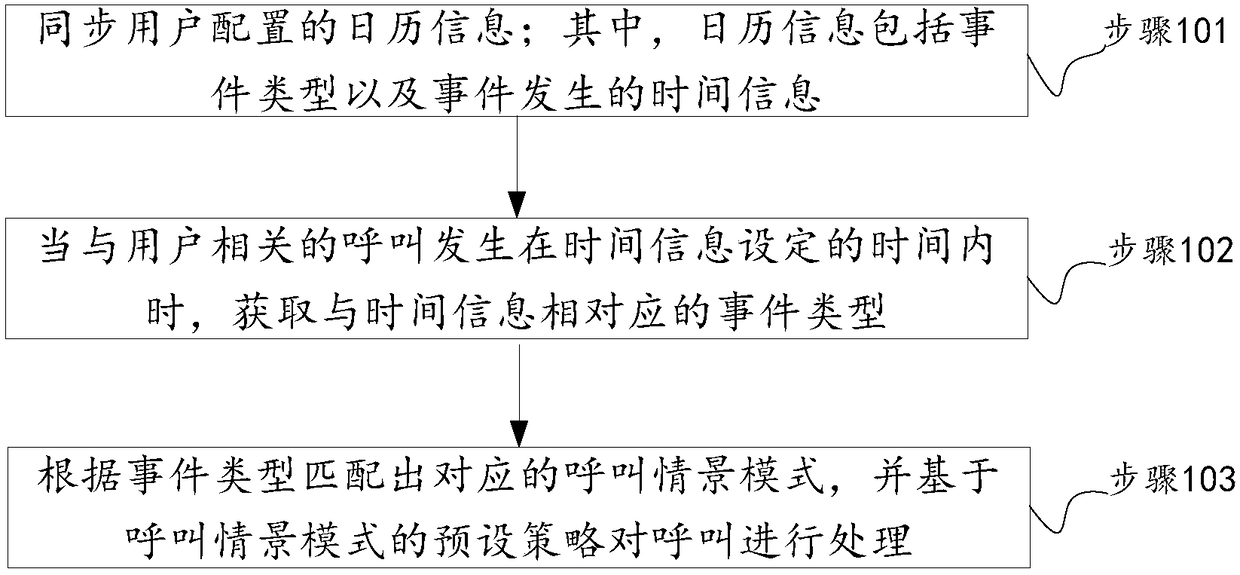
[0047] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
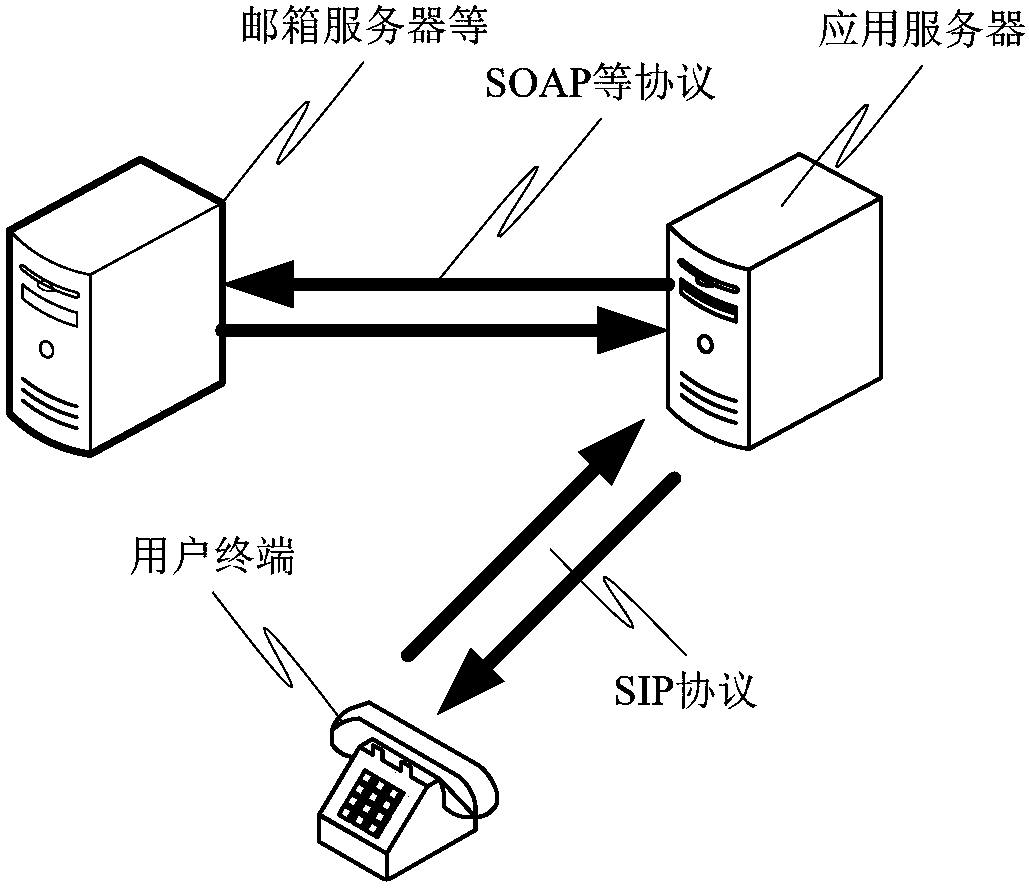
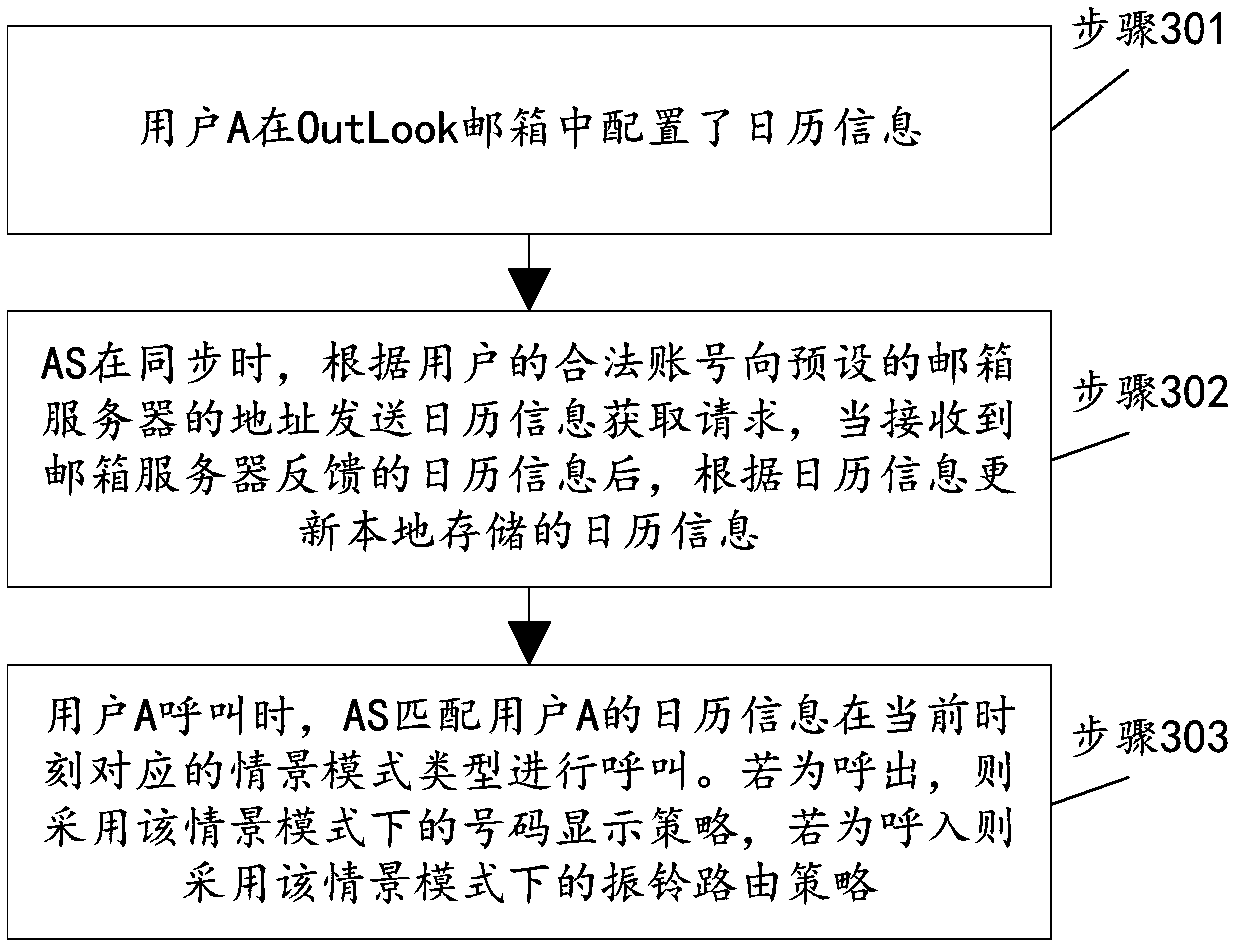
[0048] In work and life, user calendars such as mailbox calendars and mobile phone calendars, schedule reminders and other data play a very important role. Such as mailbox calendar, in mainstream mailboxes such as OutLook, Google, Notes and other mailboxes, user-specific schedule information is created based on the calendar, such as reminders, meetings, training, business trips, vacations, busy, free and other event types, as well as daily, daily The flexible setting of various time types such as week and specific day brings great convenience to people's work and life. Therefore, the calling scene mode adjustment method provided by the present invention can adaptively adjust the required call...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com