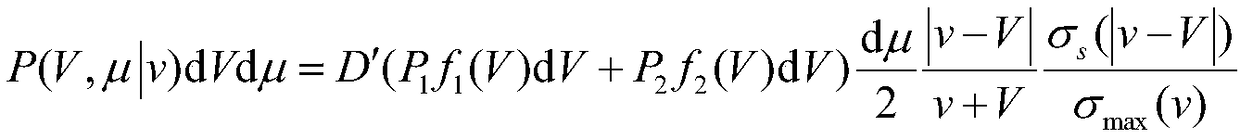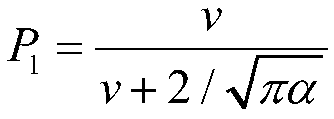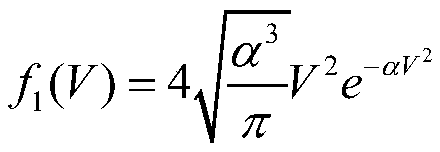A method for calculating the velocity and argument cosine of heavy nuclei in the process of epithermal neutron scattering
A computational method, a technique for thermal neutrons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0027] The existing constant scattering cross-section free gas model assumes that the heavy nuclei are unbound and their velocity distribution conforms to the Maxwell distribution, and assumes that the microscopic elastic scattering cross-section of the nuclide at absolute zero is constant, and P(V,μ|v) represents the relationship with the velocity v The conditional probability distribution function for heavy nuclei that collide elastically with neutrons is as follows:
[0028]
[0029] In the formula:
[0030]
[0031] P 2 =1-P 1
[0032]
[0033]
[0034]
[0035] Among them, P(V,μ|v)dVdμ is the probability distribution function of the velocity of heavy nuclei; D is the ratio of the elastic scattering cross section at absolute zero to the effective elastic scattering cross section; P 1 ,P 2 Respectively, the sampling probability value, f 1 (V), f 2 (V) are functions related to the velocity of heavy nuclei under the corresponding probability; V is the vel...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap