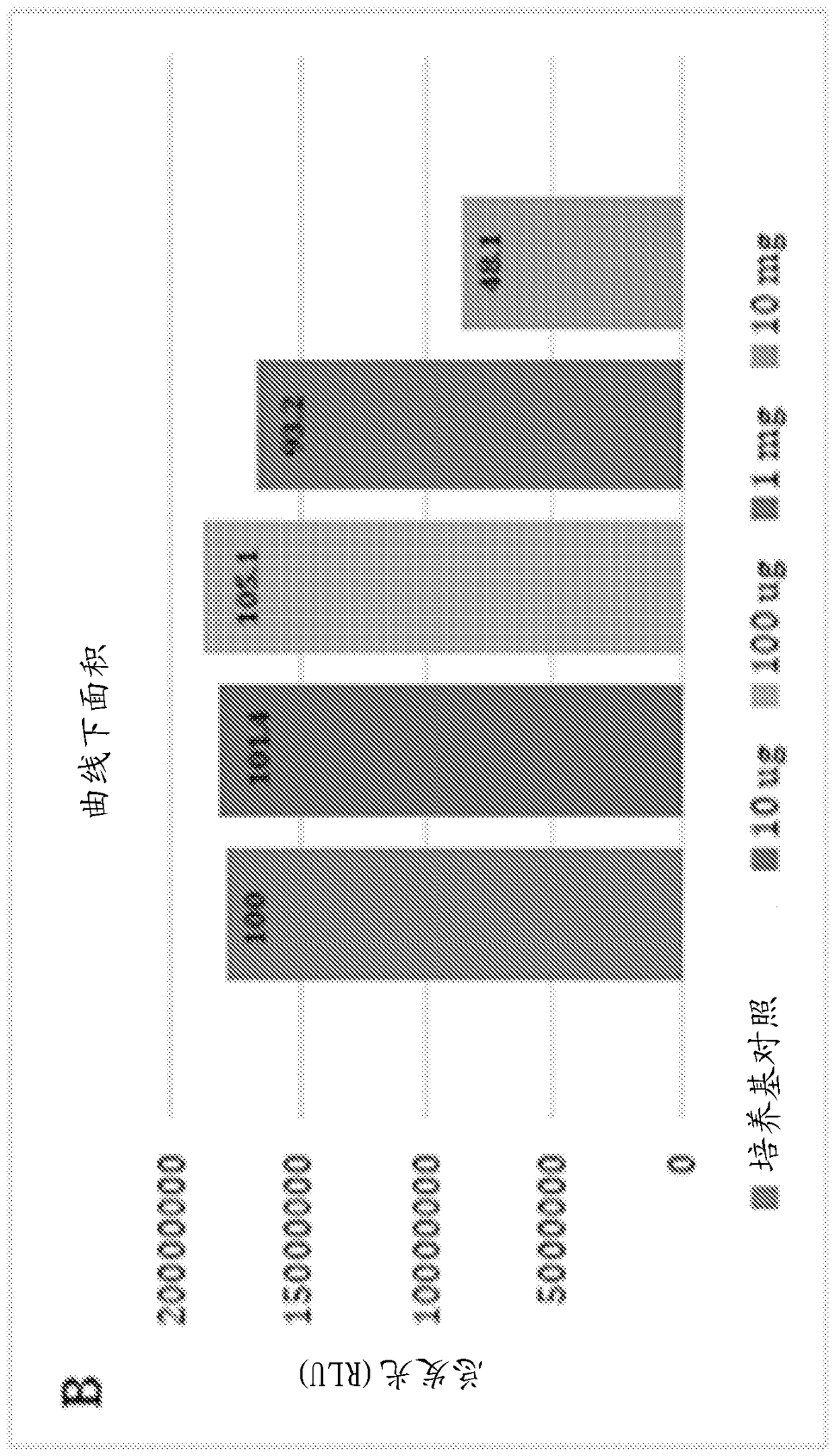
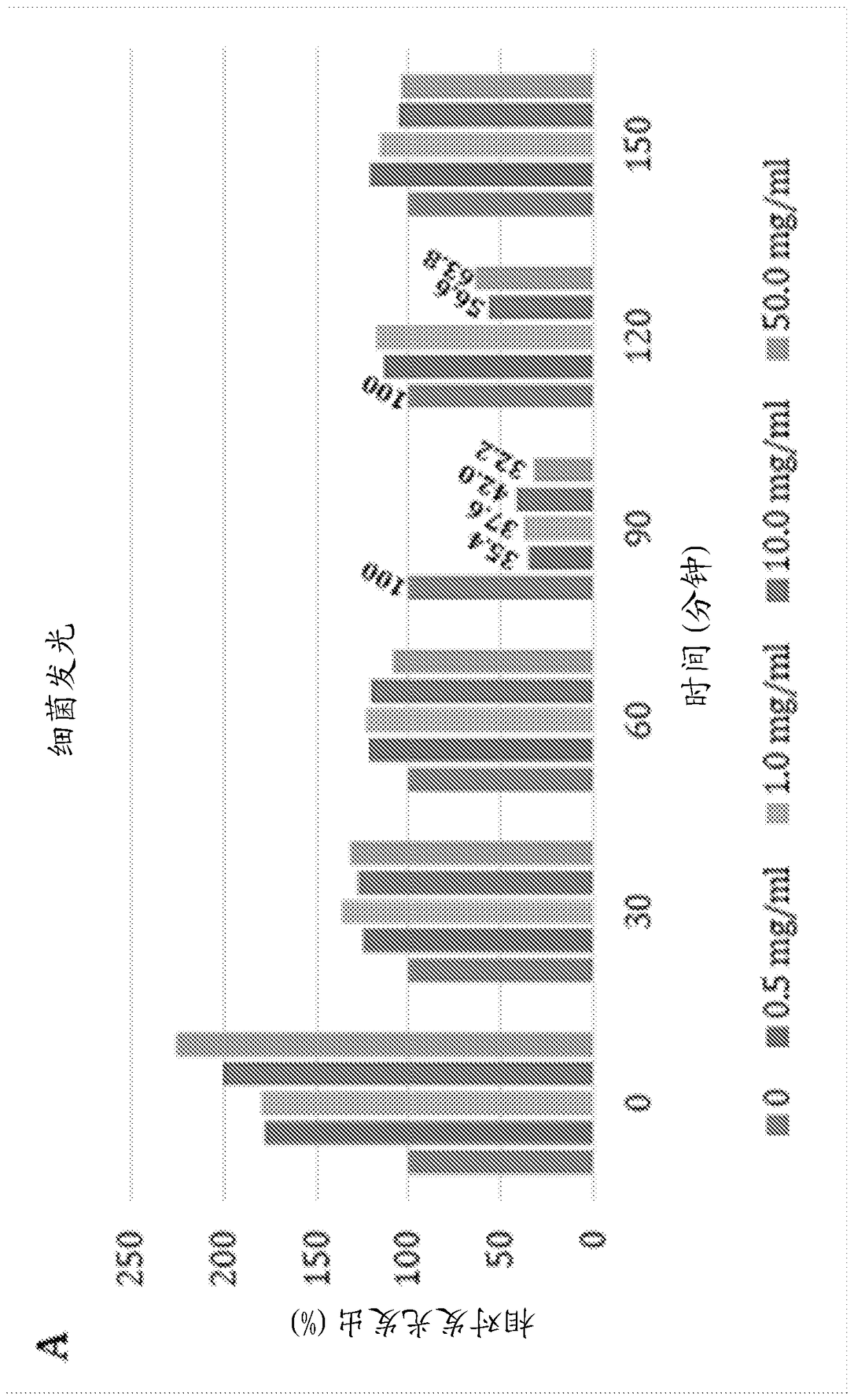
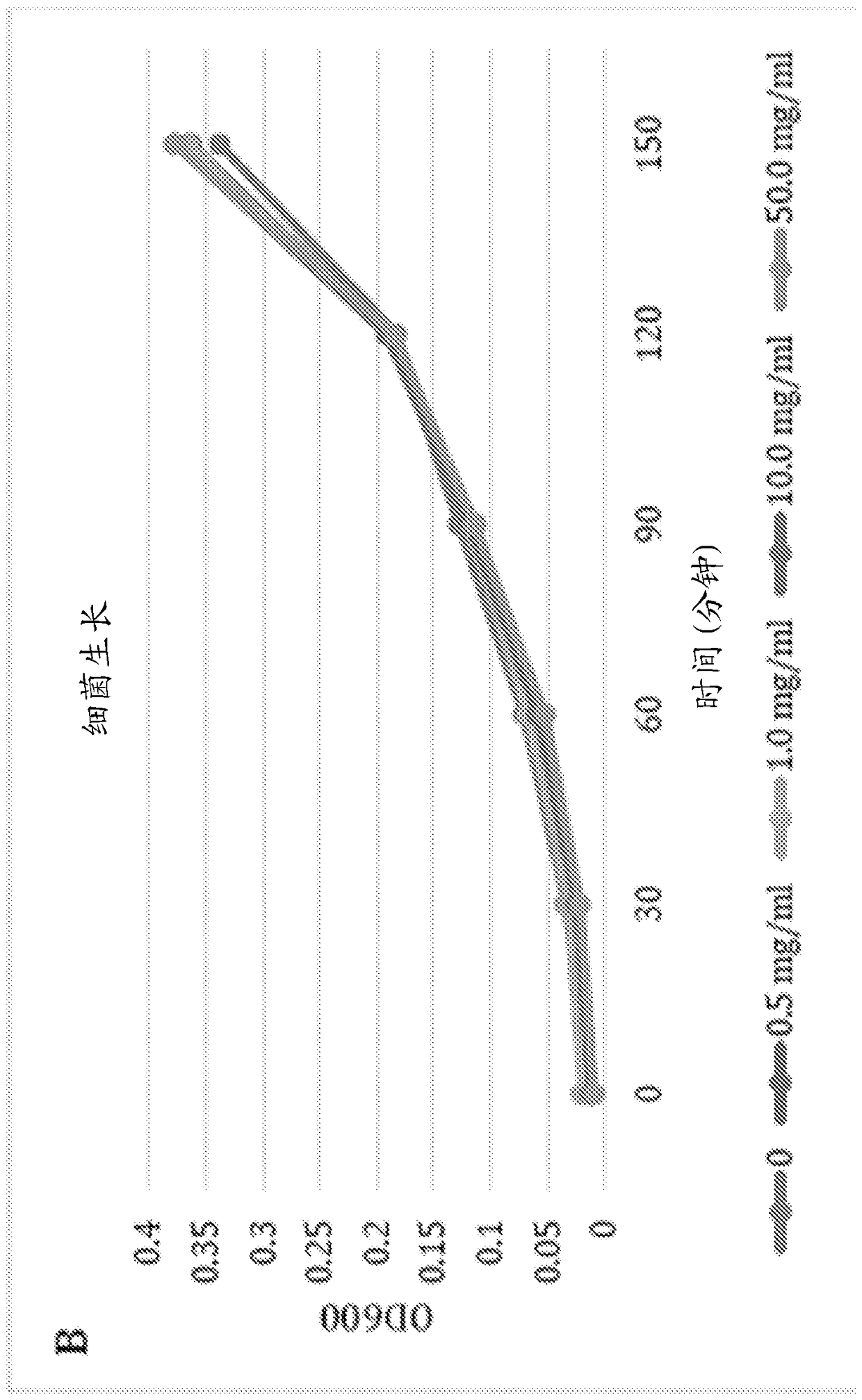
Application of porous materials for bacterial quorum sensing inhibition/disruption
A quorum sensing, bacteria technology, applied in bacteria, applications, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve problems such as destroying bacterial QS signal molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Example 1 Adsorption / catalysis of N-butyryl-DL-homoserine lactone on various adsorbents / catalytic inhibitors.
[0152] An aqueous solution of N-butyryl-DL-homoserine lactone was placed in a vial containing a fixed amount of clay to achieve an adsorbent / catalytic inhibitor / analyte ratio of 15 (mg / mg). The suspension was agitated for 30 minutes at 25°C, followed by centrifugation at 4500 rpm for 30 minutes. The supernatant was removed and analyzed directly with HPLC-DAD using the conditions listed in Table 1.
[0153] Table 1. HPLC-DAD method for quantification of N-butyryl-DL-homoserine lactone.
[0154]
[0155] The performance of different adsorbents / catalytic inhibitors for N-butyryl-DL homoserine lactone is provided in Table 2.
[0156] Table 2. Performance of different sorbents / catalytic inhibitors for the removal of N-butyryl-DL homoserine lactone at a sorbent / catalytic inhibitor / QS analyte ratio of 15 (mg / mg).
[0157] Material
Embodiment 2
[0158] Example 2 N-(3-oxooctanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone adsorption / catalytic.
[0159] A 200 ppm aqueous solution of N-(3-oxoctanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone was placed in a vial containing a fixed amount of clay to obtain a sorbent / catalytic inhibitor / QS analysis of 375 (mg / mg) material ratio. The suspension was agitated at 100 rpm for 15 minutes and centrifuged sequentially at 3,500 rpm for 30 minutes. The supernatant was removed and analyzed directly with HPLC-DAD using the conditions listed in Table 3. Degradation and aggregation products were identified by LC / MS.
[0160] Table 3. HPLC-DAD method for the quantification of N-(3-oxoctanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone.
[0161]
[0162] Table 4 provides the performance of different adsorbents / catalytic inhibitors for the removal of N-(3-oxoctanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone.
[0163] Table 4. Different sorbents / catalyst inhibitors for the removal of N-(3-oxooctanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone at a sorbent / catalyst inhibitor / QS ...
Embodiment 3
[0169] Example 3 Adsorption / catalysis of different adsorbents / catalytic inhibitors by 2-heptyl-3-hydroxyl-4-quinolone (PQS) change.
[0170] A 50% methanol solution containing 100 ppm 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone was placed in a vial with a fixed amount of clay to obtain an inhibitor / analyte ratio of 100 (mg / mg). The suspension was agitated at 100 rpm for 15 minutes and centrifuged sequentially at 3,500 rpm for 30 minutes. The supernatant was removed and analyzed directly with HPLC-DAD using the conditions listed in Table 3.
[0171] Table 6. HPLC-DAD method for quantification of 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone.
[0172]
[0173] The performance of different adsorbents / catalytic inhibitors for 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone is provided in Table 7.
[0174] Table 7. Performance of different clays / modified materials for Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) removal at an inhibitor / QS analyte ratio of 100.
[0175] Material
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com