Sodium chloride-assisted method for growth of multilayer transition metal chalcogenides
A technology of chalcogen compounds and transition metals, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of high growth temperature, uncontrollable layer number, long growth time, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient growth and controllable preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Clean the purchased soda-lime glass (5cm×5cm, thickness 2mm) by placing the soda-lime glass in deionized water (18.2MΩ·cm), acetone (analytical grade) and isopropanol (analytical grade) in sequence. ) for 10 minutes of ultrasonic cleaning, followed by drying with high-purity nitrogen to complete the cleaning. Put the cleaned soda-lime glass on the graphite boat, place a molybdenum foil with the same size as the substrate 10mm above the graphite boat, place them together in a high-temperature tubular reactor, and place elemental sulfur powder at 15cm upstream of the airflow relative to the substrate 150 g, and feed high-purity argon (50 sccm) to flush the reaction chamber for 10 minutes to remove residual air in the chamber. Introduce a certain amount of oxygen (3 sccm) and then start the heating program to heat the reaction chamber. The final temperatures of the sulfur powder and the substrate are 100°C and 750°C respectively, the heating time is 35 minutes, and the tem...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Clean the purchased soda-lime glass (5cm×5cm, thickness 2mm) by placing the glass in deionized water (18.2MΩ·cm), acetone (analytical grade) and isopropanol (analytical grade) in sequence Ultrasonic cleaning was performed for 10 minutes, followed by drying with high-purity nitrogen to complete the cleaning. Place the cleaned soda-lime glass on a graphite boat. Sodium chloride granules were dissolved in ultrapure water to prepare a certain concentration of sodium chloride solution (0.01mmol / L, 0.02mmol / L, 0.03mmol / L, respectively). Immerse the molybdenum or tungsten foil in the solution, take it out slowly after 10 minutes, and let it dry naturally. The molybdenum foil coated with sodium chloride is placed 10mm above the graphite boat, and placed together in a high-temperature tubular reactor, 50g of elemental sulfur powder is placed at 15cm upstream of the airflow relative to the substrate, and high-purity argon gas ( 50 sccm) to flush the reaction chamber for 10 minu...
Embodiment 3
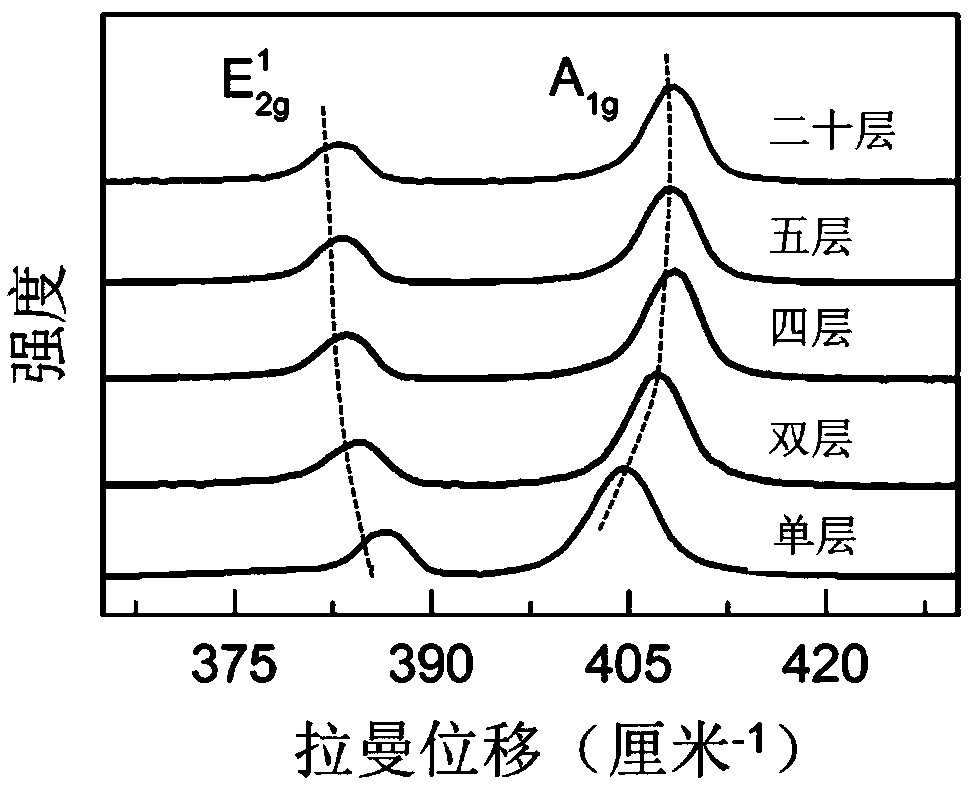
[0041] Raman spectroscopy (excitation wavelength is 532nm) and fluorescence spectroscopy were used to characterize the optical properties of molybdenum disulfide layers with or without sodium chloride assisted growth in Examples 1 and 2. Depend on image 3From the results of Raman spectroscopy, it can be seen that two characteristic peaks of molybdenum disulfide can be observed in samples with different layers, indicating that the synthesized samples are all molybdenum disulfide. As the molybdenum disulfide changes from a single layer to a multilayer, the Raman characteristic peak spacing gradually increases, which is consistent with the Raman change characteristics of molybdenum disulfide with different layers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap