Lock thread
A thread and anti-loosening technology, applied in the direction of threaded fasteners, screws, nuts, etc., can solve the problems of weakened anti-loosening ability, insufficient space, and reduced interference, and achieve good anti-loosening performance, high reliability, and prevent The effect of loose threaded connections
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
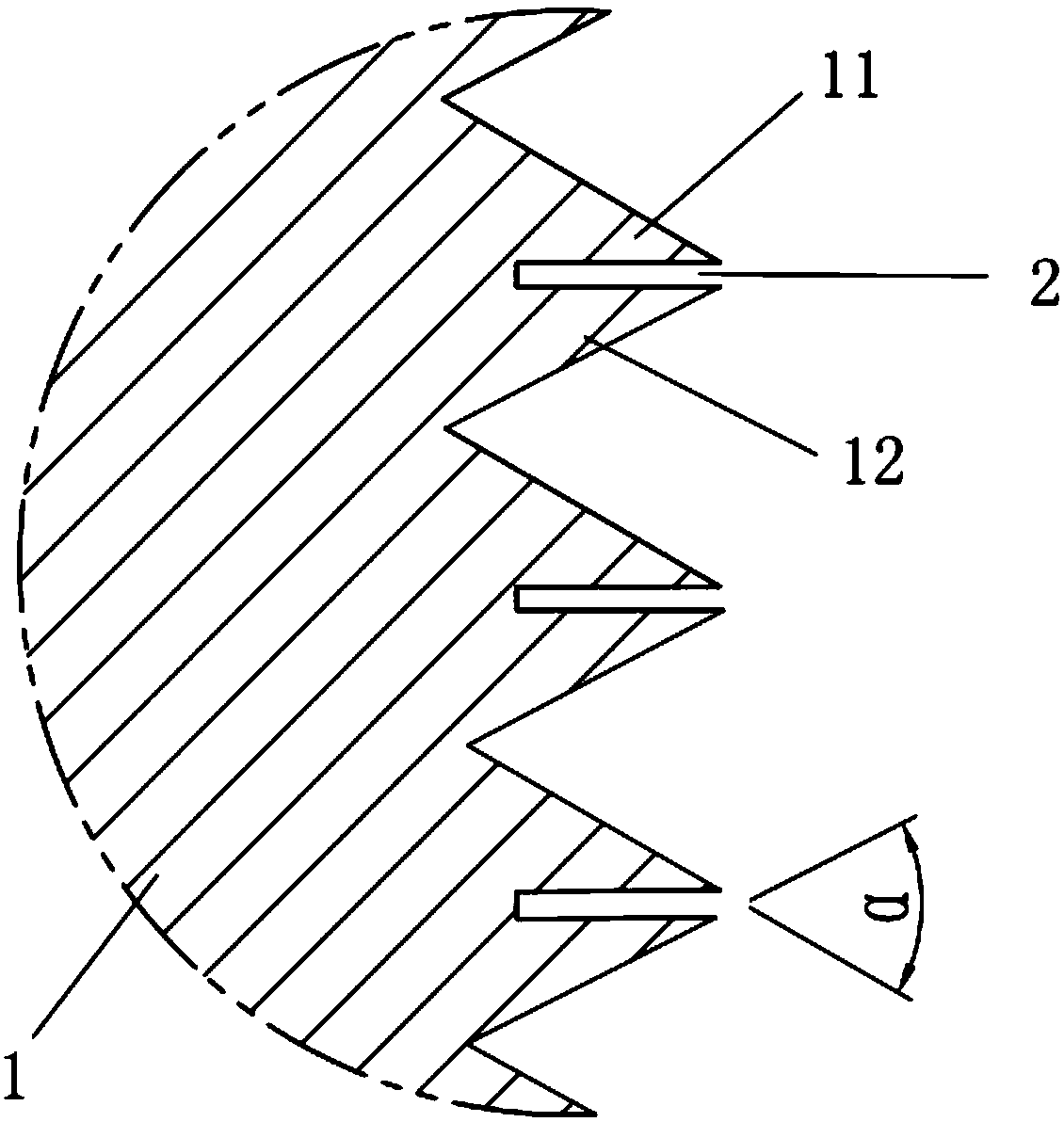
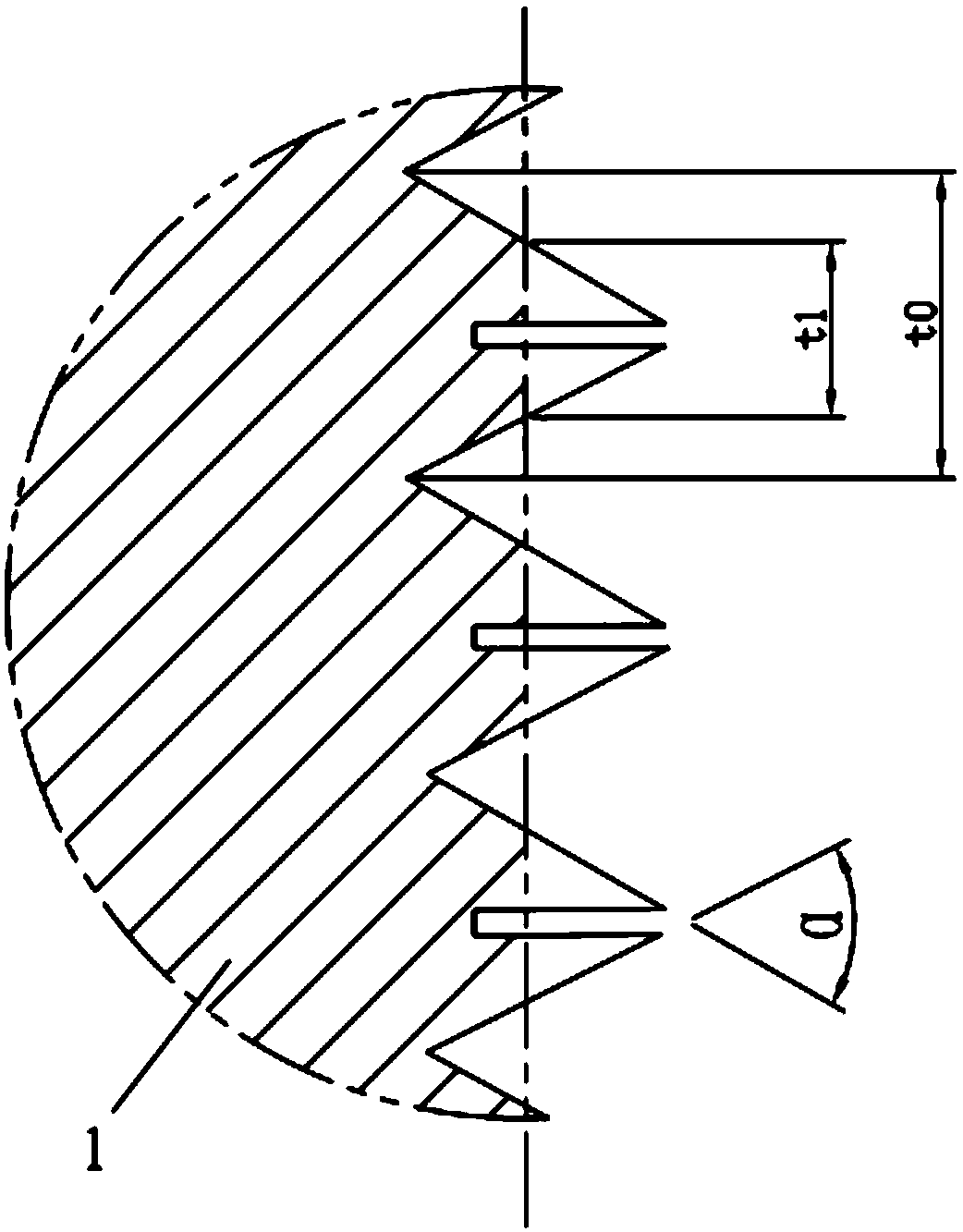
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, an anti-loosening thread 1 includes thread teeth. The tooth profile angle of the anti-loosening thread 1 is α, 45°<α<60°. The first sub-teeth 11 and the second sub-teeth 12 are formed by dividing, and the first sub-teeth 11 and the second sub-teeth 12 can be elastically deformed toward the direction of the groove 2 when pressed. After adopting this structure, the pitch diameter of the teeth of the anti-loosening thread 1 is larger than that of the standard thread. Since the thread teeth of the anti-loosening thread 1 are divided into the first sub-teeth 11 and the second sub-teeth 12 by the groove 2, so When the standard thread and the anti-loosening thread 1 are used for screw connection, the first sub-teeth 11 and the second sub-teeth 12 of the anti-loosening thread 1 are squeezed by the standard thread teeth, and then elastically deform in the direction of the groove 2, and the first sub-teeth The elastic forces F1 and F2 produced by the e...
Embodiment 2
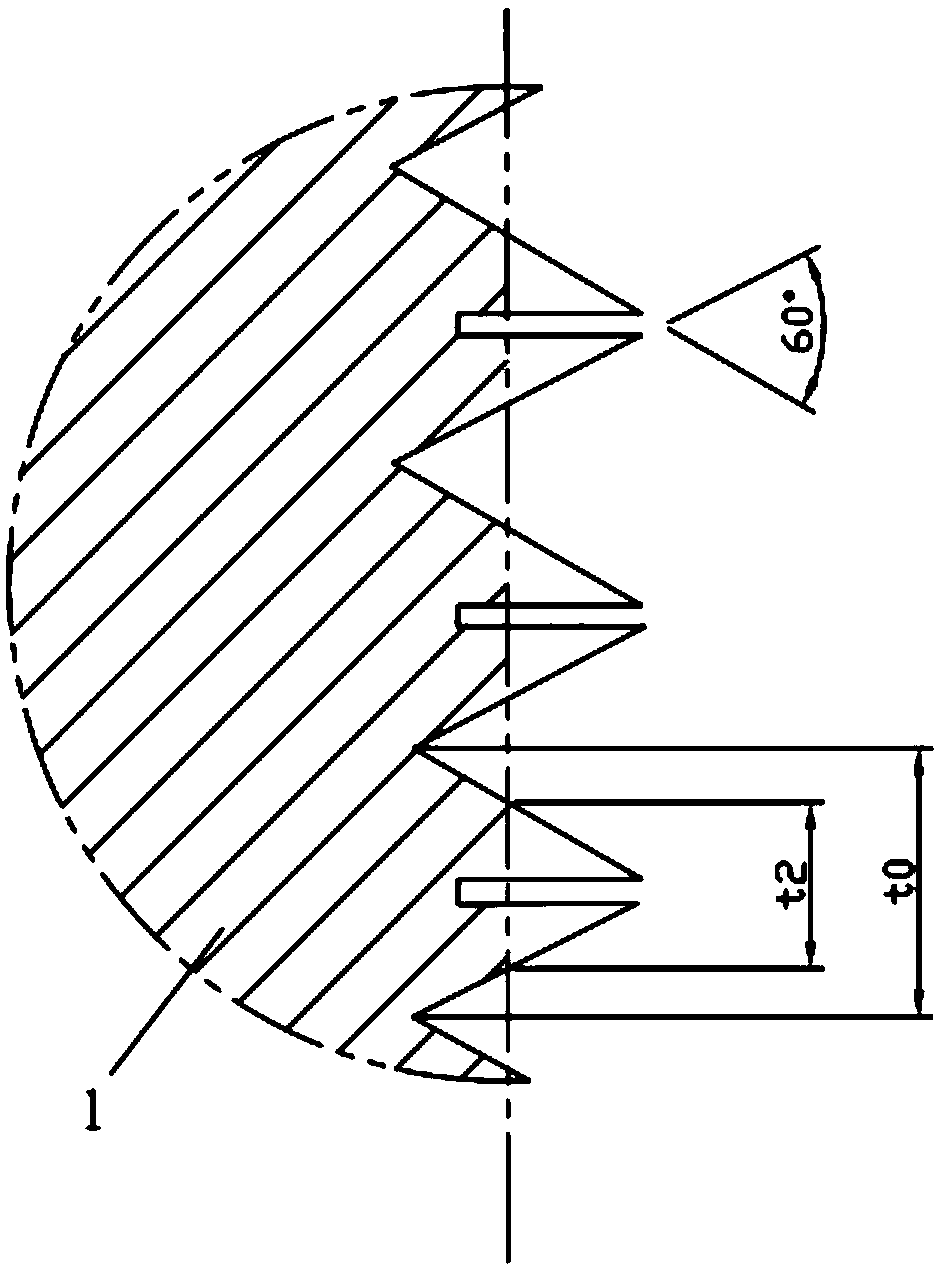
[0042] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated here. The difference is that: Figure 5 As shown, the groove 2 includes a first groove 21 and a second groove 22 , and the third child tooth 13 is arranged between the first groove 21 and the second groove 22 . After adopting this structure, when the standard thread and the anti-loosening thread 1 are used for screw connection, the first sub-teeth 11, the second sub-teeth 12 and the third sub-teeth 13 of the anti-loosening thread 1 are squeezed by the standard thread teeth, and then Elastically deform toward the first groove 21 and the second groove 22, and the elastic force generated by the elastic deformation presses against the standard screw teeth, and the third sub-teeth 13 protrude from the first groove 21 and the second groove 22 and Tightly inserted into the standard thread, it acts as a wedge to effectively prevent the threaded connection from lo...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The main structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 2, and the similarities will not be repeated here. The difference is that: Figure 6 As shown, the elastic material 3 is provided inside the first groove 21 and the second groove 22 . When the first sub-teeth 11, the second sub-teeth 12 and the third sub-teeth 13 are pressed by the standard thread teeth, and then elastically deform in the direction of the first groove 21 and the second groove 22, the first groove 21 and the second groove 22 The elastic material 3 inside the second groove 22 is also elastically deformed by extrusion, and the elastic force generated by the elastic deformation pushes the first sub-teeth 11, the second sub-teeth 12 and the third sub-teeth 13 tightly, so that the first sub-teeth 11 1. The second sub-teeth 12 and the third sub-teeth 13 tightly press the standard thread teeth to prevent the threaded connection from loosening and enhance the anti-loosening performance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com