A Method of Spectrum Resource Allocation for Vehicle Networks Based on Semi-Markov Chain
A spectrum resource allocation and vehicular network technology, which is applied in the field of vehicular network spectrum resource allocation based on semi-Markov chains, can solve the problems of failure to fully utilize idle spectrum resources, unfavorable system stable operation, and reservation methods that cannot dynamically adapt to the network, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
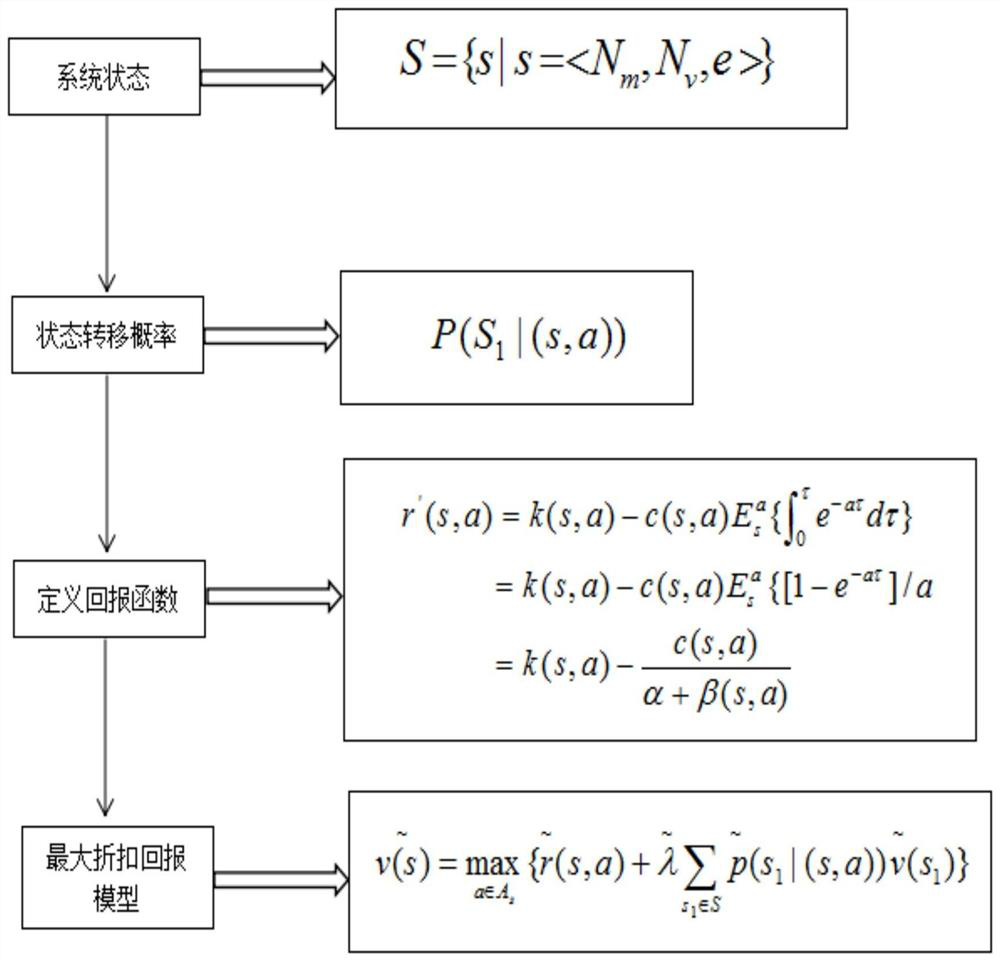
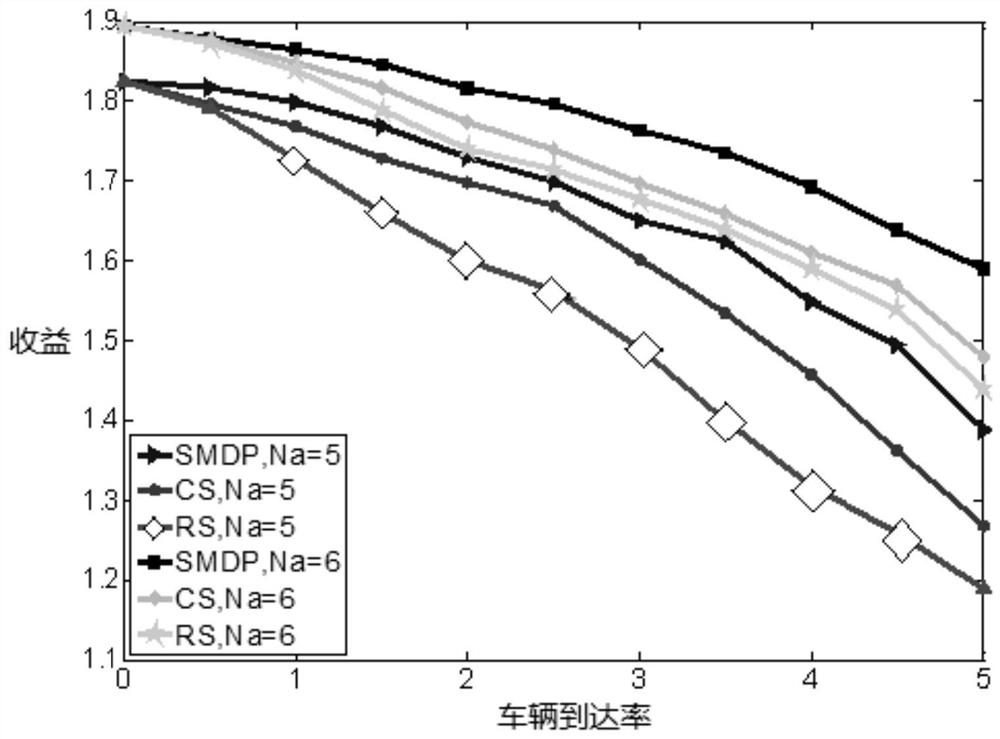
[0067] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with examples.
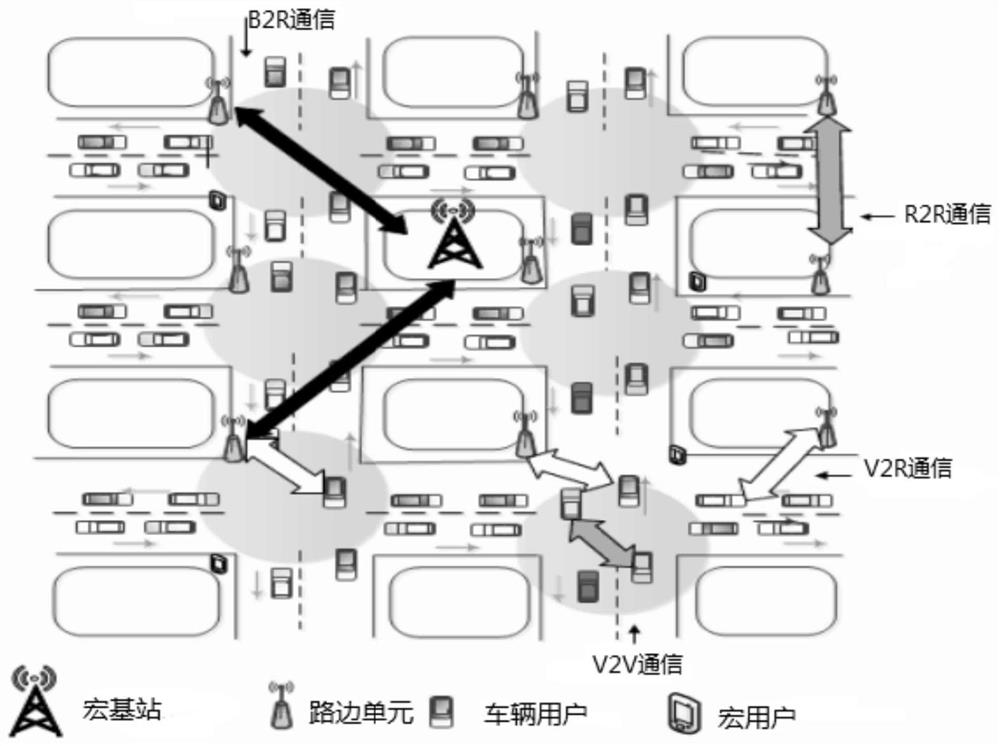
[0068] With the continuous increase of users, the traditional single network load is too large, prompting the vehicle network to develop in the direction of heterogeneity, that is, heterogeneous vehicle network HVN (Heterogeneous Vehicular Networks). HVN refers to the addition of new types of networks with small coverage in the original area, such as roadside units (RSUs), and stacking of different types of networks to achieve user offloading and improve overall system performance. Compared with the traditional vehicular network, the heterogeneous vehicular network structure is a major breakthrough in technology. It can not only provide a wide-area coverage network for more vehicles in a large scale, but also support real-time security information transmission to reduce Traffic accidents, and the resources of the same frequency band can be shared between multi-layer networks, and at th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com