Fault-arc identification unit
A technology of fault arc and identification unit, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, protection that responds to fault current, and measurement of electricity, to achieve the effect of simple method and simple determination of possibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
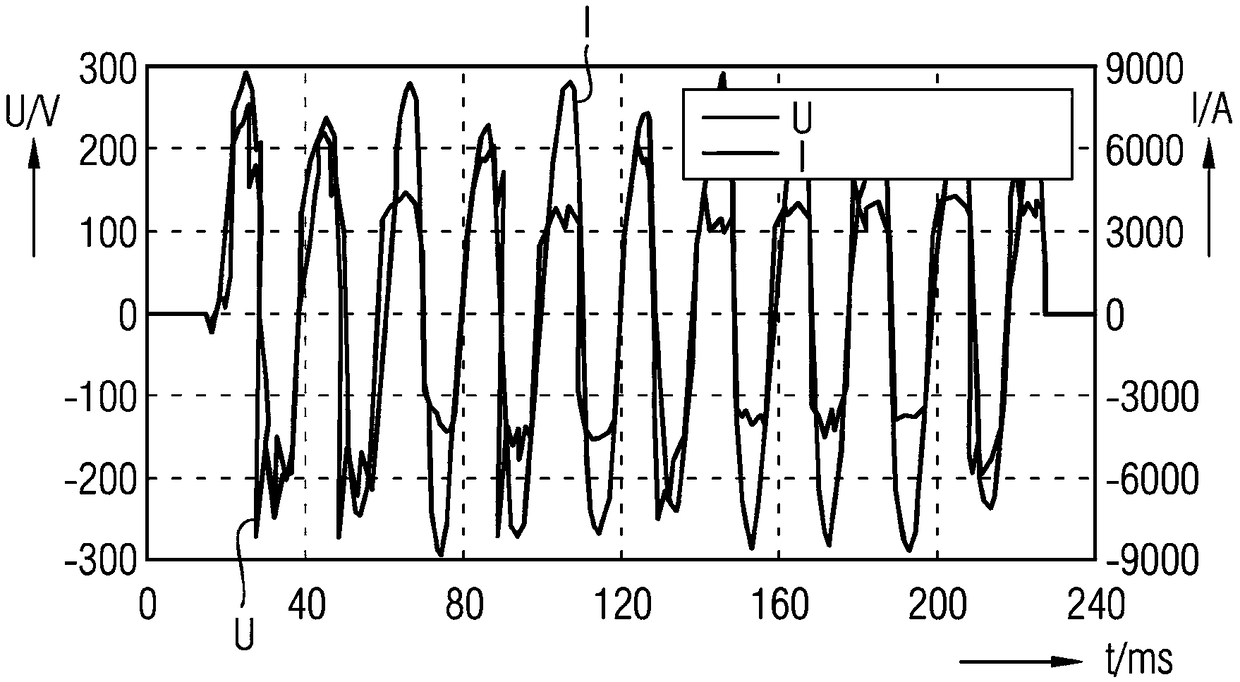
[0058] In a circuit or network in which an arc fault is burning, current and voltage curves can be measured, which have a distinct trend. A typical voltage and current curve for an arc fault is at figure 1 shown in . figure 1 An illustration of a diagram is shown in which the voltage U and the current I are plotted over time in an electrical circuit, in particular a low-voltage electrical circuit, after ignition of an arc or a fault arc, in particular a parallel fault arc.
[0059] Time t is shown in milliseconds (ms) on the horizontal X-axis. On the vertical Y axis, the magnitude of the voltage U is presented in volts (V) on the left scale. The magnitude of the current I is presented in amperes (A) on the right scale.
[0060] After ignition of the arc, the current I runs approximately sinusoidally. In this case, the voltage U runs “saw-tooth-shaped” with rapid voltage changes. Roughly speaking, the voltage profile is rectangular to a first approximation, rather than the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com