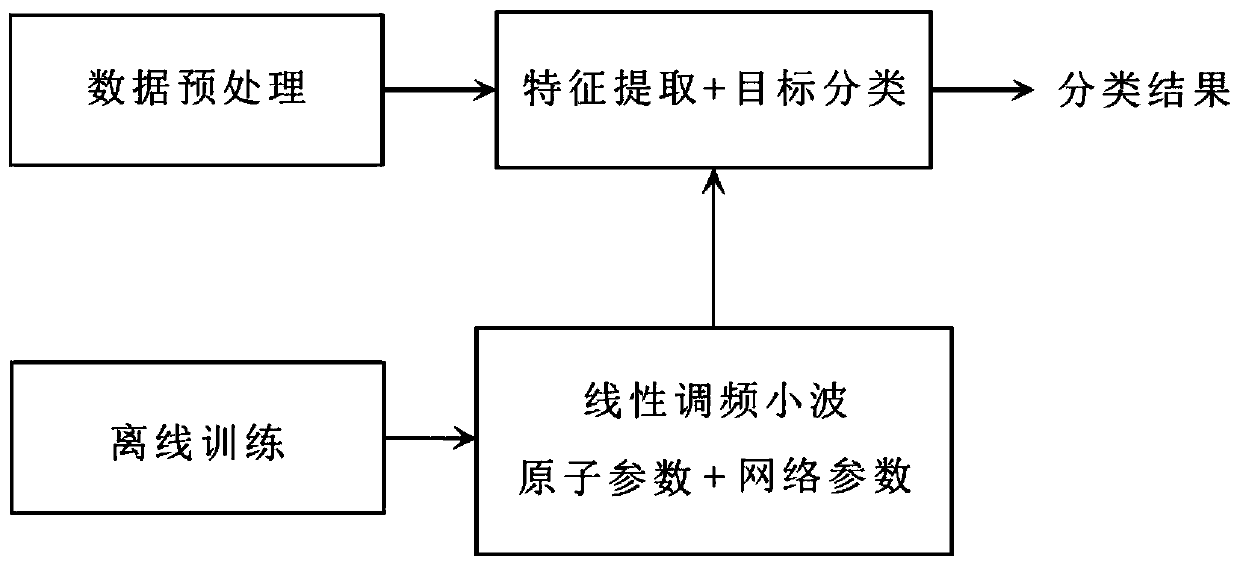
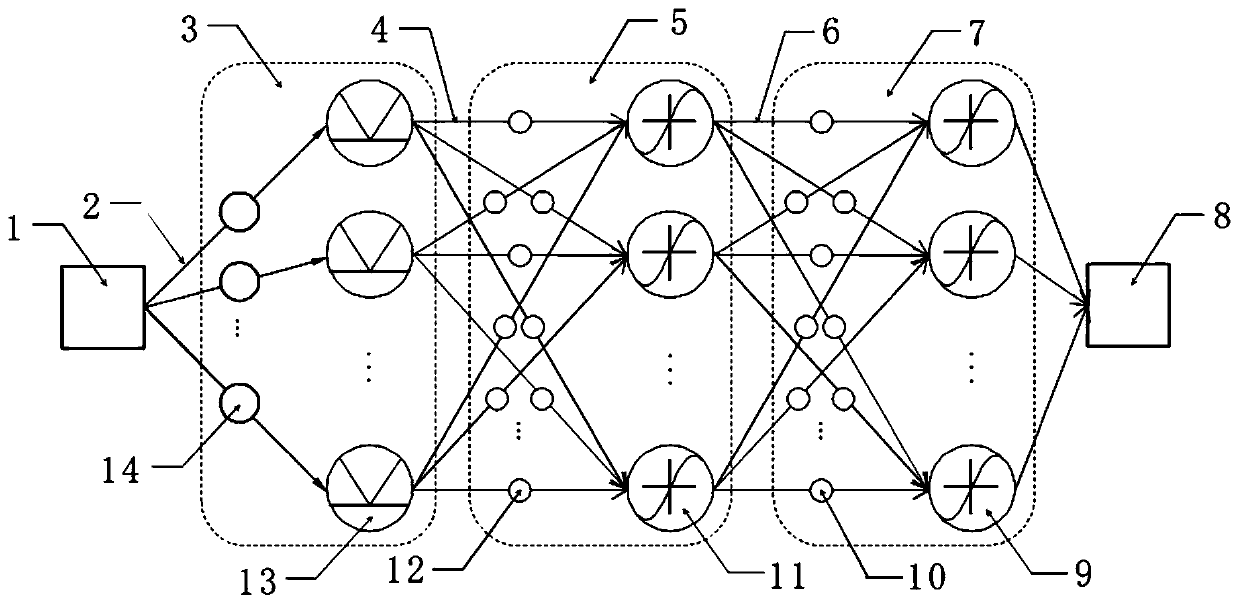
Target identification method based on linear frequency modulation wavelet atomic network
A linear frequency modulation and target recognition technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, biological neural network models, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of stable scattering model destruction, difficult to achieve effective feature extraction of targets, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
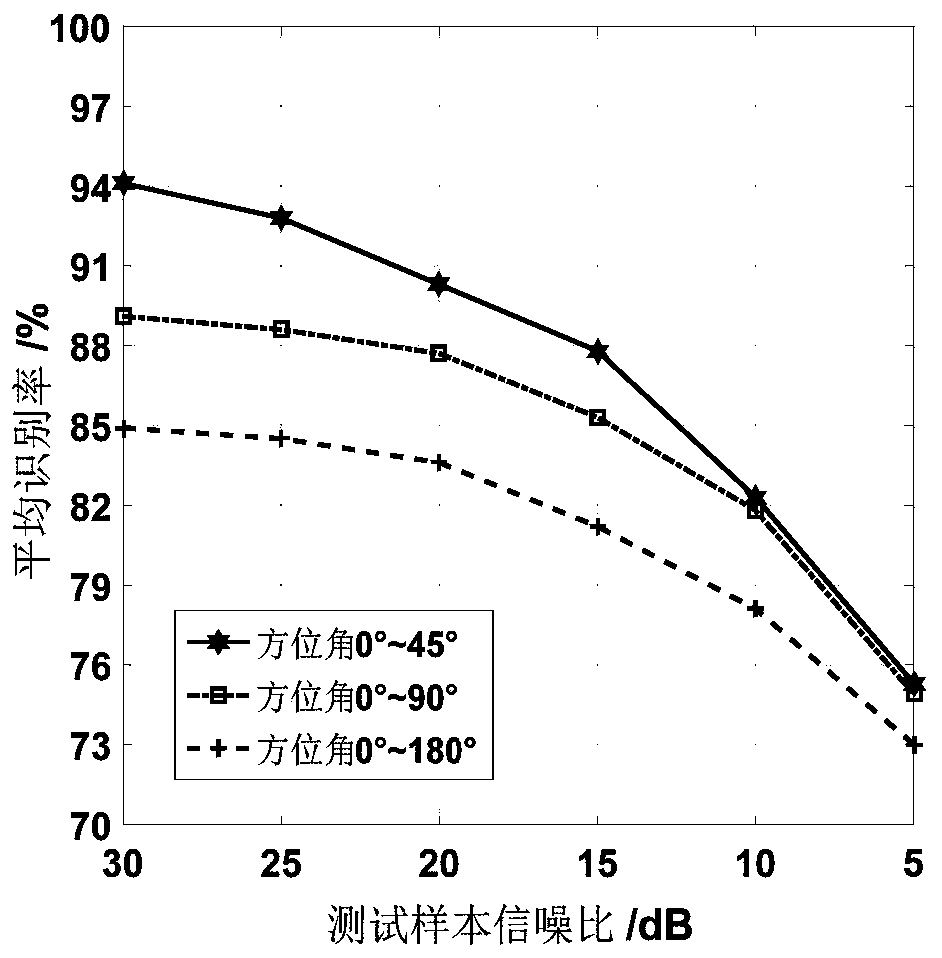
[0197] Through the target recognition method created in this paper, the linear frequency modulation wavelet atomic network is trained and tested, and the electromagnetic scattering images of four types of targets with azimuth angles from 0° to 45° and a signal-to-noise ratio of 30dB are used as sample data to compare with the existing methods ( Backpropagation neural network, wavelet neural network, Gabor atomic network), and the recognition rate results shown in Table 1 are obtained. This embodiment shows that the invention has better recognition performance on radar narrow-angle scattering images.
[0198] Table 1 Data recognition rate in the range of azimuth 0°~45° (%)
[0199]
Embodiment 2
[0201] Using electromagnetic scattering images of four types of targets with azimuth angles from 0° to 180° and a signal-to-noise ratio of 30dB as sample data, the four networks described in Example 1 were trained and tested, and the recognition rate results shown in Table 2 were obtained. . This embodiment shows that, compared with other target recognition methods in the prior art, the invention basically has a relatively high recognition rate for radar wide-angle scattering images.
[0202] Table 2 Azimuth 0°~180° range data recognition rate (%)
[0203]
[0204]
Embodiment 3
[0206] Using electromagnetic scattering images of four types of targets with azimuth angles from 0° to 180° and a signal-to-noise ratio of 5dB as test sample data, the anti-noise performance test was performed on the four types of networks trained in Example 2, and the identifications shown in Table 3 were obtained. rate results. This embodiment shows that the invention has good anti-noise performance in the recognition of radar scattering images.
[0207] Table 3 SNR 5dB data recognition rate (%)
[0208]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com