miRNA marker for assistant diagnosis of tuberculosis and application thereof
A diagnostic marker and auxiliary diagnosis technology, which can be used in the determination/examination of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of complex components and unsatisfactory effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
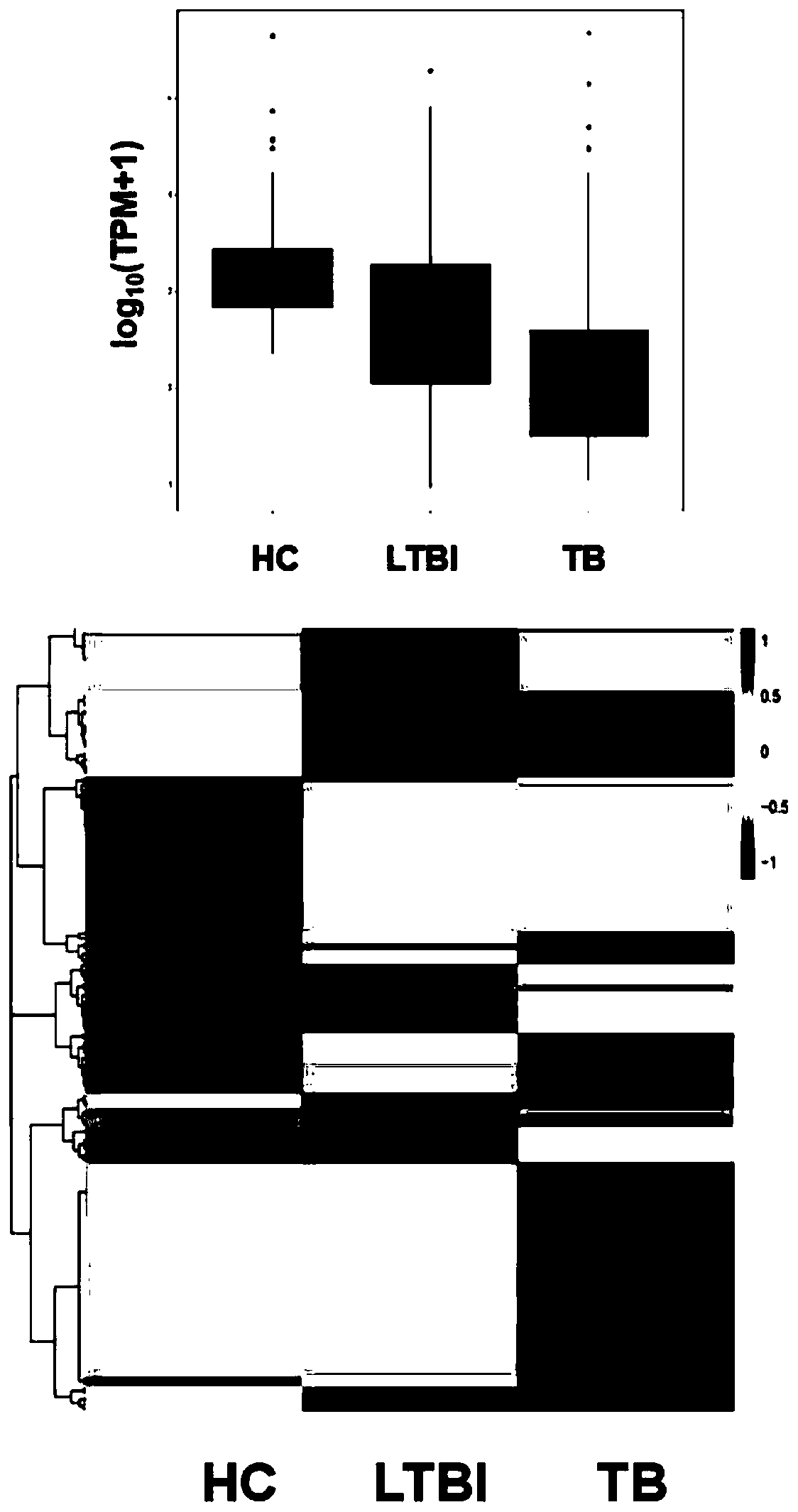
[0063] Example 1. Discovery of miRNAs that can be used as diagnostic markers
[0064] The healthy cohort (HC) consisted of 60 healthy subjects. The tuberculosis latent infection cohort (LTBI) consisted of 60 cases of latent tuberculosis infection. The active tuberculosis cohort (ATB) consisted of 60 patients with active tuberculosis.
[0065] 1. Prepare the sample pool
[0066] The serum of 60 healthy persons in the healthy group was collected respectively, and the serum was mixed (1 ml / case) to obtain a sample pool of the healthy group. The serum of 60 cases of latent tuberculosis infection in the latent tuberculosis infection group was collected respectively, and the serum was mixed (1ml / case) to obtain the sample pool of the latent tuberculosis infection group. The serum of 60 patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis in the active pulmonary tuberculosis population group was collected respectively, and the serum was mixed (1 ml / case) to obtain a sample pool of the acti...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Example 2, further screening of miRNAs that can be used as diagnostic markers from 20 miRNAs
[0092] Subjects: 10 healthy persons, 10 latent tuberculosis infection patients, and 10 active pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
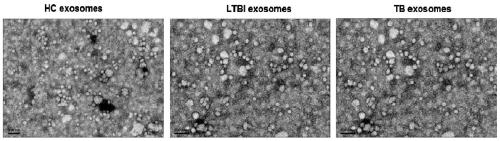
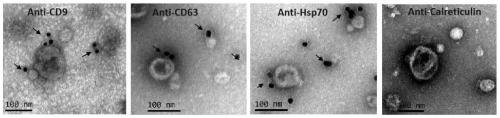
[0093] 1. Extract exosomes
[0094] Serum exosomes were extracted from each subject separately.
[0095] 1. Take the subject's serum, centrifuge at 1000g for 15min, and collect the supernatant.
[0096] 2. Take the supernatant obtained in step 1, centrifuge at 16500 g for 30 min at 4° C., and collect the supernatant.
[0097] 3. Take the supernatant obtained in step 2, filter it with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm, and collect the filtrate.
[0098] 4. Take the filtrate obtained in step 3, centrifuge at 4°C and 120,000 g for 3 hours, discard the supernatant, turn the centrifuge tube upside down on absorbent paper to drain the liquid on the tube wall, and the precipitate attached to the bottom of the centrifuge tube is exosomes prec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com