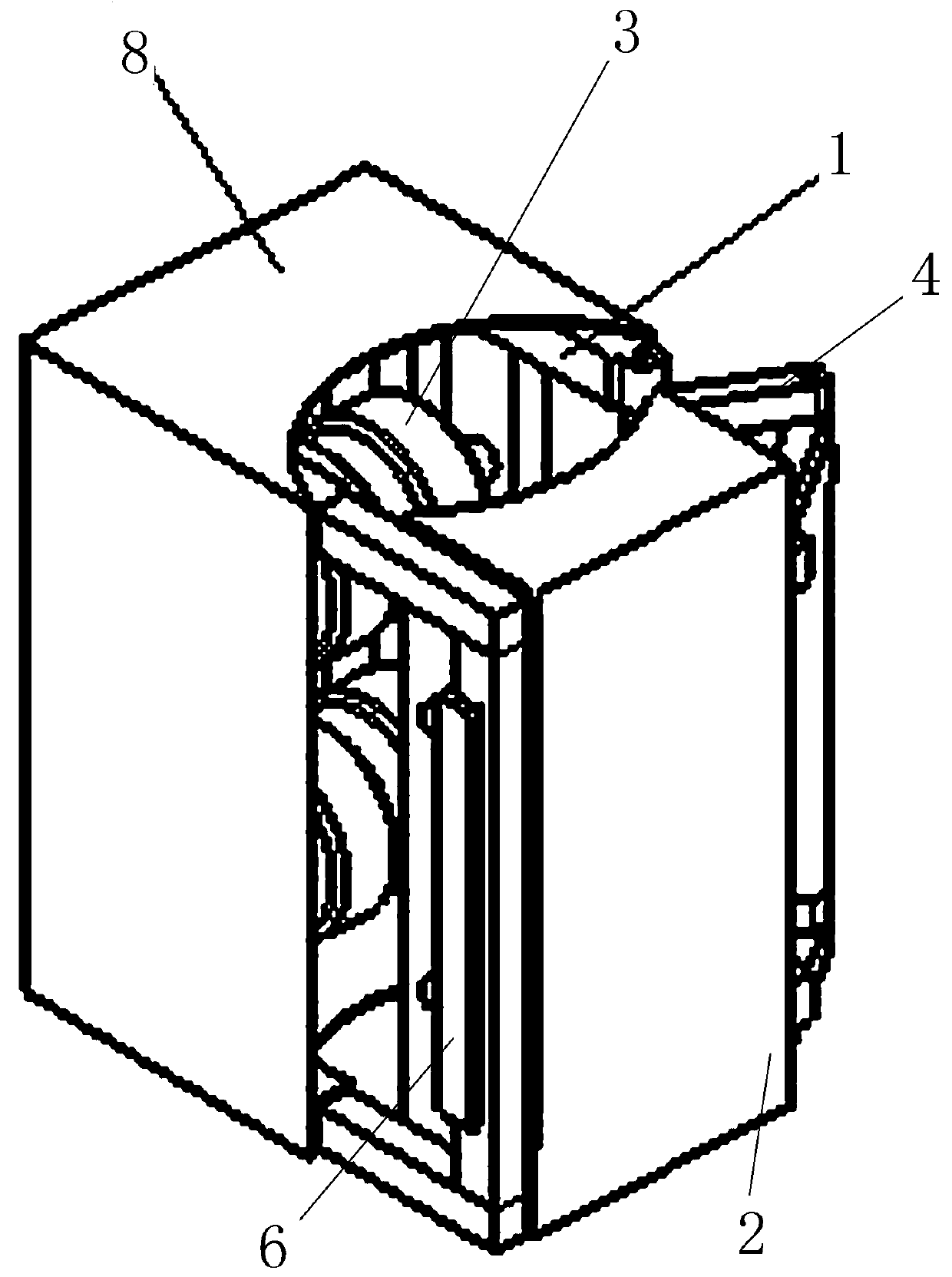
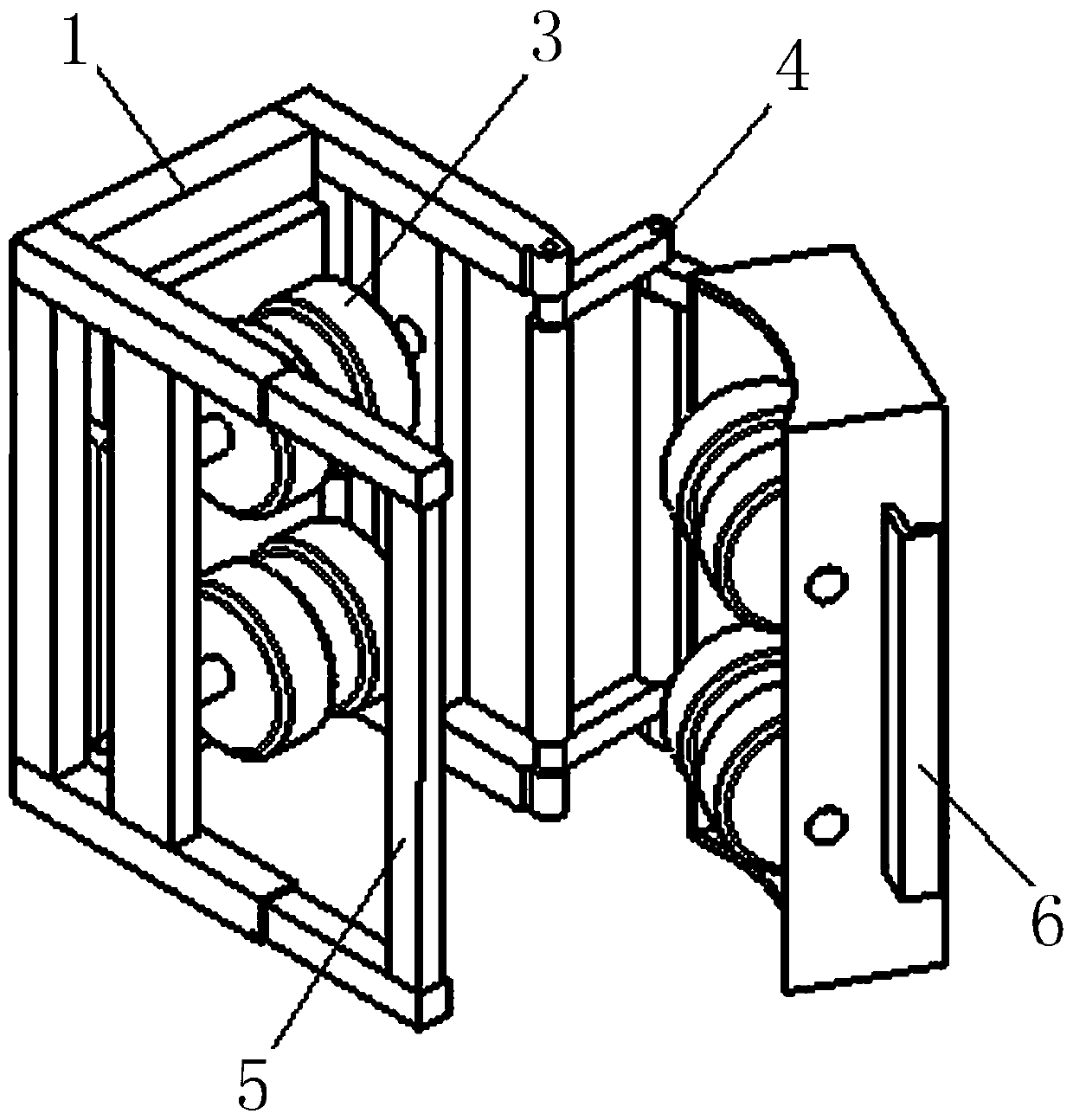
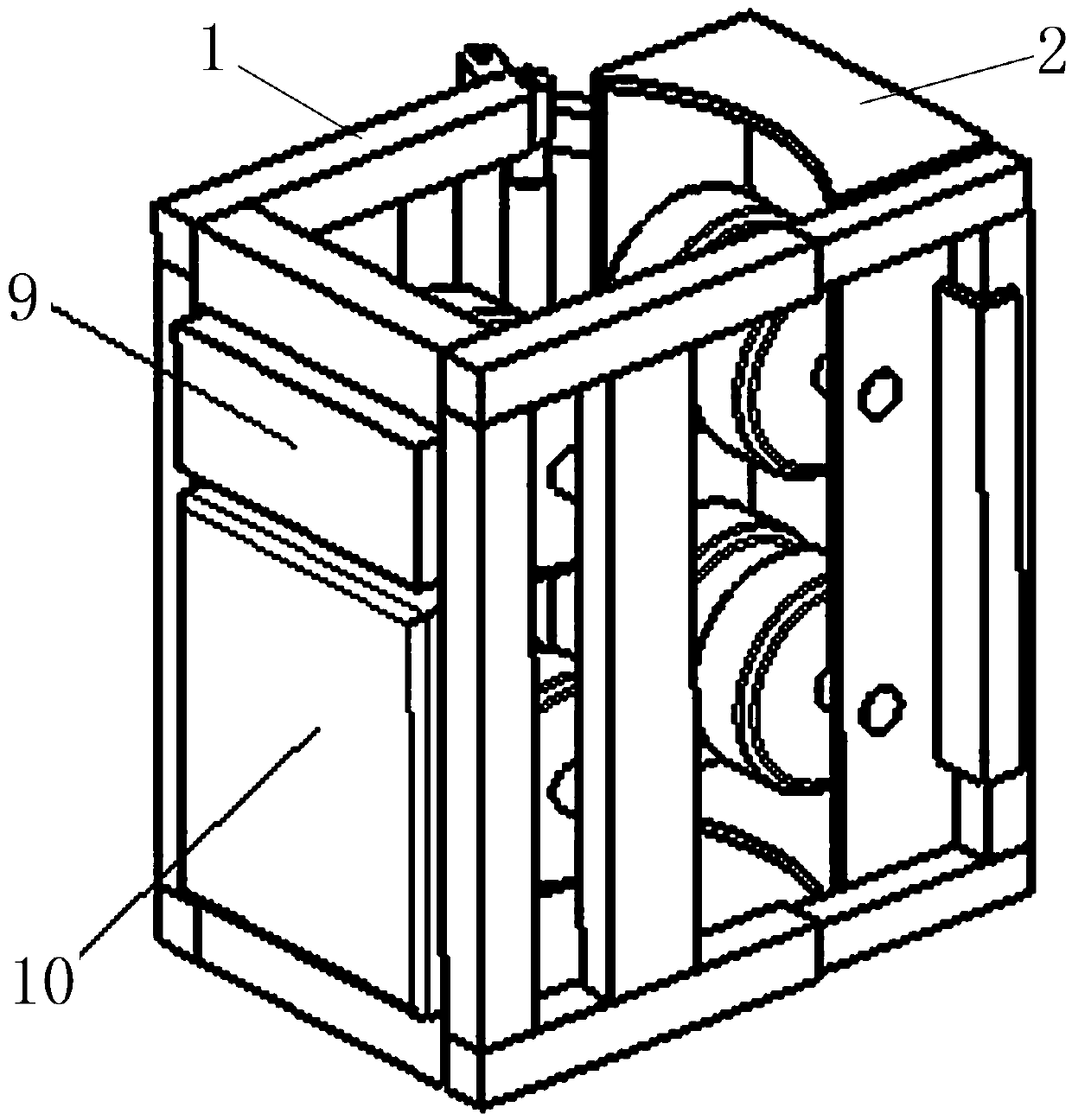
Pole-climbing robot adaptive to diameter of pole
A robot and self-adaptive technology, applied in the fields of motor vehicles, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of manual work, inability to adapt to the change of rod diameter, poor safety, etc., and achieve the effect of a wide range of application scenarios
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: The arrangement of the upper and lower rows of the traveling wheel mechanism in this embodiment, each row having two rubber-coated wheels arranged at intervals, is the same as that of the traveling wheel mechanism in Embodiment 1, the difference is that: The structural form of the frame, the structure and arrangement of the telescopic mechanism, and the structure and arrangement of other auxiliary components are all different, and may be common forms in the prior art.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: as Figure 6-8 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that telescopic mechanisms are arranged on both sides of the structure of the two frames, and telescopic springs such as air springs or coil springs are arranged between the telescopic rods, and one end of the telescopic mechanism on one side is connected to the second The two frames are rigidly connected, and the other end is softly connected to the first frame through a hinge 30 (ie, a hinge); one end of the telescopic mechanism on the other side is rigidly connected to the first frame, and the other end is connected to the second frame through an openable buckle structure. The buckle structure is connected, that is, the U-shaped movable hook 5 and the fixed hook 6. The two telescopic mechanisms are respectively rigidly connected with the first frame and the second frame to form an L-shaped frame. The two L-shaped frames are opposite to form a rectangular frame. One connection of the L-shaped f...
Embodiment 4
[0050] Embodiment 4: as Figure 9-11 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 3 is that one side of the two frames is respectively rigidly connected to the two ends of a telescopic rod 31 to form a C-shaped frame, and then a hinge 30 is hinged at the opening of the C-shaped frame. Telescopic rods 31, telescopic springs such as air springs or helical springs are arranged between the telescopic rods, and the other end of the telescopic rods 31 has a gap for the T-shaped hook to connect with the middle of the T-shaped movable hook 5 and the C-shaped frame. The hooking of the fixed hook 6 realizes the detachable connection. The telescopic rod 31 constitutes an I-shaped structure, and the C-shaped structure and the I-shaped structure form a rectangular structure. and separation, this implementation case is a C+I-shaped structure. Of course, the T-shaped movable hook 5 in this embodiment can also be replaced by a rectangular hook or a 7-shaped hook.
[0051] In other embodiments: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com