Calculation method for filling power in tight gas reservoir
A calculation method and tight gas technology, applied in the field of oil and gas reservoir exploration, can solve problems such as low precision and no specificity, and achieve the effect of simple steps and batch processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
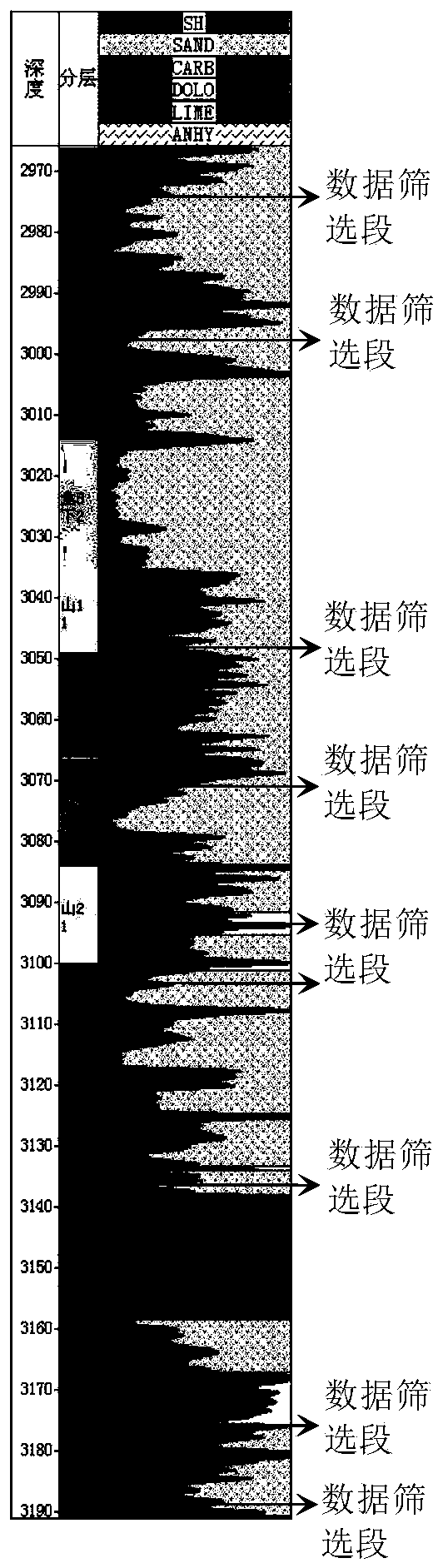
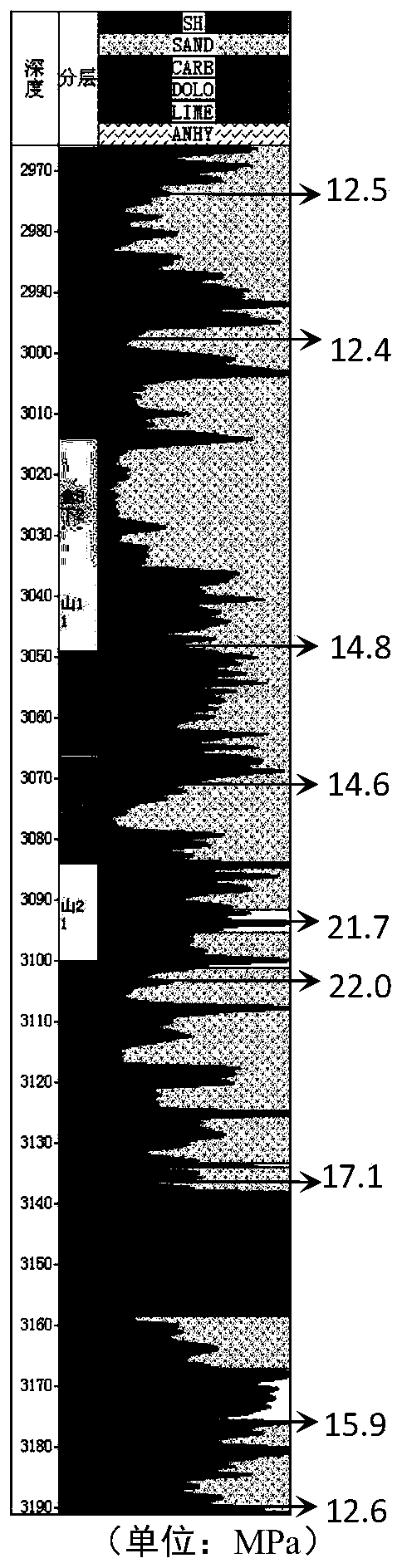
[0072] Embodiment: The example well is Zhao 25 Well in East District of Sulige (hereinafter referred to as Z-EW well).
[0073] A charging dynamic calculation method for tight gas reservoirs, comprising the following steps:
[0074] 1. Read single well mudstone compaction data
[0075] Starting from the initial depth, the acoustic time difference (AC for short) values at different depths are read on the logging curve at intervals of corresponding depth steps.
[0076] According to technical requirements, the depth of Z-EW well is 3260m, so the AC value step is 10m. From the initial depth of 500m to the bottom of the well, a total of 277 AC data can be read.
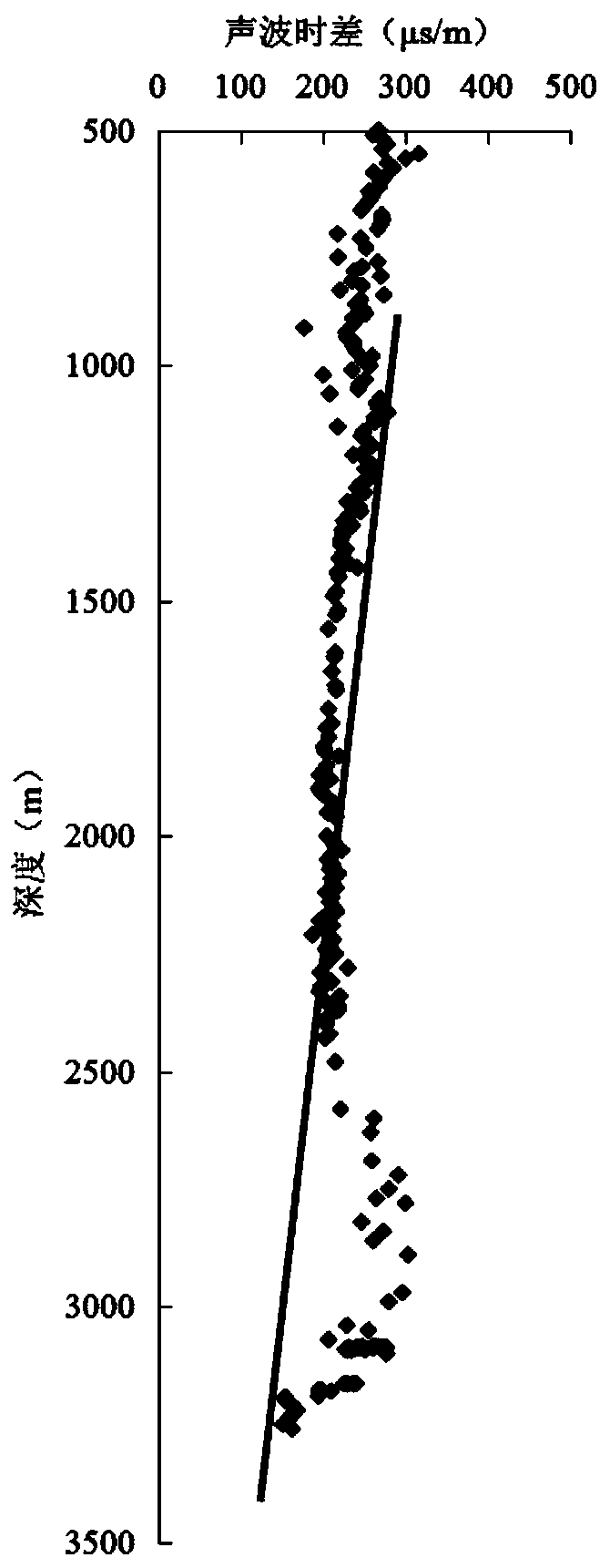
[0077] 2. Fitting the depth-AC relationship of the non-hydrocarbon generation-normal compaction section
[0078] (1) Establish a depth-AC intersection relationship diagram;
[0079] The above 277 AC values and corresponding depths are used to establish a depth-AC intersection relationship diagram, such as figur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com