Block chain cross-chain method, device and system and electronic device
An electronic device and blockchain technology, applied in the network field, can solve the problems of complex cross-chain service operations, and achieve the effect of improving cross-chain efficiency, simplifying the setting mechanism, and simplifying cross-chain services.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] refer to Figure 1a As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the steps of a blockchain cross-chain method provided by the embodiment of this specification. The cross-chain method is applied in the cross-chain system under the side chain / relay mode, wherein the cross-chain system may include The main chain, the side chain, and the relay that provides cross-chain services for the main chain and the side chain. The relay can be an independent blockchain node or a functional module located on the blockchain node. It should be understood that the application scenario of the blockchain cross-chain solution may be a decentralized transaction scenario or an asset exchange scenario.
[0042] The cross-chain method may include the following steps:
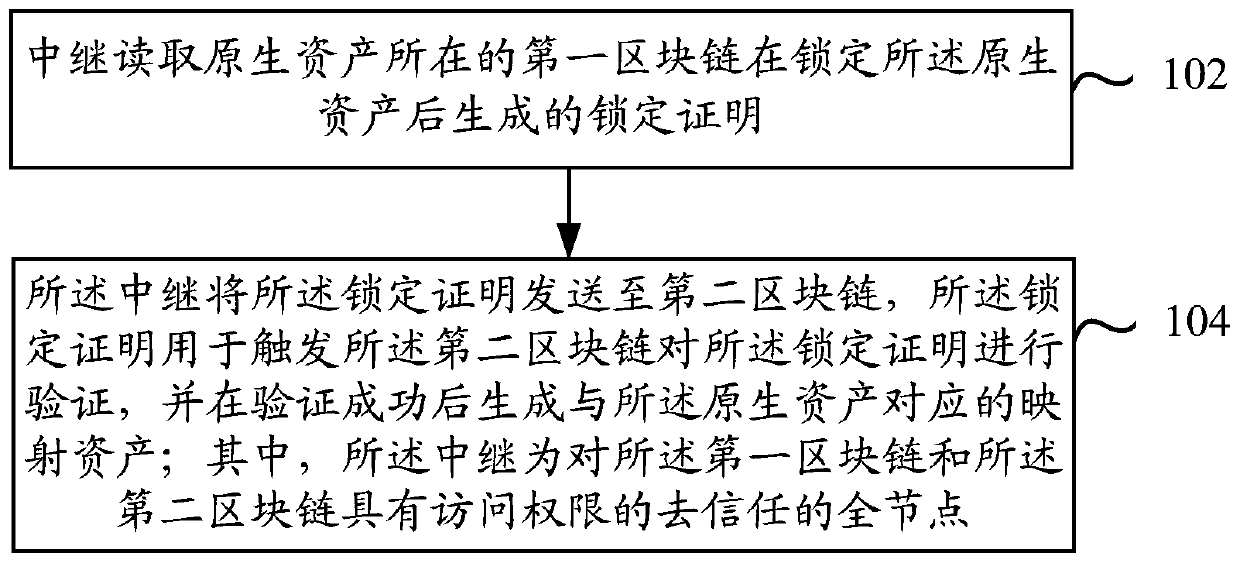
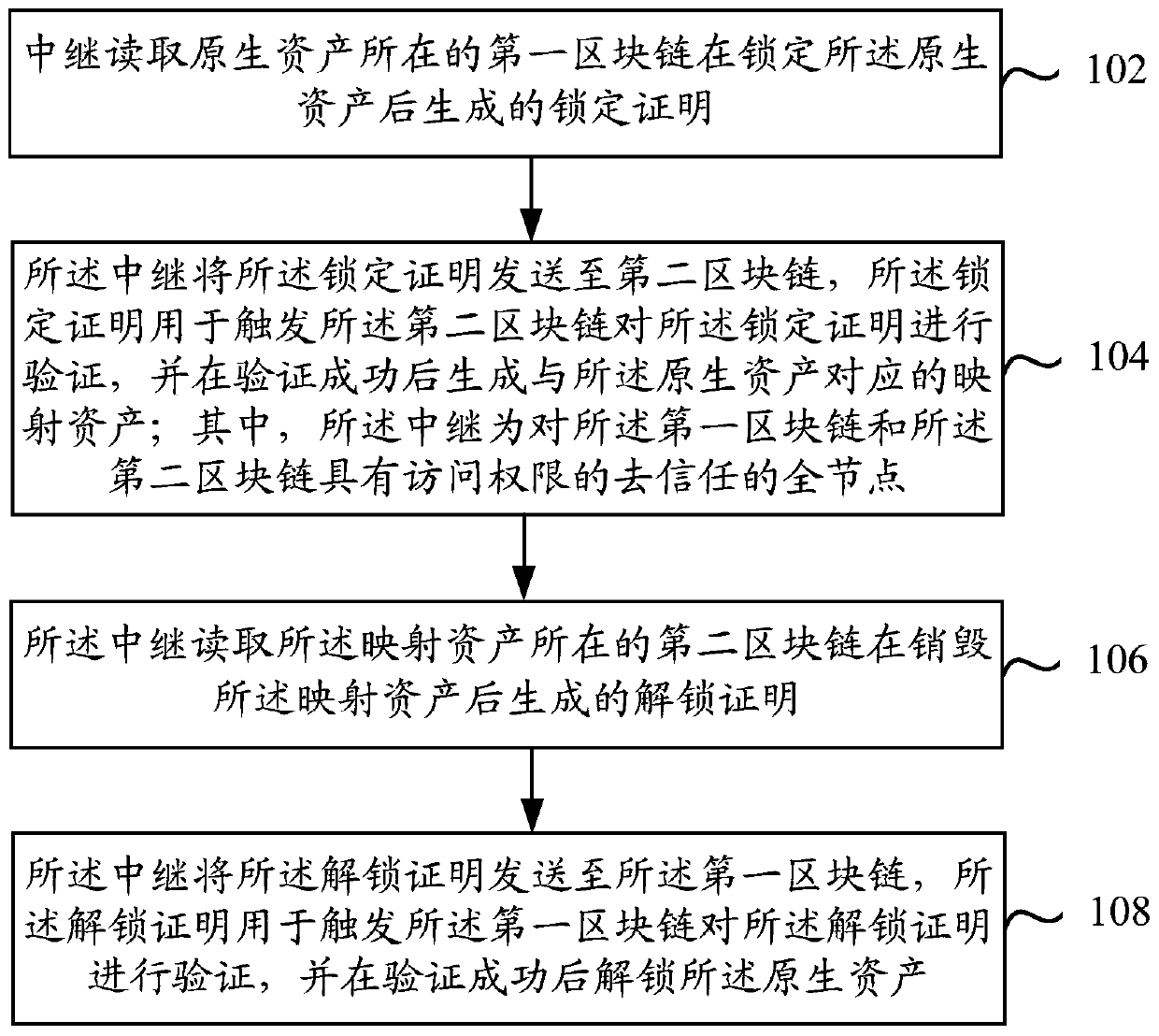
[0043] Step 102: The relay reads the lock certificate generated after the original asset is locked in the first blockchain where the original asset is located.
[0044] It should be understood that the first block chain may be a side c...
Embodiment 2
[0094] refer to image 3 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of the block chain cross-chain device provided by the embodiment of this specification. The device mainly includes:
[0095] A reading module 302, configured to read the lock proof generated by the first blockchain where the original asset is located after locking the original asset;
[0096] The sending module 304 is configured to send the lock proof to the second block chain, the lock proof is used to trigger the second block chain to verify the lock proof, and generate the lock proof after the verification is successful. Mapping assets corresponding to native assets;
[0097] Wherein, the relay is a trustless full node with access rights to the first block chain and the second block chain.
[0098] Optionally, said lock proof carries at least one block checkpoint of the first blockchain;
[0099] When the second block chain verifies the lock certificate, it specifically includes: the second block cha...
Embodiment 3
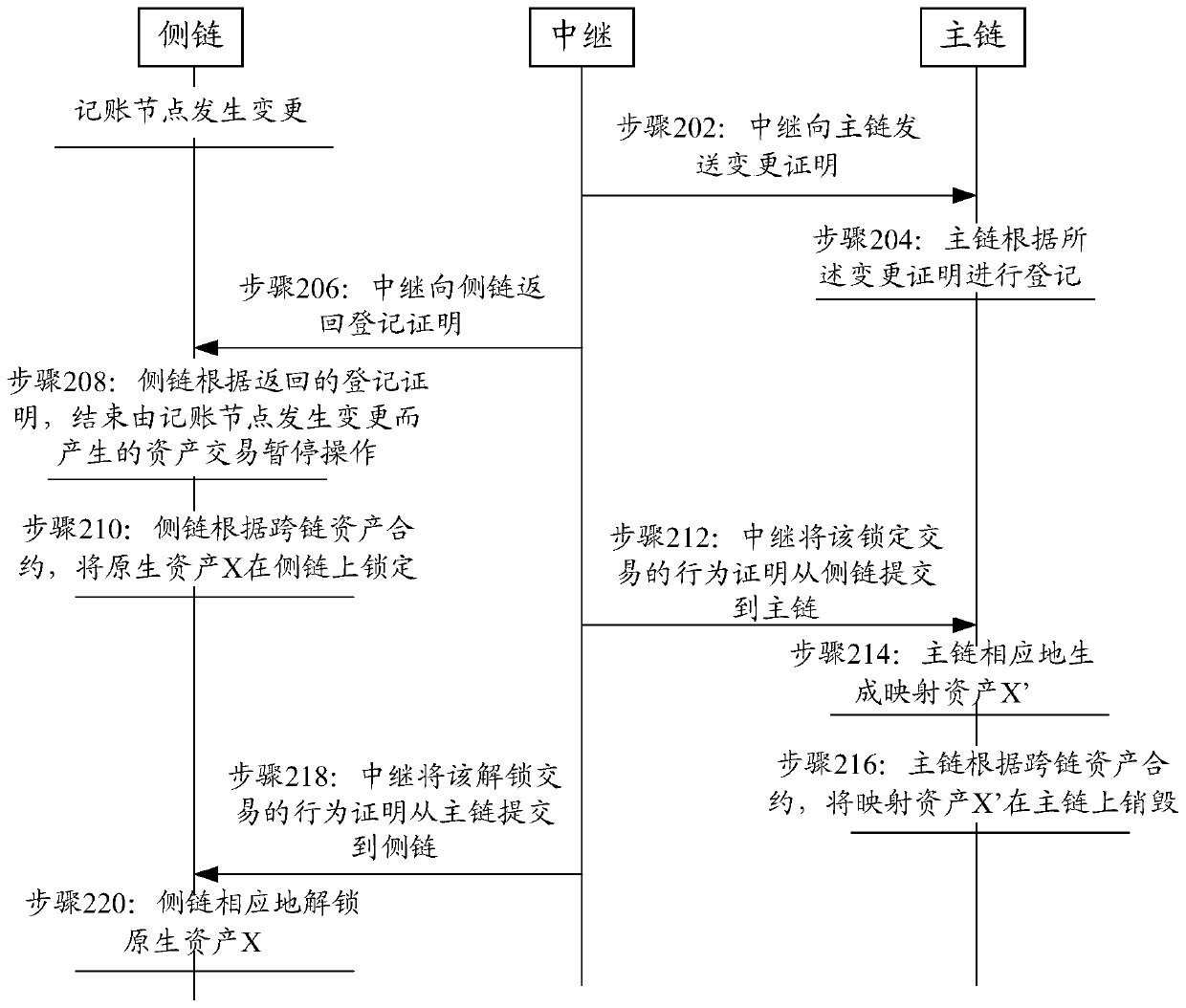
[0113] The embodiment of this specification also provides a blockchain cross-chain system, still refer to Figure 4 As shown, including: a first block chain 402, a second block chain 404 and a relay 406;
[0114] The first blockchain 402 locks native assets;
[0115] The relay 406 reads the lock certificate generated by the first block chain 402 where the original asset is located after locking the original asset; and sends the lock certificate to the second block chain 404;
[0116] The second block chain 404 verifies the lock certificate, and generates a mapping asset corresponding to the original asset after the verification is successful;
[0117] Wherein, the relay 406 is a trustless full node with access rights to the first block chain 402 and the second block chain 406 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com