A Synchronous Laser Radar Optical System for Transmitting and Receiving
A laser radar and optical system technology, applied in the direction of radio wave measurement systems, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate test results, inability to accurately guarantee the synchronous rotation of two sets of vibrating mirrors, and unsynchronized vibrating mirrors, etc., to achieve simplification The design difficulty is completely consistent with the structure and phase, and the effect of reducing the viewing angle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
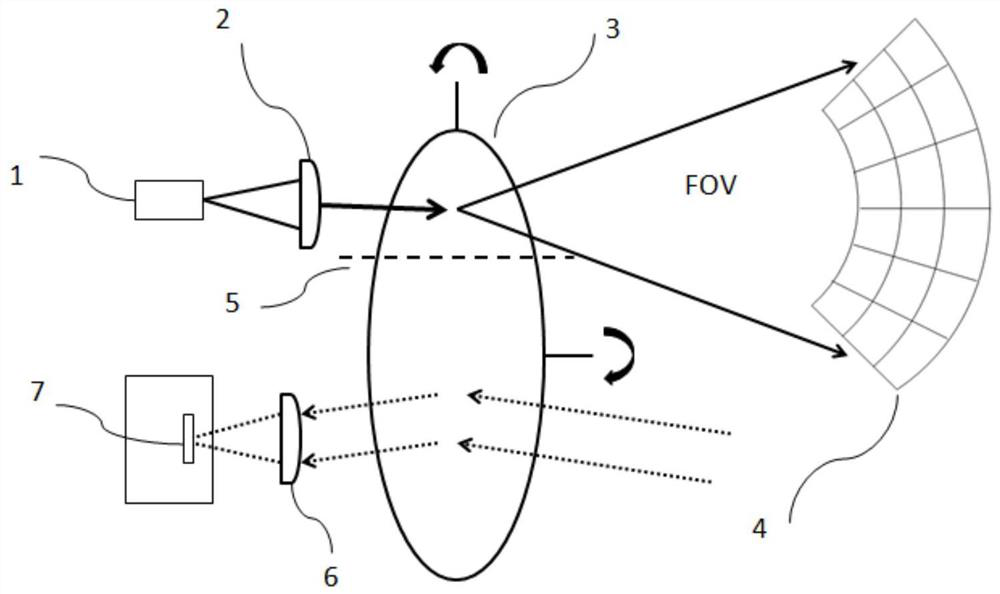
[0036] From figure 1 It can be seen that the laser radar optical system for transmitting and receiving synchronously in this embodiment includes a laser radar transmitting system and a laser radar receiving system. The laser radar transmitting system includes a pulse laser 1, a collimating lens group 2, and a two-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 3 arranged sequentially along the optical path; the laser radar receiving system includes a two-dimensional MEMS vibrating mirror 3, a receiving lens group 6 and a photoelectric Detector 7. The collimator lens group 2 in this embodiment includes at least one aspherical lens or at least two cylindrical lenses or a combination of multiple common lenses, and its main function is to achieve spot shaping of the laser light emitted by the pulse laser 1 . Because the inherent astigmatism of the laser diode is serious, it is necessary to collimate its light spot. After the laser is collimated by the collimating lens group, the laser spot ca...
Embodiment 2
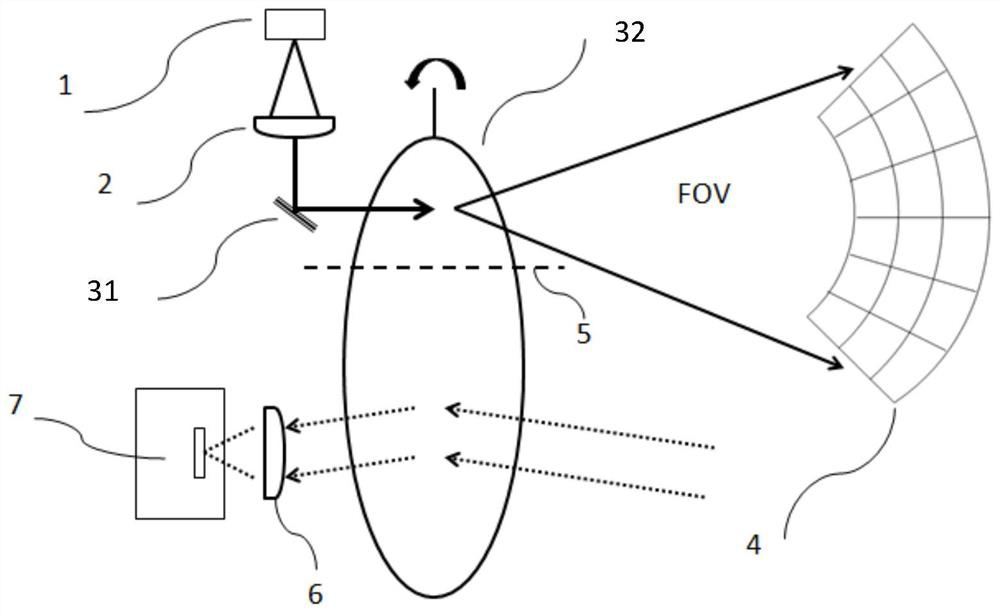
[0042] From figure 2 It can be seen that the laser radar optical system for transmitting and receiving synchronously in this embodiment includes a laser radar transmitting system and a laser radar receiving system. The laser radar transmitting system includes a pulse laser 1, a collimator lens group 2, a single-axis scanning galvanometer 31 and a single-axis scanning galvanometer 32 arranged in sequence along the optical path; the laser radar receiving system includes a single-axis scanning galvanometer arranged in sequence along the optical path 32 (the single-axis scanning vibrating mirror 32 and the single-axis scanning vibrating mirror 32 in the lidar transmitting system are the same single-axis scanning vibrating mirror), the receiving lens group 6 and the photodetector 7 . The single-axis scanning galvanometer can be a single-axis MEMS galvanometer or a one-dimensional rotating motor. The collimating lens group 2 in this embodiment includes at least one aspherical surf...
Embodiment 3
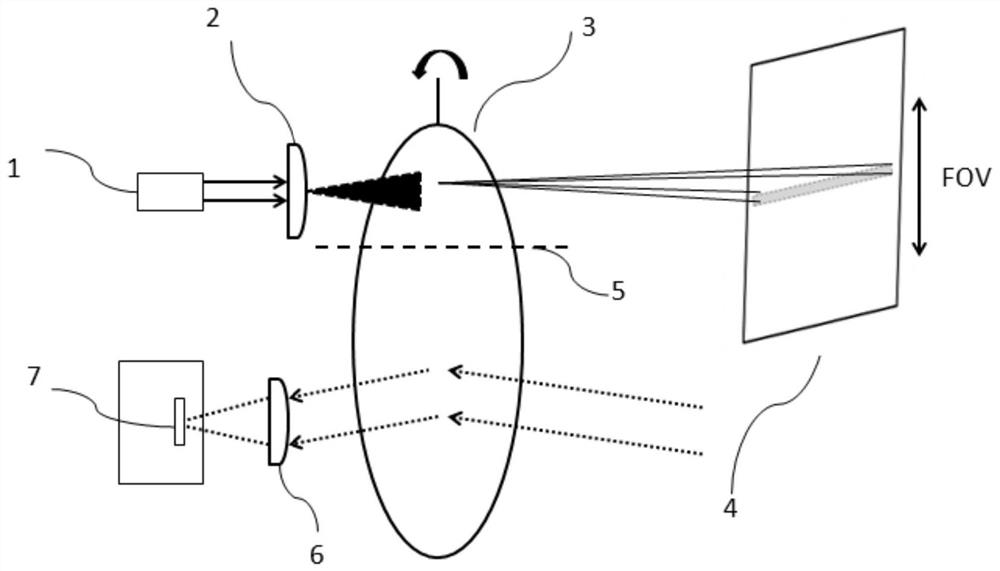
[0047] From image 3 It can be seen that the laser radar optical system for transmitting and receiving synchronously in this embodiment includes a laser radar transmitting system and a laser radar receiving system. Among them, the laser radar transmitting system includes a pulse laser 1, a collimating line expansion lens group 2 and a single-axis scanning galvanometer 3 arranged in sequence along the optical path; the laser radar receiving system includes a single-axis scanning galvanometer 3 arranged in sequence along the optical path, and a receiving lens group 6 and photodetector 7; wherein, the single-axis scanning vibrating mirror can be a single-axis MEMS vibrating mirror or a single-axis rotating motor.
[0048] The optical system of this embodiment also includes an isolation device 5, which is made of an opaque material and arranged perpendicular to the mirror surface of the uniaxial scanning vibrating mirror 3, and the uniaxial scanning vibrating mirror 3 is divided i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com