Improved complete denture maxillary blank mold tray
A technology of complete dentures and trays, which is applied in the field of improved complete dentures and maxillary primary mold trays, which can solve the problems of difficult mandibular movement, uncontrollable strength, and low initial vertical distance, so as to prevent interference and prevent mold release , more controllable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
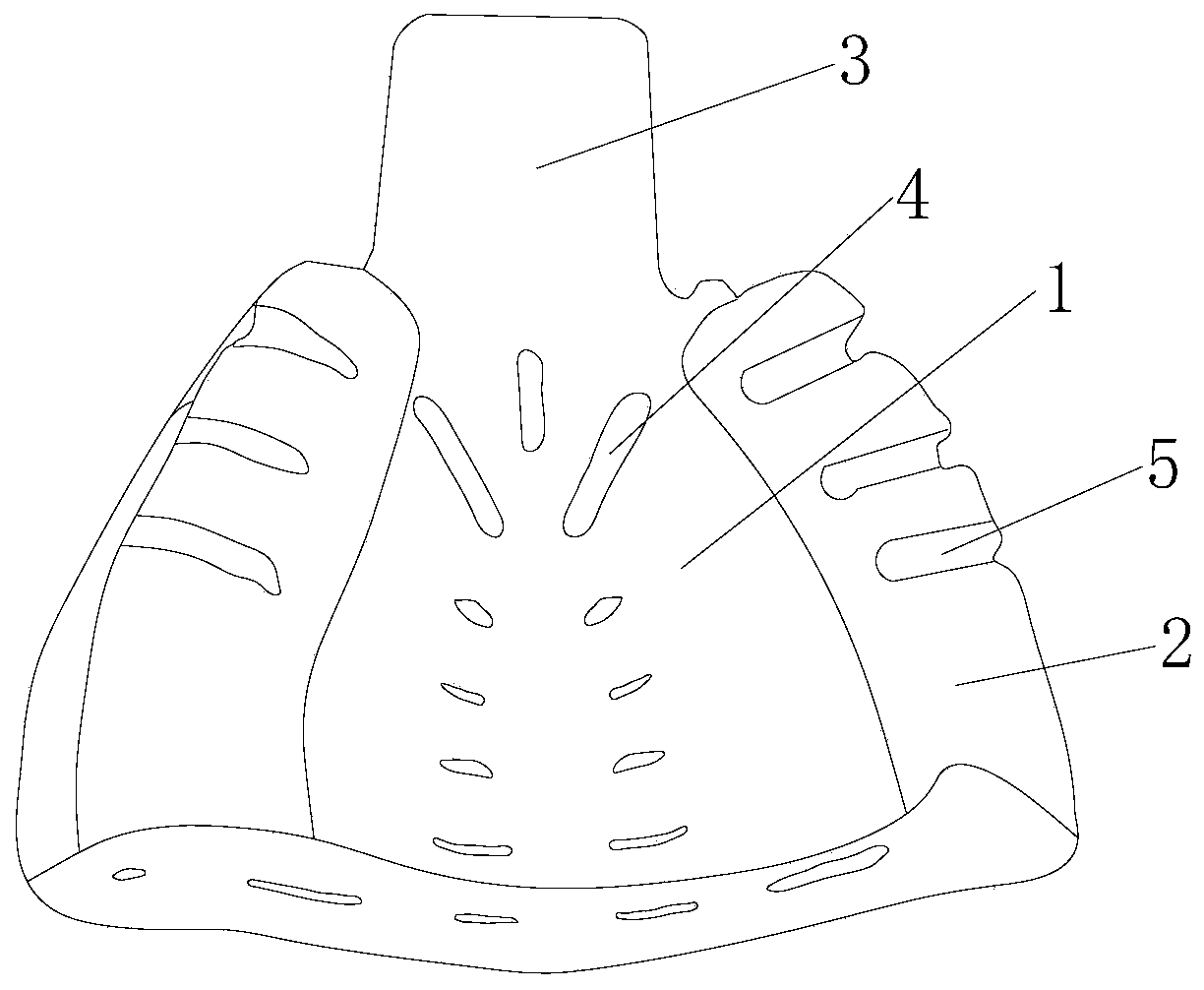
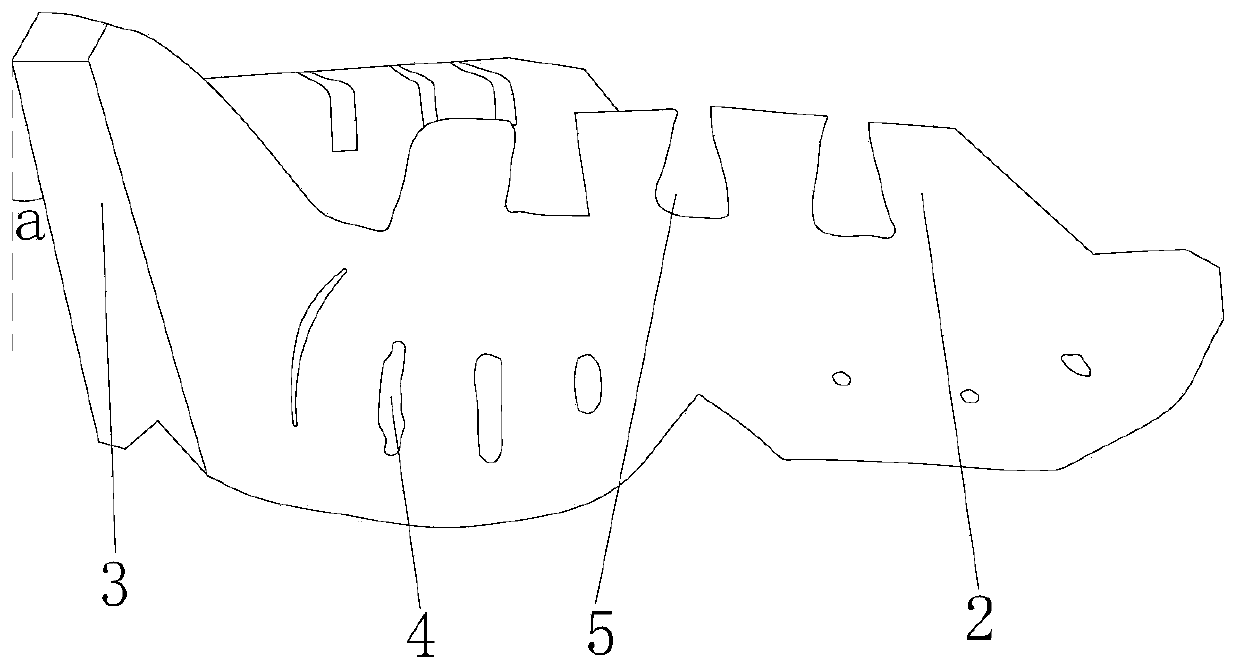
[0034] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, this embodiment provides an improved complete denture maxillary initial mold tray, including a tray body composed of a tray base 1 in the middle and occlusal dykes 2 on both sides. The positions of the two occlusal dykes 2 Corresponding to the alveolar ridges between the first premolar and the second premolar on both sides of the human teeth; one end of the tray body is provided with a tray handle 3 connected to the tray base 1; A plurality of overflow holes 4 are evenly arranged; the width of the occlusal embankment 2 gradually increases from one end close to the tray handle 3 to the other end, and three fixing grooves 5 are arranged at intervals on the occlusal embankment. It should be noted that the maxillary blank tray of the present invention is made of silicone rubber; the angle a between the end surface of the tray handle 3 away from the tray base 1 and the vertical surface is equal to 15°.
[0035] The preliminary occl...
Embodiment 2
[0037]This embodiment is a further improvement made on the basis of Embodiment 1. The specific differences between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 are:
[0038] What needs to be further explained in this embodiment is that the width of the occlusal embankment 2 is 6-8 mm. It should be further explained that the height of the occlusal embankment 2 is 10mm. Specifically, the width of the occlusal embankment 2 can be 6mm, 7mm or 8mm, etc., as long as it is within this range, there is no specific limitation. Since the average width of the maxillary wax occlusal embankment is 6-8mm, the occlusal embankment The width of 2 is between 6-8mm, which is the most appropriate range. At the same time, since the average height of the maxillary wax occlusal embankment is 12mm, after taking an impression as a tray, the impression material may raise the occlusal height by 1-2mm, so It is most appropriate to set the height of the occlusal embankment at 10mm, and the width and height of the occ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] This embodiment is a further improvement made on the basis of Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2. The specific differences between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 are:
[0041] What needs to be further explained in this embodiment is that the fixing groove 5 is a trapezoidal groove structure with a bottom width and a top narrowness. That is, the inner bottom surface of the fixing groove 5 is equivalent to the lower bottom surface with a larger area in the trapezoidal structure, and the opening at the upper end of the fixing groove 5 is equivalent to the upper bottom surface with a smaller area in the trapezoidal structure, and this trapezoidal groove structure After the material is hardened, Because the opening is smaller than the bottom, the material is not easy to separate from the occlusal embankment, and the material can be firmly stuck on the occlusal embankment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com