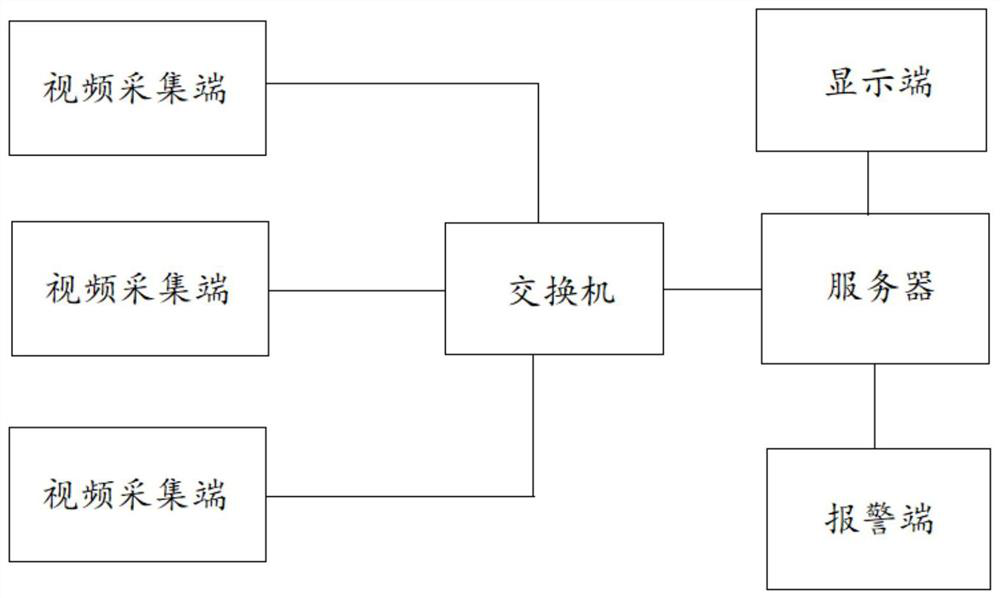
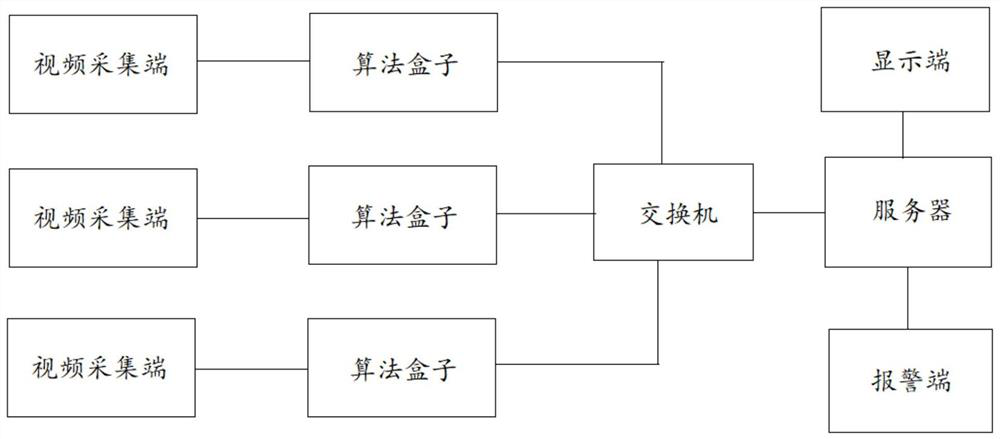
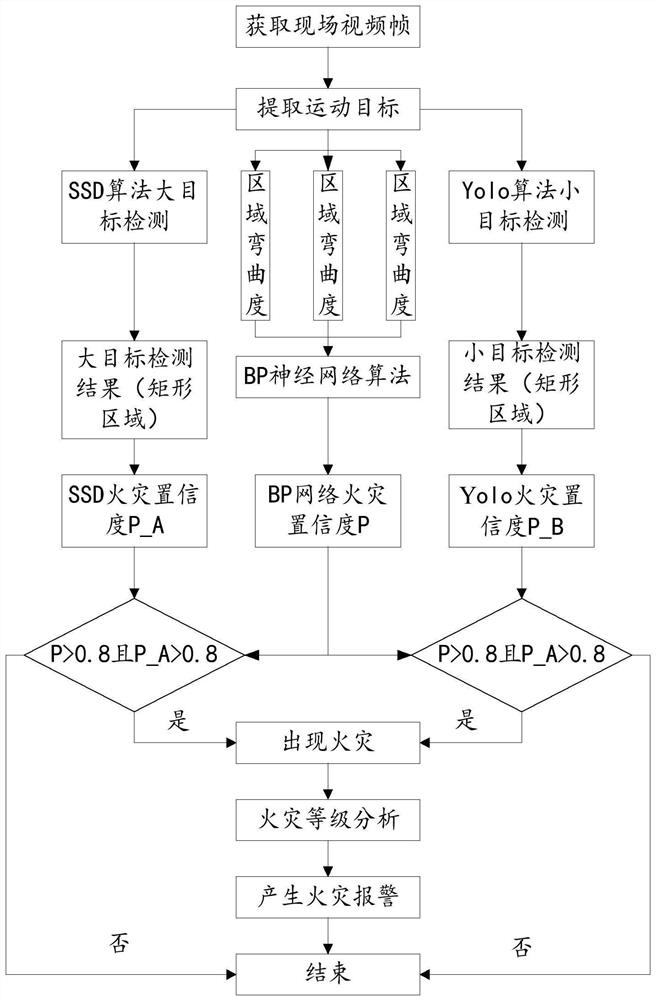
A multi-factor flame identification method suitable for embedded platforms
A flame recognition and multi-factor technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, fire alarms that rely on radiation, fire alarms, etc., can solve the problems of unable to express fire information normally, low robustness, long detection time, etc. , to achieve the effect of increasing the scope of detection, avoiding a huge amount of calculation, and facilitating investigation and evidence collection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Various embodiments of the present application will be disclosed in the drawings below, and for the sake of clarity, many practical details will be described together in the following description. It should be understood, however, that these practical details should not be used to limit this application. That is, in some embodiments of the present application, these practical details are unnecessary. In addition, for the purpose of simplifying the drawings, some well-known structures and components will be shown in a simple schematic manner in the drawings.
[0034] In addition, the descriptions such as "first", "second", etc. in this application are only for the purpose of description, and do not specifically refer to the order or order, nor are they used to limit the application, but are only for the purpose of distinguishing The components or operations are described by the same technical terms, and should not be construed as indicating or implying their relative im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com