Method for detecting dielectric constant of material by using scanning probe
A technology for detecting dielectric constant and materials, applied in scanning probe technology, scanning probe microscopy, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as difficult scanning analysis, achieve simple modeling process, and realize non-destructive detection Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0032] A method for detecting the dielectric constant of a material using scanning probe microscopy, comprising the steps of:
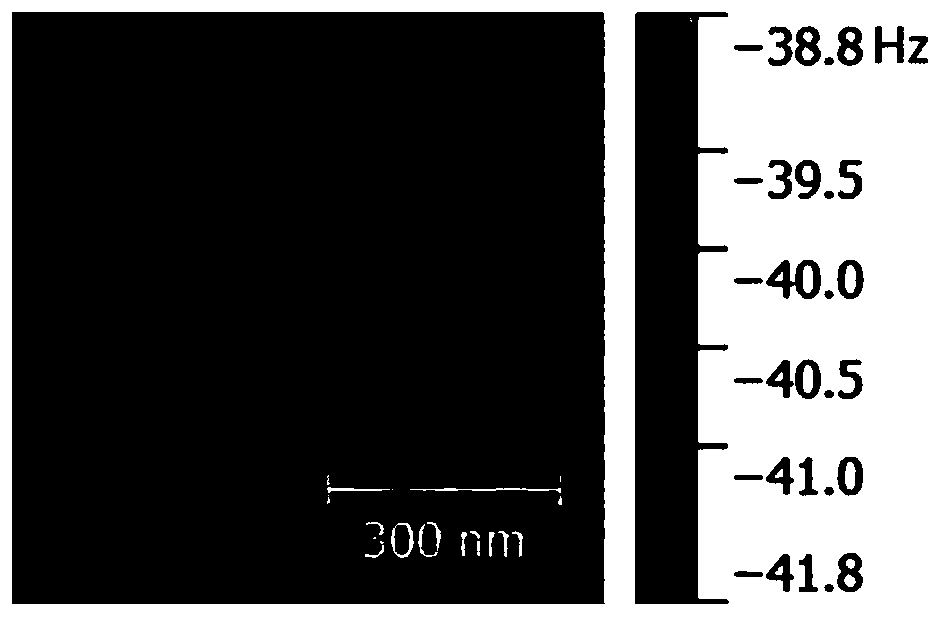
[0033] (1) Using an electrostatic force microscope: under DC bias, keep the distance z between the probe and the sample constant, detect the offset Δf of the resonance frequency of the probe, and calculate the capacitance between the probe and the sample accordingly second derivative d 2 C / dz 2 ; The second derivative d 2 C / dz 2 It can also be represented by C";
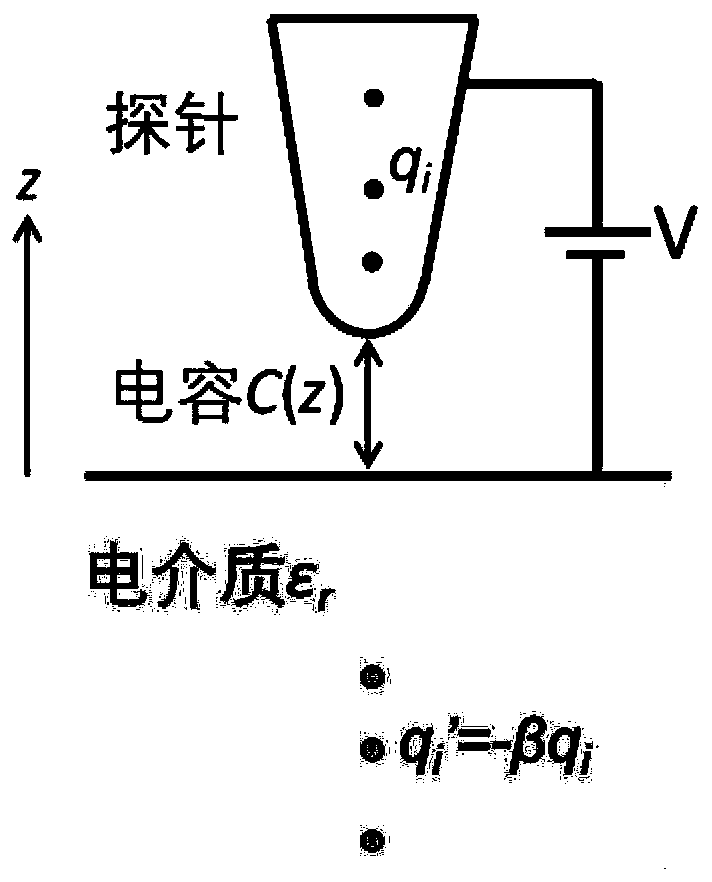
[0034] (2) Using the image charge method: construct a relationship model between the force and capacitance between the probe and the sample as the dielectric constant ε changes in the sample, and obtain the C"-ε curve;
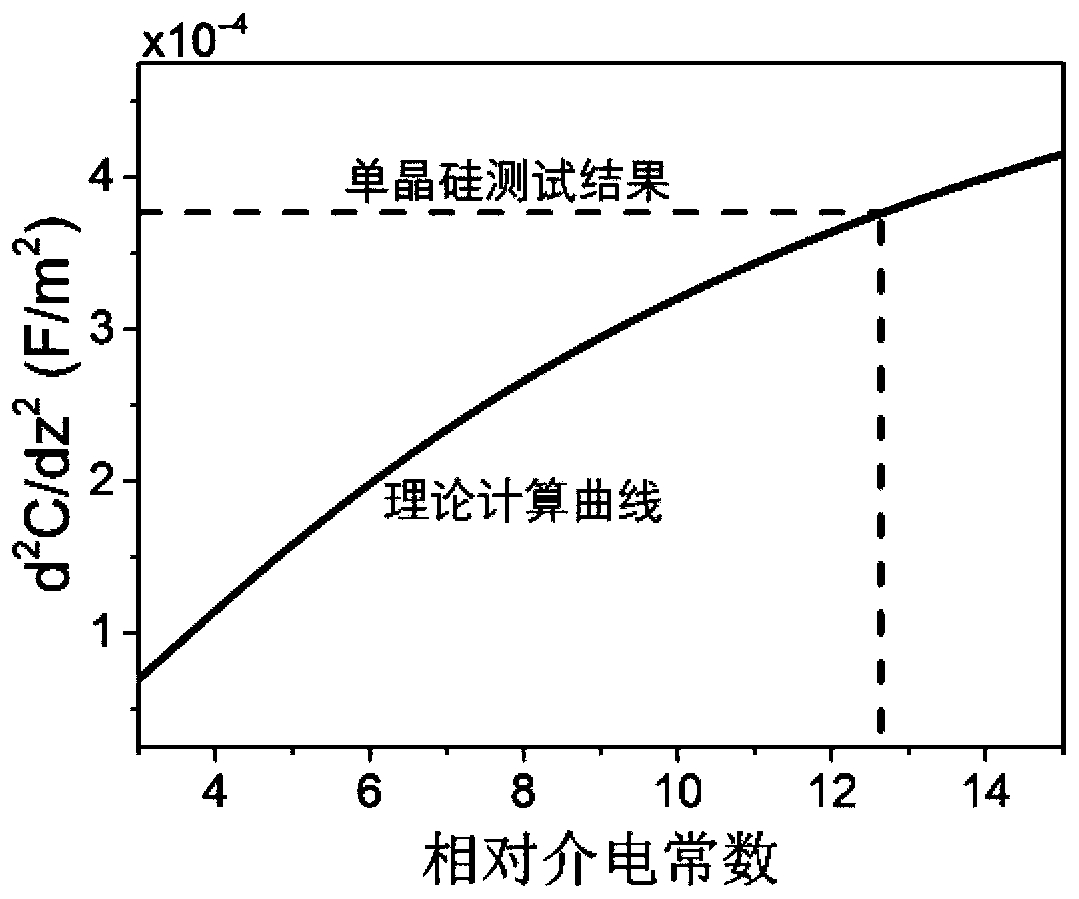
[0035] (3), d in step (1) 2 C / dz 2 The calculated experimental value is compared with the theoretical curve of C"-ε in step (2), to obtain th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com