A Coordinated Control Method of Traffic Signals at Arterial Intersections Based on Non-Isoperiod
A coordinated control and traffic signal technology, applied in the field of coordinated traffic signal control at arterial intersections, can solve the problems of limited green wave width, low utilization rate of coordinated phase green lights, and many motor vehicle parking times, so as to increase the green wave zone The effect of increasing the width, improving the utilization rate of green lights, and improving the efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
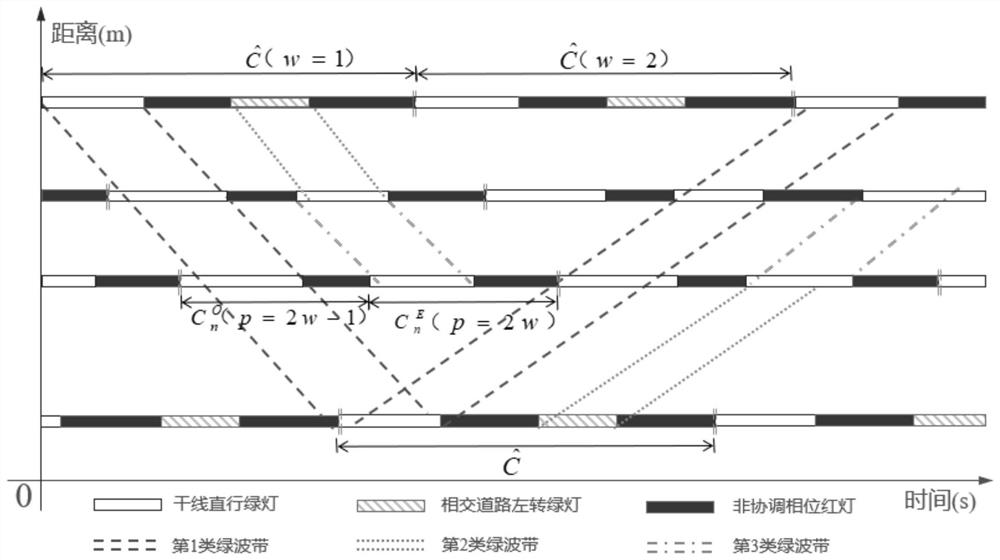
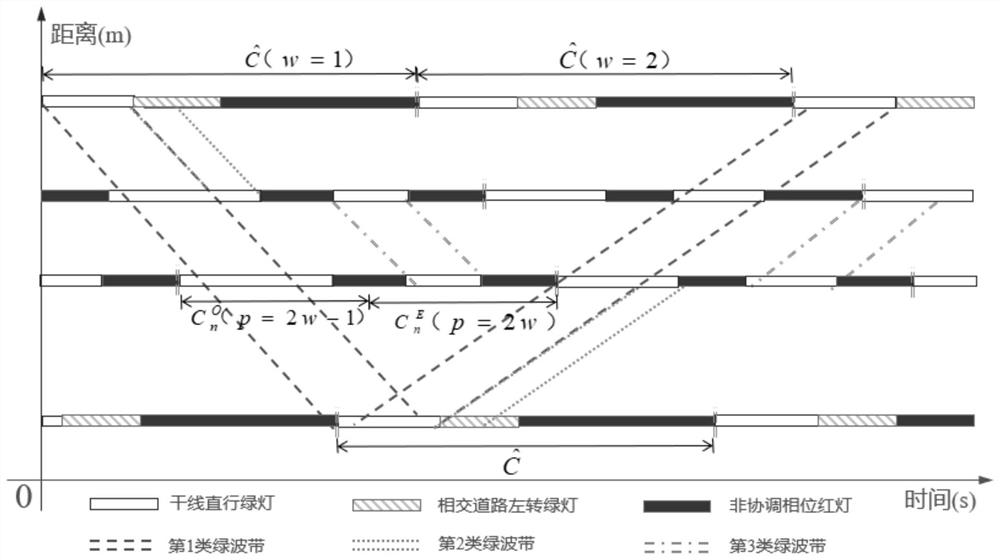
[0066] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, a method for coordinated control of traffic signals at arterial intersections based on a non-isoperiodic period. The specific process is as follows:
[0067] Step 1: The coordinated control area includes a total of N adjacent signalized intersections, collecting the entrance lane flow of each intersection within a given period of time;
[0068] Step 2: The number of the intersection is 1, 2,...,n...,N; there is I at the intersection n n Phases, numbered 1,2,…,i n ..., I n , calculate the cycle time C when intersection n executes single-point control (control of a single intersection, regardless of the control of other intersections) n , the unit is s; the specific process is:
[0069] Step 21. Calculate the initial period C of the intersection n 0,n , unit s; C 0,n The formula is:
[0070]
[0071] In the formula, L n is the total green light loss time of intersection n (green light time that cannot ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0122] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the step 6, the constraint of constructing the phase combination scheme and the equivalent relationship between the cycle and the phase green light; the specific process is:
[0123]
[0124]
[0125]
[0126]
[0127]
[0128] In the formula: g n,1 It is the duration of the green light for the downlink straight phase of an odd-numbered period at a Type I intersection or Type II intersection (use g when the intersection is Type I n,1 means that when the intersection is class II, g n,1 Indicates the straight-going phase green light duration of an odd cycle), the unit is s; g n,2 It is the duration of the green light of the up-going straight-going phase in an odd-numbered cycle of a Type I intersection or a Type II intersection, and the unit is s;
[0129] It is the green light duration of the downlink left-turn phase of an odd-numbered period at a Type I intersection or Ty...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0136] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in the step seven, when coordinating the left-turn traffic flow at the type I intersection, it is necessary to divide the intersection into different sets;
[0137] For the green wave belt formed between consecutive Type II intersections, it is necessary to divide the intersections into different sets;
[0138] The specific process is:
[0139] The left-turn traffic flow of main road 2 in the downlink and uplink direction I type intersections can be coordinated by the downstream intersection of main road 1 (the next intersection relative to the direction of vehicle travel at the current intersection), which are respectively classified into sets M, (The downlink can be classified into M by the coordinated intersection, and the uplink can be classified by the coordinated intersection into ), the number of elements in the set is and (If the downstream adjacen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com