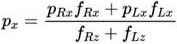A zero calibration method for the lower limb joints of a humanoid robot
A humanoid robot, zero-position calibration technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as inefficiency, robot instability, and falling, and achieve the effect of saving manpower and accurate motion control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereto.
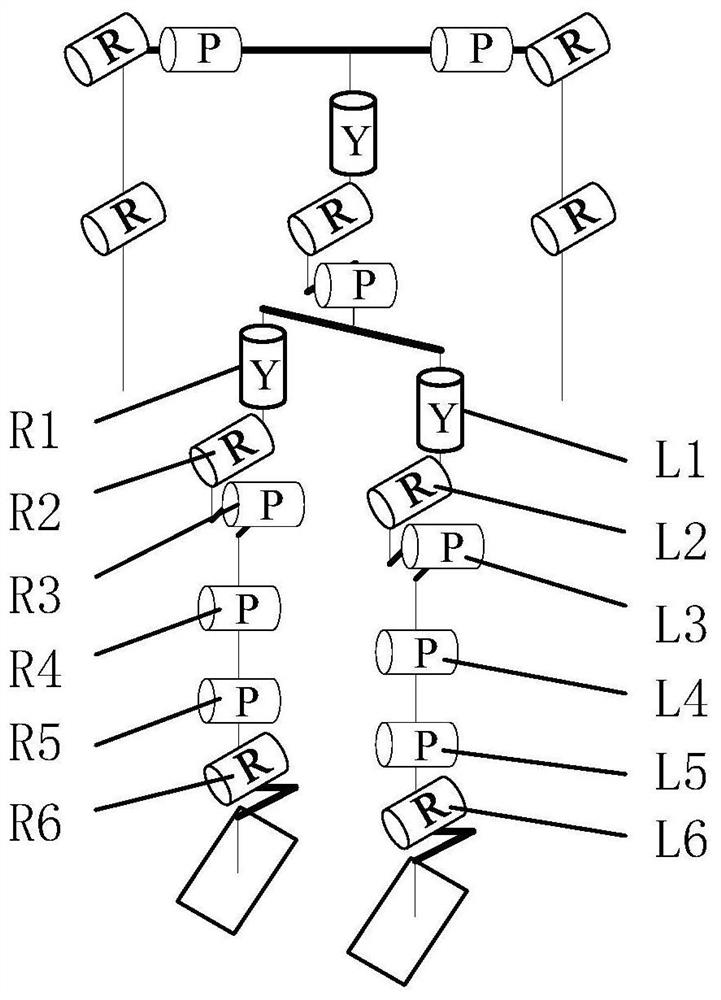
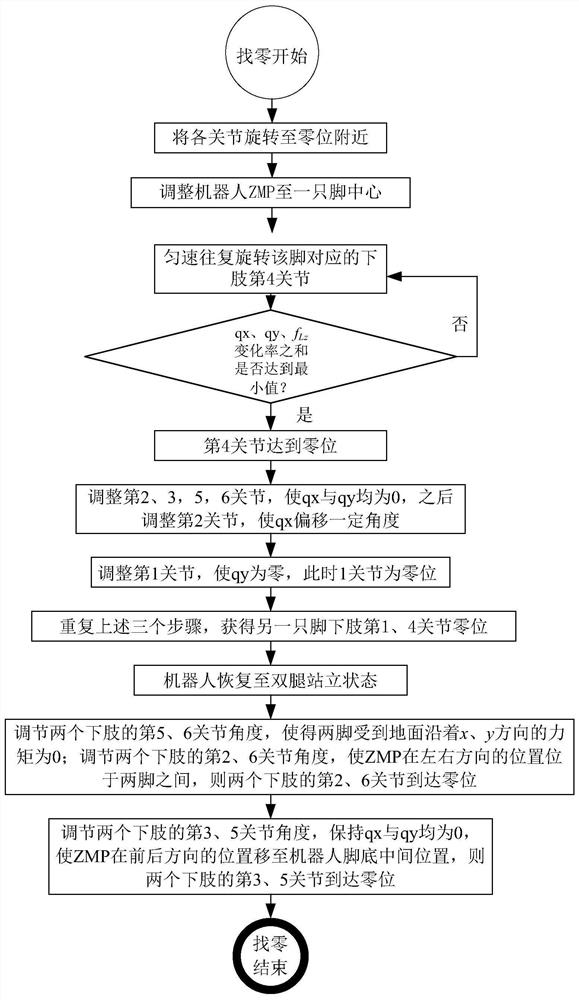
[0028] The zero position of the joints of the humanoid robot in the present invention refers to the position of each joint when the humanoid robot stands in an upright posture.
[0029] The method for calibrating the zero position of the joints of the lower limbs of the present invention is suitable for a humanoid robot, and the humanoid robot is an anthropomorphic intelligent robot with a torso, a head, two hands and two feet. The humanoid robot perceives its own state and external environment information through the sensing system, including the posture sensor installed on the torso to obtain the posture angle of the body, and the six-dimensional force / torque sensor fixed on the ankle joint to obtain the contact force between the robot and the ground, etc. The drive sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com