Cross-domain face recognition algorithm, storage medium and processor
A face recognition, cross-domain technology, applied in the field of face recognition algorithms, can solve the problems of low recognition accuracy and low recognition efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
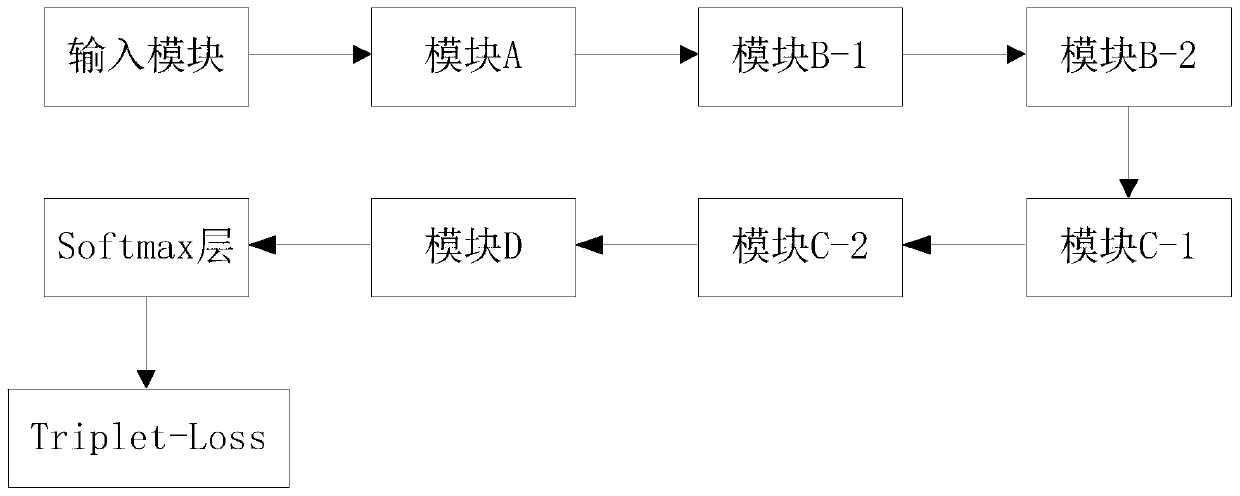
[0028] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the Facenet neural network structure in the prior art. Facenet neural network structure, the input module passes through module A, module B-1, module B-2, module C-1, module C-2, module D, and then through the Siftmax layer, and then the Triplet-Loss calculation is performed.
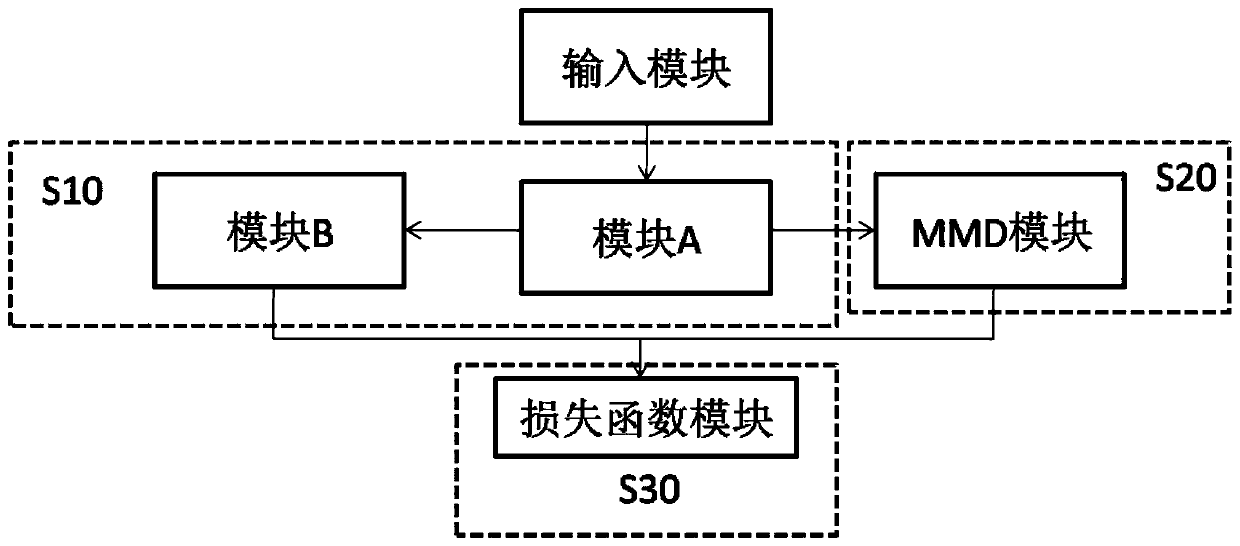
[0029] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the cross-domain face recognition algorithm module of the present invention. Such as figure 2 shown in figure 1 On the basis of the existing Facenet neural network, this embodiment adds an MMD module and a synthetic loss function module. S10 is a neural network module, S20 is a maximum difference mean module, and S30 is a loss function module. Module A to Module E are feature extraction network modules. Among them, module A is a conventional feature extraction network; modules B-1, C-1 and D draw on the idea of Inception-Resnet to reduce the amount of parameter calculation while ensuring...
Embodiment 2
[0039] An embodiment of the present invention also provides a storage medium, which includes a stored program, wherein, when the above program is running, the above-mentioned flow of the face attribute recognition method is executed.
[0040] Optionally, in this embodiment, the above-mentioned storage medium may be configured to store program codes for executing the following flow of the face attribute recognition method:
[0041] S11, building a Facenet neural network;
[0042] S12, adding the average pooling layer and the Faltten layer at the highest dimension layer of the Facenet neural network feature vector, and changing the feature vector into a single-channel one-dimensional vector;
[0043] S13. Calculate the maximum mean difference loss with a single-channel one-dimensional vector;
[0044] S14. Add the maximum mean difference loss to the loss function of the Facenet neural network, and jointly participate in backpropagation and gradient derivation.
[0045] Optiona...
Embodiment 3
[0048] An embodiment of the present invention also provides a processor, the processor is used to run a program, wherein, when the program is running, the steps in the above-mentioned face attribute recognition method are executed.
[0049] Optionally, in this embodiment, the above program is used to perform the following steps:
[0050] S11, building a Facenet neural network;
[0051] S12, adding the average pooling layer and the Faltten layer at the highest dimension layer of the Facenet neural network feature vector, and changing the feature vector into a single-channel one-dimensional vector;
[0052] S13. Calculate the maximum mean difference loss with a single-channel one-dimensional vector;
[0053] S14. Add the maximum mean difference loss to the loss function of the Facenet neural network, and jointly participate in backpropagation and gradient derivation.
[0054] Optionally, for specific examples in this embodiment, reference may be made to the above-mentioned emb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com