Thermostatic bath
A constant temperature tank and tank bottom technology, applied in the field of constant temperature tanks, can solve problems such as backwardness, achieve the effects of increased heating and cooling speed, reduced external insulation layer, and small space occupation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
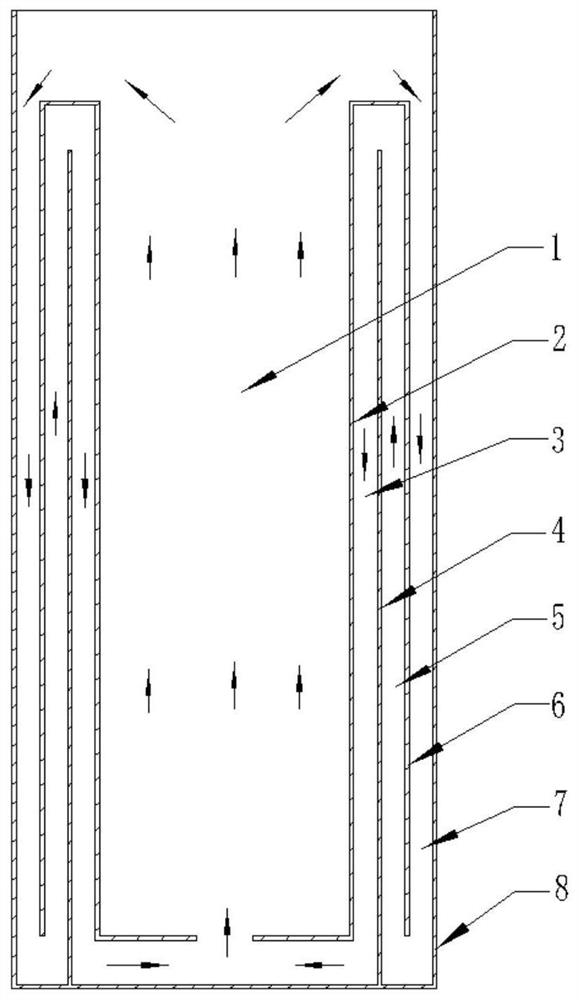
[0035] Such asfigure 1 As shown in , a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the constant temperature bath provided in this embodiment is shown. It can be seen that the thermostatic tank provided in this embodiment includes an annular outer casing 8 and a three-layer annular baffle disposed inside the annular outer casing 8, wherein the annular outer casing 8 includes an annular groove wall located at the circumference and a groove bottom located at the bottom , the three layers of baffles are the first layer of annular baffles 6 , the second layer of annular baffles 4 and the third layer of annular baffles 2 from outside to inside. Wherein the annular space formed between the first layer of annular baffle 6 and the annular groove wall of the annular outer shell 8 is the first flow insulation layer 7; the second layer of annular baffle 4 and the first layer of annular baffle 6 formed The annular space is the second flow insulation layer 5; the annular space formed bet...
Embodiment 2
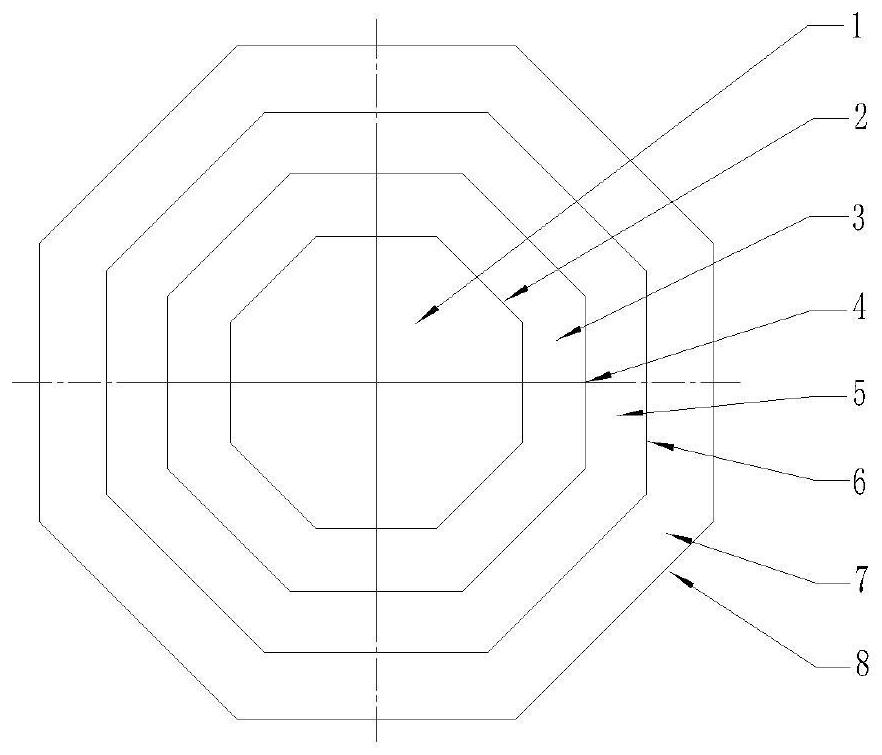
[0040] Such as figure 2 As shown in FIG. 1 , it shows a schematic top view of the thermostatic bath provided in this embodiment. It differs from the thermostatic bath provided in Example 1 only in that the annular outer shell of the thermostatic bath provided by this embodiment is a polygonal columnar outer shell (that is, the top view of the structure surrounded by the outer shell is polygonal), and the annular baffle is also polygonal. The columnar baffle (that is, the structure enclosed by the baffle is polygonal in plan view), wherein the polygon is, for example, an equilateral polygon or a non-equilateral polygon. The polygonal outer casing and the polygonal baffle plate of the constant temperature bath provided in this embodiment are all regular hexagons, and those skilled in the art should understand that they can also be regular triangles, regular quadrilaterals, regular pentagons, non-equilateral triangles, Non-equilateral quadrilaterals, non-equilateral pentagons, ...
Embodiment 3
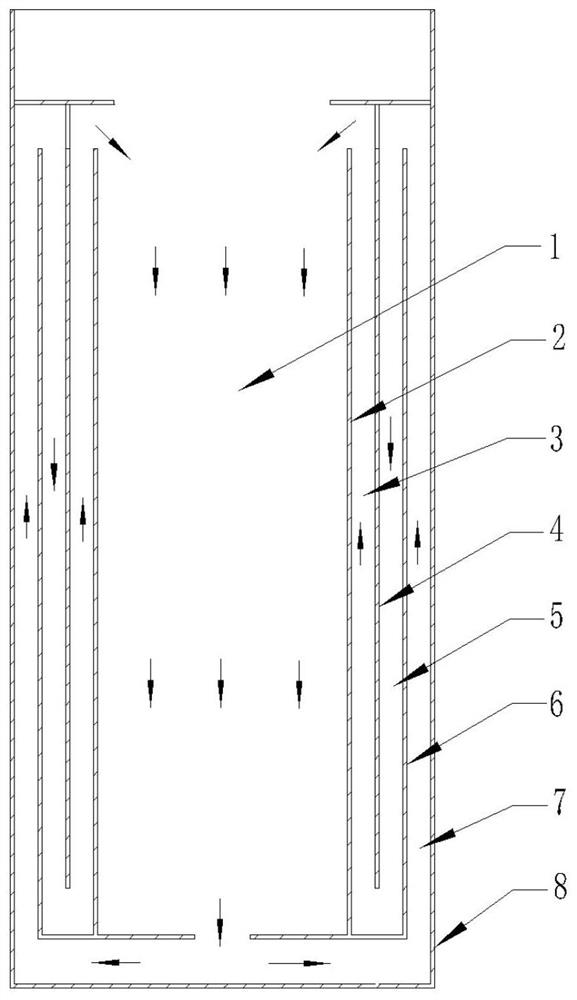
[0042] Such as image 3 As shown in , a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the constant temperature bath provided in this embodiment is shown. The difference between the thermostatic bath provided in this embodiment and the thermostatic bath provided in Embodiment 1 is that: the bottom of the first layer of annular baffle 6 and the bottom of the third layer of annular baffle 2 are sealed and connected with the bottom of the annular outer casing 8 All are provided with gaps, which allow the liquid in the tank to enter the first flow insulation layer 7 from the central constant temperature zone 1 . The top of the second layer of annular baffle 4 is sealingly connected with the groove wall of the annular outer shell 8, and a gap is provided between the sealing connection and the top of the first layer of annular baffle 6, which allows the tank liquid to flow from the first The fluid insulation layer 7 enters into the second fluid insulation layer 5 . A gap is also s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com