An electric soil heavy metal removal device
A heavy metal and soil technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problems of difficult discharge of anode electrode gas, hindering the normal operation of the DC electric field, and rainwater interference with the treatment process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
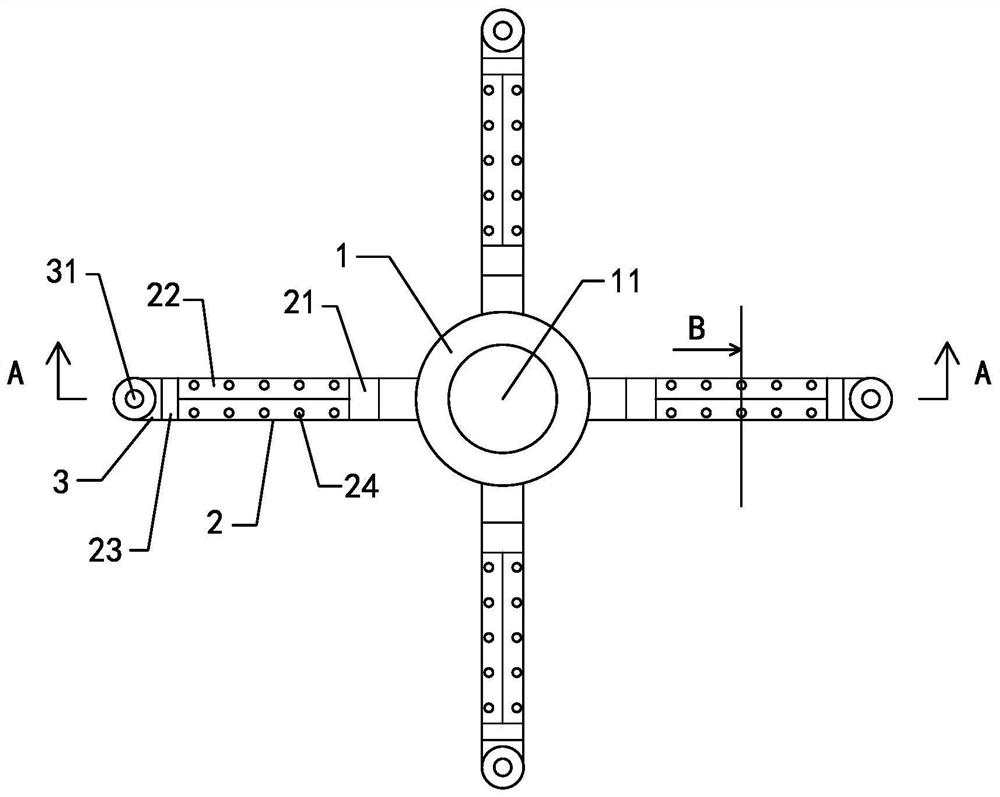
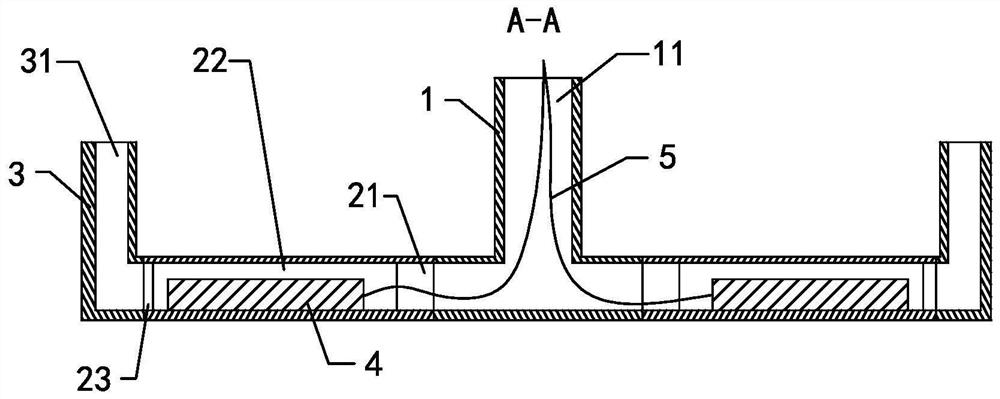
[0028] see Figure 1-3 , This embodiment provides an electric soil heavy metal removal device, including a power supply (not shown in the figure), a cathode (not shown in the figure), an anode rod 4, a water inlet pipe 1, an anode placement pipe and a water outlet pipe 3.
[0029] The power supply is located above the soil, the anode rod 4 is located in the soil, the cathode is arranged on the soil surface, and the power supply, the anode rod 4 and the cathode are electrically connected in sequence to form a loop. After the power supply is energized, a DC electric field is formed between the anode rod 4 and the cathode, that is, between the anode rod 4 and the soil surface, and the heavy metal ions in the soil continue to migrate to the cathode.
[0030] The water inlet pipe 1 , the anode placement pipe and the water outlet pipe 3 are connected in sequence, and the water enters the water inlet pipe 1 from the water inlet 11 of the water inlet pipe 1 , then flows through the an...
Embodiment 2
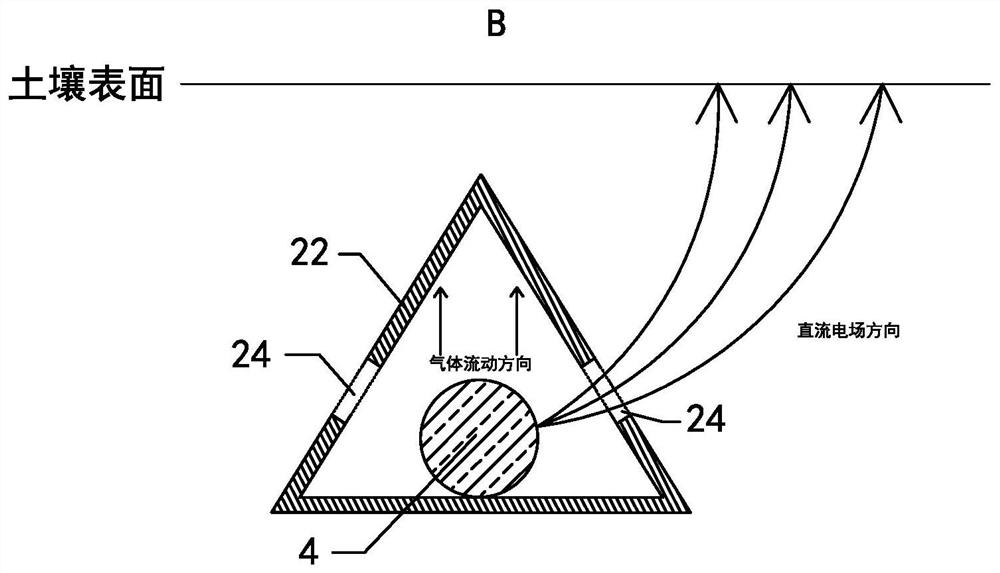
[0045] see Figure 4 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the anode placement tube also includes a triangular prism body 25 located below the placement section 22 . The bottom side edges of the triangular prism 25 can make the placing section 22 more easily pressed into the soil, and the solid triangular prism 25 can make the anode placing tube move down the center of gravity after pressing, so that the anode placing tube can be more easily placed in the soil. for stability. In this embodiment, the outer contour of the cross section of the anode placement tube at the placement section 22 is a quadrilateral. Further, the four vertices of the quadrilateral are located on the same circle, so that the cross section of the anode placement tube at the placement section 22 is closer to the round, thereby reducing the design length of the transition pipe, correspondingly, the length of the circular pipe on the first connecting section and the second connect...
Embodiment 3
[0047] see Figure 5 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the upper end of the water inlet main pipe is provided with a collecting funnel 12 that increases the area of the water inlet 11 , and the upper end of the water outlet pipe 3 is provided with a ring cover 32 that reduces the area of the water outlet 31 . When it rains, the water collecting funnel 12 can increase the amount of rainwater collected at the water inlet 11. After the area of the water outlet 31 is reduced, the amount of rainwater falling into the water outlet 31 is less than that at the water inlet 11, thereby ensuring that the rainwater is collected and utilized. In this case, the backflow of the liquid anolyte from the water outlet 31 to the water inlet 11 is prevented.
[0048] In this embodiment, an annular buffer cover 37 is also provided on the outer wall of the water outlet pipe 3 above the soil. The middle part of the buffer cover 37 is recessed downward, so that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com