SAR image target recognition method and device based on sparse representation and cascade dictionary
A sparse representation and target recognition technology, applied in the field of image processing and pattern recognition, can solve problems affecting the speed of solving sparse coefficients, affecting the speed of test sample recognition, high dictionary dimension, etc., to overcome the slow speed of sparse solving and good classification The effect of recognizing the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
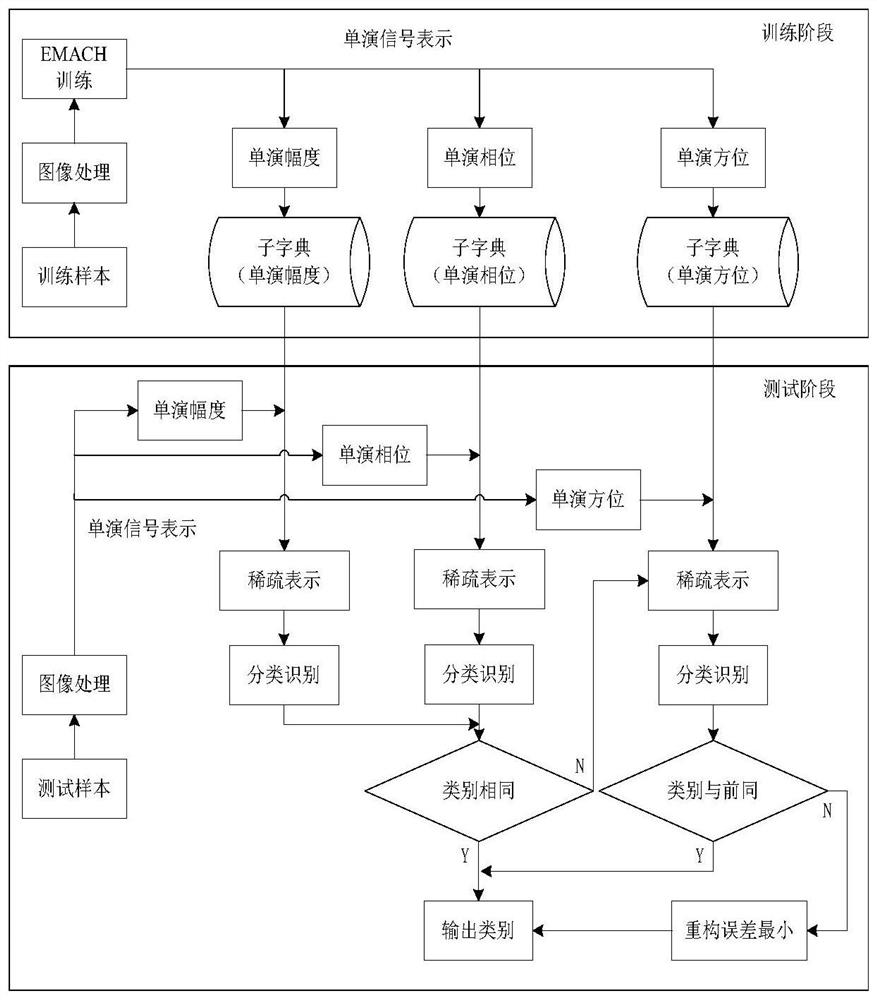
[0021] Embodiment 1, SAR image target recognition method based on sparse representation and cascaded dictionary, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
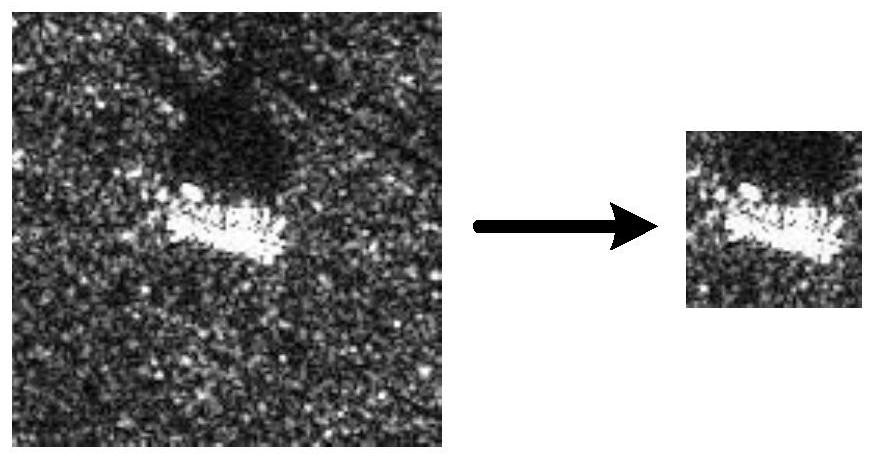
[0022] Segment the central area containing the target from the SAR image, remove the background noise to obtain the image to be recognized, and extract the single-shot amplitude, single-shot phase and single-shot azimuth features of the image to be recognized;
[0023] Based on the extracted monomorphic amplitude, monomorphic phase, and monomorphic azimuth features and the sub-dictionaries generated in advance for the monomorphic amplitude, monochromatic phase, and monochromatic azimuth features of the training sample images, the sparse coefficient is calculated by minimizing the L1 norm, The classification mechanism with the largest coefficient energy and the smallest reconstruction error is used for target classification recognition to obtain recognition results.
[0024] In this embodiment, optionally, a ...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Embodiment 2. On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a SAR image target recognition method based on sparse representation and cascaded dictionary. The method also includes:
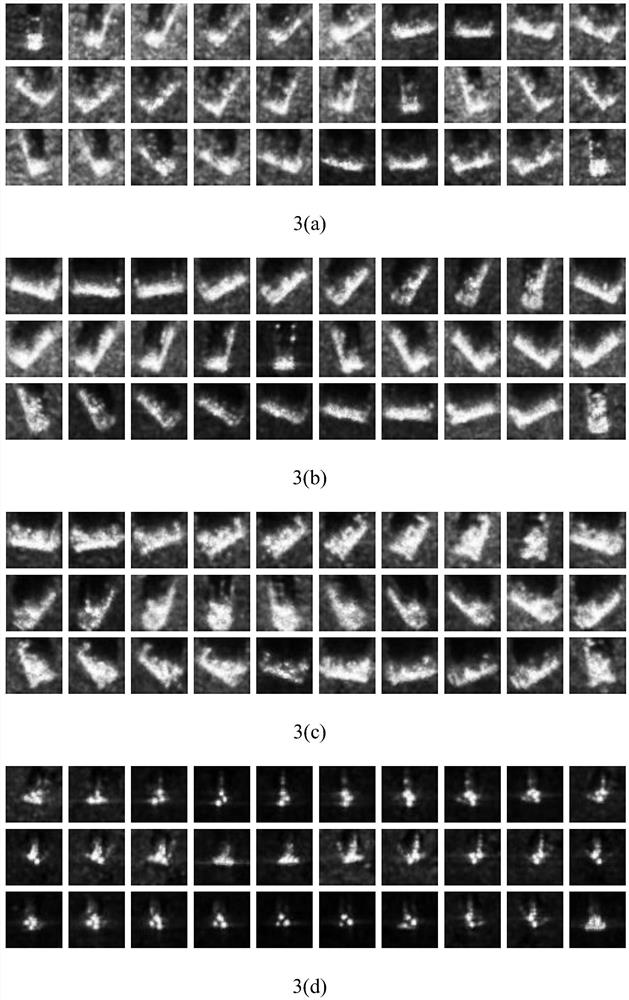
[0079] Utilize the EMACH filter training sample image, generate the template image of the training sample image by every set azimuth (set every 12 degrees in this embodiment), specifically include;
[0080] (3.1) Input N training sample images, from left to right, from top to bottom to expand each pixel into a one-dimensional vector x i , where i=1,2,…,N, calculate x i the mean of the vector m;
[0081] (3.2) Define h as EMACH filter, FFT() means Fourier operation, let β∈(0,1), M=FFT(m), X i =FFT(x i ), calculate the intermediate parameter and as follows:
[0082]
[0083]
[0084] Among them, the symbol "+" represents matrix transposition;
[0085] (3.3) when the formula When the value is the largest, h is The eigenvectors corresponding to the eigenvalues of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com