Transformer area line impedance calculation method and calculation system, and computer readable storage medium
A line impedance and calculation method technology, applied in the field of distribution network, can solve the problem of inaccurate monitoring of line impedance in the station area, so as to improve the reliability of power supply, improve the calculation accuracy, and reduce the occurrence of faults
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
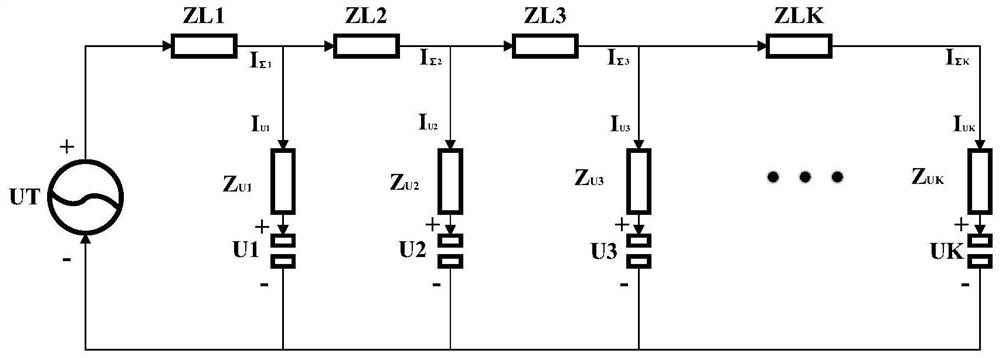
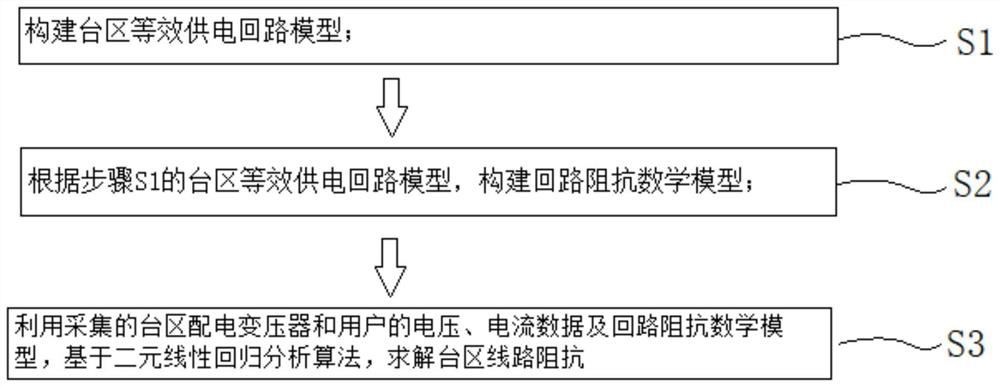
[0068] like Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, a method for calculating line impedance in a station area includes the following steps:
[0069] S1: Construct the equivalent power supply circuit model of the station area;
[0070] S2: Construct a mathematical model of loop impedance according to the equivalent power supply loop model of the station area in step S1;
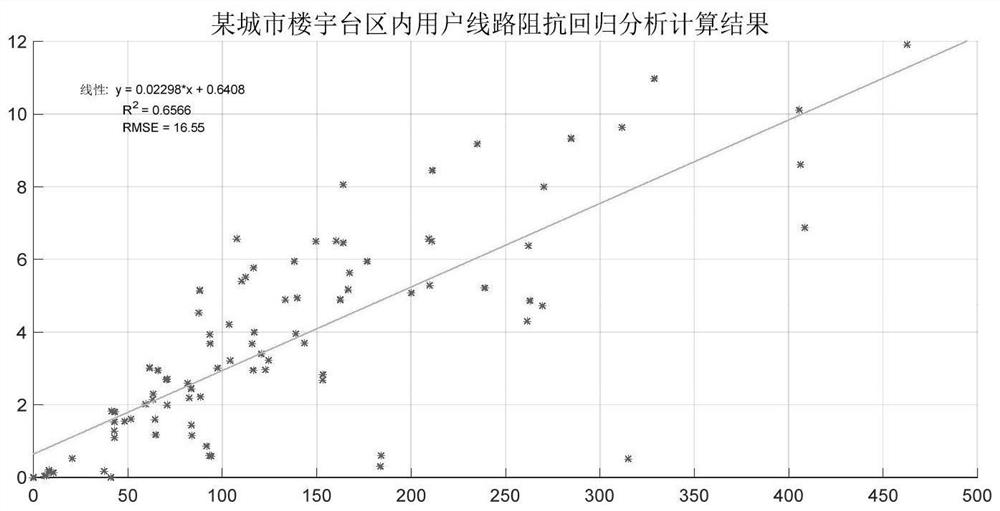
[0071] S3: Using the collected voltage and current data of distribution transformers and users in the station area and the mathematical model of loop impedance, based on the binary linear regression analysis algorithm, solve the line impedance in the station area.
[0072] Wherein, step S1 specifically includes the following steps:
[0073] s11: if figure 1 As shown, it is the equivalent power supply circuit diagram of the urban building station area. According to the voltage distribution characteristics of each user and distribution transformer in the low-voltage distribution station area, the closer the user's po...
Embodiment 2
[0119] The modeling process is as follows:
[0120] 1. According to the voltage distribution characteristics of each user and distribution transformer in the low-voltage distribution station area, the closer the user's power supply position is to the same-phase outlet position of the distribution transformer, the closer the user's voltage is to the same-phase voltage of the distribution transformer to which the user belongs. Reflected on the equivalent power supply circuit diagram of the urban building station area, the voltage distribution characteristics of the distribution transformer in the station area and the k users connected to each phase at any time are as follows:
[0121] UT(t)>U1(t)>U2(t)>U3(t)>…>UK(t)
[0122] Considering the possible impact of the instantaneous measurement error of the smart meter, this feature can be further established on the basis of the daily average voltage, that is, the 96-point daily average voltage distribution between the distribution tr...
Embodiment 3
[0147] A system for calculating line impedance in a station area includes a memory and a processor. The memory includes a program for calculating the line impedance in a station area. When the program for calculating the line impedance in a station area is executed by the processor, the following steps are implemented:
[0148] S1: Construct the equivalent power supply circuit model of the station area;
[0149] S2: Construct a mathematical model of loop impedance according to the equivalent power supply loop model of the station area in step S1;
[0150] S3: Using the collected voltage and current data of distribution transformers and users in the station area and the mathematical model of loop impedance, based on the binary linear regression analysis algorithm, solve the line impedance in the station area.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com