Compositions and methods for in vivo post translational modification
A post-translational modification and composition technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical equipment and methods, antibody mimics/scaffolds, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the functionality of biological products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
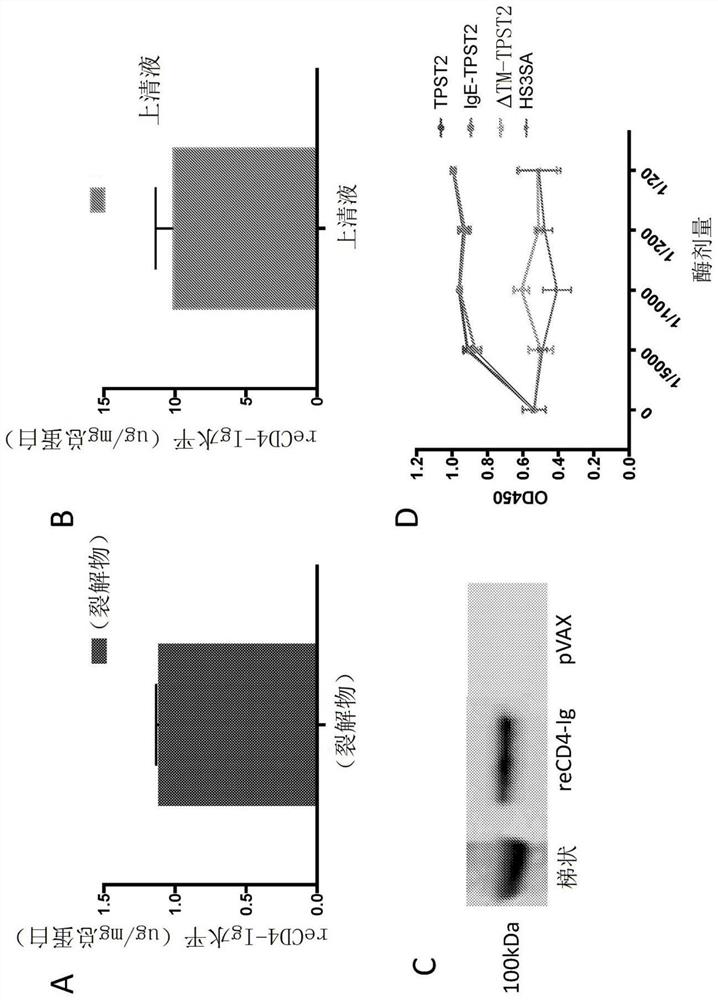
[0332] Example 1: Synthetic DNA Delivery by Electroporation Promotes Robust In Vivo Sulfation of the Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV Immunoadhesin ECD4-IG
[0333] Transfection of HEK293T cells enables expression and secretion of ReCD4-Ig in vitro
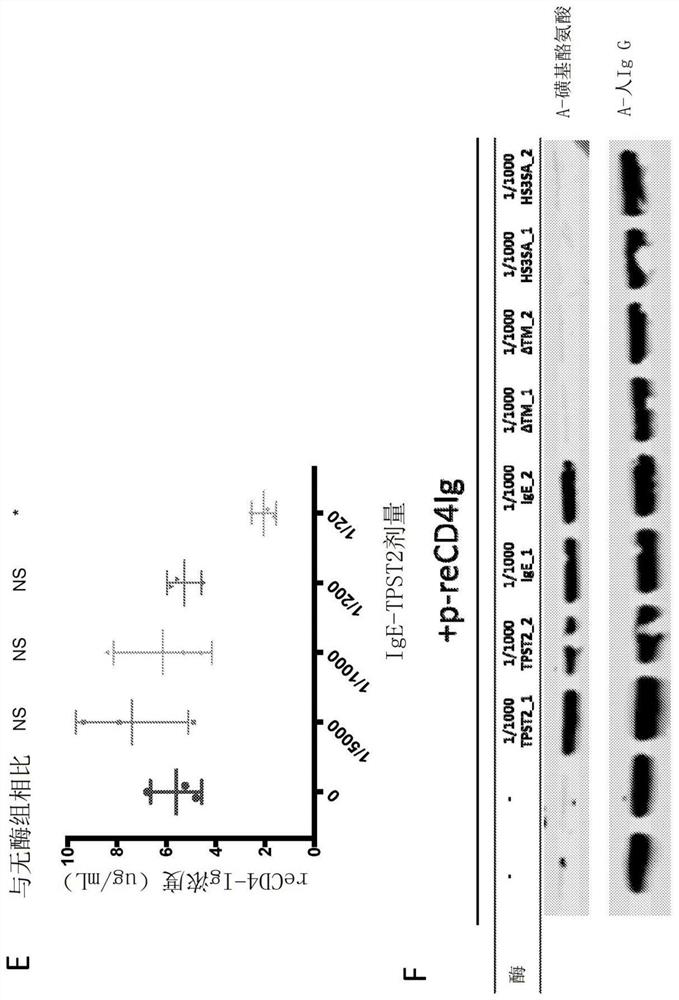
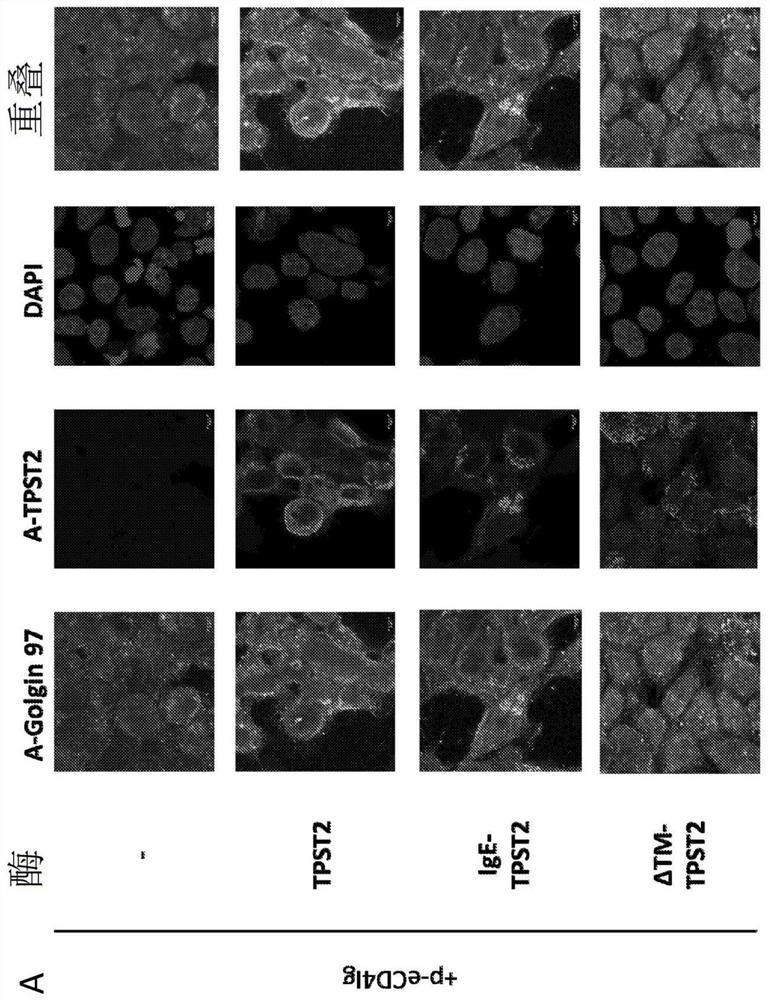
[0334] A transgene encoding ReCD4-Ig with an N-terminal IgGκ-leader sequence was designed, then synthesized de novo, and cloned into the pGX00001 backbone plasmid. Transgene nucleotide sequences were optimized for codon bias and structure and stability of mRNA transcripts in both mice and humans (Graf et al., 2004; Patel et al., 2017). An N-terminal IgG leader sequence is incorporated to facilitate targeting of the transgene to the ER and facilitate secretion (Haryadi et al., 2015). Strong expression of ReCD4-Ig was observed in cell lysates and supernatants (Fig. 1A-B). Immunoblot of transfection supernatants with anti-human IgG confirmed secretion of ReCD4-Ig by transfected cells (Fig. 1C).
[0335] Co-transfection of HEK293T...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap