A method for predicting viscosity properties of cellulose bioinks
A technology of bio-ink and characteristic prediction, applied in genetic rules, special data processing applications, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as inability to use linear fitting methods, inaccurate prediction results, lack of model comparison and selection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0081] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but the following embodiments do not limit the present invention by any means.
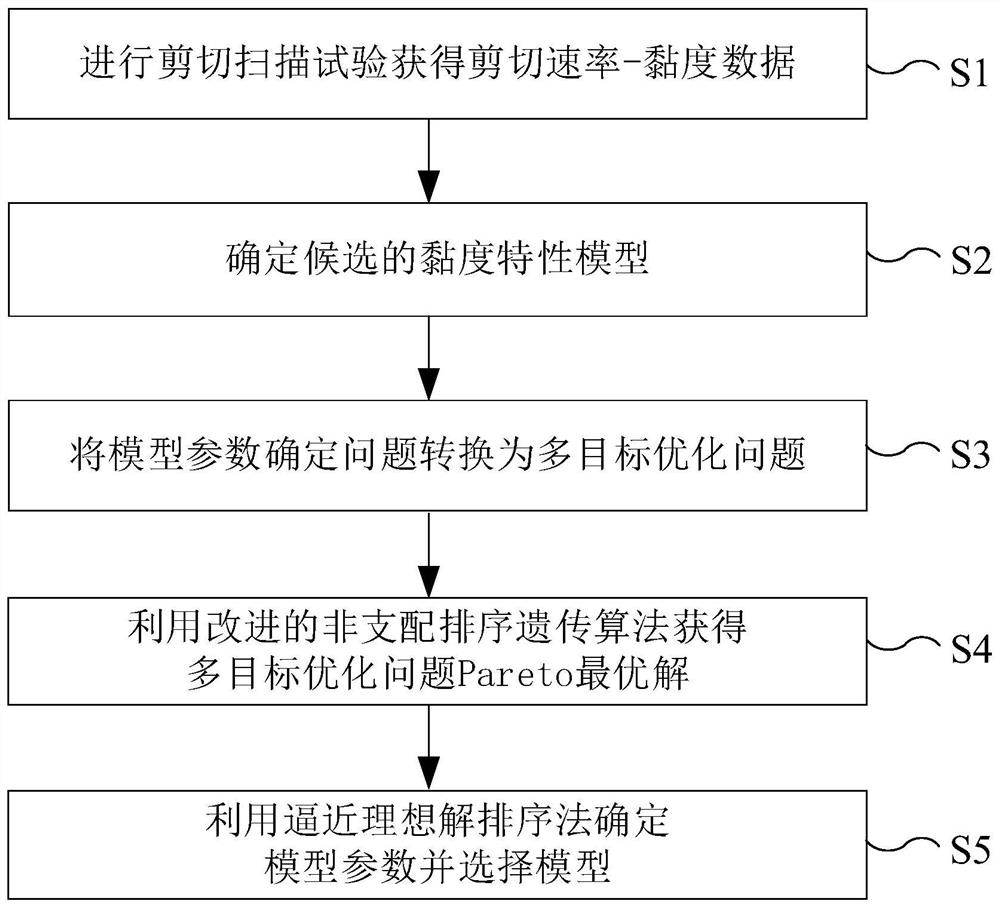
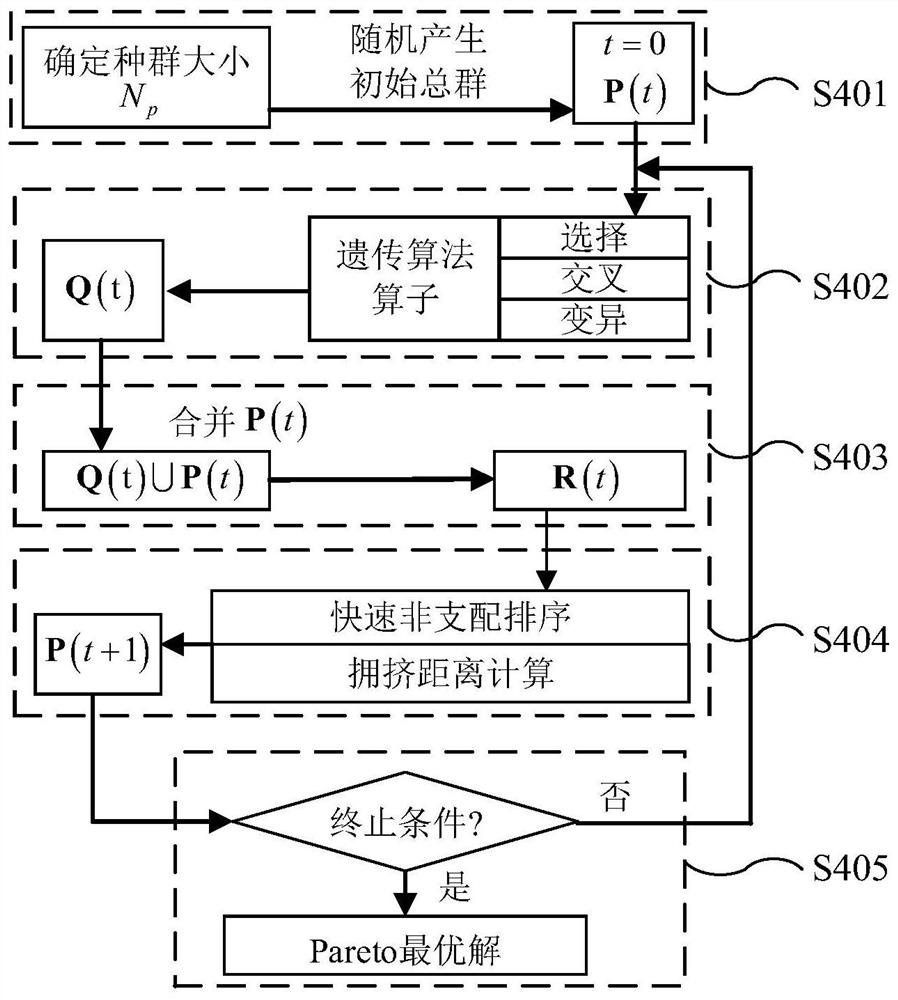
[0082] like figure 1 As shown in the figure, taking the prediction of the viscosity characteristics of a cellulose bio-ink as an example, the specific implementation steps of the method for predicting the viscosity characteristics of a cellulose bio-ink of the present application are described, and the steps are as follows:
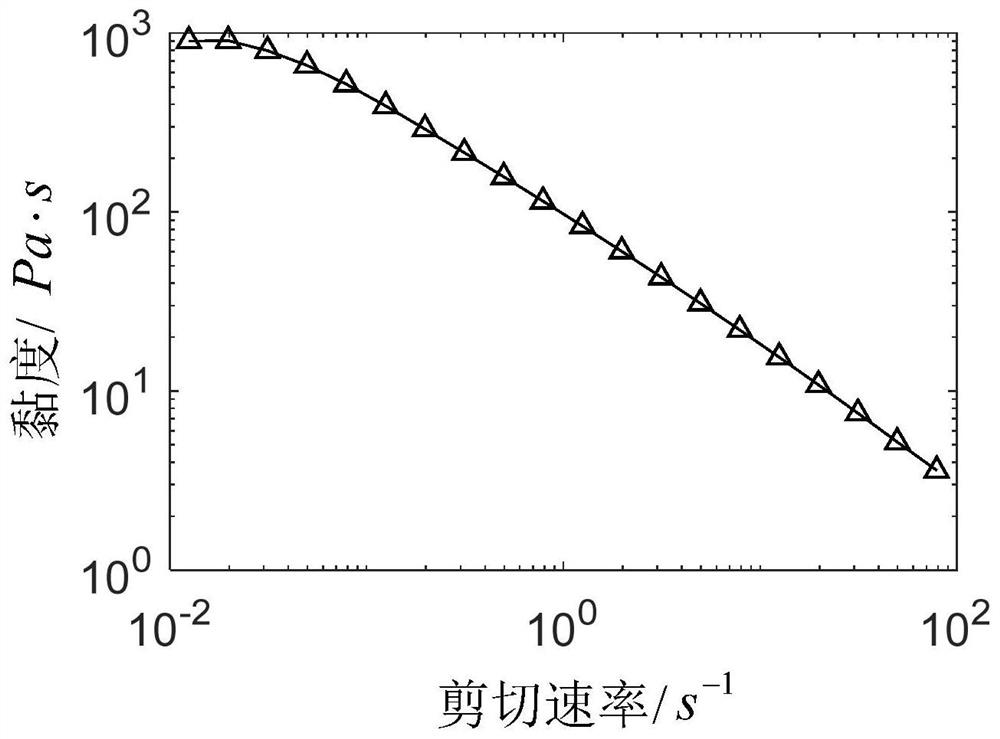
[0083] S1. Use a rotational rheometer to perform a shear scanning test on the cellulose bioink to obtain shear rate-viscosity data; specifically,
[0084] In this step, the rotational rheometer adopts the rotational rheometer ARES (Texas Instruments, USA), and selects two circular plate structures with a diameter of 25 mm as the geometric structure for the viscosity characteristic test, and sets two circular plates arranged in parallel. The spaci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com