Cloud platform vGPU load balancing scheduling method, medium and device
A technology of load balancing and scheduling method, which is applied in multi-programming devices, program control design, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as unbalanced processing task time and waste of efficient computing unit performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
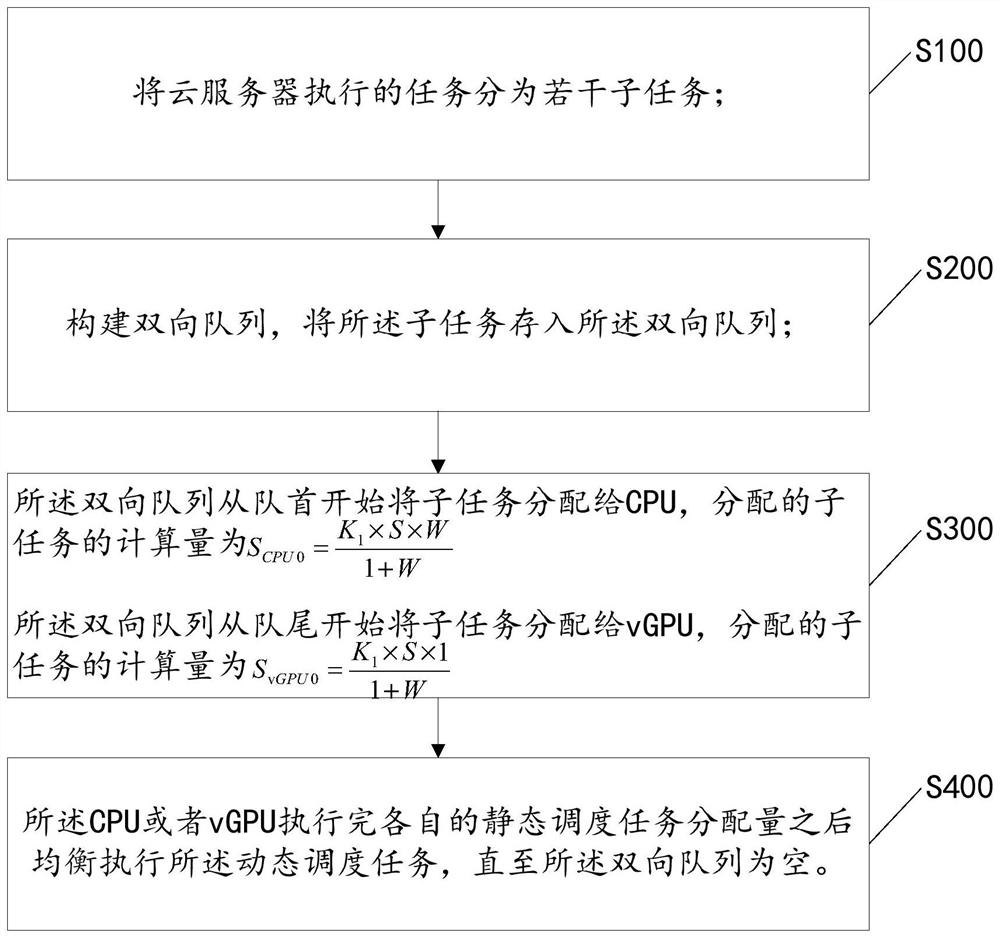
[0037] refer to figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a cloud platform vGPU load balancing scheduling method, including:
[0038] S100, dividing the tasks performed by the cloud server into several subtasks;
[0039] S200. Construct a two-way queue, and store the subtasks in the two-way queue;
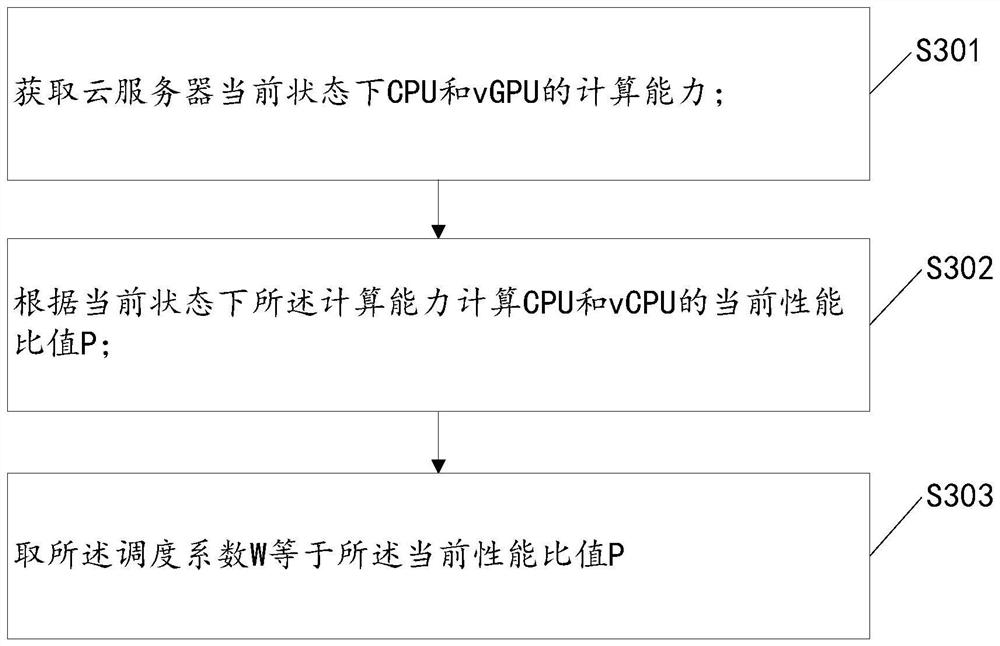
[0040] S300, the two-way queue assigns subtasks to the CPU from the head of the queue, and the calculation amount of the assigned subtasks is The two-way queue assigns subtasks to the vGPU from the end of the queue, and the calculation amount of the assigned subtasks is Among them, S is the total calculation amount of the task, K 1 is the first proportional coefficient, in the specific implementation process, the first proportional coefficient K 1 The value is 80%-90%, so that most of the total tasks are statically scheduled tasks, and W is the scheduling coefficient. refer to figure 2 As shown, in the specific implementation process, the scheduling coefficient W i...
Embodiment 2
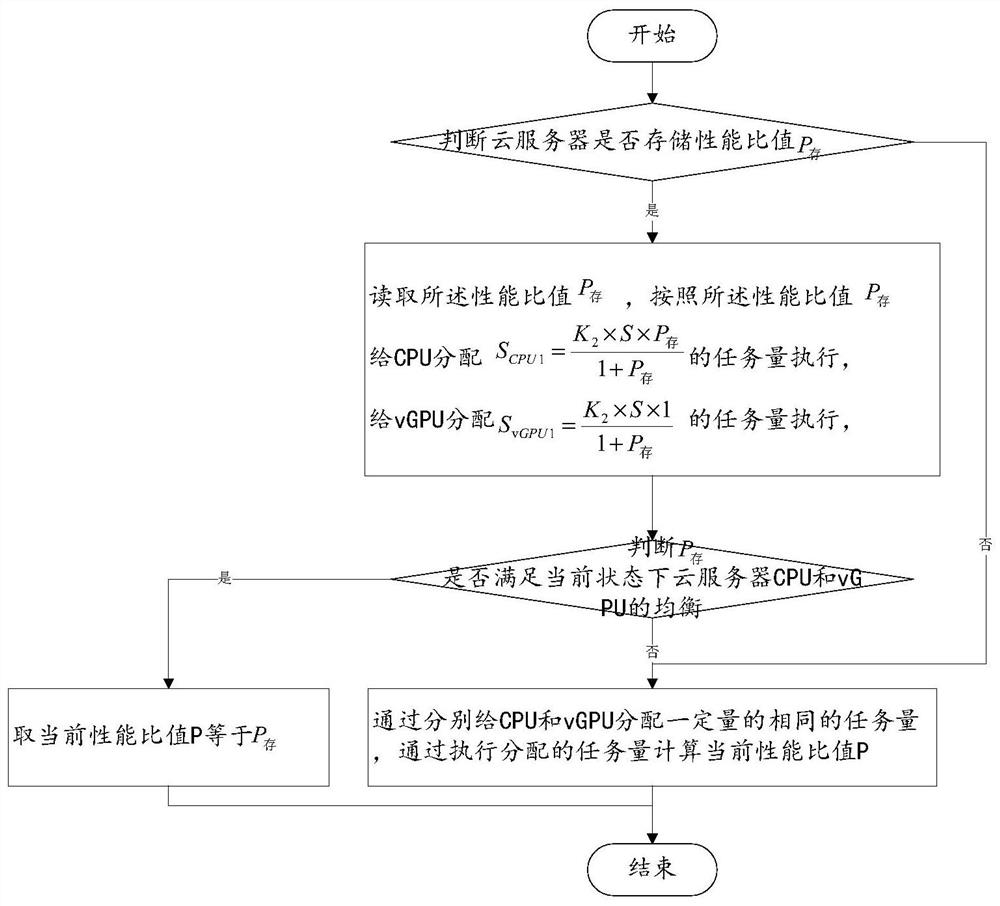
[0049] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that, refer to Figure 4 As shown, the remaining (1-K 1 )×S tasks are dynamic scheduling tasks, and the CPU or vGPU executes the dynamic scheduling tasks in a balanced manner after executing their respective allocated amounts until the two-way queue is empty. Another feasible way to balance the execution of the dynamic scheduling tasks is: if the CPU finishes executing the allocated amount earlier than the vGPU, start the dynamic scheduling tasks from the head of the queue The two-way queue allocates the remaining subtasks in the dynamic scheduling task to the idle CPU or vGPU one by one; compared with embodiment 1, in embodiment 2, most of the vGPUs are executed during task scheduling After a subtask in a dynamic scheduling task is dynamically allocated to a vGPU, finally, if the CPU executes a fully partially allocated dynamic scheduling task, the remaining tasks are allocated one by one to the idle CPU or vGPU...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 differs from Embodiment 1 in that, refer to Figure 5 As shown in , the task executed by the cloud server is divided into several subtasks; and the attribute of the amount of threads required to execute the subtasks is obtained;
[0053] The subtasks are sorted according to the number of threads required, and the subtasks are stored in the two-way queue according to the number of threads from low to high. In this way, during allocation, the CPU is often assigned subtasks with a small number of threads, while the vGPU is often assigned subtasks with a large number of threads. Further optimization is achieved to increase the speed of cloud server processing tasks.
[0054] The present invention provides a cloud platform vGPU load balancing scheduling medium, which stores at least one instruction, and executes the instruction to implement the cloud platform vGPU load balancing scheduling method.
[0055] The present invention also provides a cloud platform vG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com