Unsupervised knowledge graph entity alignment method and equipment
A technology of knowledge graphs and entity pairs, applied in the field of knowledge graphs in natural language processing, can solve problems such as relying on labeled data, entities without corresponding matching, and entity alignment methods without matching, so as to achieve good knowledge graph embedding and accurate The effect of matching and alignment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
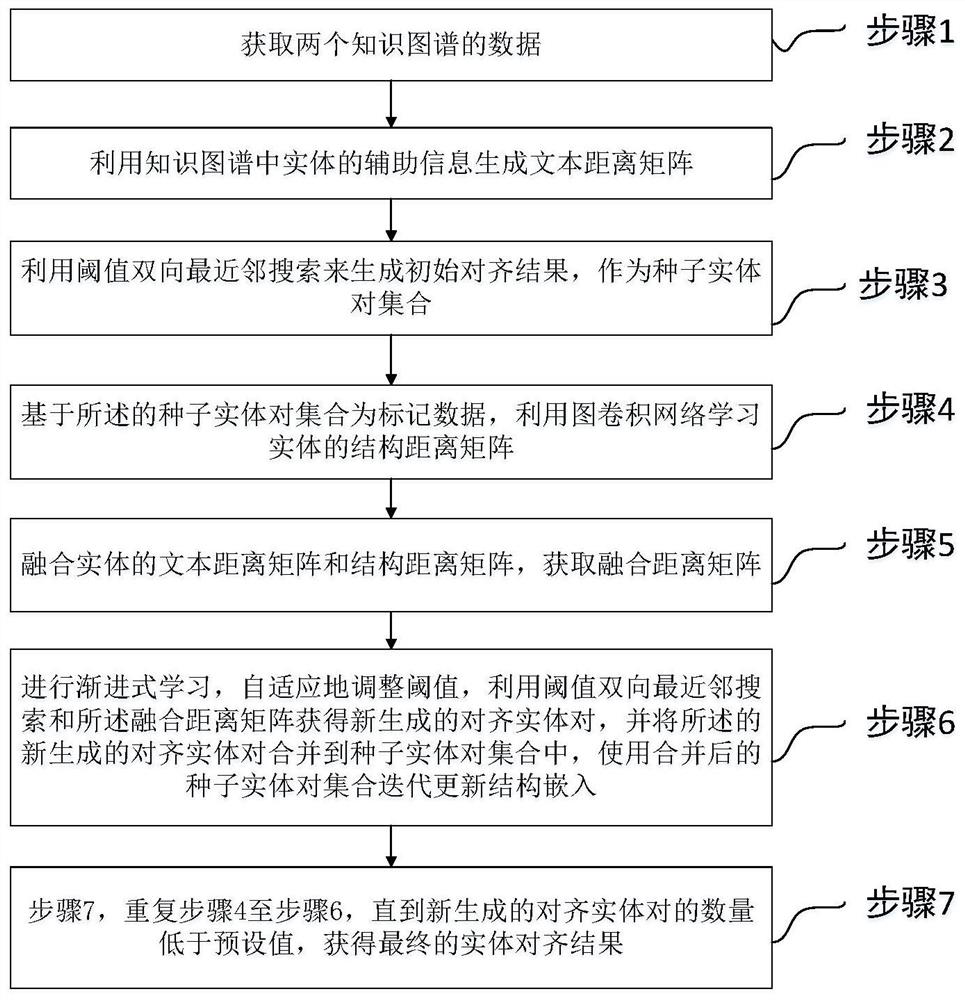
[0031] figure 1 A schematic flowchart of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown. An unsupervised method for aligning knowledge graph entities, including the following steps:
[0032] Step 1, obtain the data of two knowledge graphs;
[0033] Step 2, using the auxiliary information of entities in the knowledge map to generate a text distance matrix;
[0034] Step 3, using the threshold bidirectional nearest neighbor search to generate an initial alignment result as a set of seed entity pairs;
[0035] Step 4, based on the set of seed entity pairs as labeled data, use the graph convolutional network to learn the structural distance matrix of the entity;
[0036] Step 5, fusing the text distance matrix and the structure distance matrix of the entity to obtain the fusion distance matrix;
[0037] Step 6. Carry out progressive learning, adaptively adjust the threshold, use the threshold bidirectional nearest neighbor search and the fusion distance matrix to obtain a newl...
Embodiment 2
[0055] An unsupervised knowledge map entity alignment device, including:
[0056] processor;
[0057] And, a memory for storing executable instructions of the processor;
[0058] Wherein, the processor is configured to execute the entity alignment method in Embodiment 1 by executing the executable instruction.
[0059] Those skilled in the art should understand that the embodiments of the present application may be provided as methods, systems or computer program products. Accordingly, the present application can take the form of an entirely hardware embodiment, an entirely software embodiment or an embodiment combining software and hardware aspects. Furthermore, the present application may take the form of a computer program product embodied on one or more computer-usable storage media (including but not limited to disk storage, CD-ROM, optical storage, etc.) having computer-usable program code embodied therein.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com