Hyperspectral image band selection method and system based on neighbor subspace division
A technology of band selection and hyperspectral, which can be used in the analysis of materials, material analysis by optical means, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as not meeting actual needs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
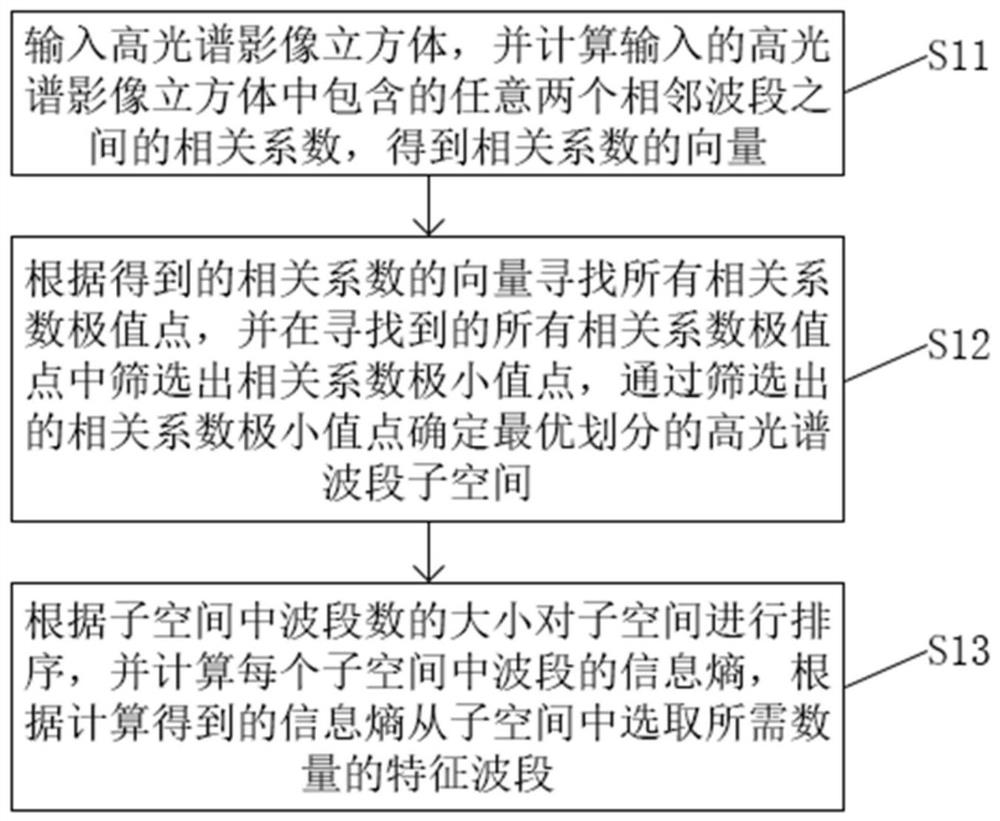
[0052] This embodiment provides a method for selecting a hyperspectral image band based on neighbor subspace division, such as figure 1 , 2 shown, including:
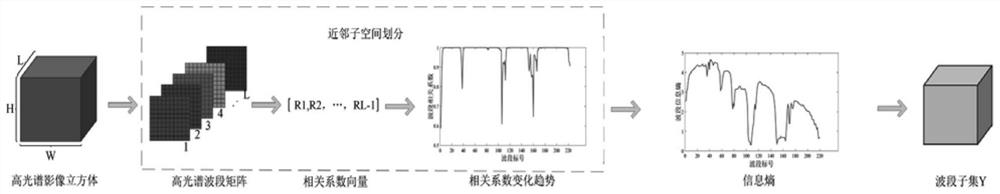
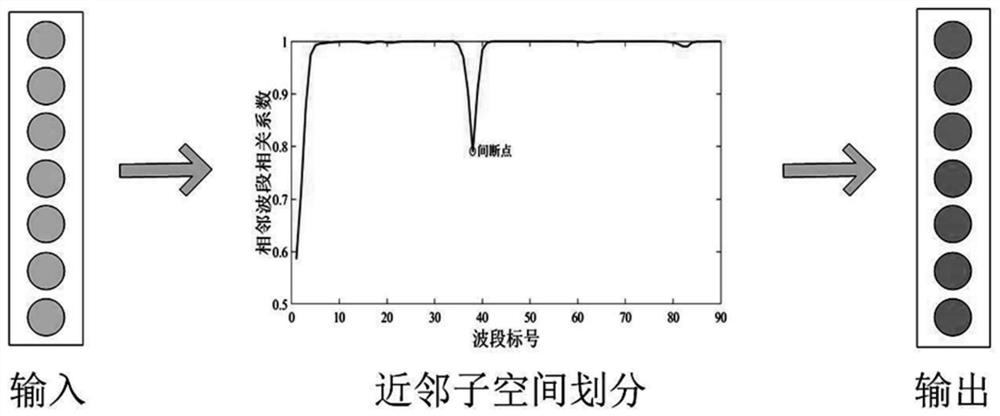
[0053] S11. Input the hyperspectral image cube, and calculate the correlation coefficient between any two adjacent bands contained in the input hyperspectral image cube, and obtain the vector of the correlation coefficient;
[0054] S12. Find all the correlation coefficient extreme points according to the obtained correlation coefficient vector, and filter out the correlation coefficient minimum value points from all the correlation coefficient extreme value points found, and determine the minimum value point of the correlation coefficient through the selected correlation coefficient minimum value points. Well-divided hyperspectral subspace;
[0055] S13. Sort the subspaces according to the size of the number of bands in the subspace, calculate the information entropy of the bands in each subspace, and select a requir...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The difference between the method for selecting a hyperspectral image band based on neighbor subspace division provided in this embodiment and the first embodiment is that:
[0092] In this embodiment, in order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed SEASP algorithm in hyperspectral band selection, a large number of related experiments are carried out.
[0093] In the experiment, three public datasets are mainly selected, namely the Botswana dataset, the Salinas dataset and the Indian Pines dataset. The selected classifiers are KNN, SVM and LDA. The parameter k of the KNN classifier is set to 5. The distance function uniformly used by SVM is a Gaussian kernel function. The penalty coefficient of the Indian Pines and Botswana datasets is 10000, and the penalty coefficient of the Salinas dataset. is 100. Since the above three classifiers are all supervised classification methods, 10% of the entire data set is randomly selected as training samples and the rest of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] This embodiment provides a hyperspectral image band selection system based on neighbor subspace division, including:
[0104] The calculation module is used to input the hyperspectral image cube, and calculate the correlation coefficient between any two adjacent bands contained in the input hyperspectral image cube, and obtain the vector of the correlation coefficient;
[0105] The screening module is used to find all the correlation coefficient extreme points according to the obtained correlation coefficient vector, and filter out the correlation coefficient minimum value points from all the found correlation coefficient extreme value points, and pass the selected correlation coefficient minimum value points. point to determine the optimally divided hyperspectral band subspace;
[0106] The selection module is used to sort the subspaces according to the size of the number of bands in the subspace, calculate the information entropy of the bands in each subspace, and sel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com