Method for determining fault activity in structural stable period
A stable stage and fault technology, applied in the field of oil and gas exploration, can solve the problems of limited popularization and application, unsuitable analysis of fault activity stages in the structural stable stage, difficulty in obtaining downhole core samples, etc., and achieves the effect of wide applicability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
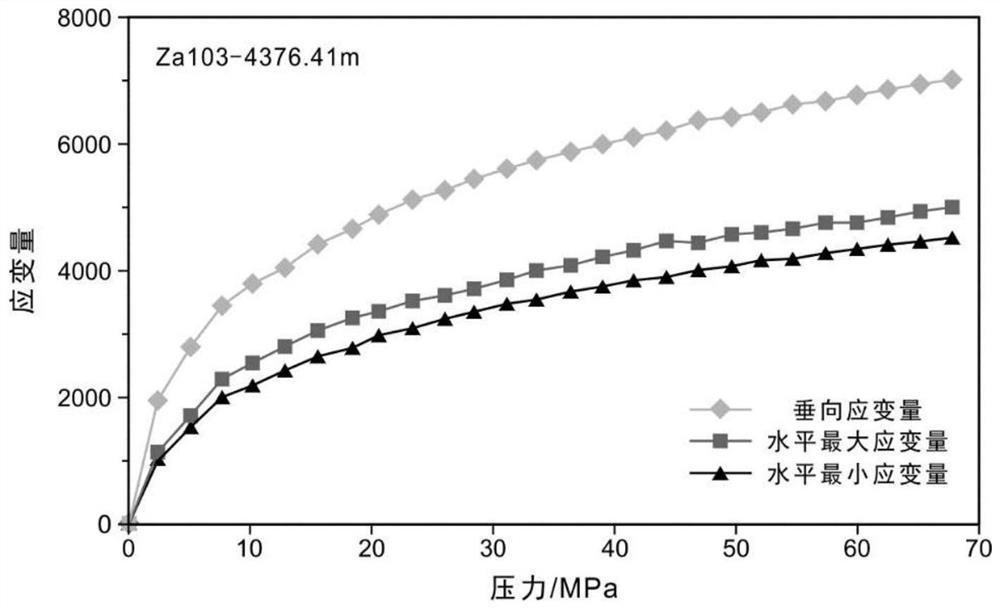
[0076] Experimental analysis of differential strain in rocks (Sun Lianhuan, Research on Wellbore Stability in the Junggar Basin [D], China University of Petroleum, 2009) shows that the in-situ stress field in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin has the vertical principal stress (σ V )>horizontal maximum principal stress (σ H )>horizontal minimum principal stress (σ h ), i.e. conform to the stress conditions of the structurally stable period according to the present invention, such as figure 1 shown.
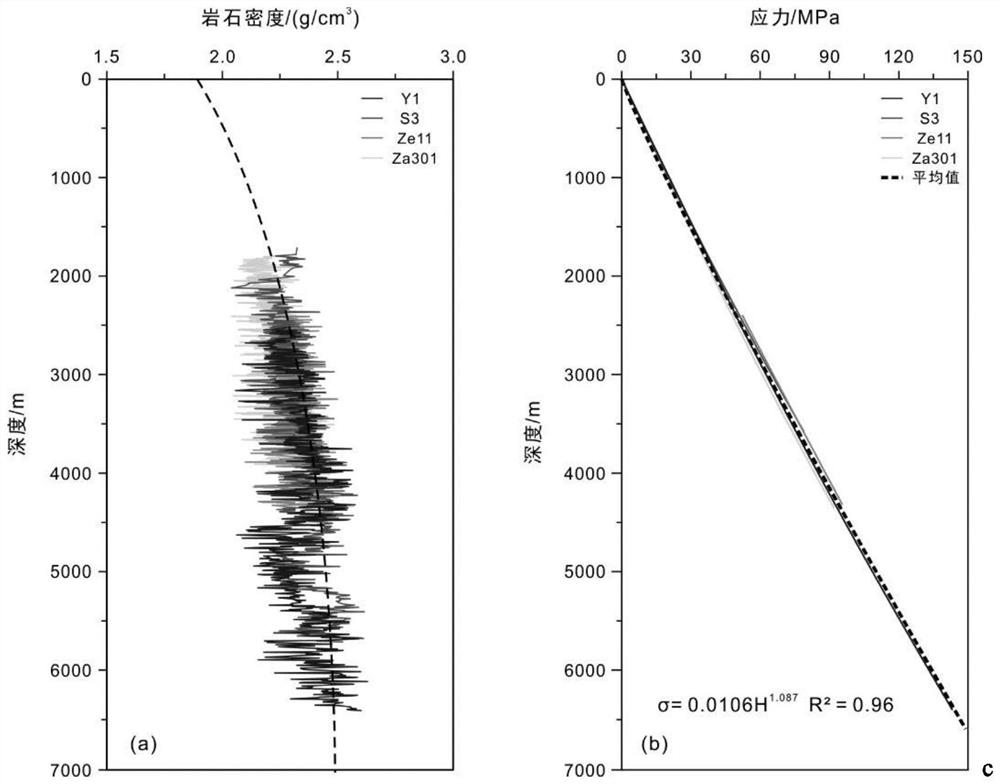
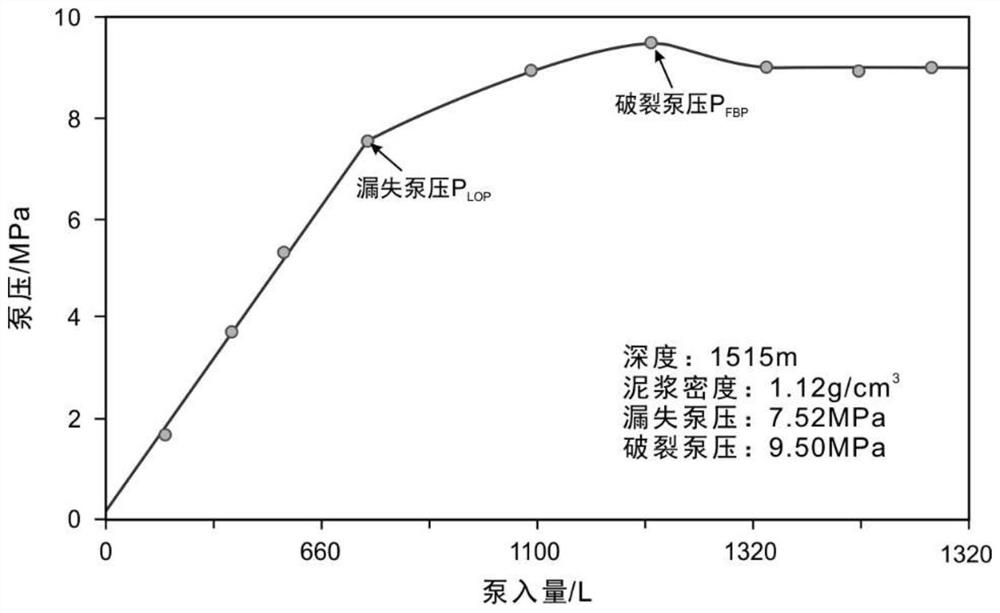
[0077] The sonic logging curves of fault drilling are obtained by conventional density logging methods. figure 2 The left panel shows density logs from fault-drilled wells in the Junggar Basin hinterland. According to the density log curve, the variation law of rock volume density with depth is determined, the rock density-depth function equation (1) is integrated to obtain the vertical principal stress at a specific depth, and the vertical principal stress (i.e. the maximum ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com