Multi-source-domain adaptive cross-subject EEG cognitive state evaluation method based on label alignment
A state assessment and self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of neurophysiological signal analysis, which can solve the problems of falling into a local optimal state, changes, and confusion of decision boundary features.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example.
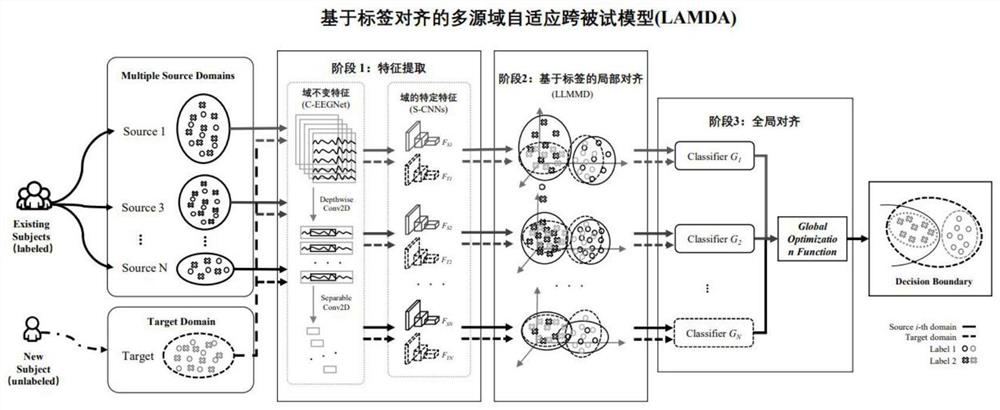
[0048] Such as figure 1 Shown is a structural diagram of a multi-source domain adaptive cross-subject EEG cognitive state assessment method based on label alignment, which mainly includes the following steps:
[0049] Step 1: Data Acquisition
[0050] The data in the fatigue driving EEG data set used in the present invention are the EEG data of 15 healthy subjects with good driving experience, and each subject fills out the NASA-TLX questionnaire after the test to provide subjective workload perception. According to the NASA-TLX questionnaire, the present invention selects two mental states of TAV3 and DROWS as analysis.
[0051] Step 2: Data Preprocessing
[0052] Taking the EEG data of fatigue driving as an example, the processing steps of the original EEG data are as follows:
[0053] 2-1. Artifact removal: Perform artifact removal operation on the acqui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com