Method for degrading dibenzothiophene by artificial nicotinamide cofactor mediated enzyme method
A dibenzothiophene and nicotinamide technology, applied in the petroleum industry, hydrocarbon oil treatment, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency, heavy pollution, easy decoupling, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing costs and having a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
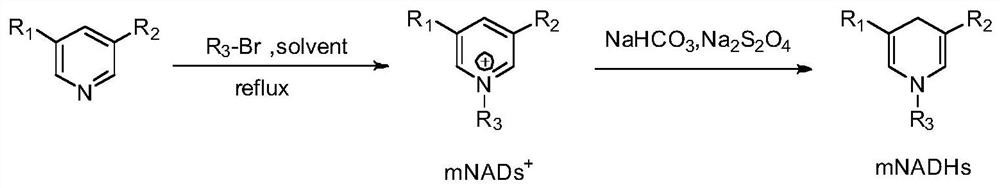
[0040] Example 1 takes figure 1 Reduced cofactors were synthesized in the manner indicated
[0041] (1) Synthesis of oxidized cofactors
[0042]Add nicotinamide (10mmol) in 80mL acetonitrile solution, then add benzyl bromide (12mmol), 1-bromobutane (12mmol), 1-bromooctane (12mmol), ethyl 4-bromomethylbenzoate ( 12mmol), 4-methoxybenzyl bromide (12mmol), the reaction temperature was 80°C, heated and stirred under reflux for about 12h, during the reaction, a white precipitate was precipitated. After the reaction was completed, the crude product was obtained by filtration, washed with ethyl acetate (15mL×3), and dried in vacuo. The yields were as follows:
[0043] 1a (1-benzyl-3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium salt): 94%,
[0044] 3a (1-butyl-3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium salt): 91%,
[0045] 5a (1-octyl-3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium salt): 92%,
[0046] 6a (3-carbamoyl-1-(4-ethoxy-4-oxobutyl)pyridin-1-ium salt): 45%.
[0047] Add 5-methyl nicotinamide (10mmol) in 80mL acetonitrile solution,...
Embodiment 3
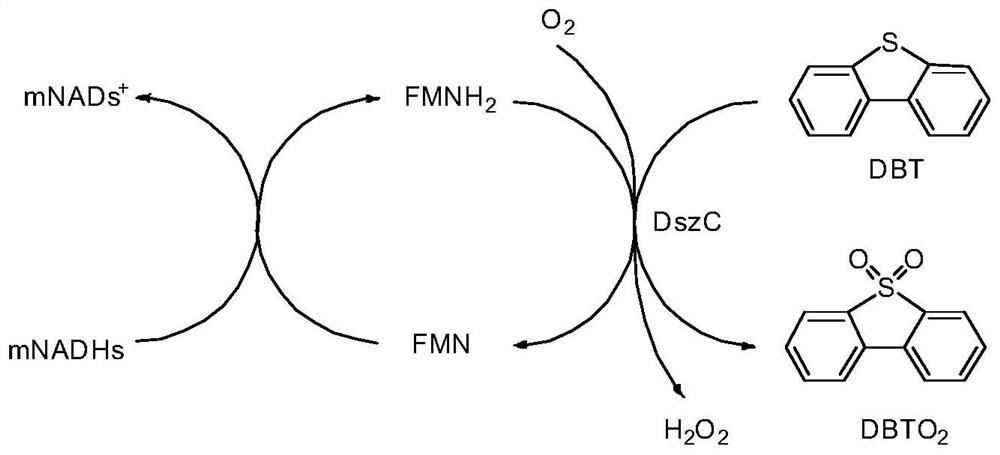
[0065] 50 mM 1 mL pH 7.5 Tris-HCl buffer containing 1 mM dibenzothiophene, 10 mM NADH or mNADHs (1b-8b), 10 μM FMN, 3 U DszC enzyme, 1 U DszD enzyme, 50 U catalase. 37°C, 200rpm, the reaction was carried out in a closed 1.5mL centrifuge tube, respectively take 200μL of the reaction solution for 2h, 4h, 8h, 12h, and 24h, add 3×200μL ethyl acetate to extract, ultrasonically mix, and centrifuge at 10000rpm for 2min, take The organic phase was detected by liquid phase, and the conversion rate (%) is shown in Table 1.
[0066] Table 1
[0067] time (h) NADH 1b 2b 3b 4b 5b 6b 7b 8b 2 57.23 17.93 20.79 21.53 22.11 22.78 15.03 55.98 59.87 4 68.36 21.65 25.81 39.82 40.51 38.98 28.99 84.76 63.77 8 99.28 43.78 50.70 57.58 66.39 57.22 39.73 93.92 82.10 12 99.41 76.93 89.23 96.23 94.58 81.11 54.78 97.90 96.88 24 100.0 89.14 92.54 99.69 98.65 89.32 67.80 98.93 100.0
Embodiment 4
[0069] 50 mM 1 mL pH 7.5 Tris-HCl buffer containing 1 mM dibenzothiophene, 2-30 mM mNADHs (3b, 4b, 7b, 8b), 10 μM FMN, 3 U DszC enzyme, 50 U catalase. 37°C, 200rpm, the reaction was carried out in a closed 1.5mL centrifuge tube, after 12h, take 200μL of each reaction solution, add 3×200μL ethyl acetate for extraction, ultrasonically mix, and centrifuge at 10000rpm for 2min, take the organic phase for liquid phase detection, the conversion rate (%)As shown in table 2.
[0070] Table 2
[0071] Equivalent (mM) 3b 4b 7b 8b 2 34.55 44.14 42.55 47.93 5 74.55 79.14 71.78 77.93 8 94.84 97.54 97.21 90.69 10 90.43 94.65 96.00 96.93 15 90.28 92.58 92.33 91.92 20 86.63 90.19 72.90 83.16 25 88.21 89.25 74.12 84.09 30 70.19 69.21 70.11 65.45
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap