Patents
Literature
195 results about "Flavolipin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
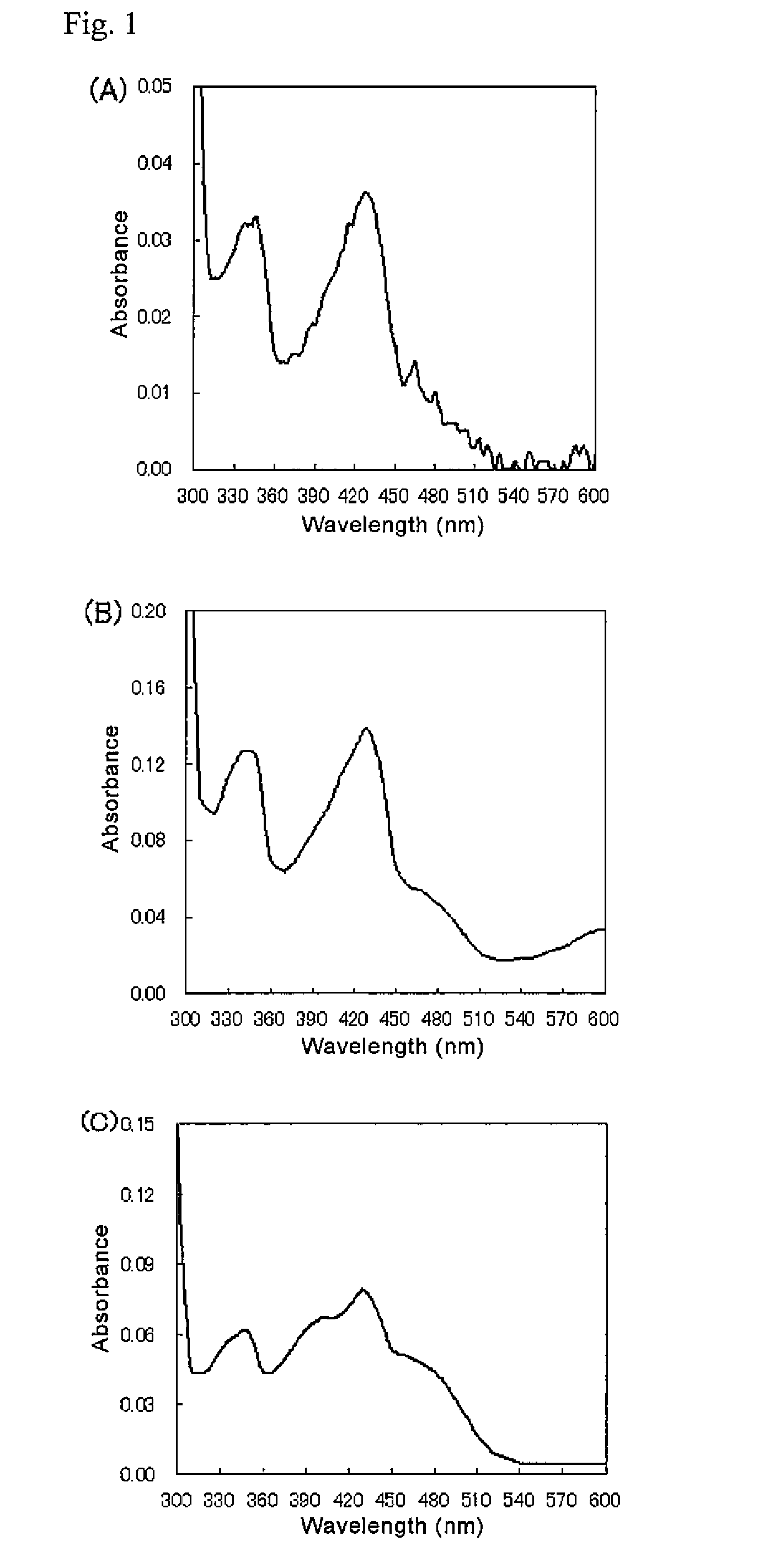
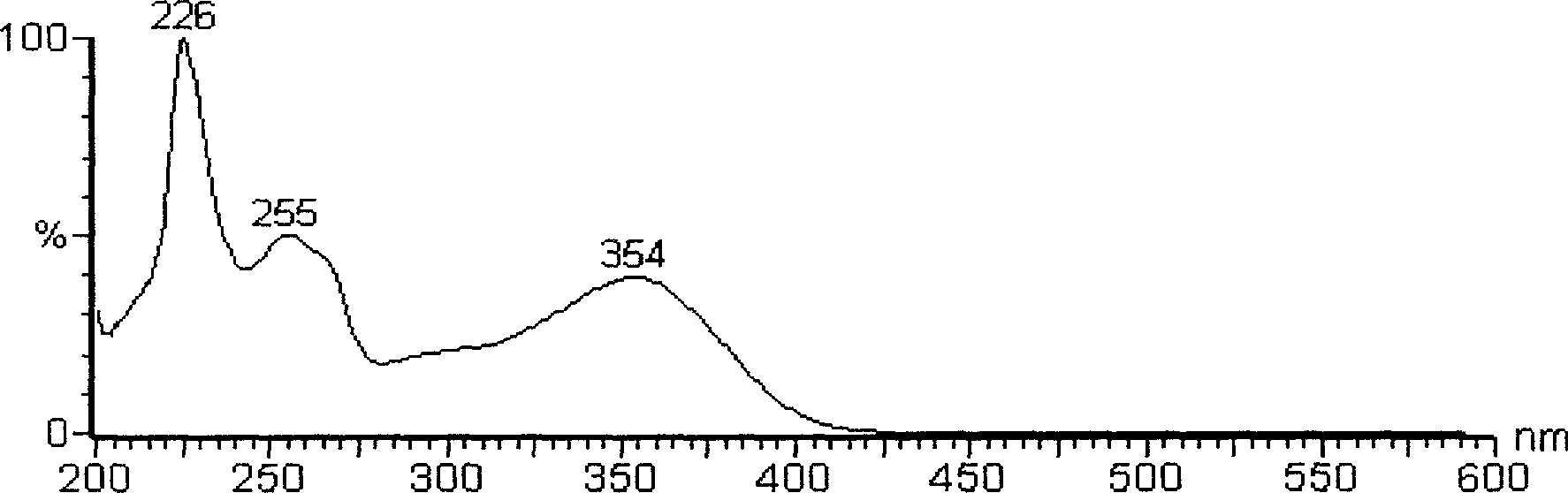
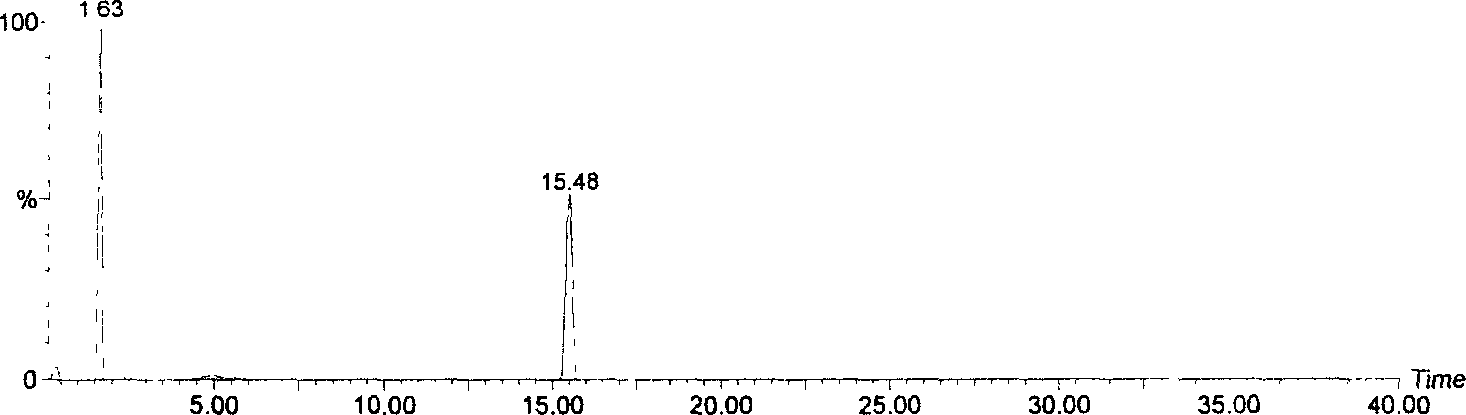
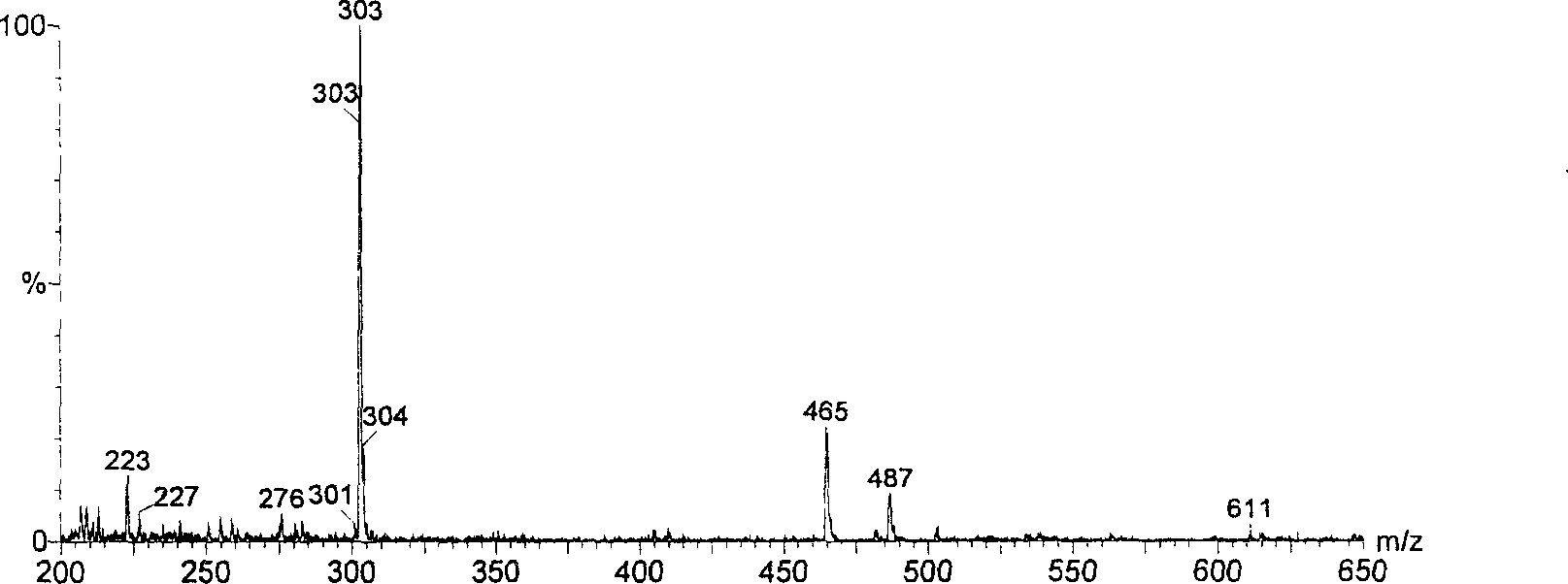
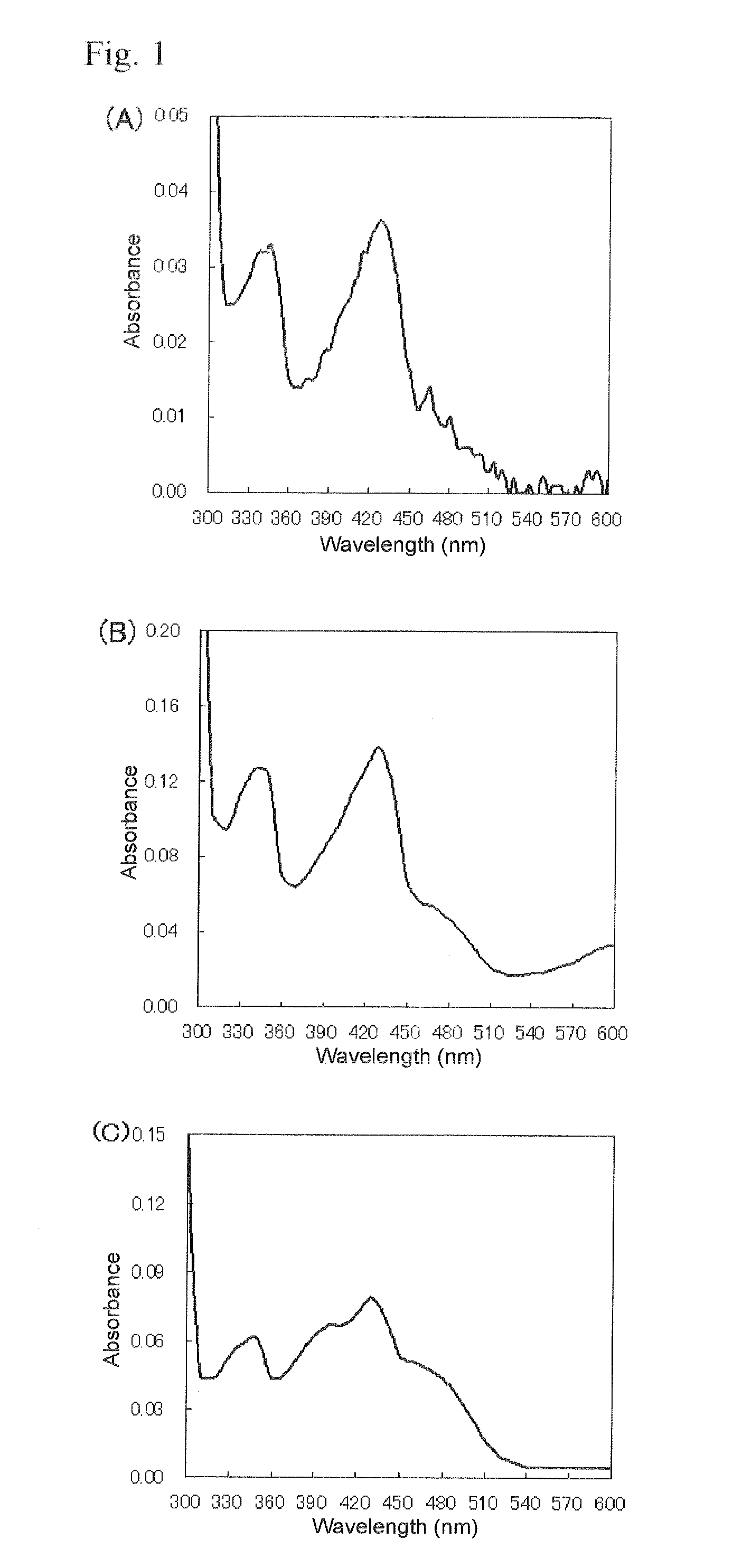
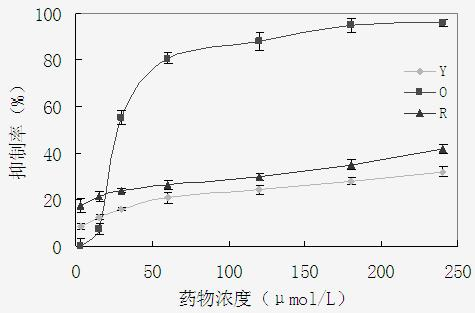
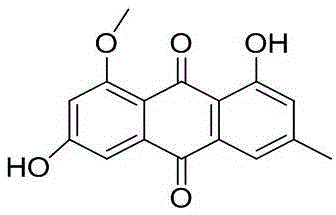
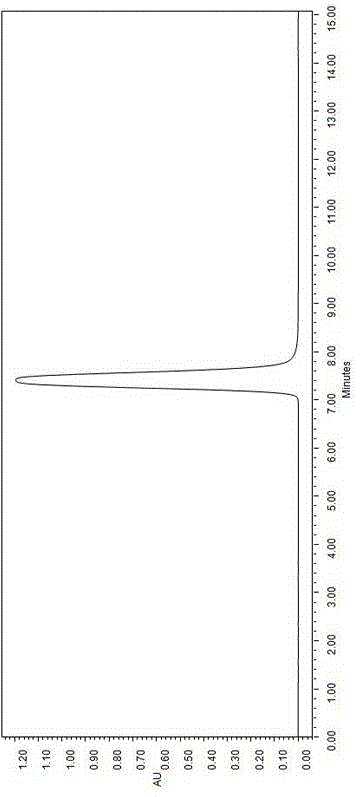
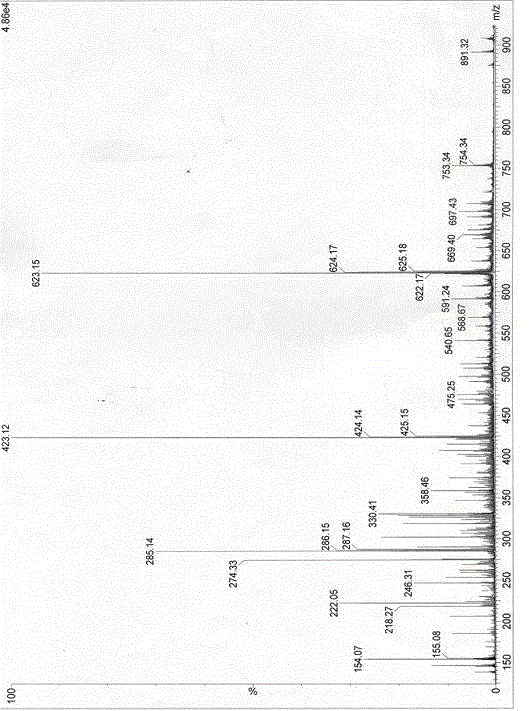
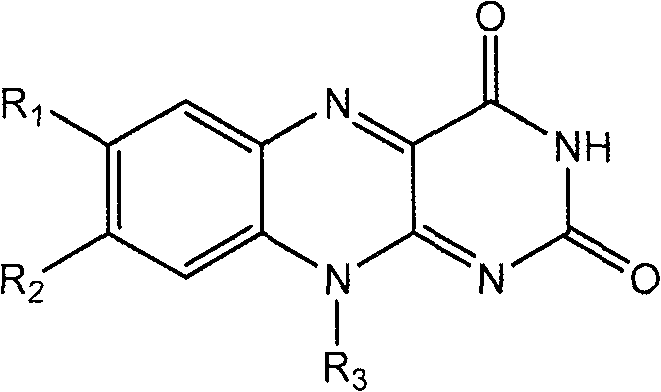
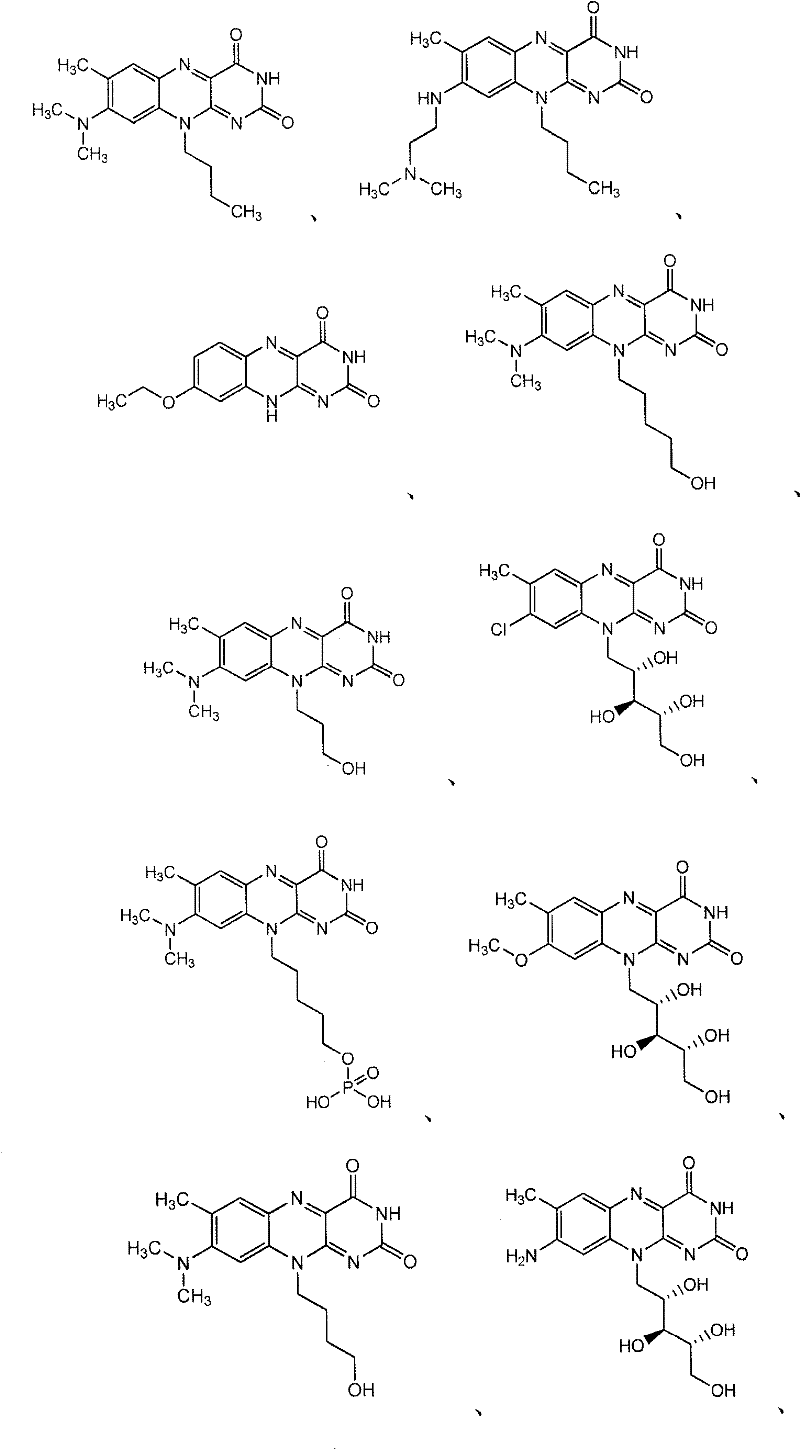
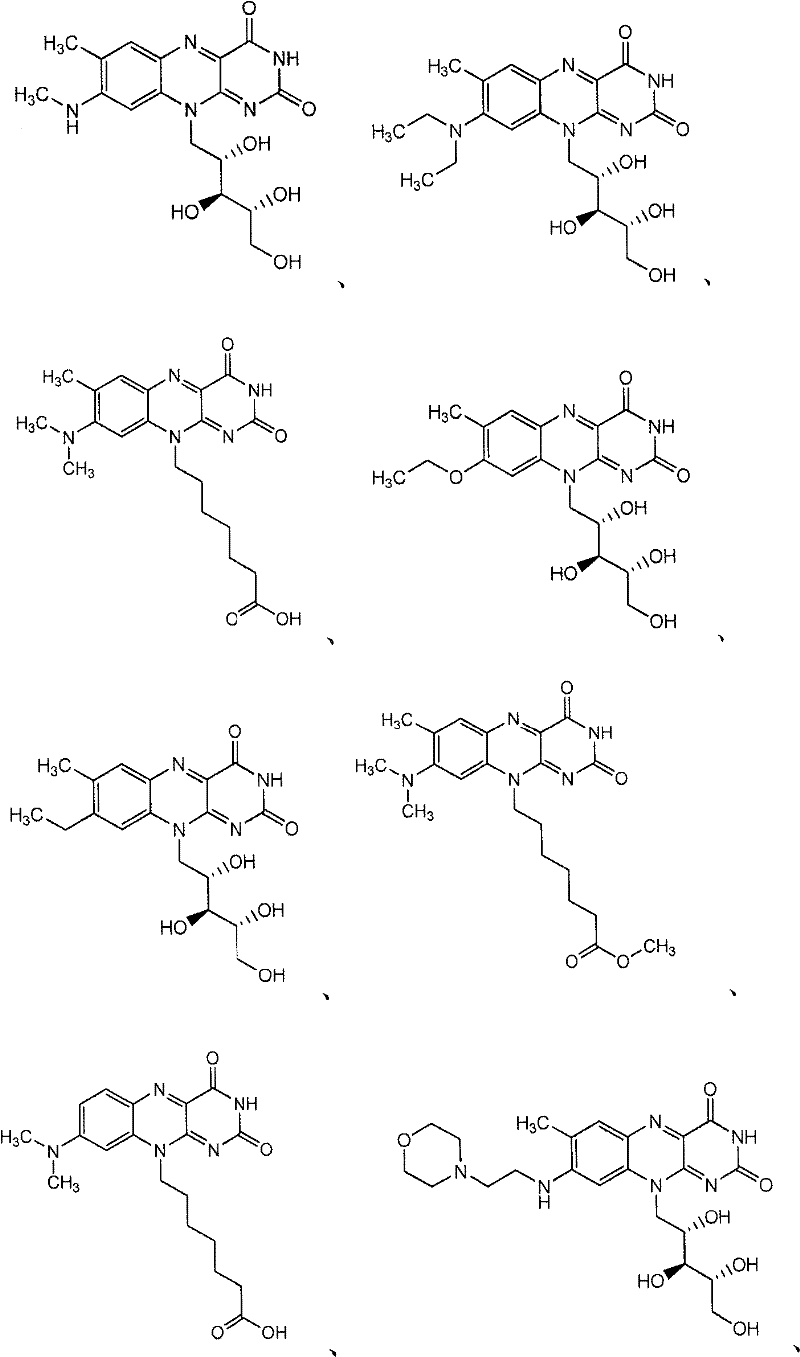
This fact suggests that flavolipin is a nontoxic immunoactivator [4]. Therefore, we tried to synthesize the proposed flavolipin (16) to determine the configuration of the natural flavolipin and to investigate the biological activities of its stereoisomers.
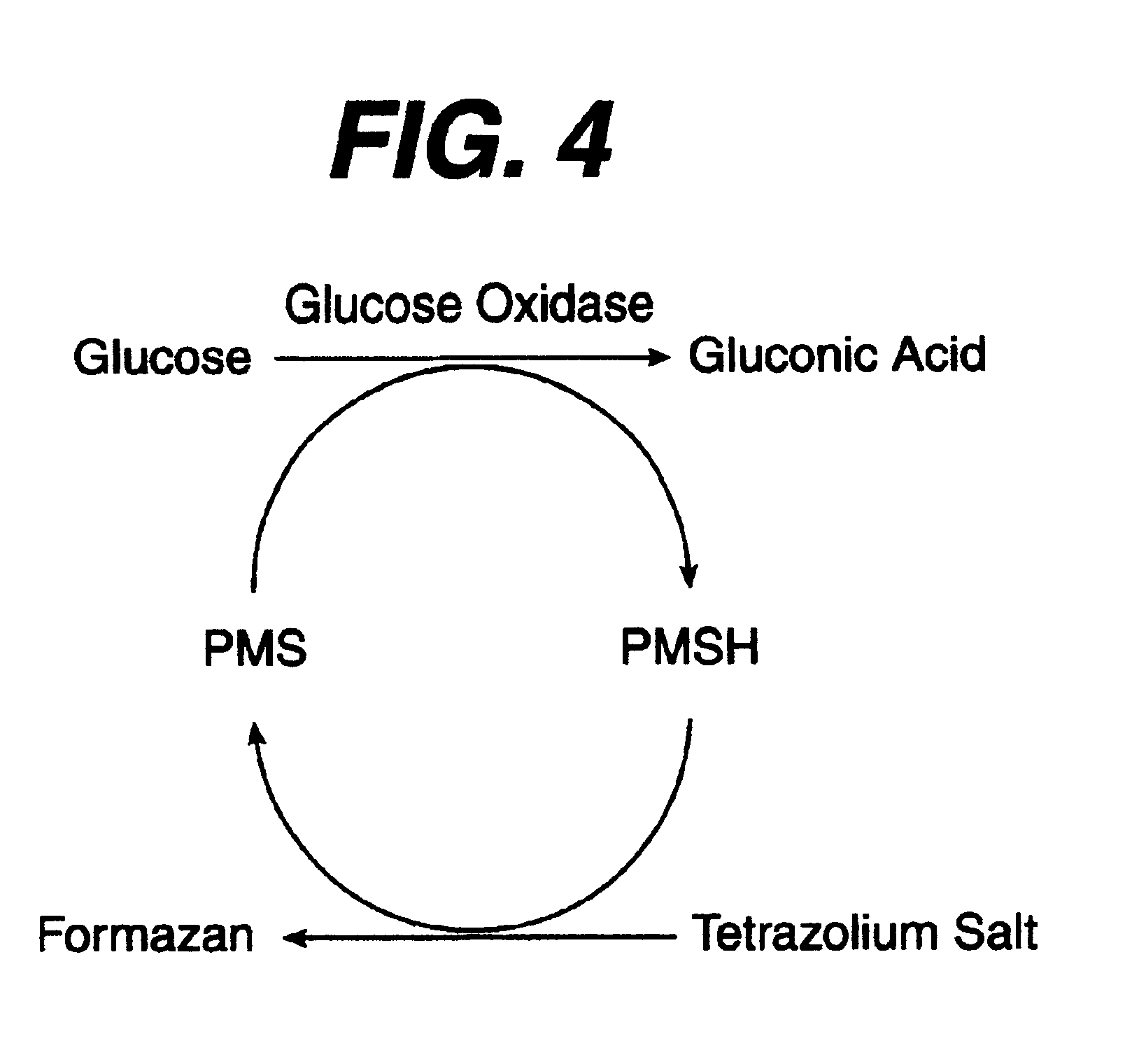
Diagnostics based on tetrazolium compounds
InactiveUS6656697B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon enzymaticElectron transfer
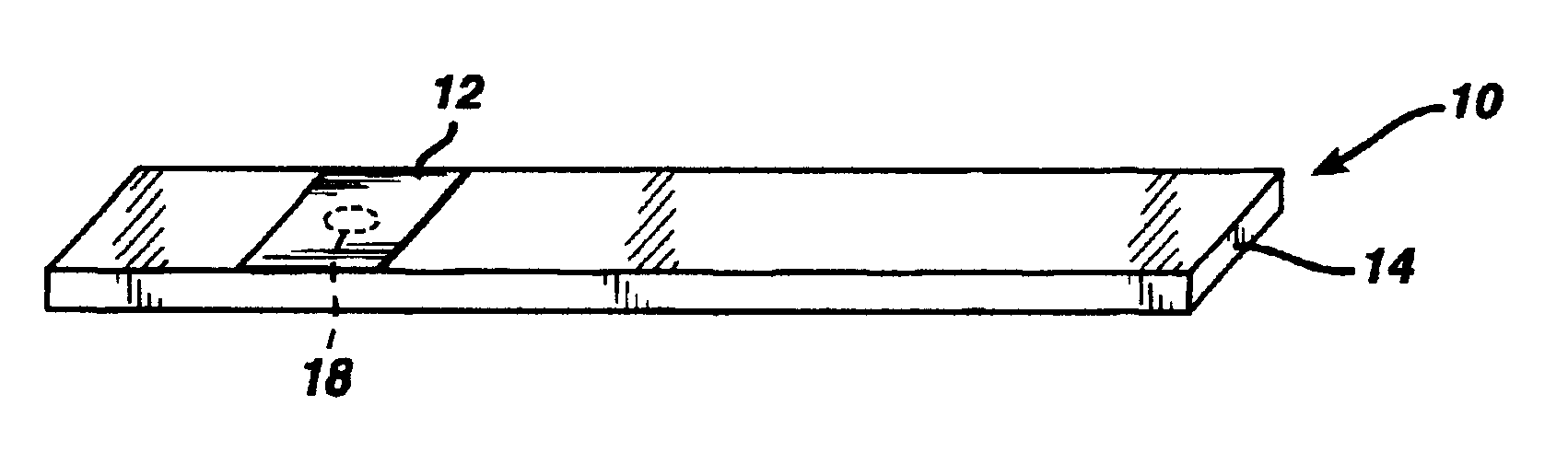
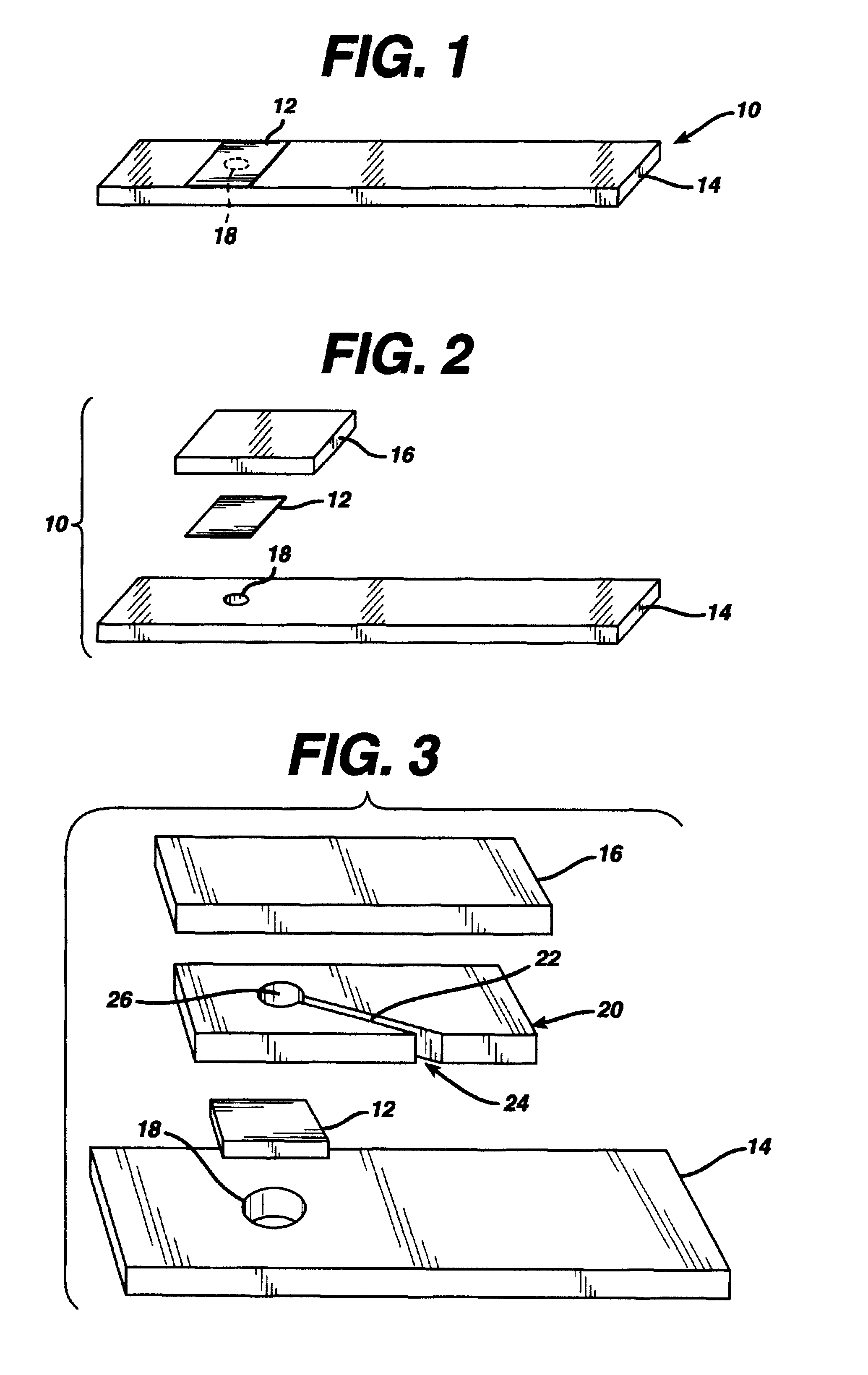
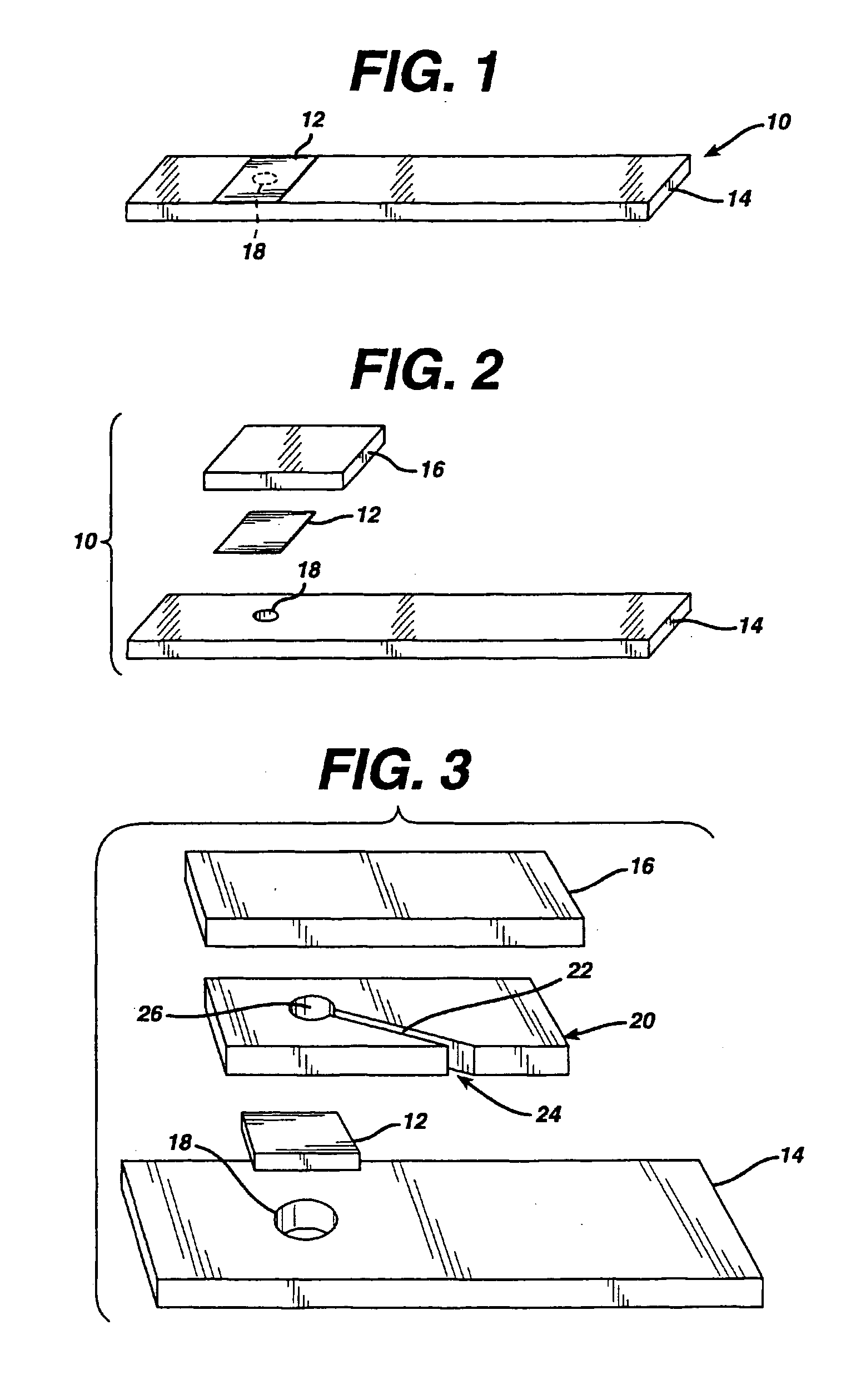
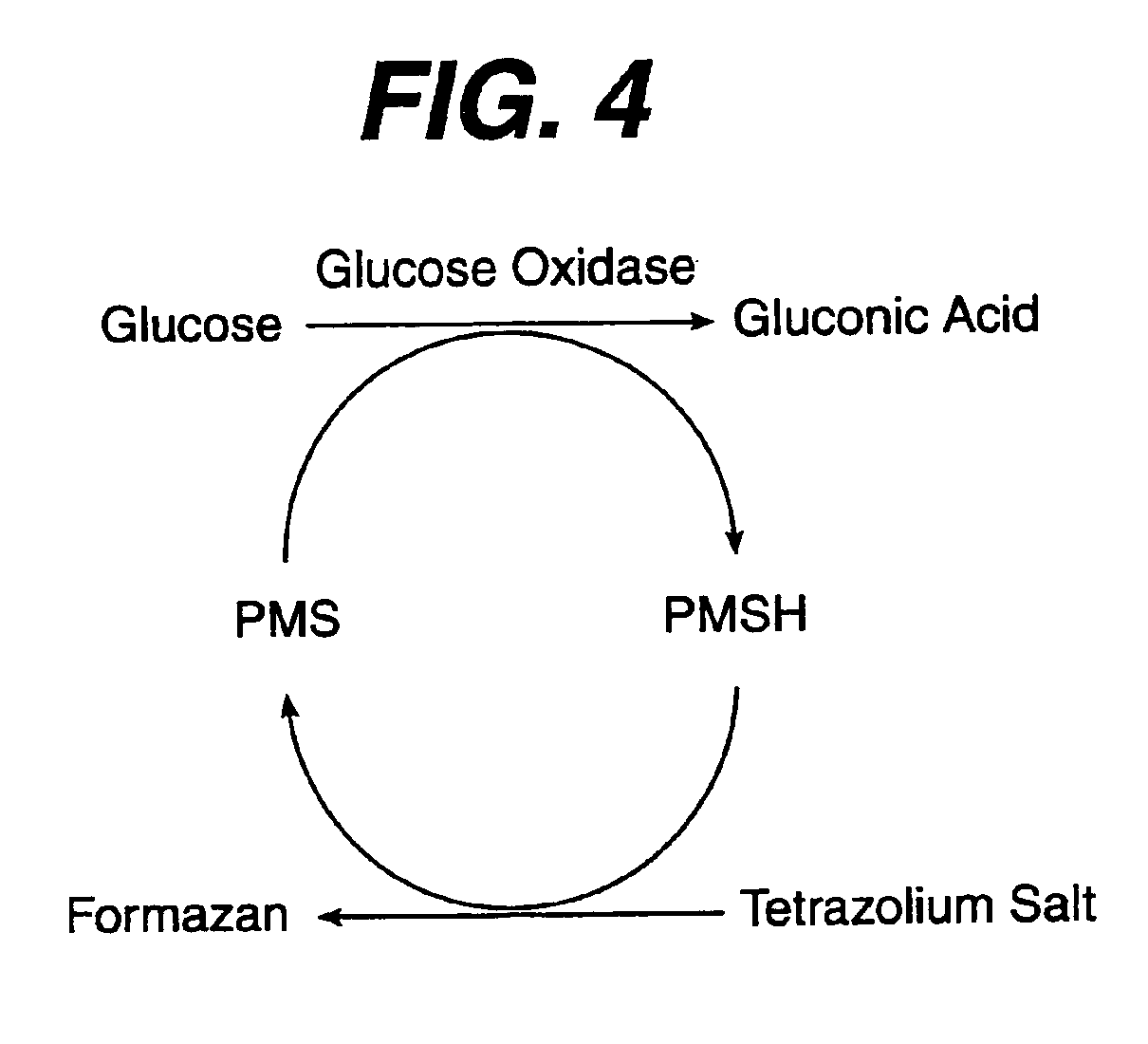
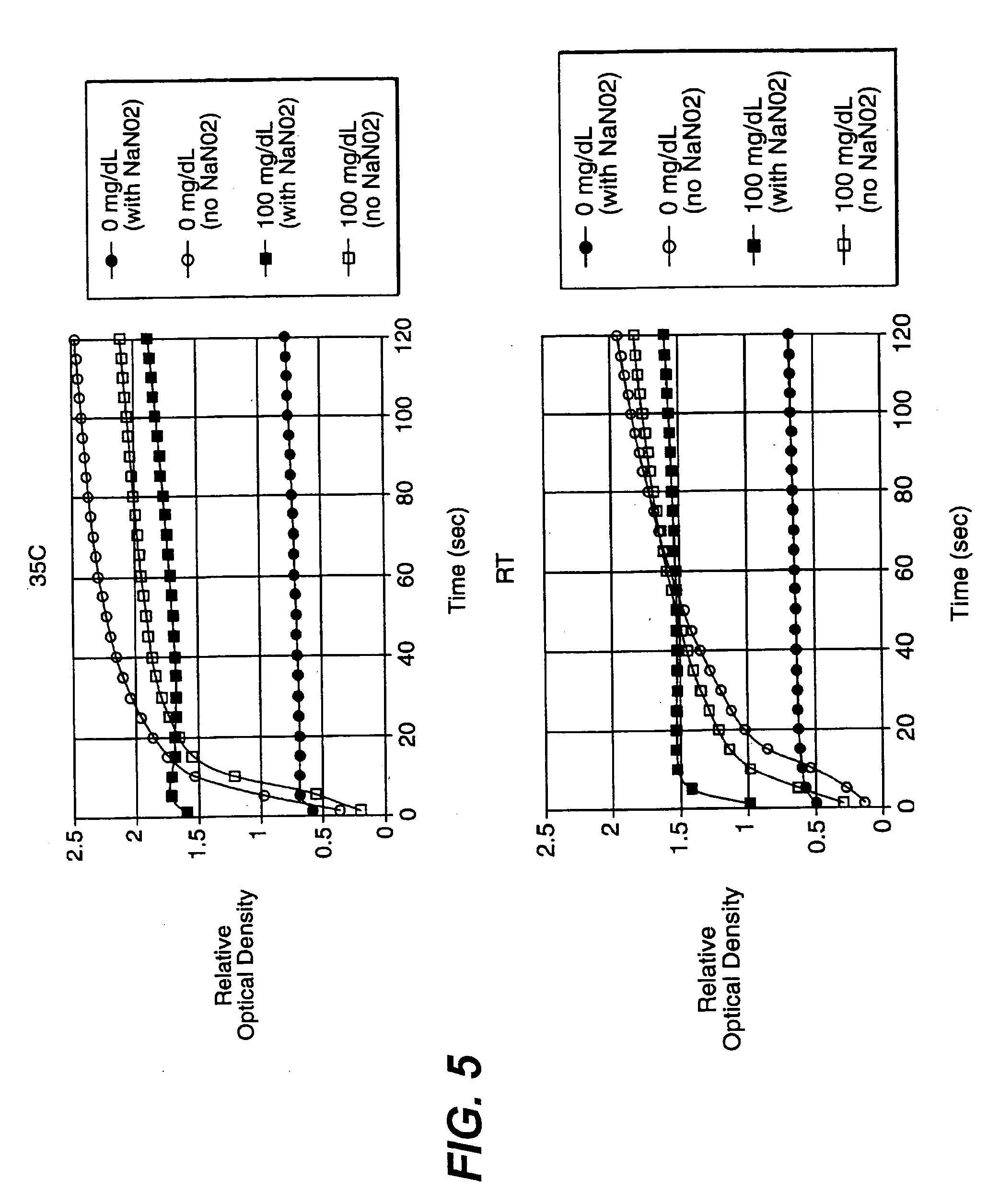
A reagent is suitable for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a hemoglobin-containing biological fluid, such as whole blood. The reagent comprises a flavin-dependent enzyme that has specificity for the analyte, a flavin cofactor if, and only if, a flavin is not bound to the enzyme, a tetrazolium dye precursor, an electron transfer agent, and a nitrite salt. The reagent causes dye formation that is a measure of the analyte concentration. The nitrite salt suppresses interfering dye formation caused non-enzymatically by the hemoglobin. Preferably, the reagent is used in a dry strip for measuring glucose in whole blood.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Diagnostics based on tetrazolium compounds
InactiveUS20040053352A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme bindingElectron transfer
A reagent is suitable for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a hemoglobin-containing biological fluid, such as whole blood. The reagent comprises a flavin-dependent enzyme that has specificity for the analyte, a flavin cofactor if, and only if, a flavin is not bound to the enzyme, a tetrazolium dye precursor, an electron transfer agent, and a nitrite salt. The reagent causes dye formation that is a measure of the analyte concentration. The nitrite salt suppresses interfering dye formation caused non-enzymatically by the hemoglobin. Preferably, the reagent is used in a dry strip for measuring glucose in whole blood.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Diagnosis of body metabolic emergency state
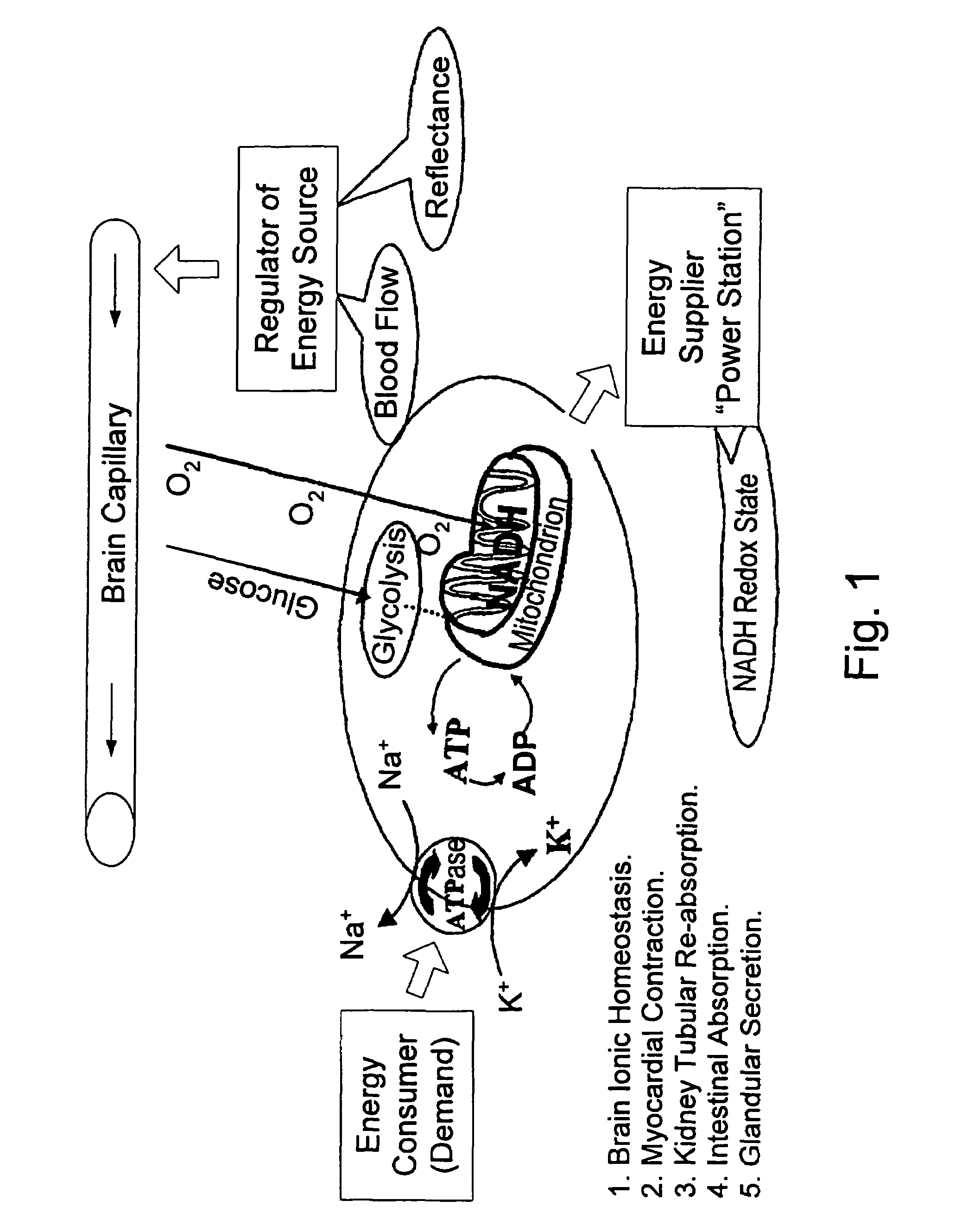
An apparatus, system and method are provided for diagnosing the degree of body metabolic emergency state. A non-vital organ with respect to the metabolic emergency state is first chosen. One or more tissue viability parameters including at least one of NADH and Flavoprotein (Fp) concentration are monitored in the non-vital organ, whereupon the degree of body metabolic emergency state may be determined based on the monitored tissue viability parameters.
Owner:CRITISENSE
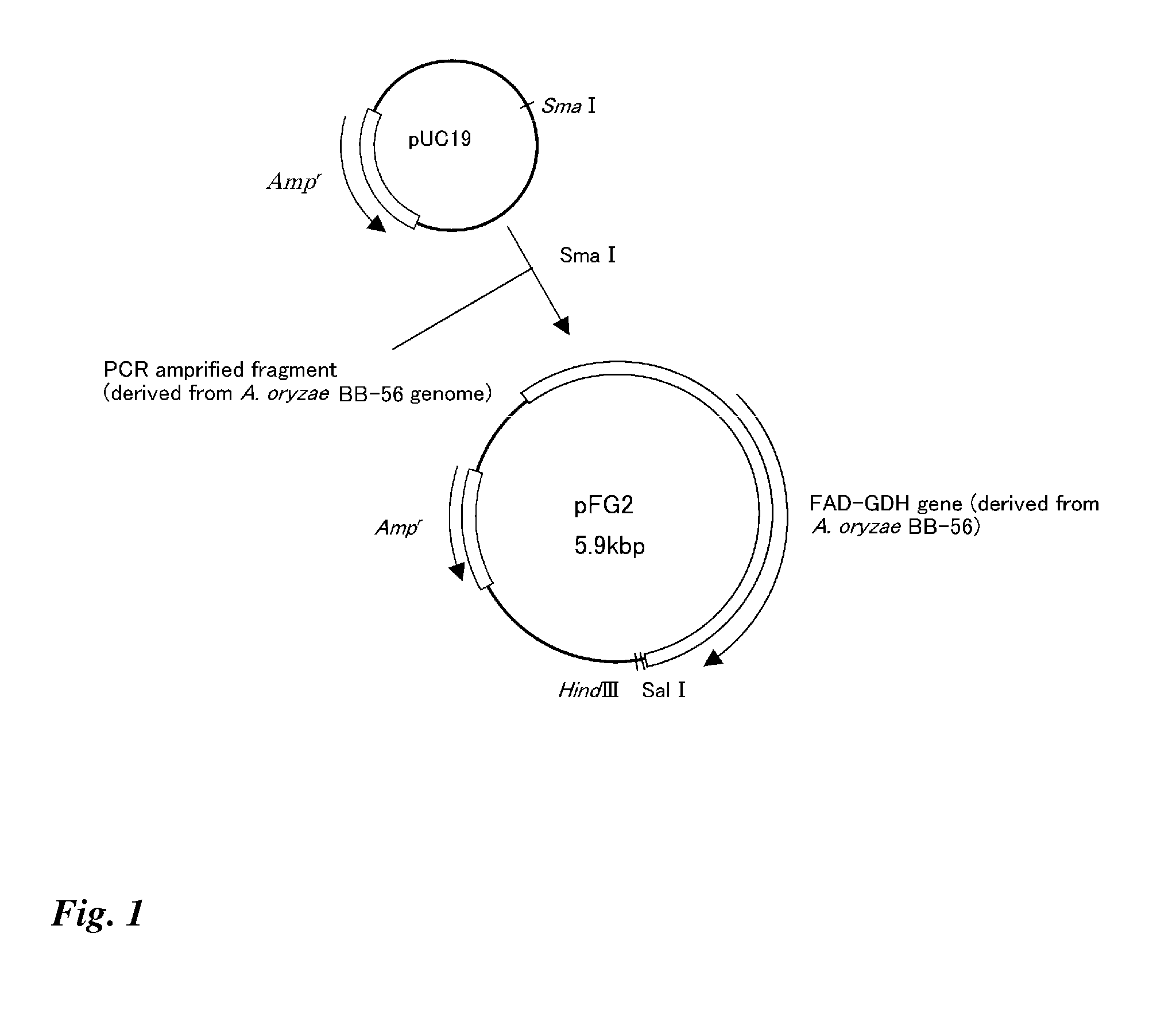
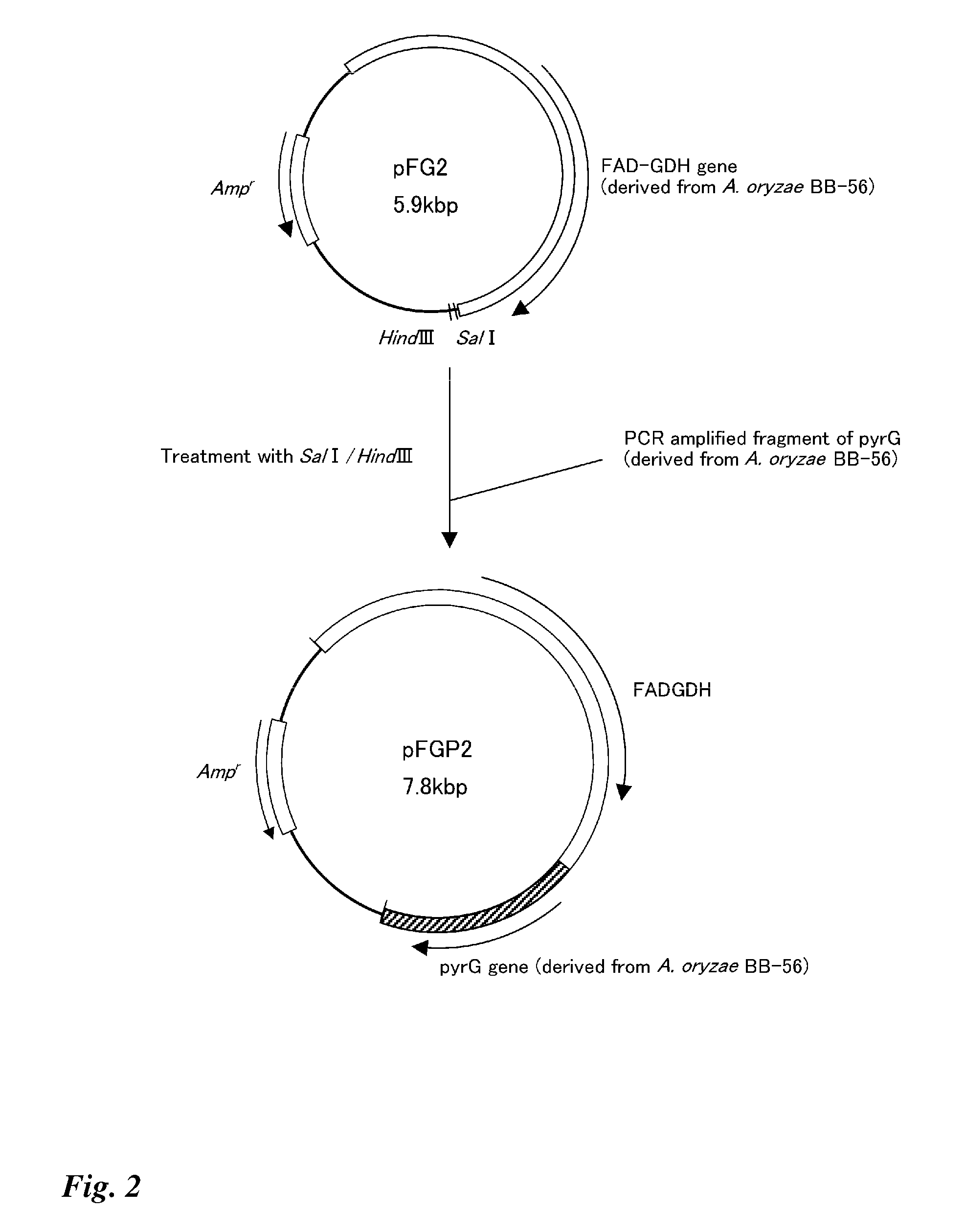
E. coli transformant, method for producing flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase using the same, and mutant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20130309750A1Accurate measurementEfficiently obtainedBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH) with high substrate specificity for D-glucose. A gene encoding a mutant FAD-GDH with its N-terminal region, containing an amino acid sequence corresponding to MKITAAIITVATAFASFASA that exists in the N-terminal region, deleted from the amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-GDH derived from Mucor is introduced into E. coli to obtain an E. coli transformant. Subsequently, this E. coli transformant is cultured to obtain an FAD-GDH with a specific N-terminal region deleted. The transformant allows the production of a large amount of GDH in a short time as compared with the original microorganism. An FAD-GDH that is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Extraction separation purification and identification of flavonoid monomers in oriental blueberry melanin
This is a method for flavonoid monomer's extraction, separation, purification and structural identification, belonging to flavonoid field. In this invention, the original source blueburry leaves turn to be blueburry leaves melanin solution after ethanol extraction. Then, macroreticular resinous adsorbent is used for crude separation of flavonoid in melanin solution, polyamide and HW-40 for flavonoid monomer's pufification, high efficiency liquid chromatography-mass spectrum and NMRR for structural identification. Finally, we obtain 7 kinds of flavonoid monomer, named A B C D E F and G. Exact structural identification help to determine B C D E and F is quercetin, chrysin, versulin, Kacmpferol and digitoflavone respectively, and their relative contents are 37.51%,2.26%,9.57%,1.72% and 15.16%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20110318810A1Accurate measurementAccurate blood glucose levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismLactose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Glucose Sensor
ActiveUS20130075276A1Reduced responseIncreased substrate specificityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnvironmental chemistryWorking electrode
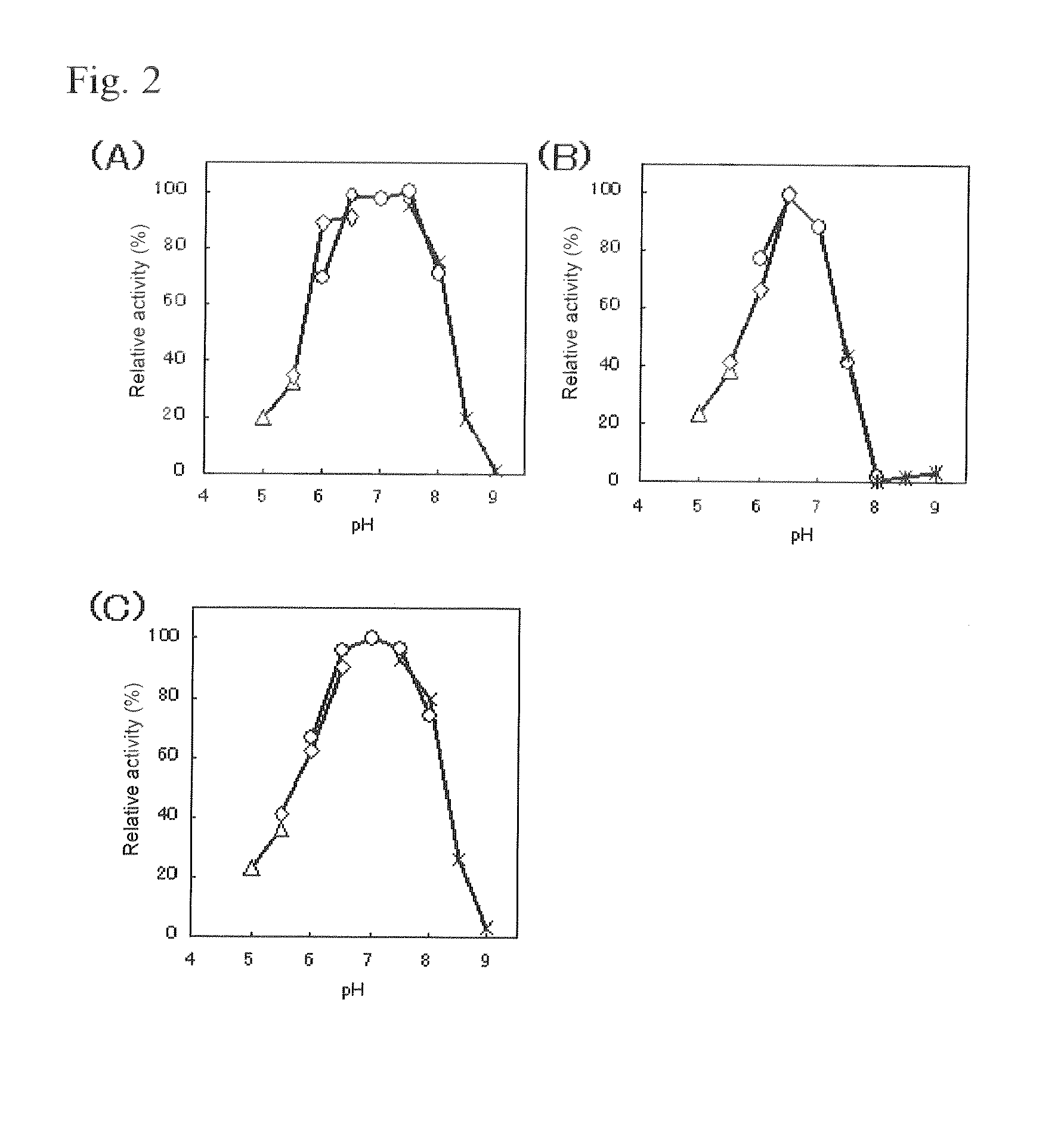
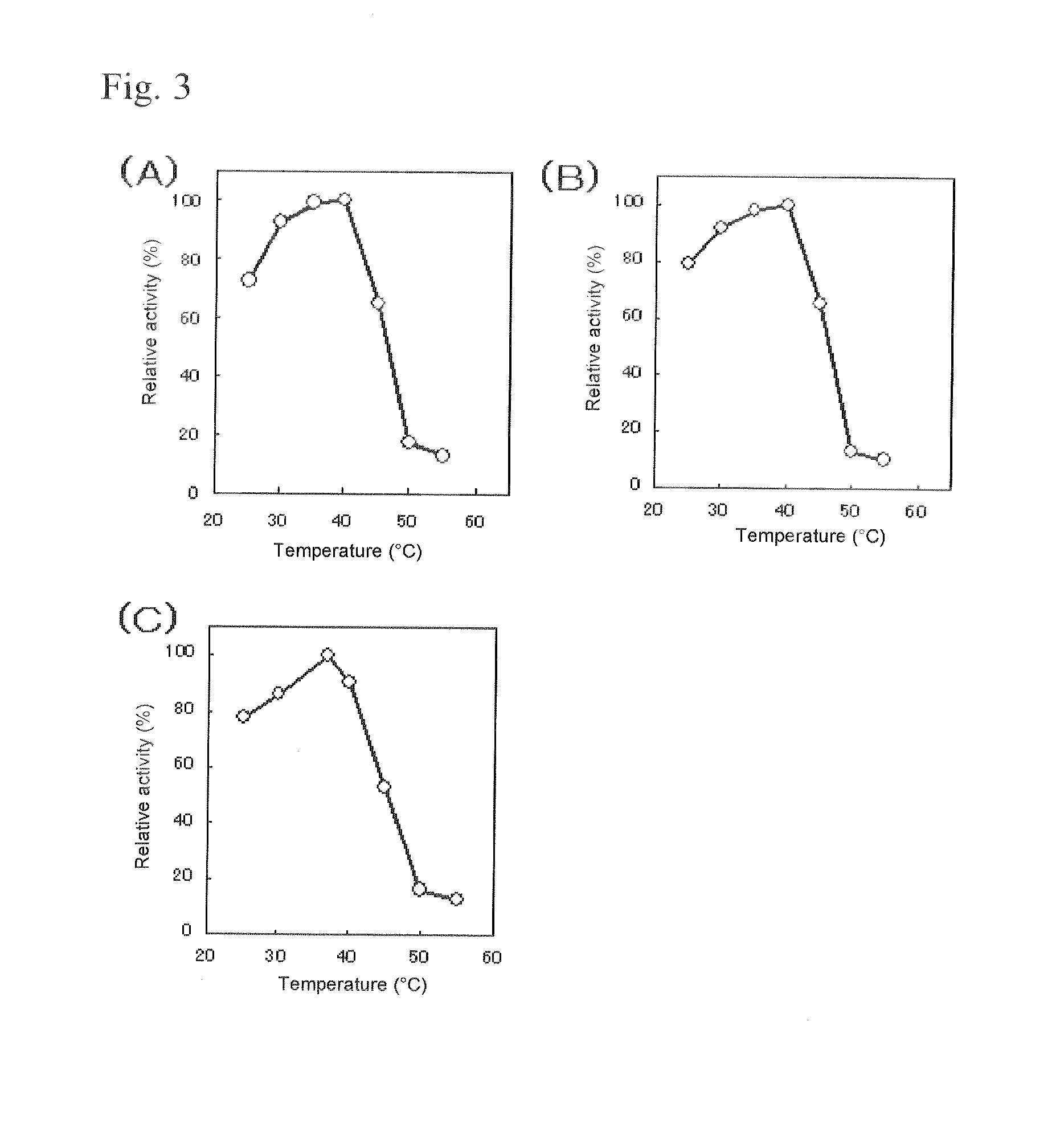
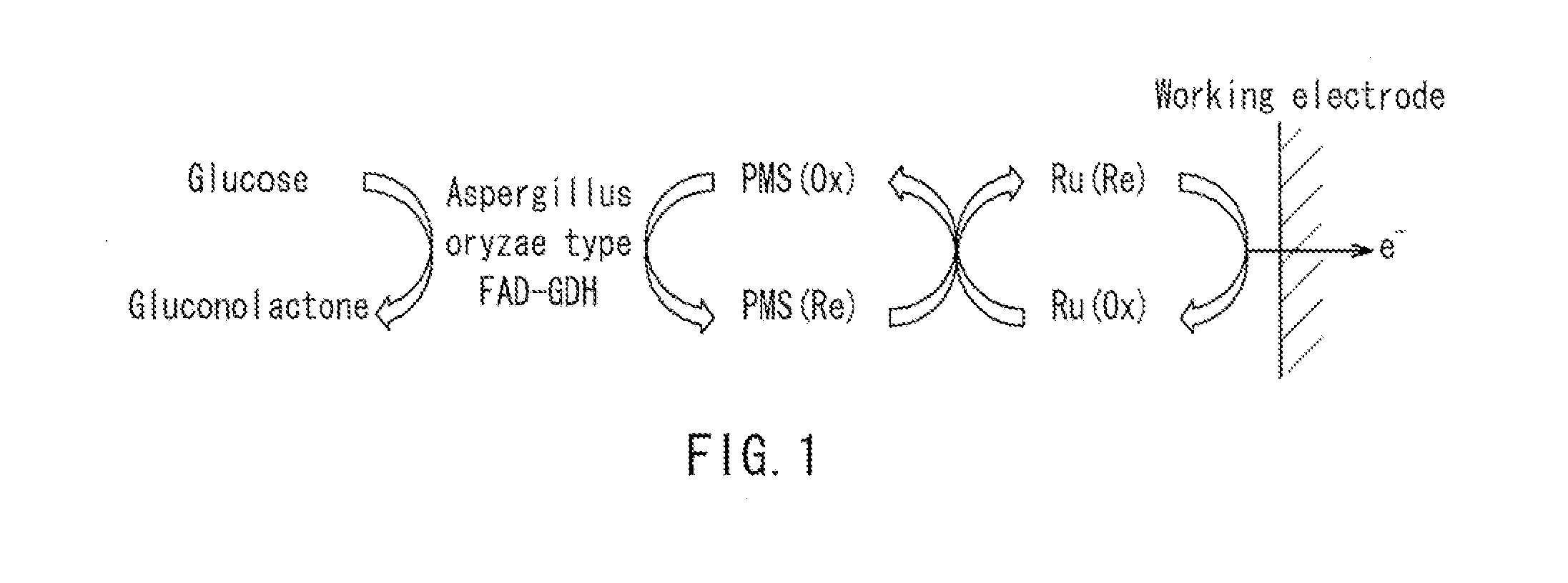
Provided is a glucose sensor that is capable of measuring a glucose concentration even in the case where Aspergillus oryzae type FAD-GDH (flavin adenine dinucleotide-glucose dehyrogenase) and a ruthenium compound are used in combination. The glucose sensor includes an insulative substrate, an electrode system having a working electrode and a counter electrode provided on the substrate, and a reagent layer provided on the electrode system, wherein the reagent layer contains Aspergillus oryzae type FAD-GDH, a ruthenium compound, and PMS (phenazine methosulfate).
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Soy daidzin composition and preparation process and use thereof
InactiveCN1449763AIncrease contentSimple extraction methodOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseIsoflavones
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Flavin monooxygenase mutant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107384880AIncreased specific enzyme activityEasy to produceFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastRandom mutation
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and particularly relates to a flavin monooxygenase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The error-prone PCR technology is used to conduct random mutation on wild type flavin monooxygenase to obtain the flavin monooxygenase mutant. The specific enzyme activity of the flavin monooxygenase mutant is improved by 35% compared with that of the wild type flavin monooxygenase. Meanwhile, a yeast expression system is adopted, when the flavin monooxygenase is displayed on the surface of yeasts, yeast cells can serve as enzyme producers and can also serve as carriers in immobilized enzymes, operation of purification, fixation and the like of the enzymes are omitted, the production link is simplified, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
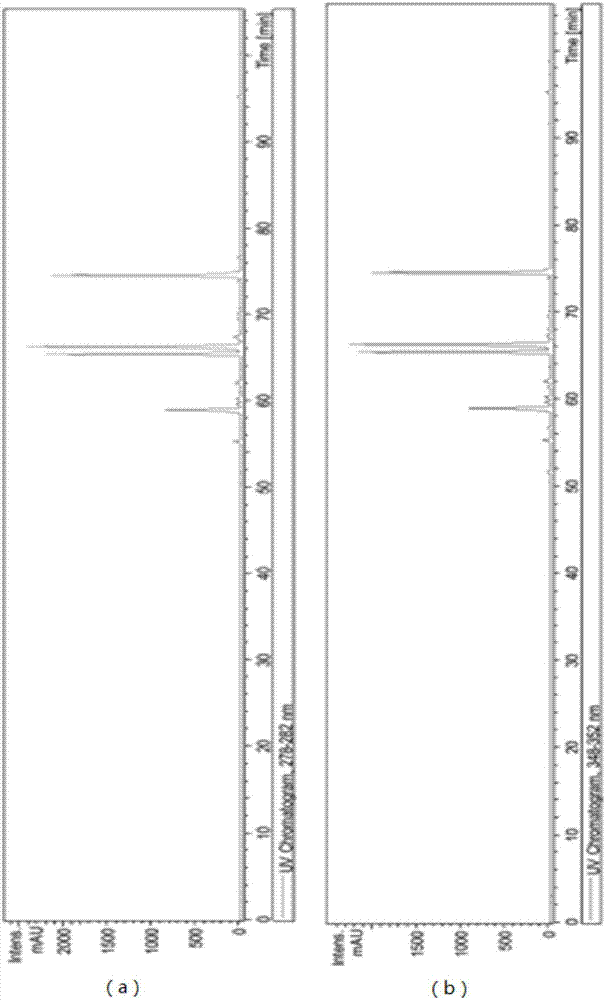
Method used for separating and identifying flavonoid matters in tobacco by adopting liquid chromatography-mass spectrography
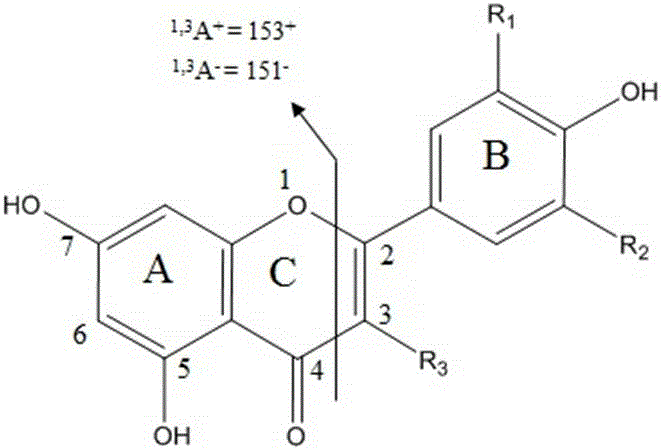
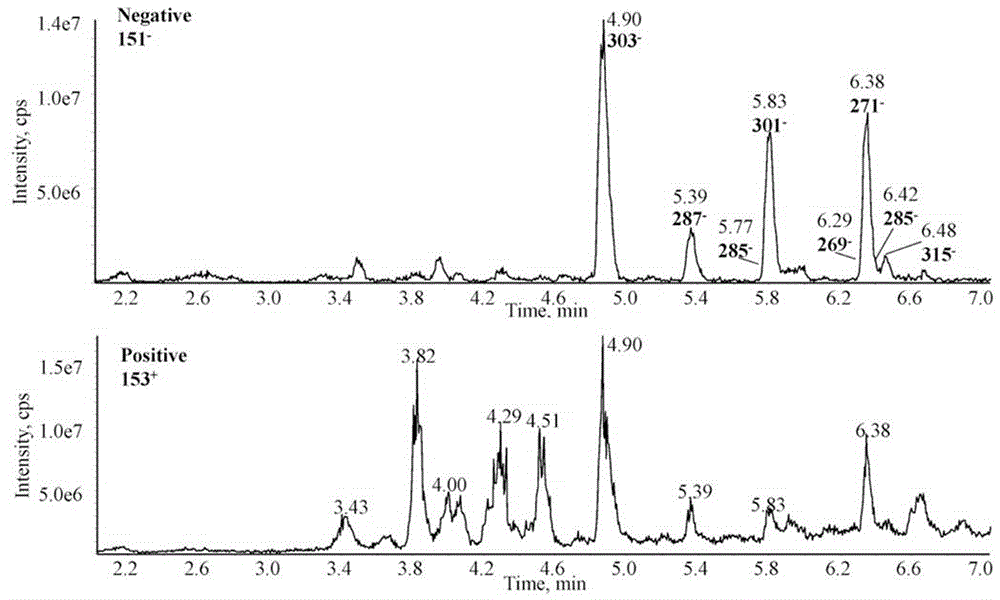
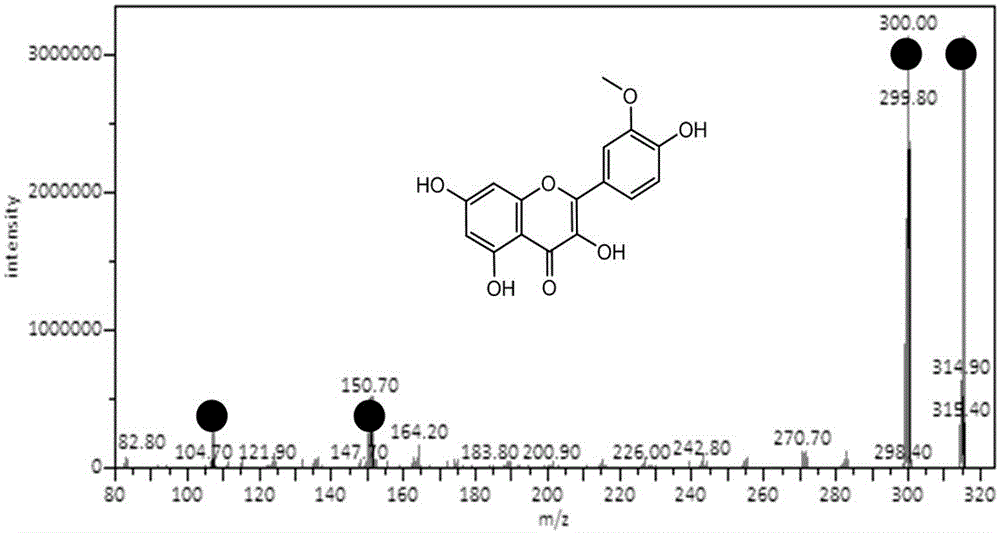
The invention discloses a method used for separating and identifying flavonoid matters in tobacco by adopting liquid chromatography-mass spectrography. The method comprises the following steps: a sample is ground and dried, an extractant is added according to the standard that 0.1 ml of the extractant is added into 1 mg of the sample for extraction and centrifugation, a supernatant liquor is collected, water and chloroform are added according to the standard that 0.5 ml of the water and 1 ml of the chloroform are added into 1 ml of the supernatant liquor for centrifugation, and the supernatant liquor is collected for analysis; 153+ and 151- are adopted as characteristic ions for scanning, parent ions are extracted for second level mass spectrum scanning, and an obtained spectrogram is compared with a spectral library to determine a chemical structure and verified through a reference substance; the molecules and ions of the identified matters and myricetin, dihydromyricetin, catechinic acid / epicatechin, daidzein, glycitein and glycyrrhizin / isoliquiritigenin are adopted as characteristic ions for scanning, the molecules and ions of the searched glycosylation flavonoid matters are used as the parent ions for the second level mass spectrum scanning, an obtained spectrogram is compared with the spectral library to determine a chemical structure and verified through the reference substance. According to the invention, the method is suitable for the analyzing and detecting micro even trace flavonoid matters.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Application of monascus color components and derivatives thereof in fighting cancers
InactiveCN101862324ABroaden the field of useEfficient inducing apoptosis activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMonascus ankaSide effect
The invention provides application of monascus color components and derivatives thereof in preparing the drugs for fighting cancers, belonging to the technical field of monascus compound application. The invention solves the problem of narrower application range of the monascus color components and derivatives thereof in the prior art. The series compound comprises rubropunctamine, monascorubramine, monascin, ankaflavin, rubropunctatin, monascorubrine, monasfluore A, monasfluore B and derivatives thereof. The compound can be used as the drug and health care product additive for preventing and treating cancers and has little toxic or side effects on normal cells of human bodies.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing questin by utilizing ocean aspergillus flavipes HN4-13 bacterial strain and application of questin
ActiveCN104946693AReasonable designEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyVibrio anguillarum
The invention discloses a method for preparing questin by utilizing an ocean aspergillus flavipes HN4-13 bacterial strain. The method comprises the following steps: conducting separation and purification on antibacterial active substances generated through fermentation of the aspergillus flavipes HN4-13 bacterial strain according to silica-gel column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, preparation of high performance liquid chromatography (PHPLC) and the like by taking vibrio harveyi as an indicator bacterium, so as to obtain a vibrio harveyi-preventing active compound HY2; indentifying the structure of the active compound HY2 according to spectra data such as ESI-MS, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR, so as to determine that the active compound HY2 is questin. The questin is obtained through separation of a metabolic product of aspergillus flavipes HN4-13; experiments show that the questin can perform a certain inhibiting function of the pathogenic bacteria, such as vibrio harveyi, vibrio anguillarum, vibrio parahaemolyticus and vibrio cholerae, of aquatic products, and can be used for preparation of medicine preventing pathogenic vibrio of the aquatic products.
Owner:JIANGSU MARINE RESOURCES DEV RES INST LIAN YUNGANG
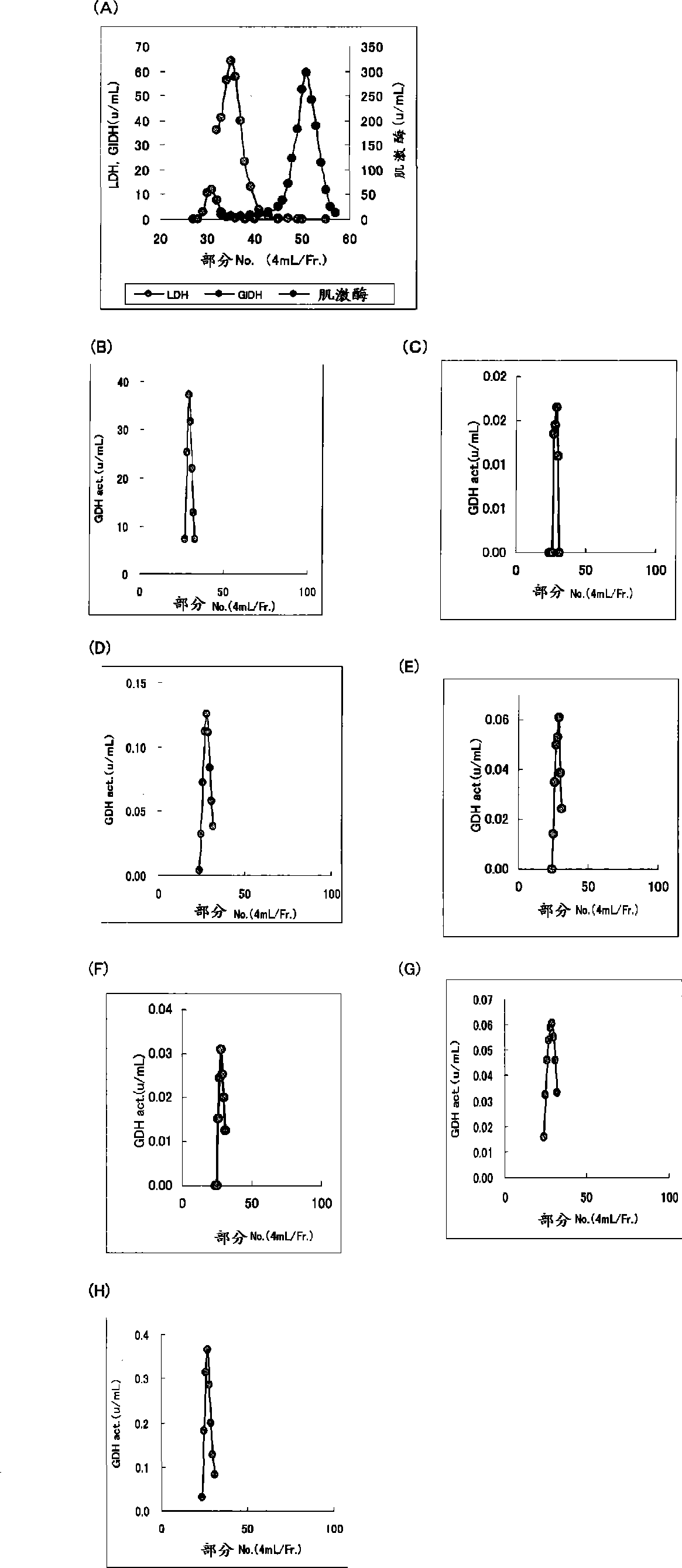
Novel glucose dehydrogenase
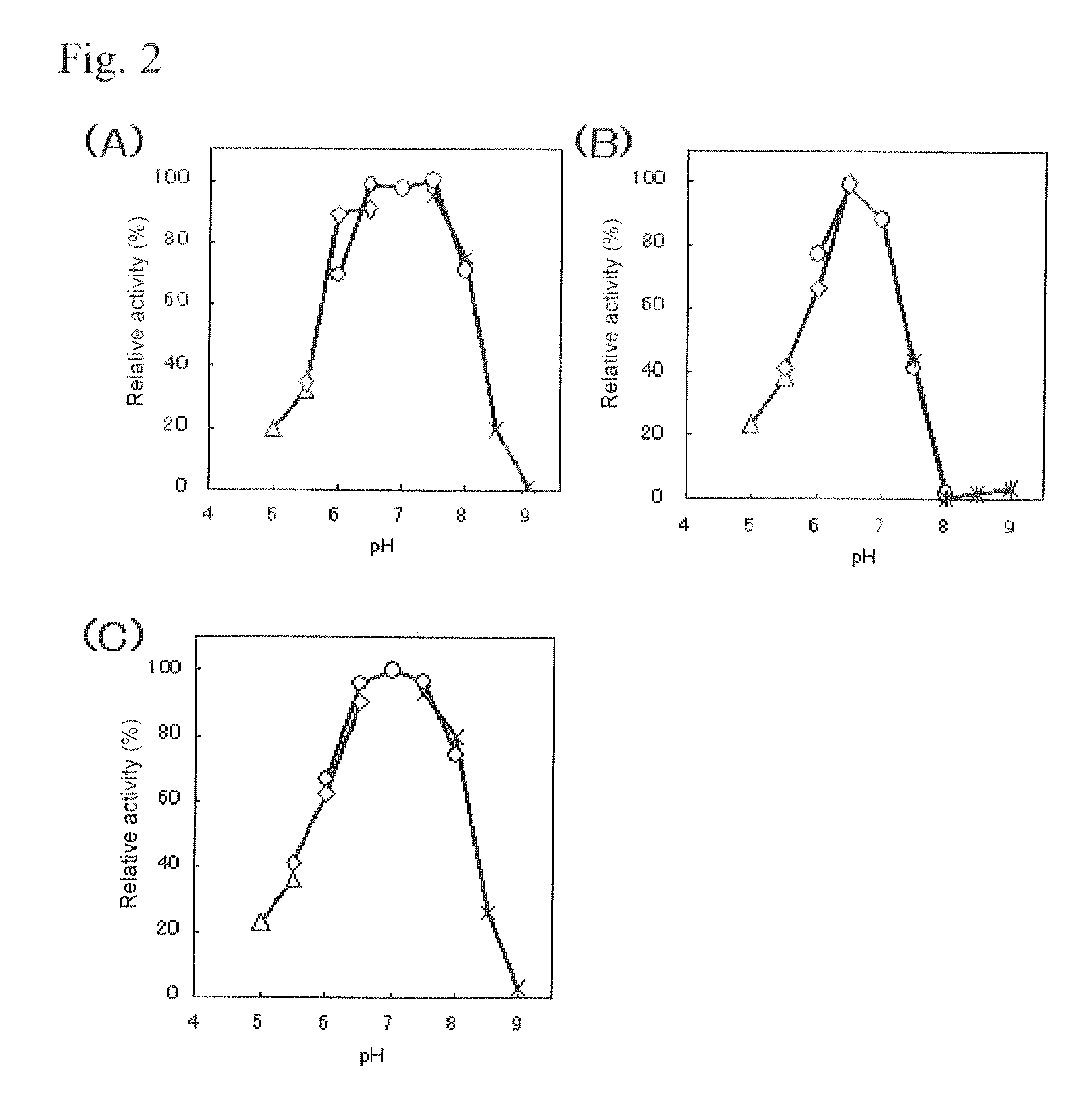
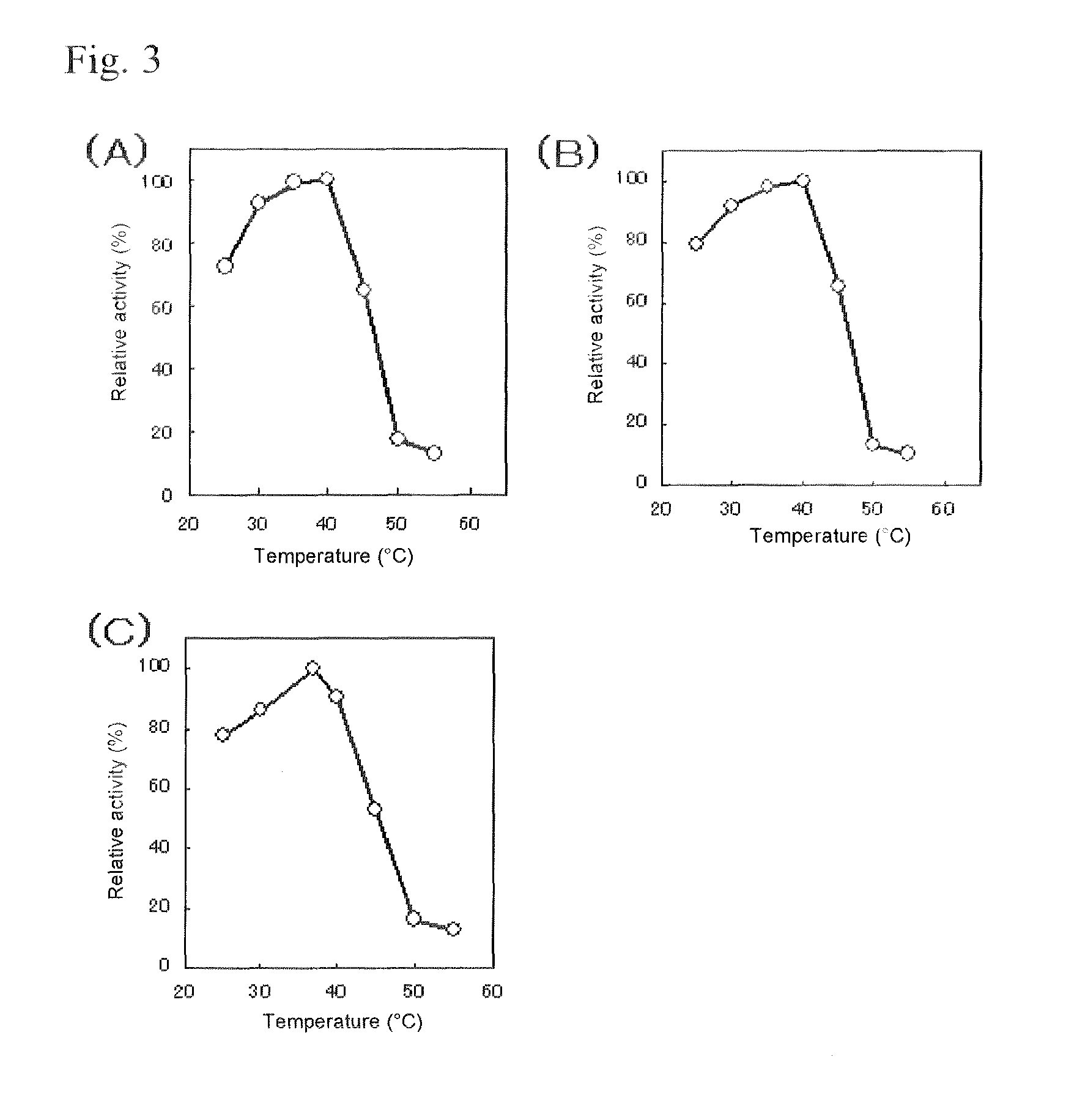
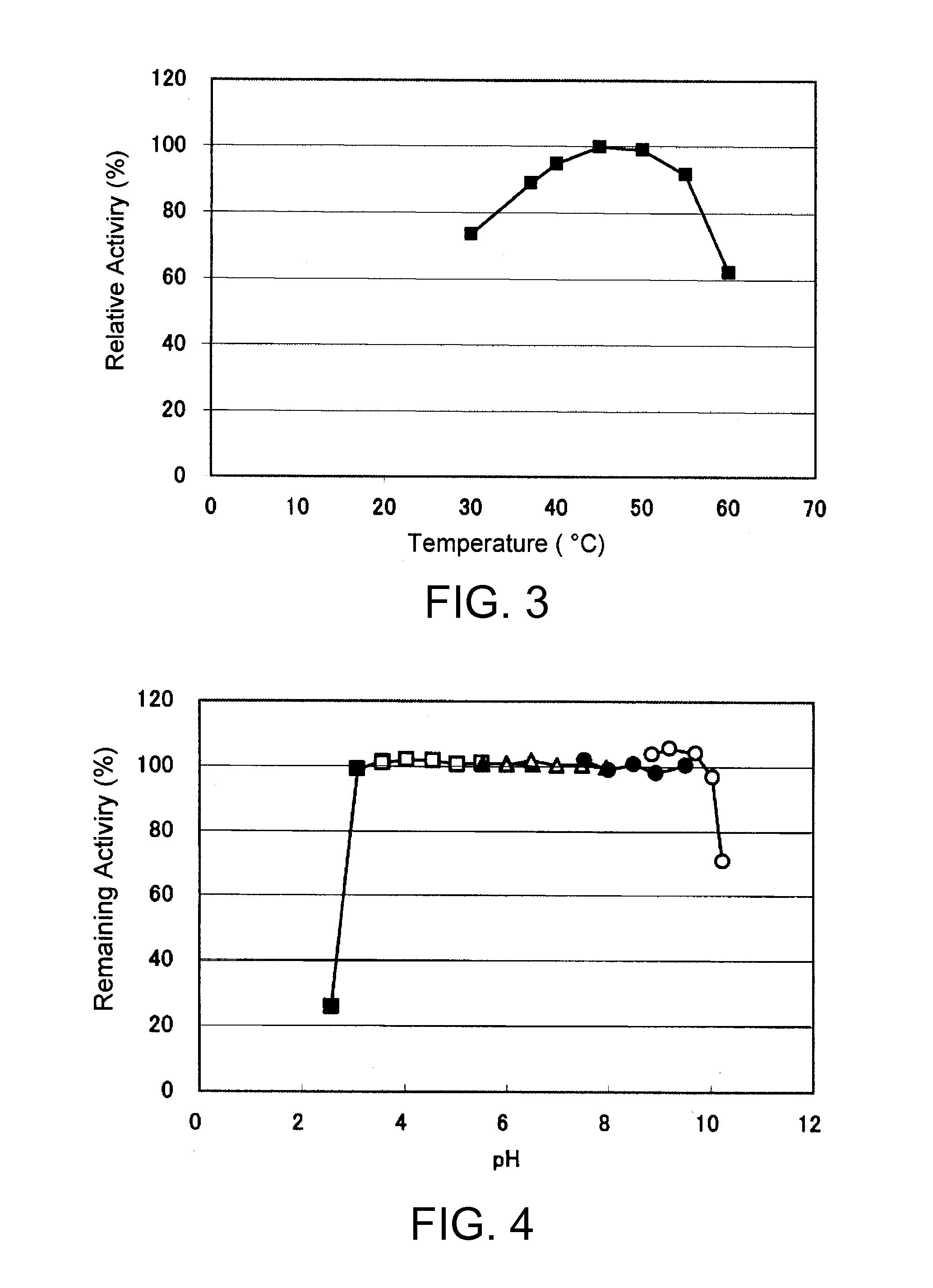
ActiveUS20150031059A1High affinityReduced responseSugar derivativesMicroorganismsElectrophoresesFlavolipin
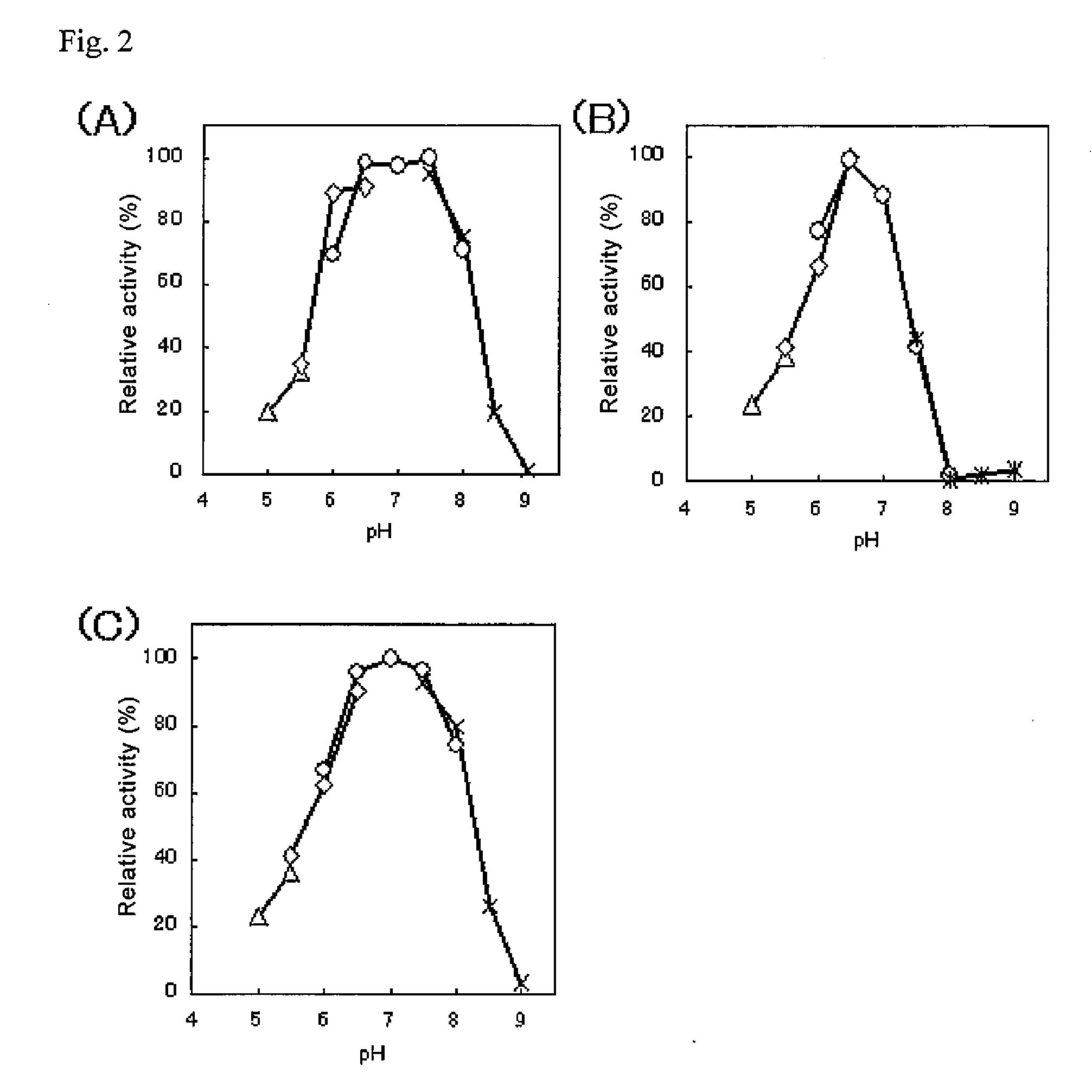
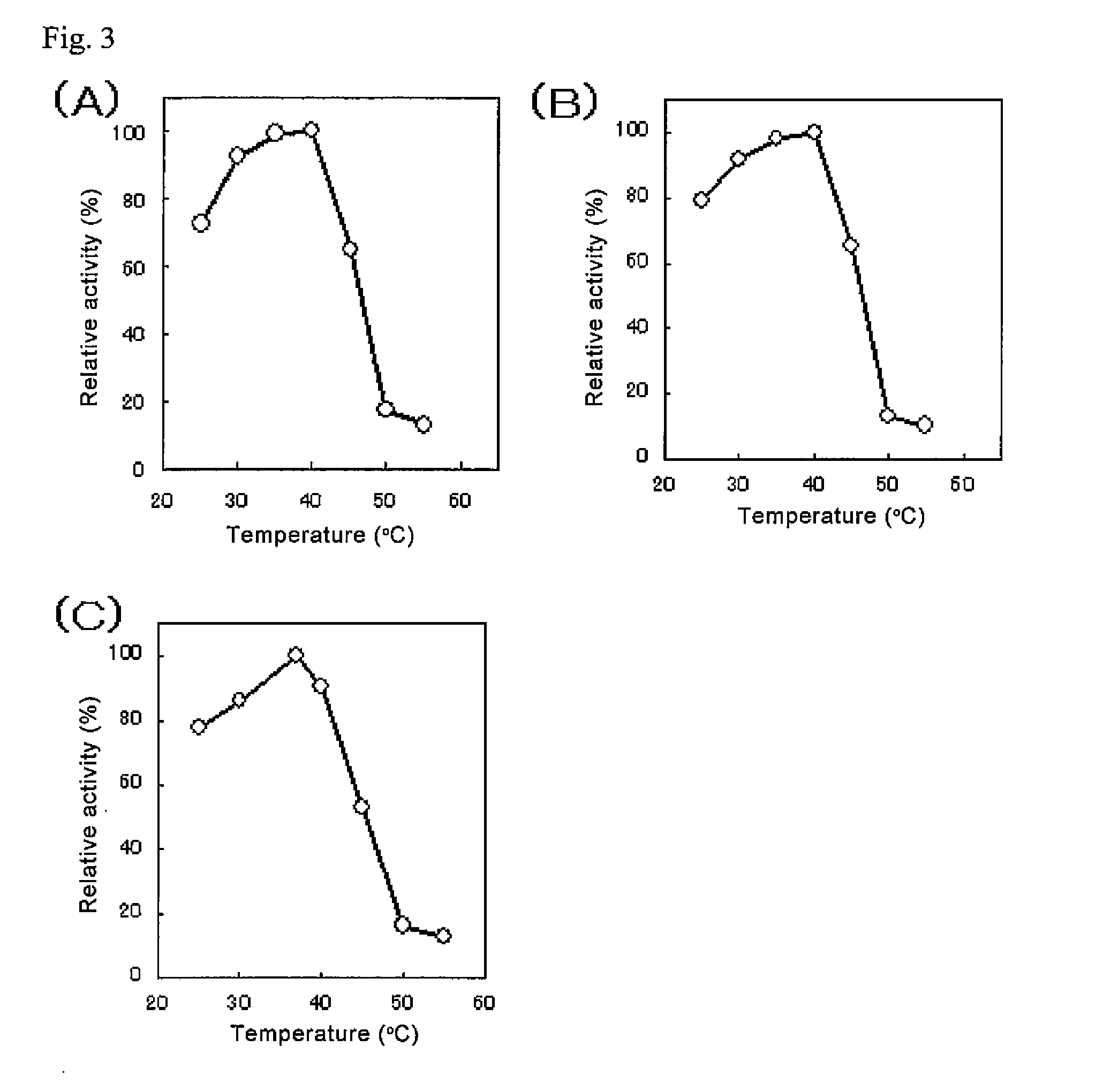
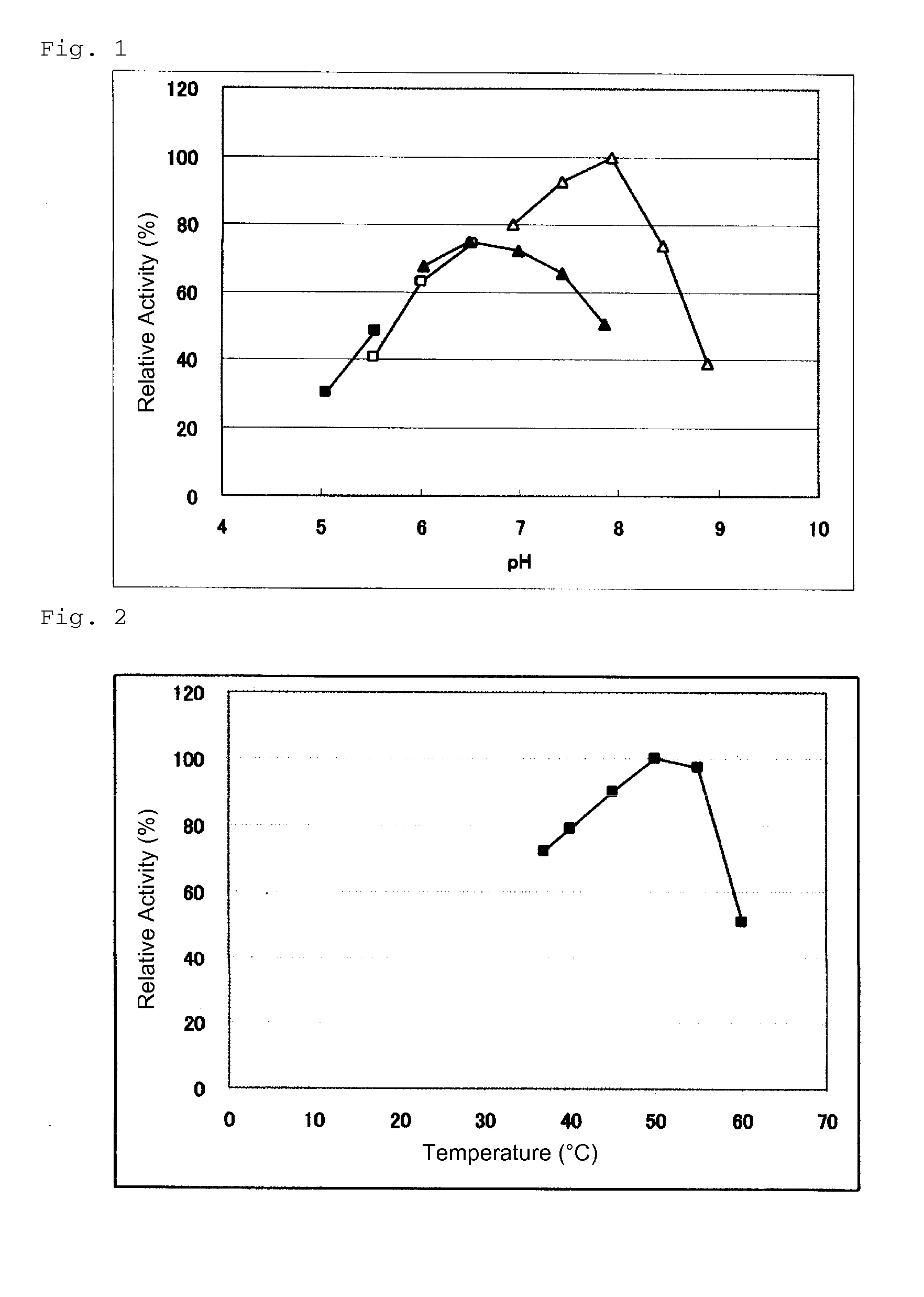
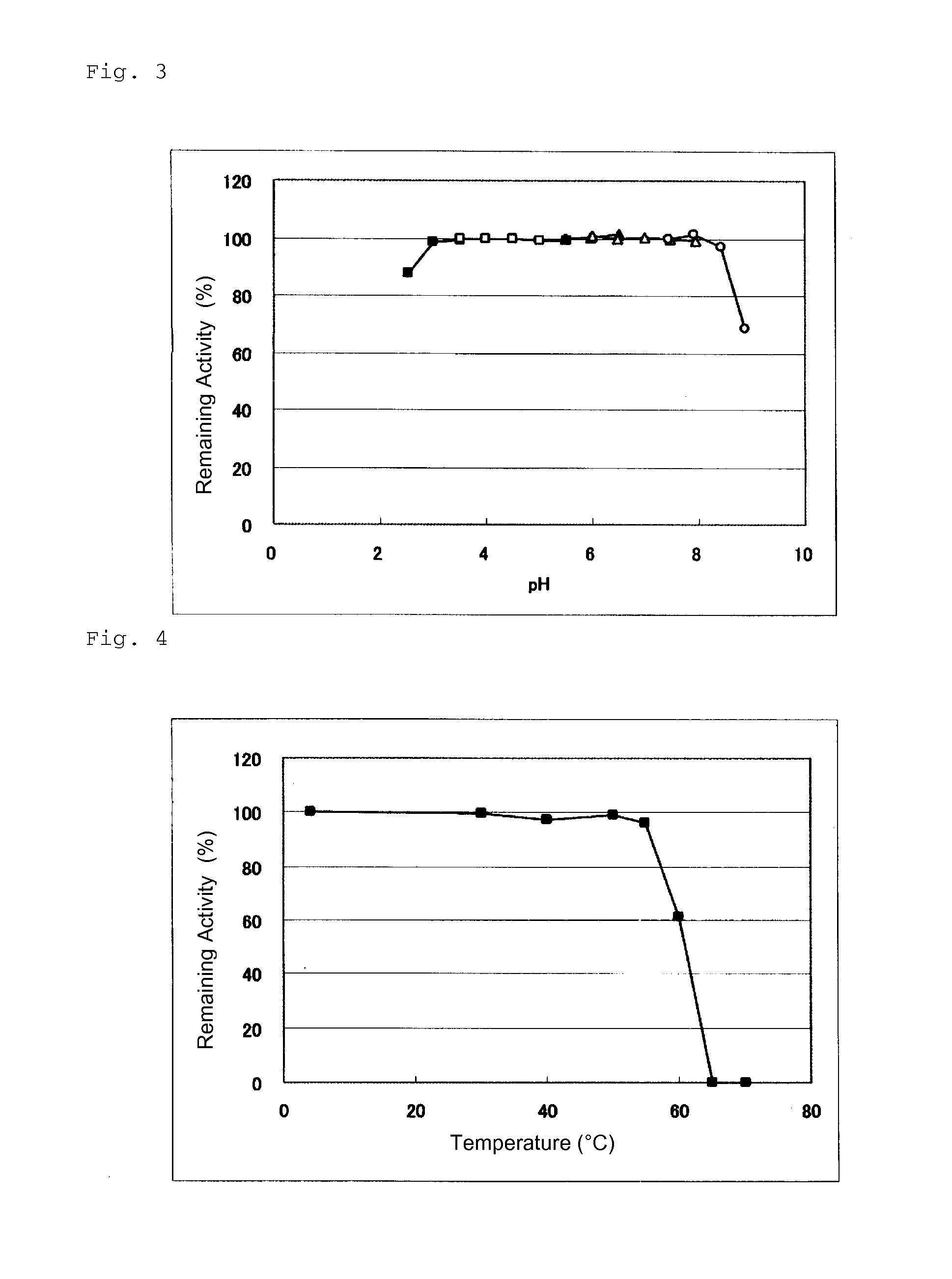
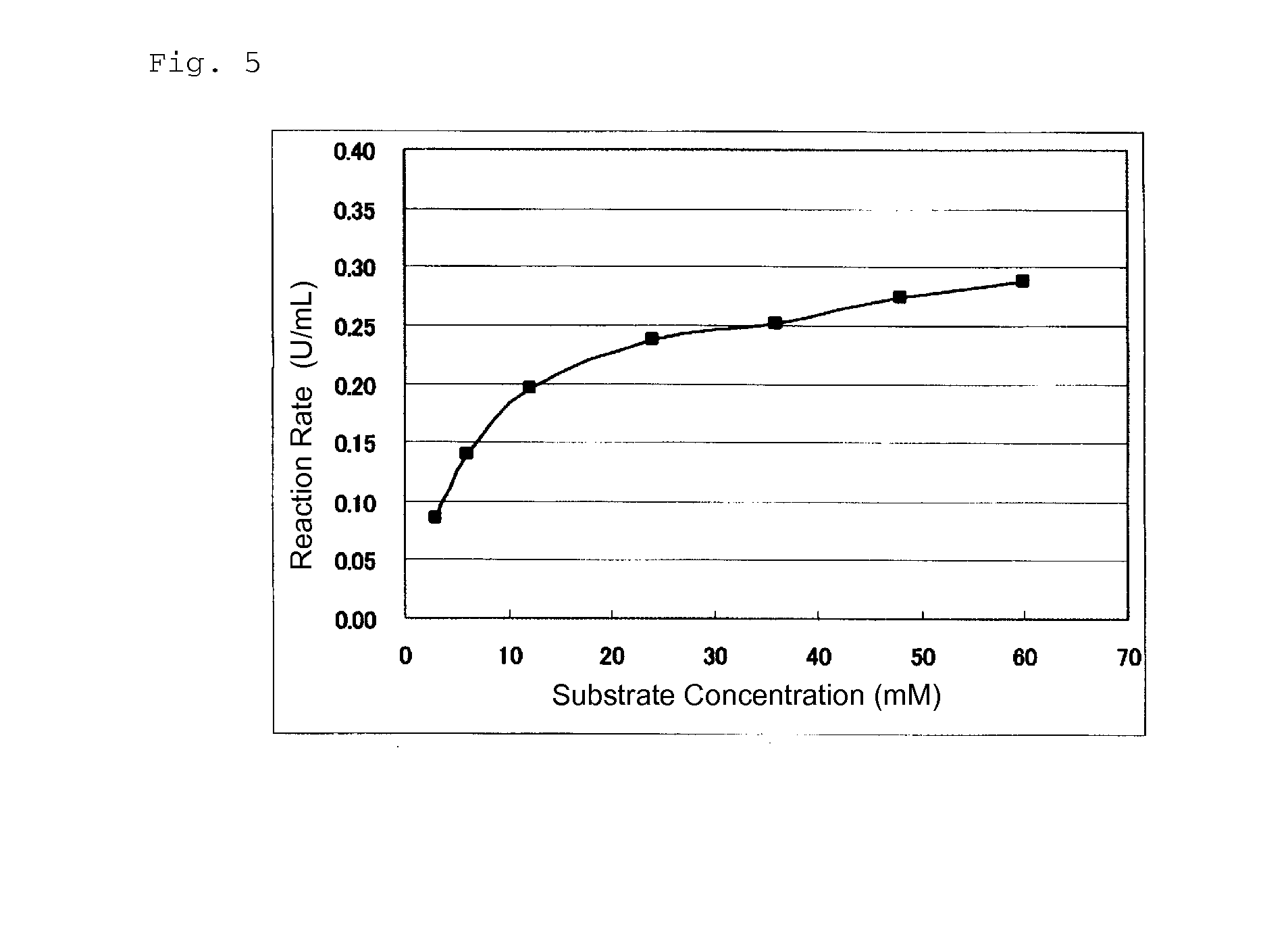
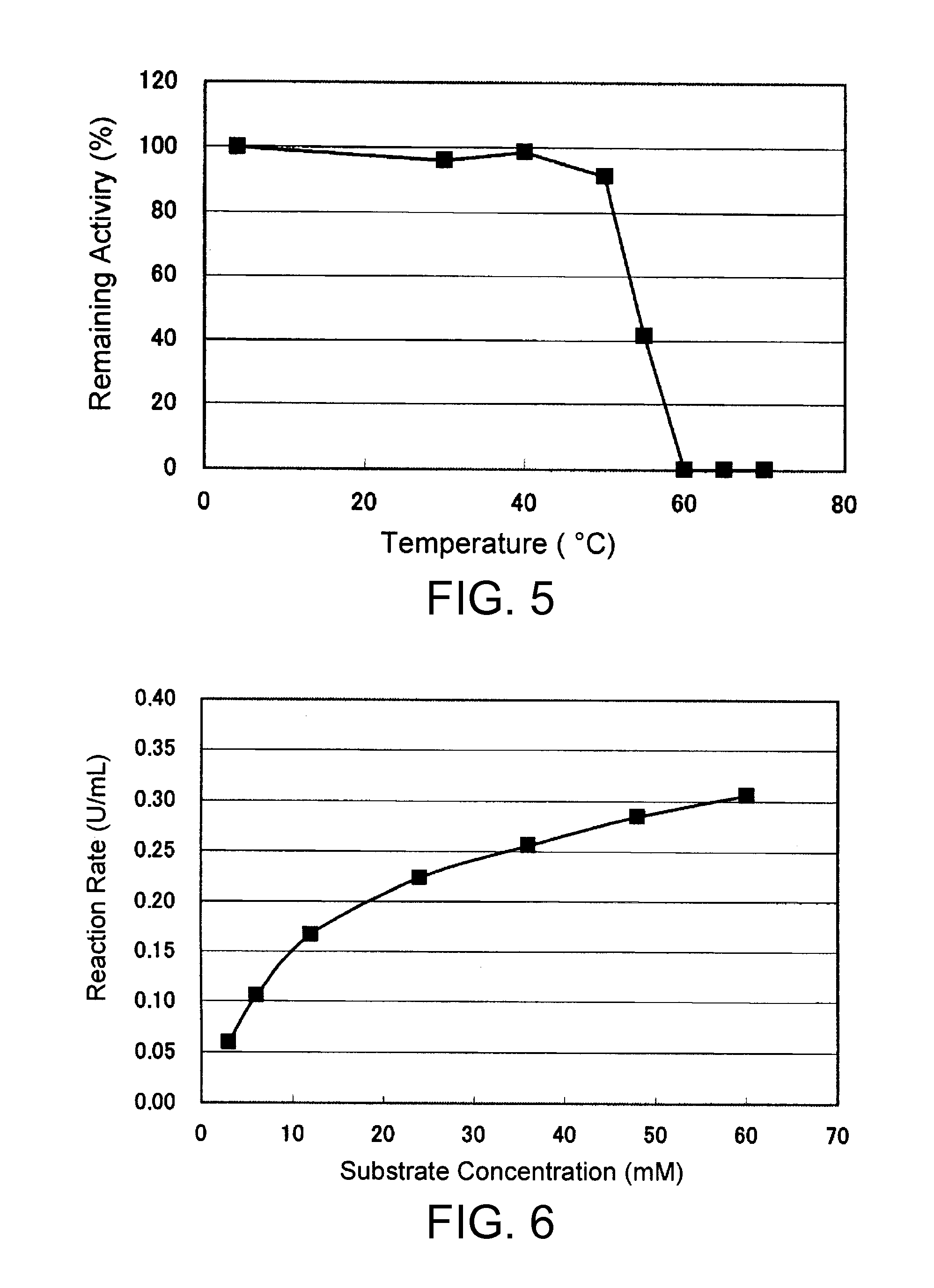
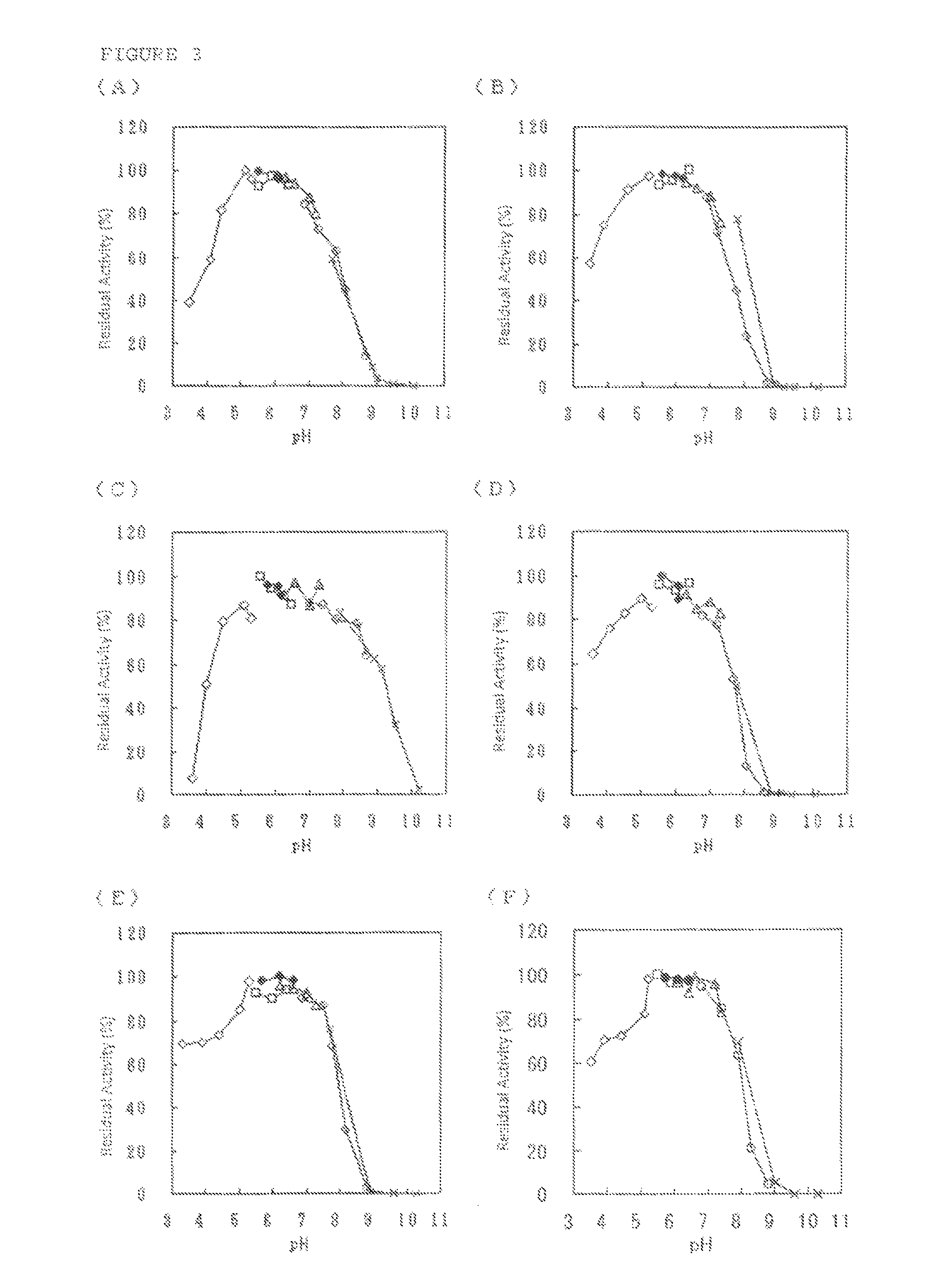
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel glucose dehydrogenase, a method for producing the glucose dehydrogenase, and applications of the glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase of the invention has the following characteristics (1) and (4): (1) Molecular weight: the molecular weight of a polypeptide moiety in the enzyme is about 68 kDa as measured by SDS-polyacrylamide electrophoresis; (2) Km value: the Km value for D-glucose is about 15 mM or less; (3) Temperature stability: stable at a temperature of 55° C. or less; and (4) pH stability: stable at a pH range of 3.0 to 8.5.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS8445246B2Accurate measurementLeveling precisionSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismFlavolipin
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Novel glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20140287478A1High affinityReduced responseMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesGlucose dehydrogenase activityDehydrogenase
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel glucose dehydrogenase, a method for producing the glucose dehydrogenase, and applications of the glucose dehydrogenase. An isolated flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase comprising a polypeptide having an amino acid sequence with 80% or more identity to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, and having glucose dehydrogenase activity is provided.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Health food containing pearl and kudzuvine root and its preparation method
InactiveCN101356969AInorganic CalciumMeet needsMetabolism disorderDermatological disorderDaidzinTrace element
The invention discloses a series health-care food containing pearl and kudzu root and a preparation method thereof. The food is prepared by matching natural pearl and kudzu root which can be taken both as food and medicine with vitamin, medlar, a sweetening agent and appropriate accessories according to a certain proportion. The health-care food contains organic calcium, inorganic calcium, vitamin and a plurality of trace elements which are needed by human body, and the food further contains components such as flavonoid daidzin, daidzein, xylopuerarin, kudzu powder flavin, and great amount of starch, therefore, the food has the functions of beautifying the face and enlarging the breast, nourishing the tendons and channels and preventing cerebral-cardiovascular diseases, and is taken as health products which are fit for women, the middle aged people and the old, thus delaying senility, strengthening the body and maintaining the beauty and youth of skin.
Owner:湖南今珠生物科技有限公司
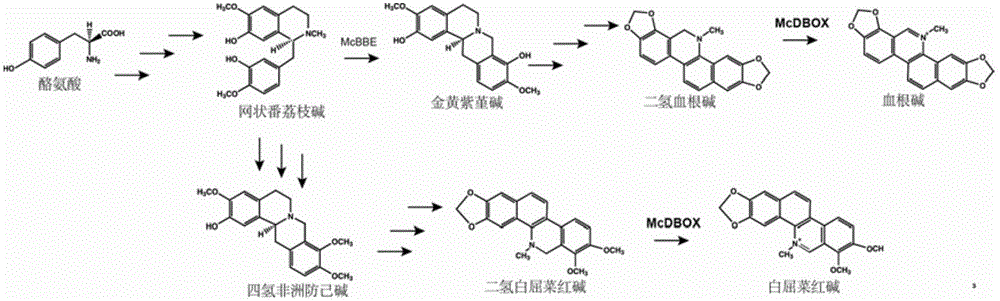
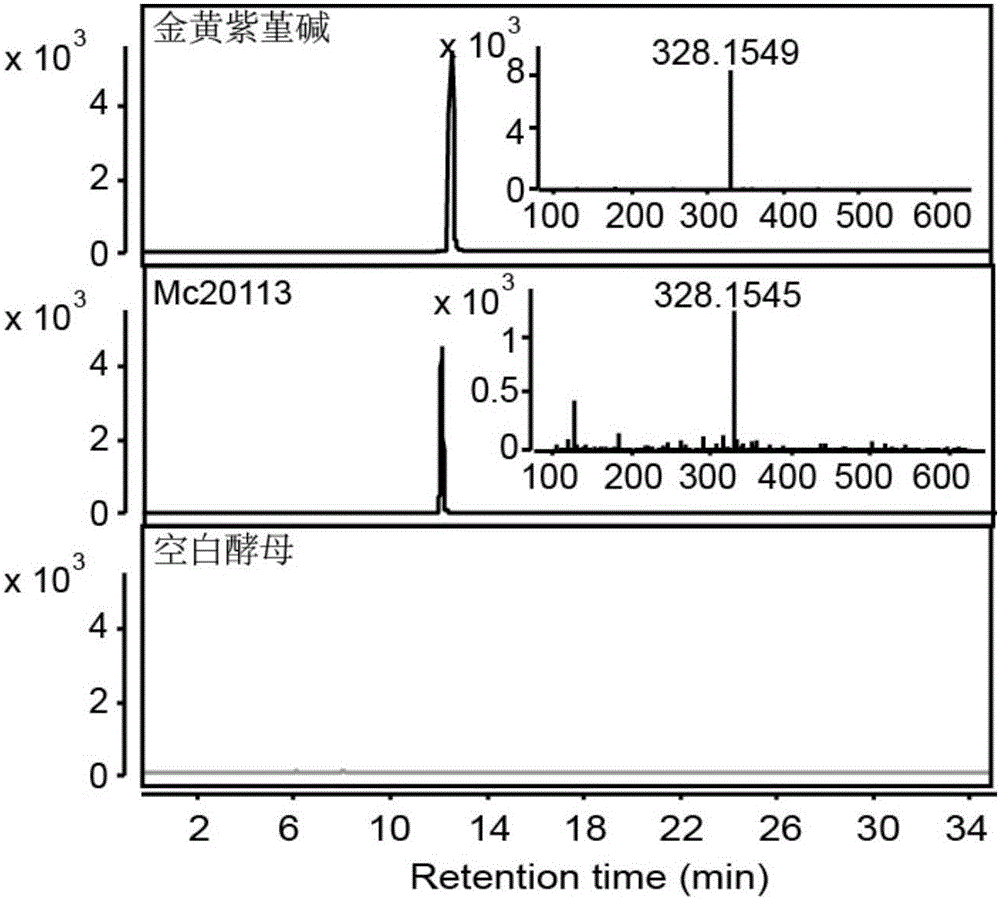
Flavoprotein oxidase genes of macleaya cordata in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and application of flavoprotein oxidase genes
ActiveCN106047904AAchieve synthesisAchieve in vitro synthesisOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringHeterologousFlavoprotein
The invention discloses flavoprotein oxidase genes of macleaya cordata in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and application of the flavoprotein oxidase genes. Three flavoprotein oxidase genes joining in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine are found in a macleaya cordata genome for the first time, including genes Mc20113, Mc6407 and Mc6408. Steps of reaction are respectively verified by using a brewer's yeast system through upstream precursor feeding, and synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and midbodies can be achieved. The conversion efficiency of same functional genes of macleaya cordata and opium poppy is further compared by using a brewer's yeast heterologous expression system, and the result shows that the conversion rate of the gene of macleaya cordata is remarkably higher than that of opium poppy. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism of synthesis of sanguinarine in macleaya cordata, and a theoretic basis and molecular assistant breeding targets are provided for breeding of macleaya cordata with high contents of sanguinarine and chelerythrine; and meanwhile, precious experience is provided for in-vitro artificial synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Method for extracting isoflavonoids compound in all-grass of Twining Rhynchosia with ionic liquid
The invention relates to a method for extracting isoflavonoids compound in all-grass of Twining Rhynchosia with ionic liquid, comprising: obtaining extractum after smashed all-grass of Twining Rhynchosia is extracted with alcohol the concentration of which is 70%; mixing the extractum with water which accounts for 7-12 wt% of extractum to obtain slurry; while stirring at room temperature, adding ionic liquid the volume of which is 1-2 times of slurry; after reacting for 6-10h, obtaining solid-liquid mixture a; and after filtrate obtained by separating the solid-liquid mixture a is dewatered, carrying out chromatographic separation by a silicagel column or a polyamide column, and obtaining isoflavonoids compound. The method of the invention is simple and quick, and utilizes [Bmim] BF4 as extraction and separation solvent to successfully separate and obtain 4'-(1''-methoxy group)-propyl group oxo-5,7-dihydroxyisoflavone and biochanin A from the all-grass of Twining Rhynchosia at room temperature, thus solving the difficulty that the traditional plant chemical means can not effectively separate and purify isoflavonoids compound in all-grass of Twining Rhynchosia.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
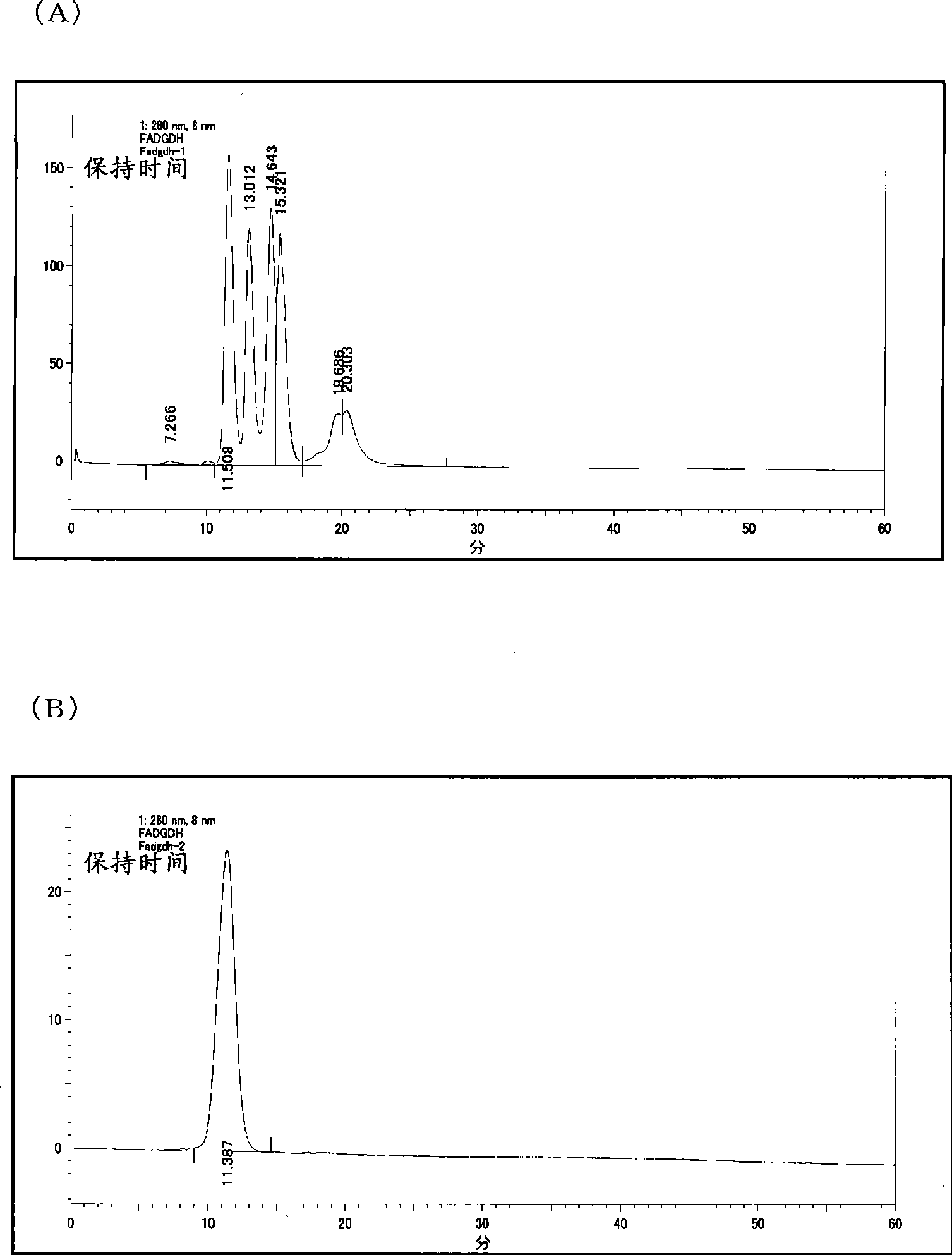
Transformant transfected with flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase gene and method for producing flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the same
InactiveUS20110053194A1Accurate measurementIncrease production capacityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideA-DNA
It is intended to highly efficiently produce a large amount of novel FAD-GDH capable of more accurately measuring a glucose level. Provided is a transformant in which a DNA encoding a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase selected from the group consisting of (a) a DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 20; (b) a DNA consisting of the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 19; (c) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 19 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase activity; (d) a DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 34; (e) a DNA consisting of the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 33; and (f) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 33 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase activity has been introduced. Further, a method for producing a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the transformant is provided.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Flavin derivatives
The present invention relates novel flavin derivatives and other flavin derivatives, their use and compositions for use as riboswitch ligands and / or anti-infectives. The invention also provides method of making novel flavin derivatives.
Owner:BIORELIX
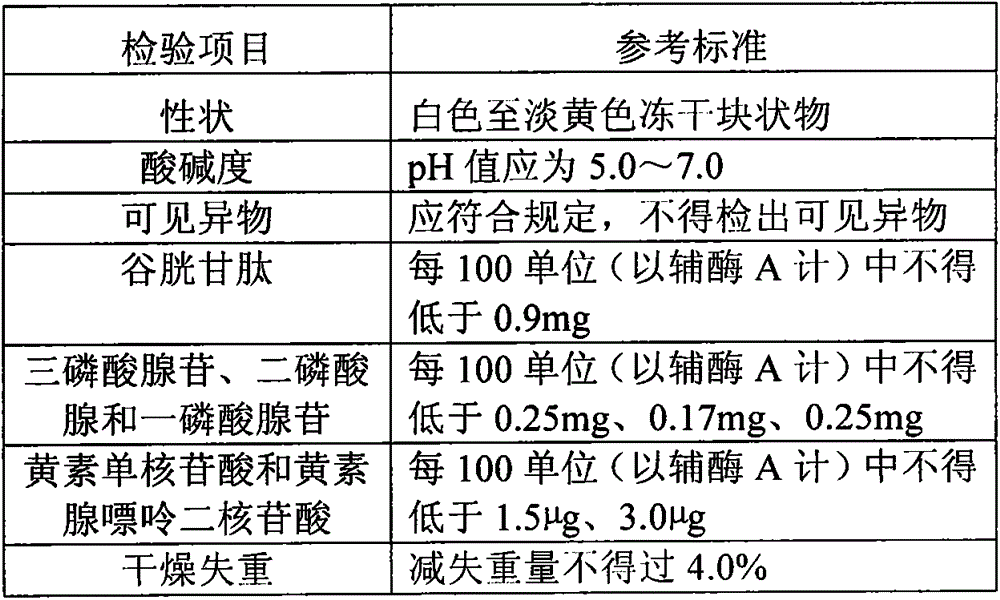
Stable compound coenzyme preparation as well as preparation method and applications thereof
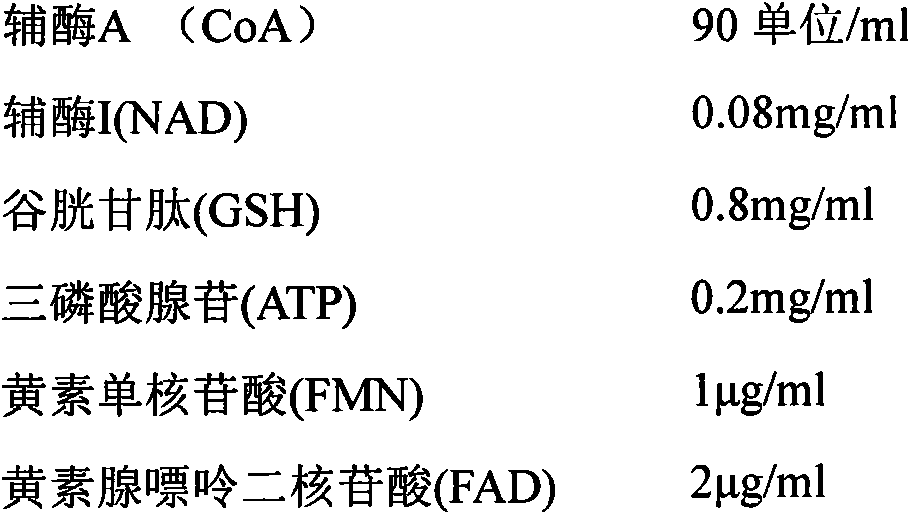
InactiveCN104623626AGood repeatabilityReduce lossOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFlavin adenine dinucleotideDisease
The invention provides a stable compound coenzyme preparation and a preparation method thereof. The main compositions and proportions of the stable compound coenzyme preparation are as follows: 90-120 U of coenzyme A (CoA), 0.1-0.3 mg / ml coenzyme I (NAD), 1-5 mg / ml glutathione (GSH), 1-2.5 mg / ml adenosine triphosphate (ATP), 1.8-12 mu g / ml flavin mononucleotide (FMN), 3-13 mu g / ml flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), 0.1-0.4 mg / ml adenosine diphosphate (ADP), 0.2-0.4 mg / ml adenosine monophosphate (AMP), 1.2-15 mu g / ml of adenosine methionine (SAM), 1-5 mg / ml calcium gluconate, 0.5-1.5 mg / ml cysteine hydrochloride, and 0.6-5 mg / ml mannitol. The preparation method overcomes the defects that high-speed centrifugalization is adopted, freeze-drying conditions are not clear and the product stability is poor in the existing method, and the stable compound coenzyme preparation is widely applied to the practices of preparing drugs for treating cardia-cerebrovascular diseases and digestive system diseases.
Owner:BEIJING SL PHARMA +2
Flavin protein of trypanosoma cruzi, method of screening vermicide with the use of the same and diagnostic
InactiveUS20060275329A1Promote decompositionHighly specific and simple methodCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFlavoproteinTrypanocidal Drugs
It is intended to provide a method of diagnosing infection with Chagas disease by screening a trypanocidal drugs for Trypanosoma cruzi which is the pathogen of Chagas disease. Using a flavin protein TcOYE specific to Trypanosoma cruzi, a trypanocidal drugs effective against Trypanosoma cruzi is screened. Using the gene sequence of TcOYE and an antibody therefor, infection with Trypanosoma cruzi is diagnosed.
Owner:OSAKA BIOSCI INST +1
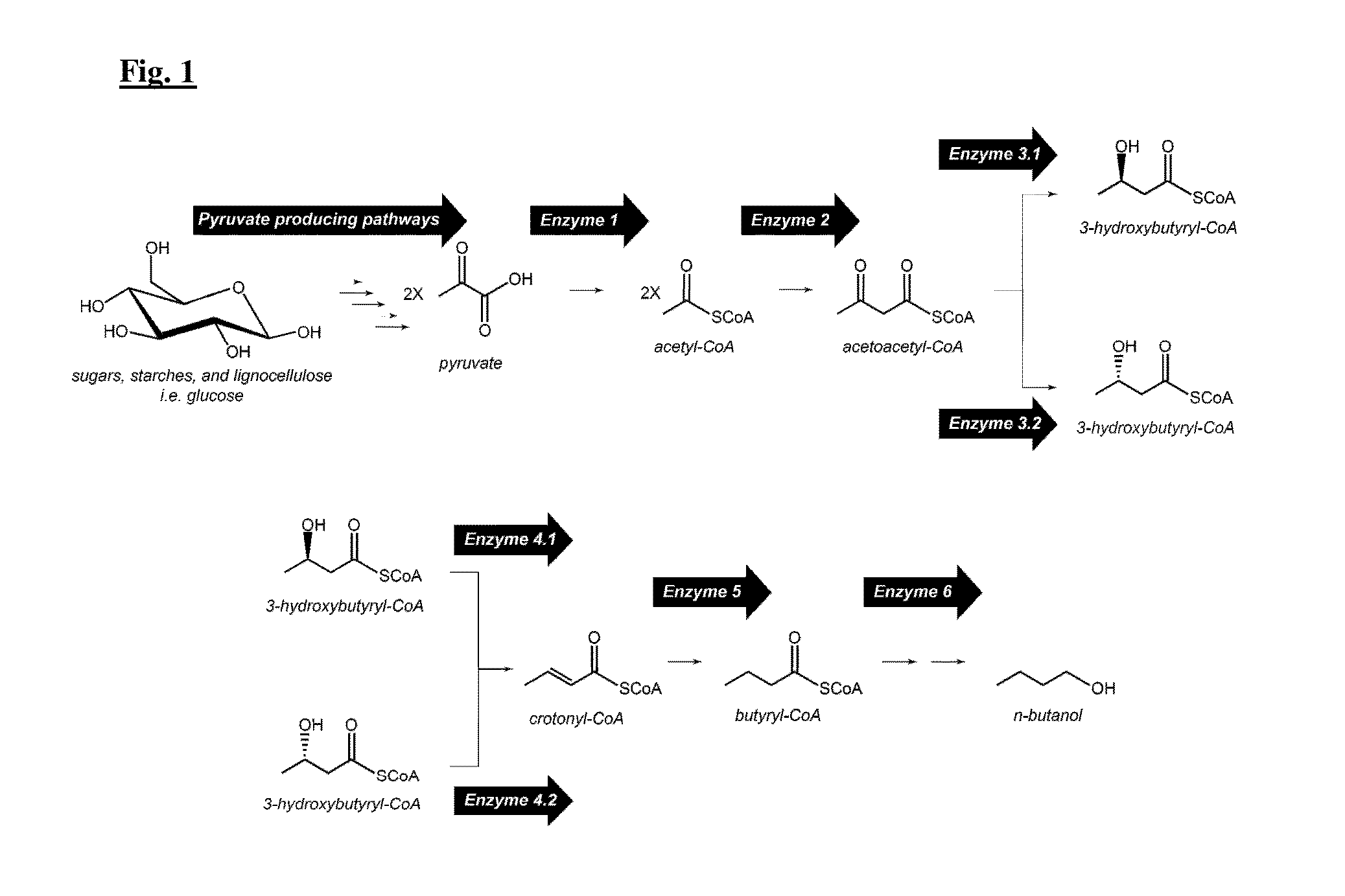
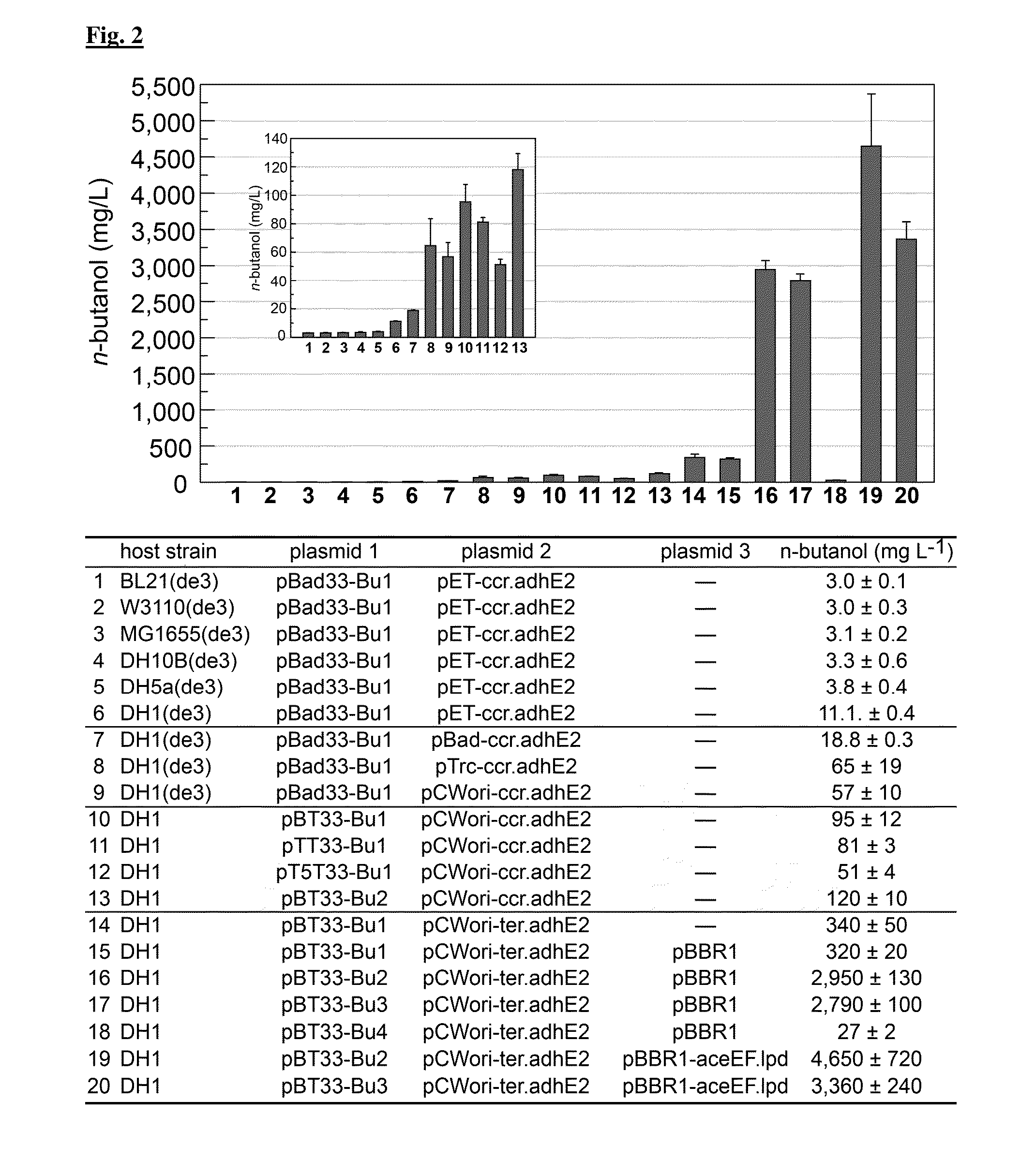
Synthetic pathways for biofuel synthesis
The present disclosure provides optimized recombinant cells for the production of n-butanol. Methods for the use of these cells are also provided. Specifically, the utility of acylating aldehyde dehydrogenases and pyruvate:flavodoxin / ferredoxin-oxidoreductase for the improvement of n-butanol yields from recombinant cells is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS8945359B2Good reproducibilityImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConcentrations glucoseMaltose
The invention provides a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase exhibiting reduced fluctuation of activity depending on temperature environment, and a method for measuring glucose concentration using the flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has the following properties (1) to (3): (1) activity: which exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity in the presence of an electron acceptor; (2) substrate specificity: which exhibits an activity of 10% or less against maltose, D-galactose, D-fructose, sorbitol, lactose and sucrose when the activity against D-glucose is defined as 100%; and (3) temperature characteristics: which exhibits lower fluctuation of activity in a wide temperature range of 10 to 50° C.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase
The object is to provide a novel enzyme which enables to determine the glucose level more accurately, a bacterium capable of producing the enzyme, and use of the enzyme. Disclosed is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase having the following properties (1) to (3):(1) the enzyme has an activity of catalyzing a reaction for oxidizing a hydroxyl group in glucose in the presence of an electron acceptor to produce glucono-delta-lactone; (2) the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 100 kDa as measured by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or about 400 kDa as measured by gel filtration chromatography; and (3) the enzyme is less reactive to maltose, D-fructose, D-mannose and D-galactose. Also disclosed is a microorganism Aspergillus oryzae which can produce the enzyme. Further disclosed are a glucose determination method, a reagent for the determination of glucose, and a kit for the determination of glucose, each utilizing the enzyme.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Application of ginkgo biflavonoids to preparation of medicine for preventing and treating asthma
InactiveCN107998120ANo obvious side effectsLong-term medication is safe and reliableOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsSide effect
The invention discloses application of ginkgo biflavonoids to preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating asthma. The ginkgo biflavonoids are at least one of 7-demethylated biflavones, ginkgetin, sciadopitysin, and isoginkgetin. The invention discloses a medicinal composition for preventing and treating the asthma, the composition comprises ginkgo biflavonoids, and further comprises at least one of radix glycyrrhizae, white mulberry root-bark and semen armeniacae amarum. The invention further discloses a pharmaceutical composition formed by mixing ginkgo biflavonoids and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and the mass percent of ginkgo biflavonoids is greater than and equal to 2.5%. The ginkgo biflavonoids can inhibit the recruitment of inflammatory cells in lungs, reduce the expression of inflammatory factors in the lungs, and lower the expression of PI3K-related proteins in inflammation pathways, and are free of obvious toxic or side effects and safe and reliable after being taken for a long term.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Halogenation enzymes
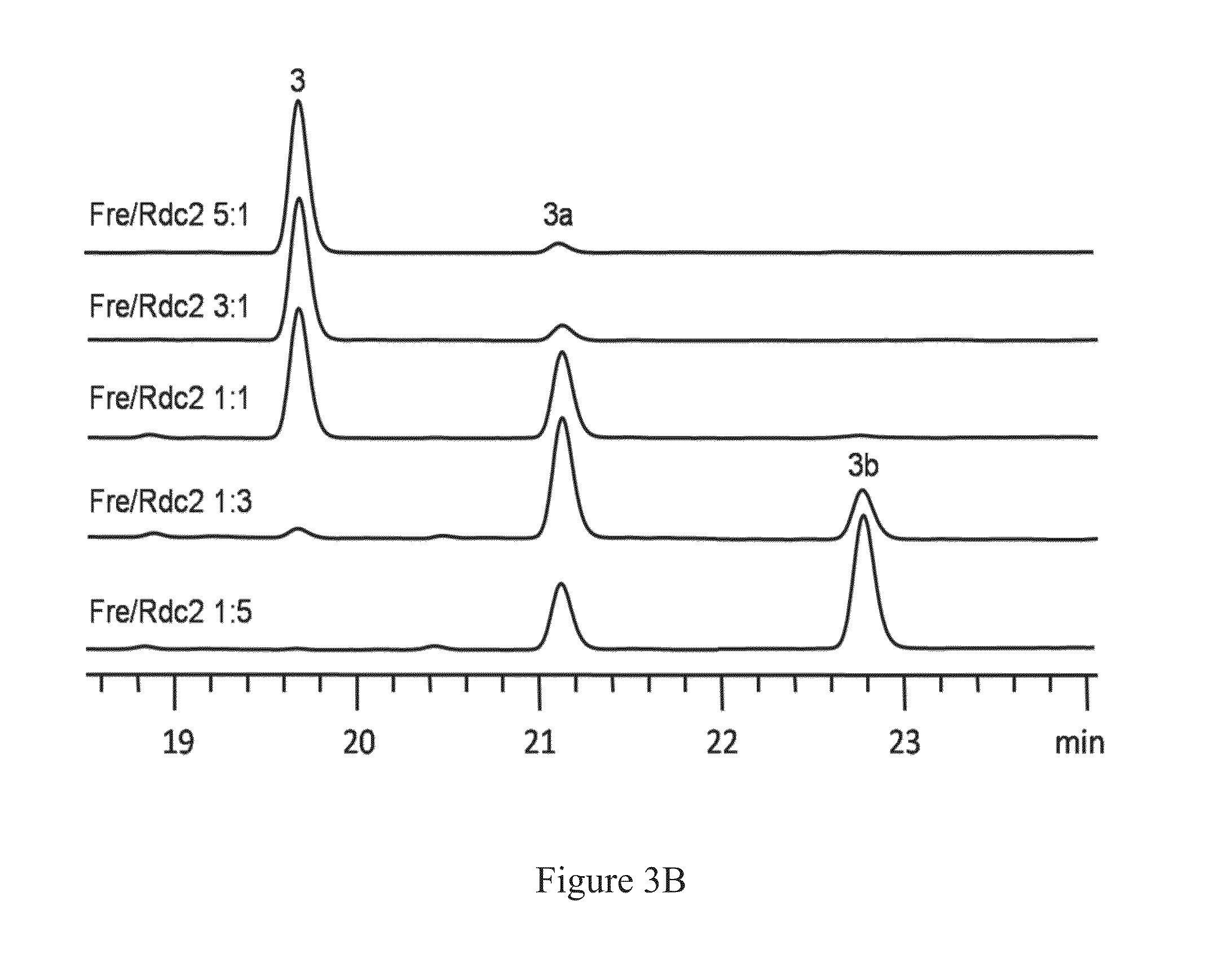
The present disclosure relates to an isolated or purified nucleotide sequence comprising a cDNA sequence of an rdc2 at least 60%, 70%, 90%, 95%, 98%, or 100% identical to SEQ ID NO. 1. In a second embodiment, the invention provides for a flavin-dependent halogenase comprising an amino acid sequence of an Rdc2 halogenase at least 60%, 70%, 90%, 95%, 98%, or 100% identical to SEQ ID NO. 2. In related embodiments there are provided herein methods for halogenating compounds by using an Rdc2 halogenase of the present invention.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
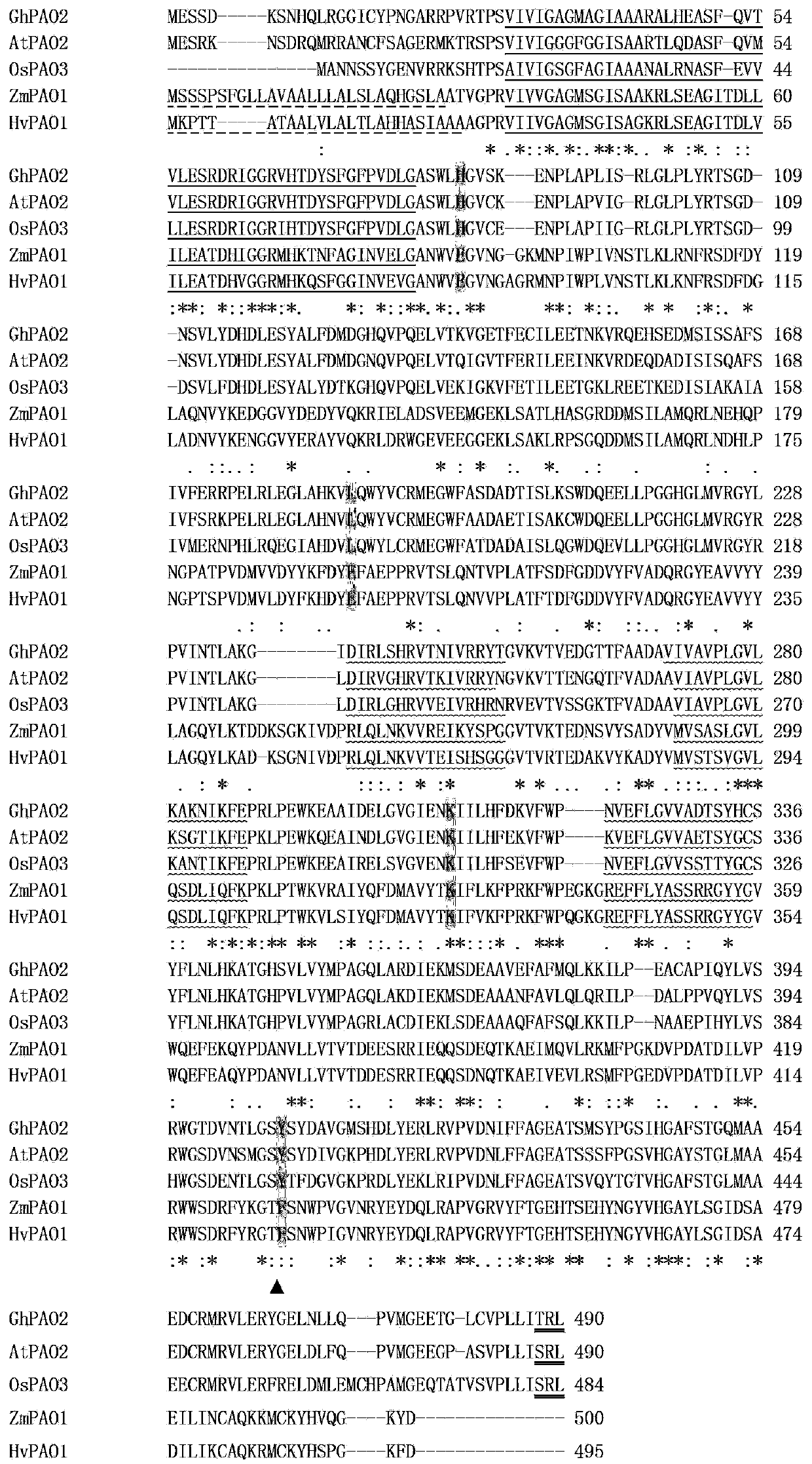
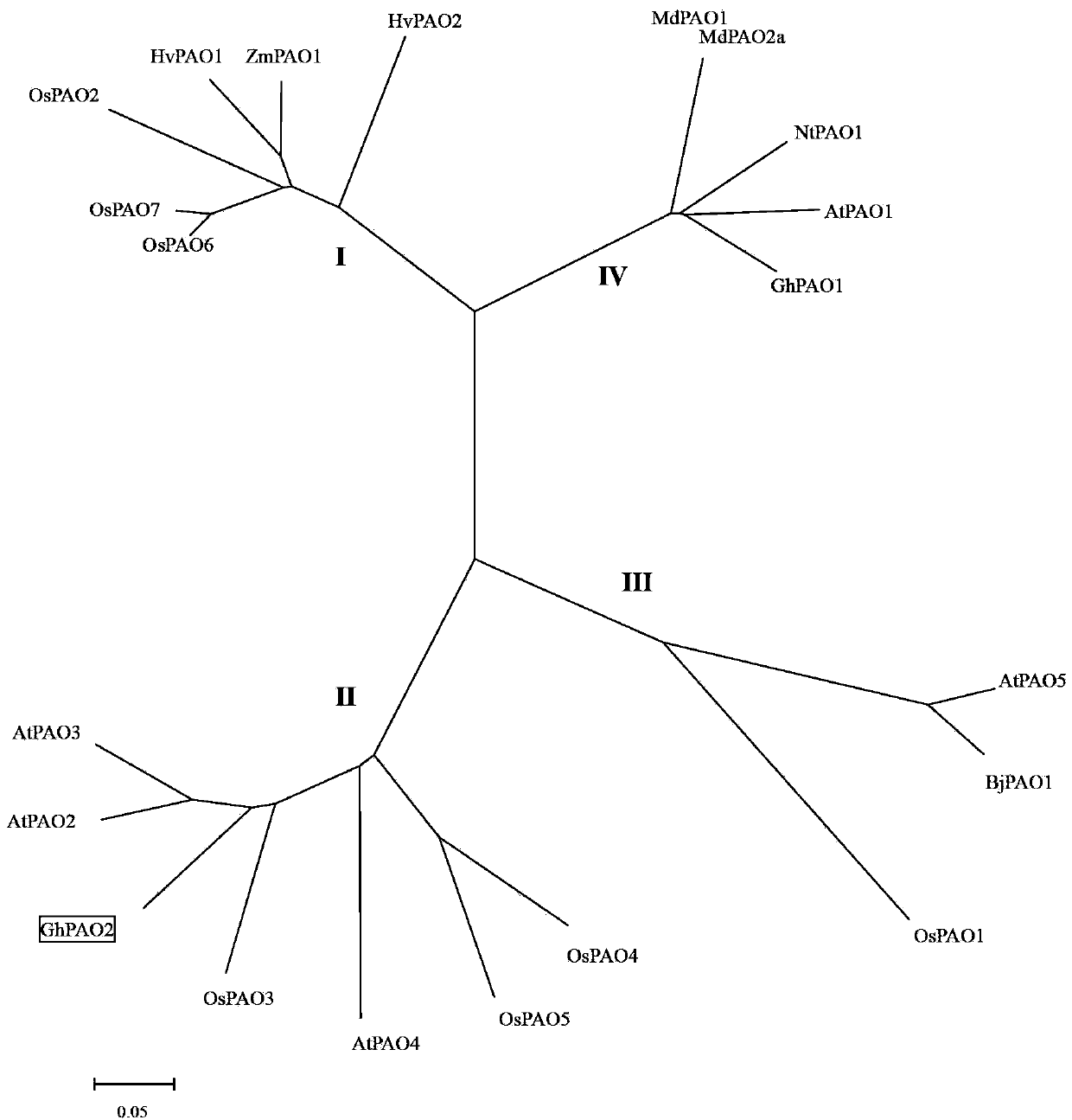
The invention discloses cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103421749AImprove salt toleranceImprovement of plant genetic traitsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSpermine oxidase activity
The invention discloses a cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 gene and application thereof. The sequence of the cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 gene is shown in SEQ ID No. 3. According to the invention, the root tissue of Jimian 20 is taken as raw material; the whole-length cDAN sequence of the cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 gene is cloned through bioinformatics and the RT-PCR technology; the cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 gene is constructed to a prokaryotic expression vector and expresses a heterologous protein in an escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) successfully. An in-vitro experiment proves that purified cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 GhPAO2 is a flavoprotein taking FAD as a prothetic group and has the activity of a spermidine oxidase and a spermine oxidase. A bacterial strain capable of expressing the cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 and a contrast bacterial strain containing an empty carrier are treated with sodium chloride solution with different concentrations; with the same treatment, the quantity of cells of the transgenic bacterial strain is remarkably increased when compared with that of the cells of the contrast bacterial strain, which shows the expression of the cotton polyamine oxidase GhPAO2 in the escherichia coli improves the salt tolerance of the host bacteria.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
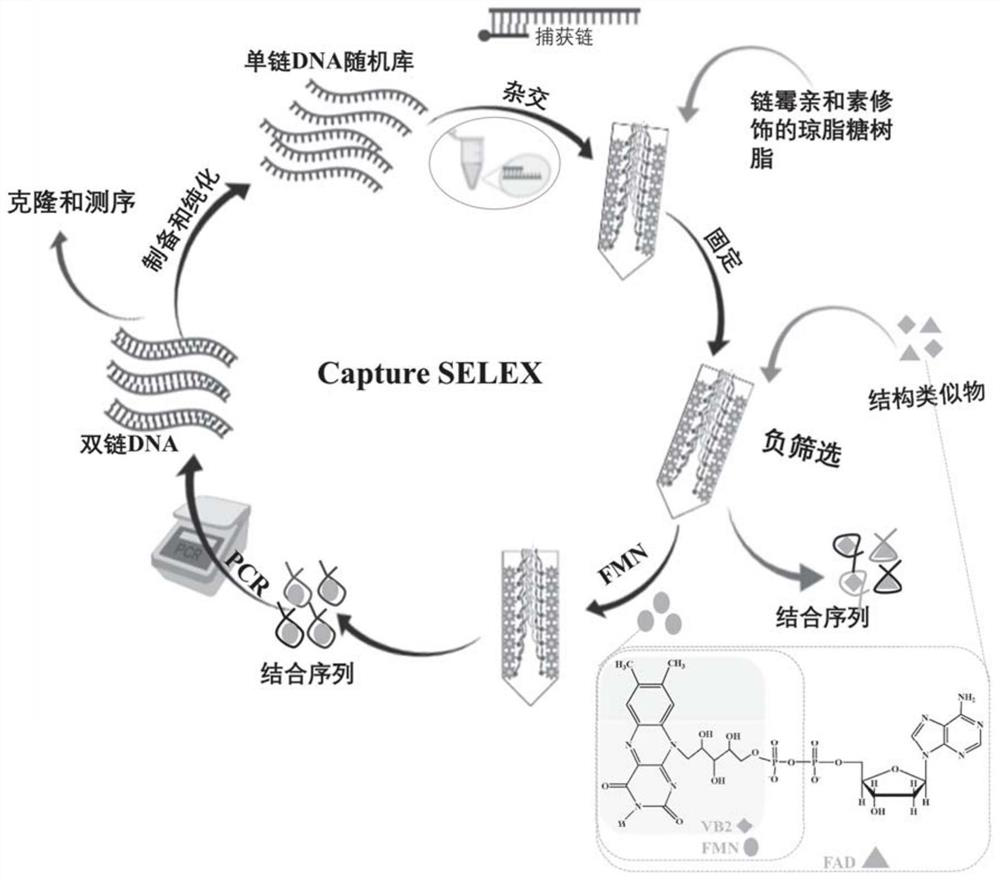
Nucleic acid aptamer of flavin mononucleotide as well as screening method and application of nucleic acid aptamer
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer of flavin mononucleotide as well as a screening method and application of the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 or SEQ ID No. 2. The invention also provides the screening method of the nucleic acid aptamer, and the nucleic acid aptamer can be obtained through SELEX screening. The invention also provides a separation and purification method of the flavin mononucleotide. The nucleic acid aptamer of the flavin mononucleotide can specifically recognize the flavin mononucleotide and does not act with another two flavin compounds (VB2 and FAD), so that the nucleic acid aptamer of the flavin mononucleotide can be applied to separation and purification of the flavin mononucleotide.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Medicine composition for treating acute or chronic cholecystitis and acute or chronic pancreatitis
ActiveCN102579730AAnti-inflammatoryHas analgesiaDigestive systemPlant ingredientsChronic cholecystitisChlorogenic acid
The invention relates to a medicine composition for treating acute or chronic cholecystitis and acute or chronic pancreatitis, which belongs to the field of Chinese medicines and is prepared by saikosaponin 8-15 parts, baicalin 5-12 parts, magnolol 7-16 parts, rheum emodin 1-5 parts, immature total bitter orange flavonoid 9-18 parts, caffeic acid 8-16 parts, paeoniflorin 7-13 parts, chlorogenic acid 10-17 parts, rhizoma pinellinae praeparata 7-13 parts and glycyrrhizic acid 2-7 parts. The medicine composition for treating acute or chronic cholecystitis and acute or chronic pancreatitis has the advantages that the medicine has anti-inflammation, analgesia and antibacterium functions according to Chinese medicine theories and modern pharmacological experimental methods, has a main function of cleaning and discharging liver-gallbladder damp and heat, and is used for acute or chronic cholecystitis and acute or chronic pancreatitis.
Owner:JILIN ZIXIN PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com