Mechanical foot
A technology of mechanical foot and angle, applied in the field of mechanical foot, can solve the problem of easy fall of patients, and achieve the effect of reducing patient discomfort and the possibility of tripping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The present embodiment provides a mechanical ankle joint comprising a leg portion for securing to the patient's leg and a foot portion for securing to the patient's foot, the two portions They can be connected with each other, so that people who have lost their walking function can walk or perform rehabilitation training. They are especially suitable for patients with hemiplegia, or people with lower limbs who are paralyzed for lower limb rehabilitation training. The lower limb paralysis or half paralysis here is mainly because the lower limbs are not controlled by the brain nerves, and through rehabilitation training, patients who can restore nerve control wear mechanical feet. In some embodiments, the articulation here is a rotational connection, and the mechanical ankle joint includes a rotational joint so that the leg portion and the foot structure portion can rotate relative to each other. In some approaches, the foot portion is secured to the patient's foot by con...
Embodiment 2
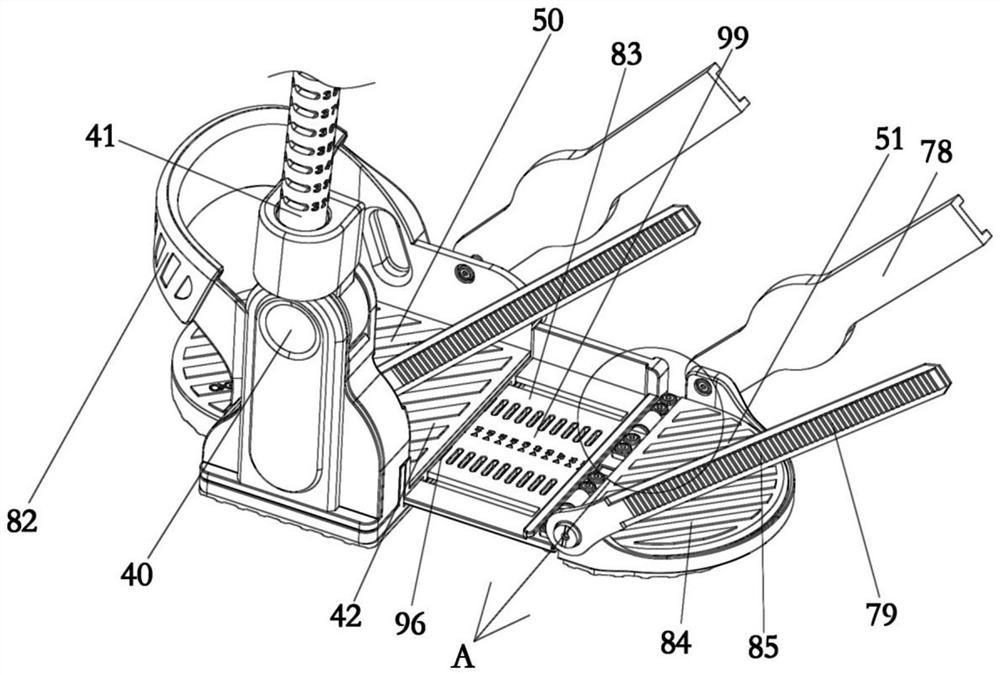
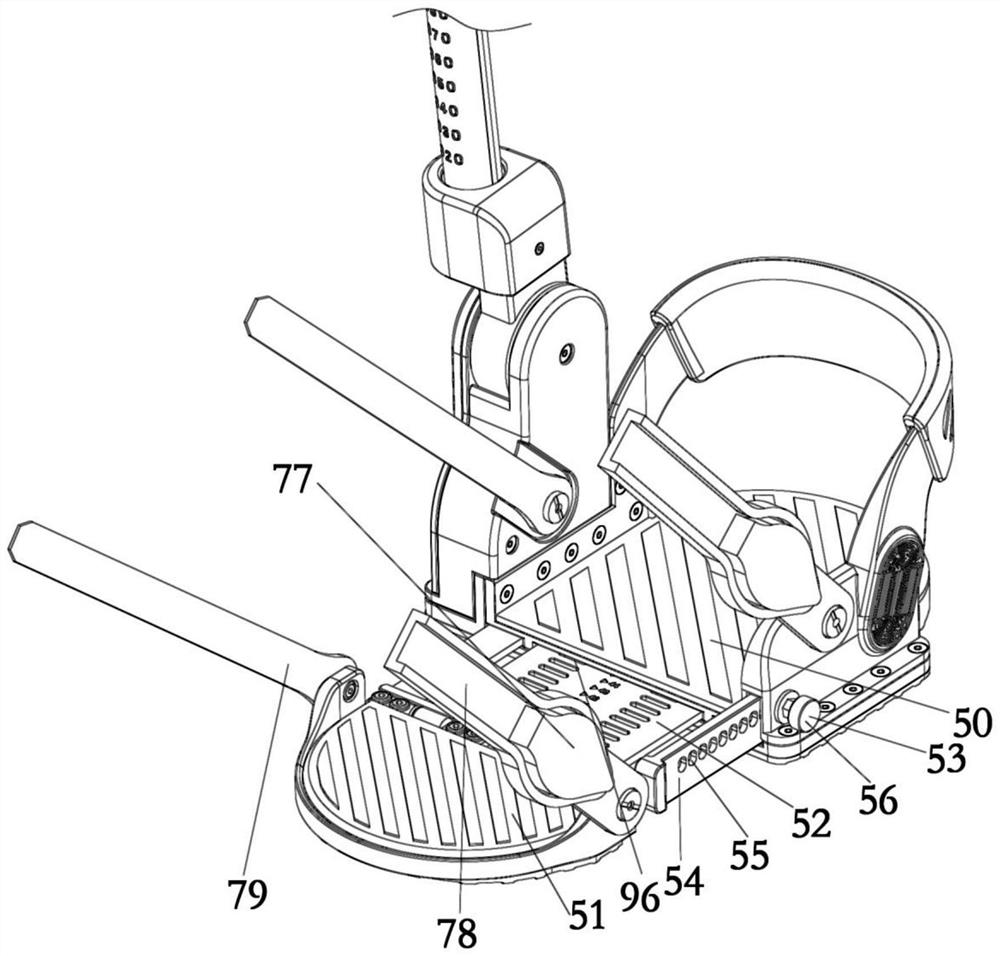
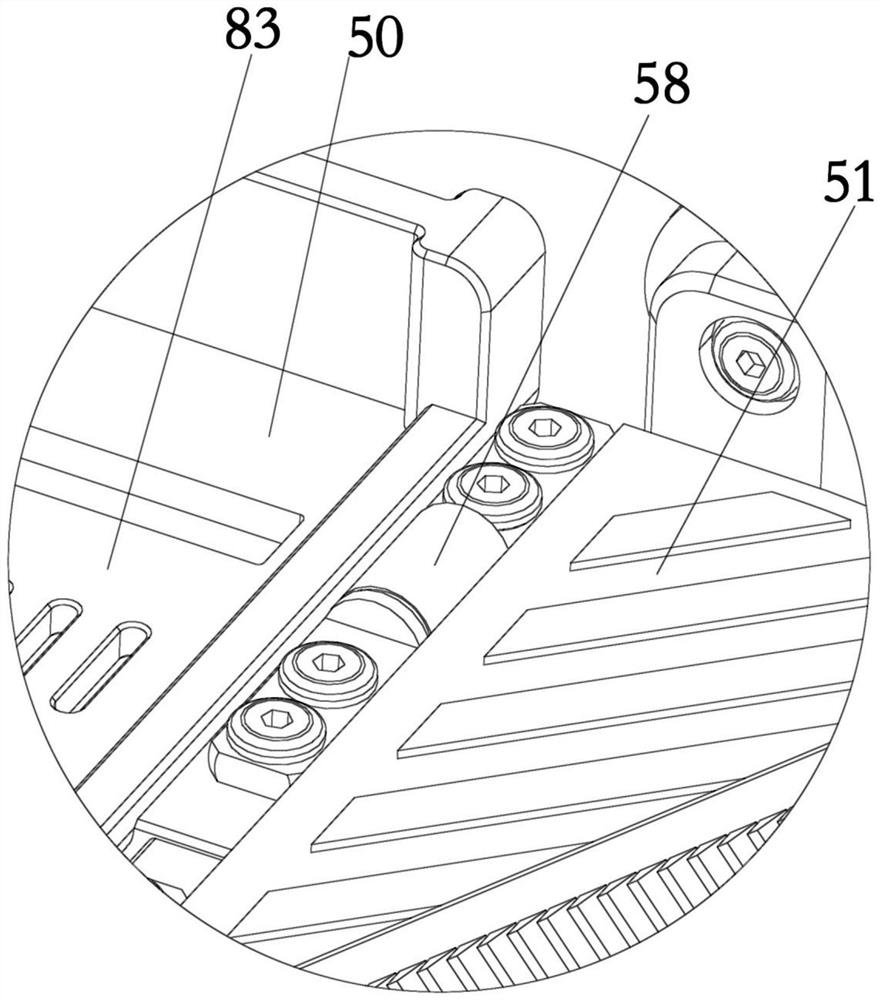
[0044] This embodiment provides a shoe with adjustable wearing size, including a first part 50 and a second part 51. The first part 50 and the second part 51 constitute the bottom surface on which the foot of the patient steps on in Embodiment 1, and the patient's foot can step on it. On the first part 50 and the second part 51, due to the different foot sizes of different patients, in order to enhance the adaptability of the shoes to the patient, the first part 50 is movably connected with the second part 51, by adjusting the first part 50 and the second part of the activity The relative position of 51 makes the length of the sole stepped on by the adjusted foot match the patient's foot. Specifically, a slidable connecting plate 52 is provided between the first part 50 and the second part 51, and the connecting plate 52 is connected with one of the first part 50 and the second part 51, and embedded in the other, the connecting plate 52 is also provided with a second locking s...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3, with reference to attached Figure 9 .
[0050] The traditional mechanical foot has a leg part 41 and a stepping bottom surface 99. The leg part 41 is used to connect the patient's leg, and the stepping bottom surface 99 is used to fit the patient's sole. When in use, the leg part 41 is fixed to On the patient's leg, the patient's foot steps on the bottom surface 99, but the axis of the leg part 41 in the traditional mechanical foot is perpendicular to the plane where the bottom surface 99 is located, which makes the patient feel uncomfortable when wearing the mechanical foot. A feeling of turning the foot inward, which can cause discomfort. The present embodiment provides a mechanical foot, which also includes a leg portion 41 and a step-on bottom surface 99, wherein the axis of the leg portion 41 is not perpendicular to the plane where the step-on bottom surface 99 is located, which conforms to the ergonomic design, allowing the patient to wear the mech...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com