Self-locking puller for zipper and zipper
A self-locking and zipper technology, applied in applications, sliding fastener components, fasteners, etc., can solve problems such as stiff, thin sliders, clumsy, and eye-catching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
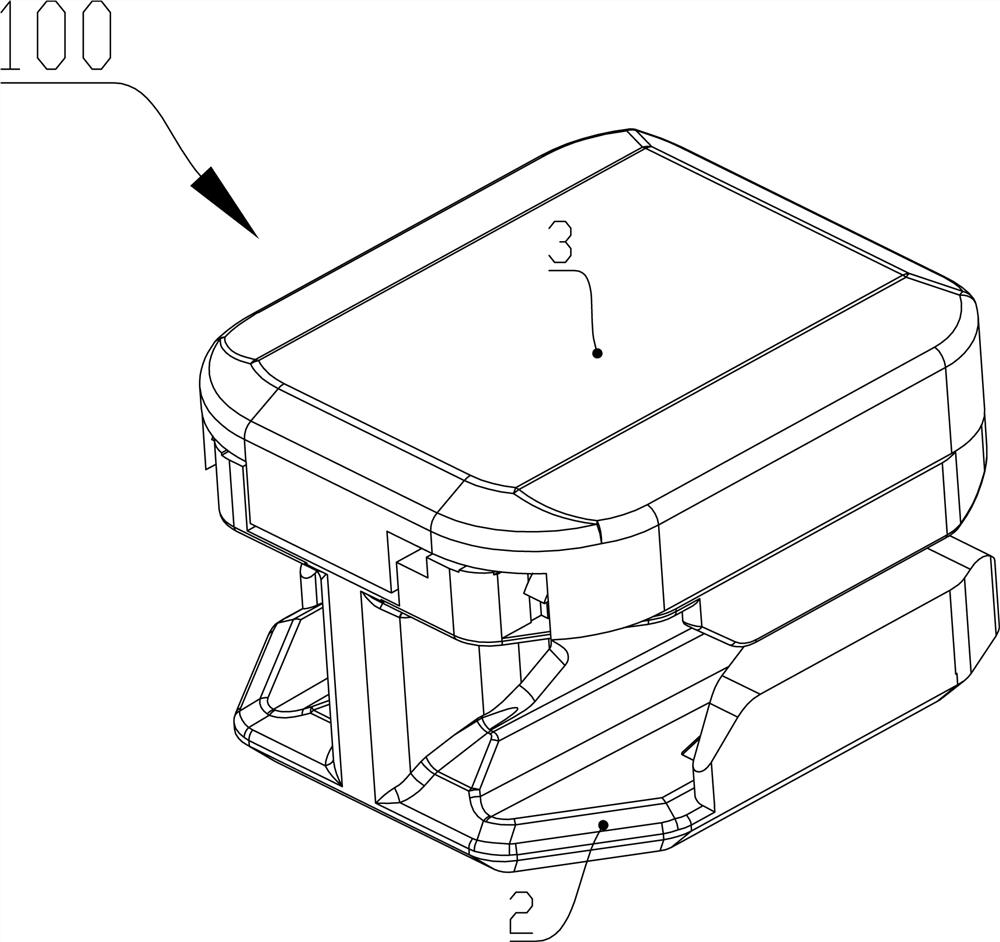
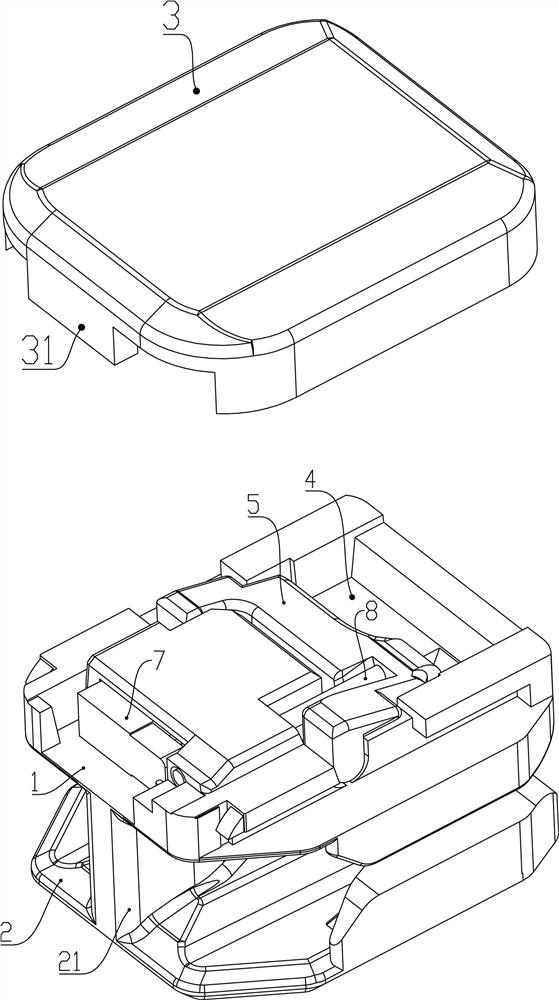
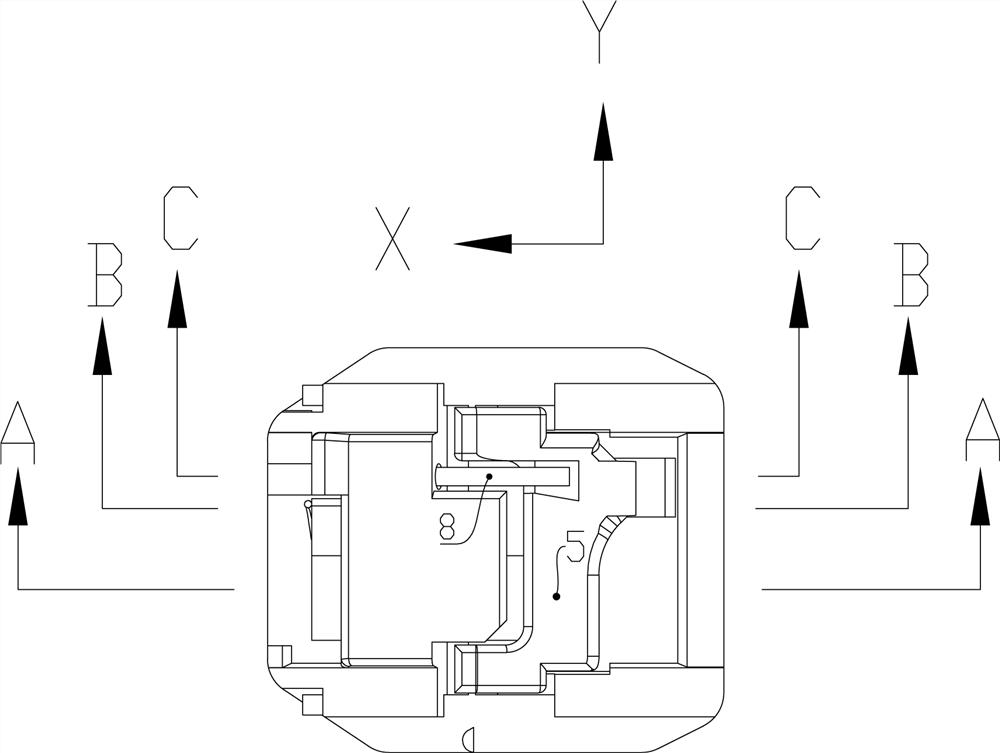
[0059] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 11 As shown, the present invention also proposes a slide fastener (not shown in the figure), including a chain belt and a self-locking slider 100 , and the self-locking slider 100 is slidably arranged on the chain belt. The self-locking slider 100 includes a first wing plate 1 and a second wing plate 2 separated up and down, and a chain element channel 22 is formed between them; an outer cover 3 is arranged on the first wing plate 1 , a storage space 4 is formed between the outer cover 3 and the first wing plate 1; it also includes a locking piece 5 arranged on the storage space 4, the locking piece 5 includes a support portion 52 and can be wound around The support part 52 is swingably inserted into the claw part 51 in the chain element passage 22; it also includes a first elastic body 8 arranged in the storage space 4, and the first elastic body 8 can act on the On the locking part 5, the claw portion 51 is inserted into the chain element ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0068] Such as Figure 12 to Figure 19 As shown, the self-locking slider 100a in Embodiment 2 has a similar structure to the self-locking slider 100 in Embodiment 1. The main differences between them will be introduced in detail below. Other features of the self-locking slider 100a The structure can be understood with reference to the relevant drawings and the above description of the self-locking slider 100 .
[0069] The locking member 5a includes a transverse connecting rod 54a, a pair of support parts 52a are located at the left and right ends of the transverse connecting rod 54a, and the first force receiving part 53a, the second force receiving part 55a, and the claw part 51a are arranged on the transverse connecting rod 54a. On the connecting rod 54a. Viewed laterally, the support portion 52a is located between the first force-receiving portion 53a and the claw portion 51a. A pair of wing plate pits 12a are arranged on the first wing plate 1a along the lateral directi...
Embodiment approach 3
[0072] Such as Figure 20 ~ Figure 26 As shown, the self-locking slider 100b in Embodiment 3 has a similar structure to the self-locking slider 100 in Embodiment 1. The main differences between them will be introduced in detail below. Other features of the self-locking slider 100b The structure can be understood with reference to the relevant drawings and the above description of the self-locking slider 100 .
[0073] The structures of the locking part and the first elastic body in this embodiment are different from those in the above two embodiments. The locking part and the first elastic body adopt an integral structure to form the spring piece 5b. The spring piece 5b includes a substrate portion 51b, a crest portion 52b and a claw portion 53b arranged in sequence. The uphill portion 521b, the gentle portion 522b, the downhill portion 523b extending obliquely downward relative to the gentle portion 522b, the claw portion 53b is connected to the downhill portion 523b, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com