Large-scale MIMO downlink channel estimation method based on reconstructed Hankel matrix
A Hankel matrix and channel estimation technology, which is applied in the field of massive MIMO downlink channel estimation based on reconstructed Hankel matrix, can solve problems such as mismatch, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and reducing pilot overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
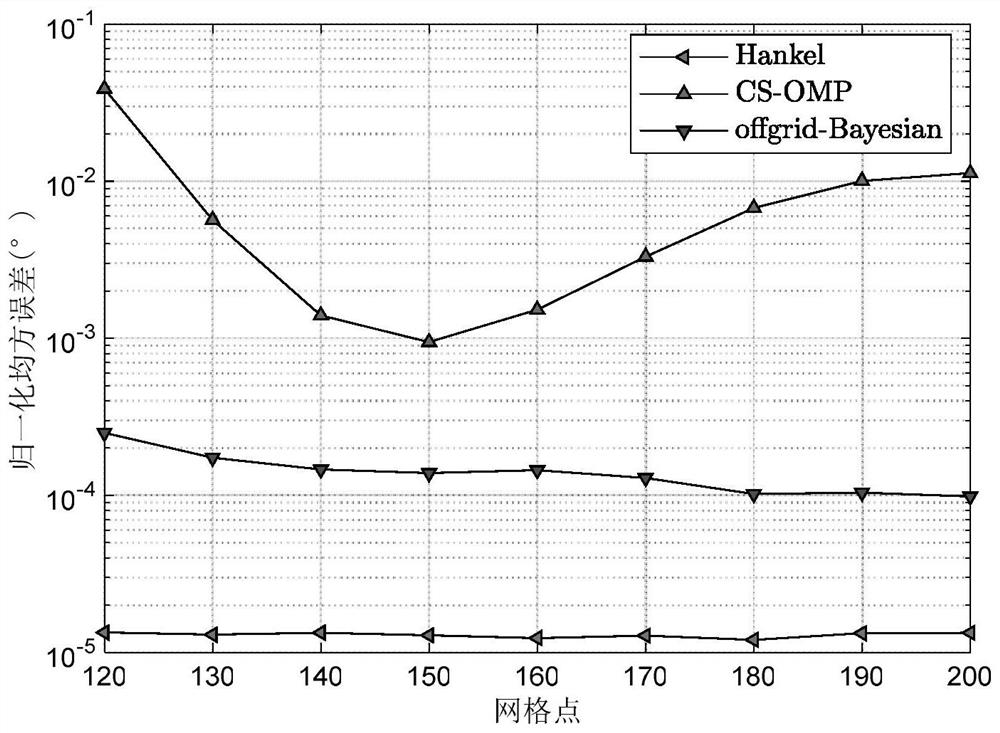
[0046] Simulation example 1: Select the number of base station antennas N=123, the number of snapshots T=120, the antenna spacing d=λ2, use the LOS channel, and scatter clusters N c = 3, the sub-path N of each scattering cluster s =10, then the total channel number L=N c N s = 30, Angular expansion Δ θ = 1°, the number of Monte Carlo experiments M c =500. The channel path gain is set as a random complex gain, and the angles of arrival AOD at the center of the three channel paths are uniformly distributed within [-π / 3, π / 3]. The antenna at the base station adopts a uniform linear array, and the number of grid points varies from 120 to 200. The algorithm proposed in the present invention is compared with the channel estimation algorithm based on the compressed sensing algorithm OMP and the offgrid-Bayesian algorithm.
example 2
[0047] Simulation example 2: Select the number of base station antennas N=123, the number of snapshots T=120, the antenna spacing d=λ2, use the LOS channel, and scatter clusters N c = 3, the sub-path N of each scattering cluster s =10, then the total channel number L=N c N s =30, Angular expansion Δ θ = 1°, the number of Monte Carlo experiments M c =500. The channel path gain is set as a random complex gain, and the angles of arrival AOD at the center of the three channel paths are uniformly distributed within [-π / 3, π / 3]. The antenna at the base station adopts a uniform linear array, and the signal-to-noise ratio ranges from -10dB to 10dB. The algorithm proposed in the present invention is compared with the channel estimation algorithm based on the compressed sensing algorithm OMP and the offgrid-Bayesian algorithm.
example 3
[0048] Simulation example 3: Select base station antenna number N=123, SNR=-5dB, antenna spacing d=λ2, use LOS channel, scattering cluster N c = 3, the sub-path N of each scattering cluster s =10, then the total channel number L=N c N s =30, Angular expansion Δ θ = 1°, the number of Monte Carlo experiments M c =500. The channel path gain is set as a random complex gain, and the angles of arrival AOD at the center of the three channel paths are uniformly distributed within [-π / 3, π / 3]. The antenna at the base station adopts a uniform linear array, and the number of pilots varies from 60 to 110. The algorithm proposed in the present invention is compared with the channel estimation algorithm based on the compressed sensing algorithm OMP and the offgrid-Bayesian algorithm.
[0049] Depend on image 3 It can be seen from the normalized mean square error performance comparison diagram that the reconstructed Hankel-based method is significantly better than the other two metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com