Mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on pedestrian prediction
A mobile robot and robot technology, applied in the field of automation, can solve problems such as slowing down the obstacle avoidance time, and achieve the effect of improving the effect and avoiding falling into local optimum.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
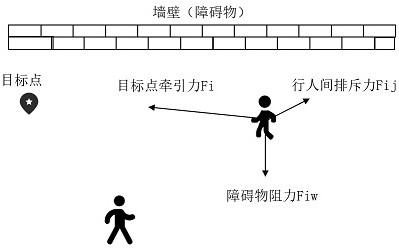
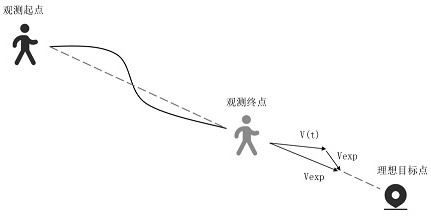
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
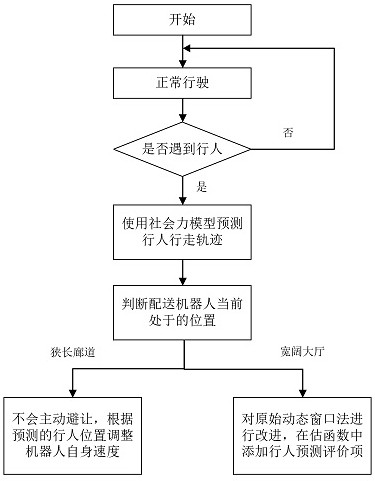
[0046] Embodiment 1 is used to verify the effect of the obstacle avoidance method proposed by the present invention in the long and narrow corridor, such as Figure 6 shown. In the embodiment, a pedestrian is set up in the long and narrow corridor and walks in the same direction as the robot. The initial speed of the robot is 0.7m / s, the speed of the pedestrian is 0.8m / s, the initial distance between the robot and the pedestrian is 1.9m, and the danger radius is 1.5m. The black curve uses the original DWA algorithm for obstacle avoidance. Since the pedestrian’s walking intention is not predicted, the original algorithm is relatively conservative when avoiding obstacles. The distance between the robot and the robot is relatively long during the walking process, which is about 3m after stabilization; while the optimized Since the algorithm judges that the pedestrian will continue to walk forward, the distance between the pedestrian and the pedestrian can be further shortened, a...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 is used to verify the obstacle avoidance effect of the obstacle avoidance algorithm proposed by the present invention in the wide hall, such as Figure 7 shown. Five pedestrians are set up in the lobby, and their movement directions are marked with black arrows in the figure. Among them, pedestrians 1 and 4 slow down when encountering the robot, which means avoidance behavior occurs. The rest of the pedestrians will not actively avoid and walk normally. Depend on Figure 7 (b) It can be seen that the original DWA algorithm before optimization approached pedestrian 2 at P1 after avoiding pedestrians 1 and 4. Since the walking intention of the pedestrian was not predicted, the forward direction of the robot was not affected. Thus, in Figure 7 In (c), there is a conflict with pedestrian 3 at P2, and the pedestrian 3 is bypassed from above after decelerating to a stop. During the entire obstacle avoidance process, the number of executions of the evaluation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com