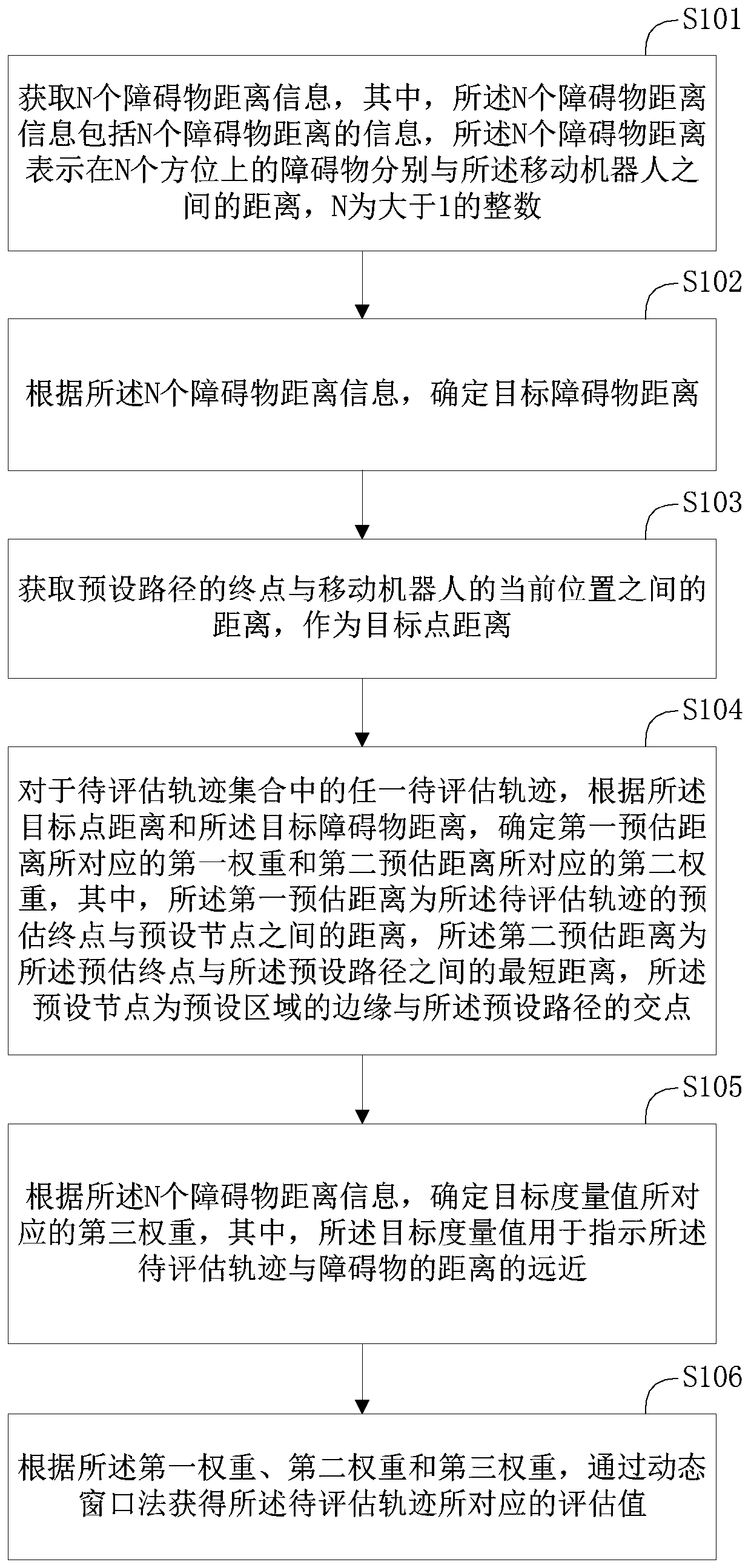
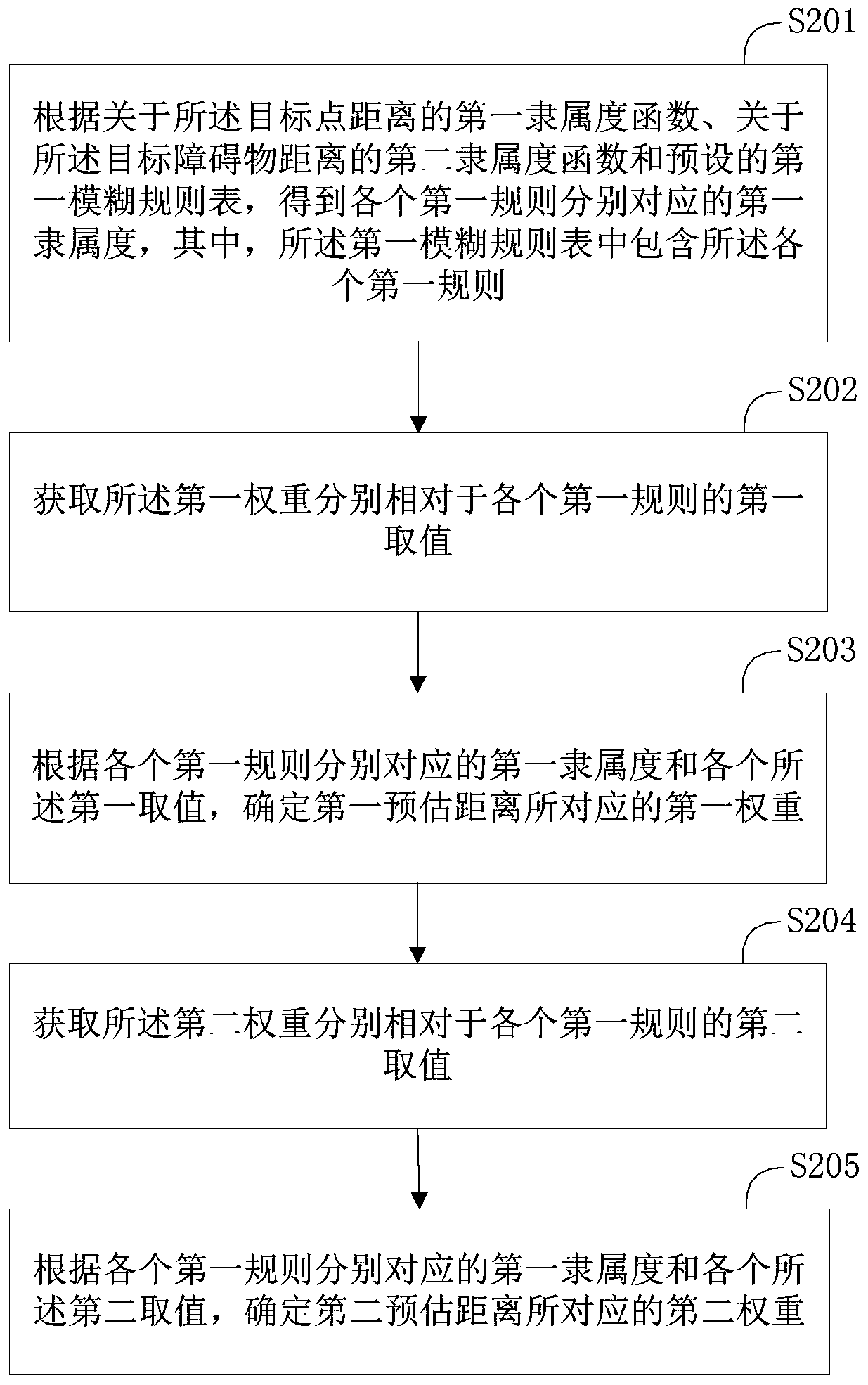
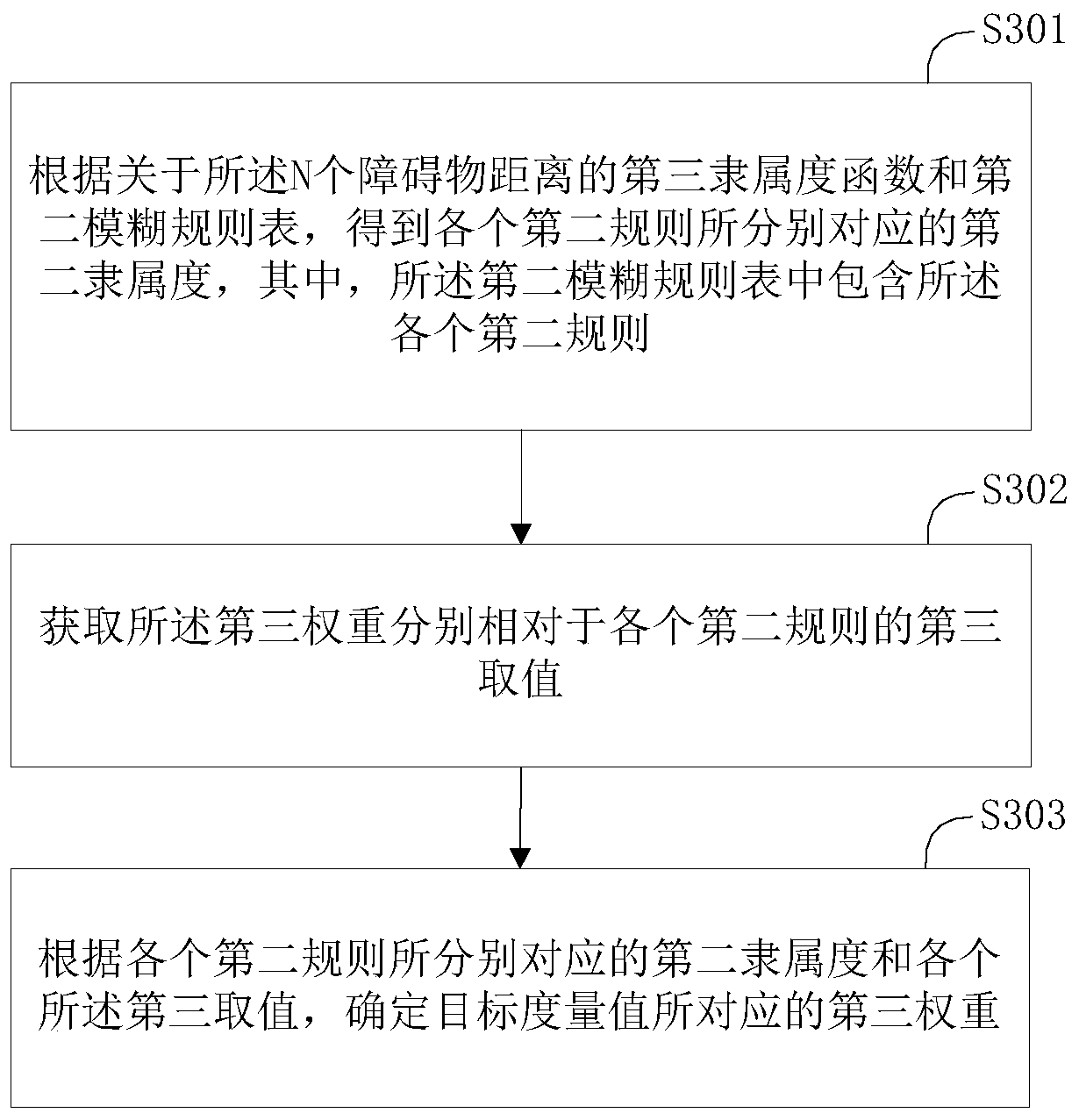
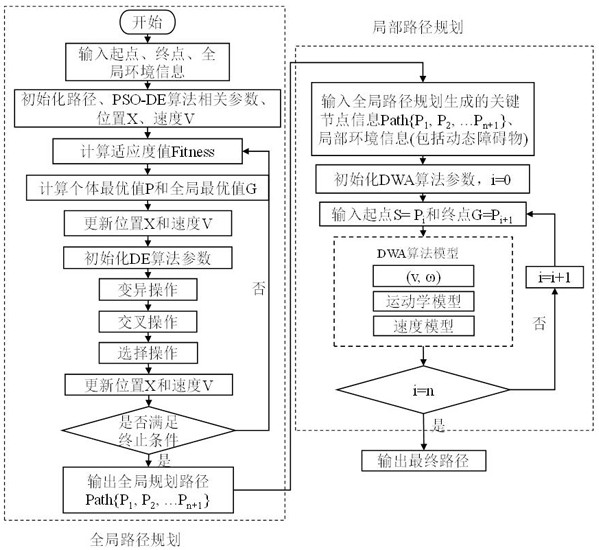
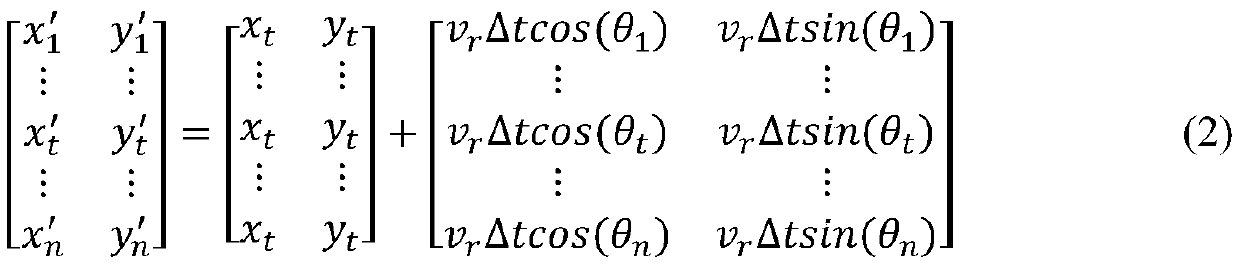Patents
Literature
33 results about "Dynamic window approach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
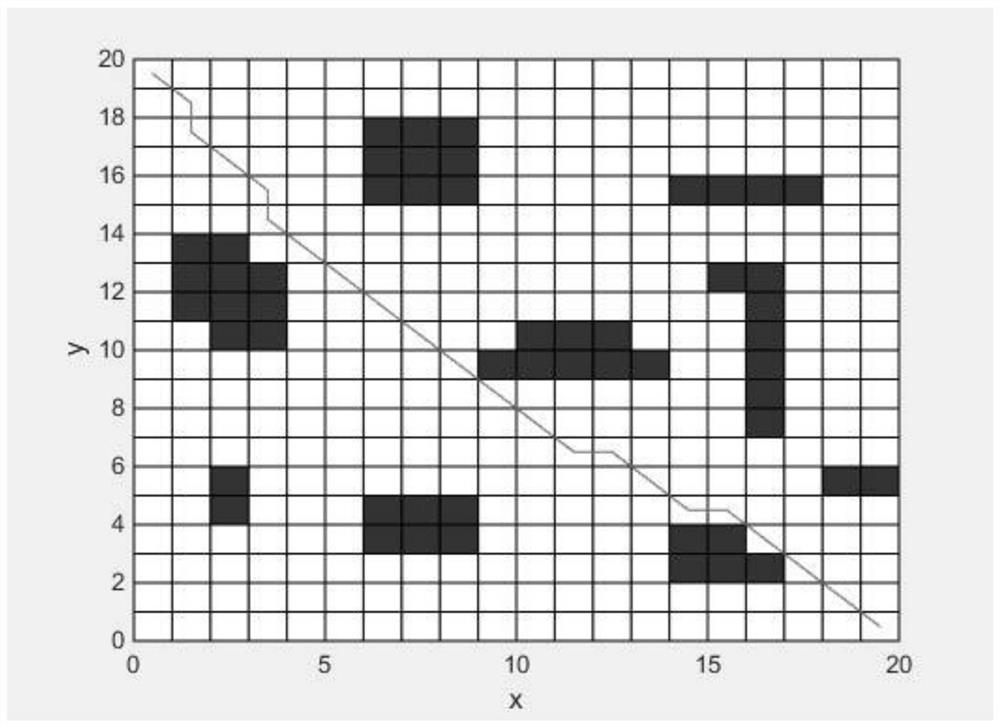
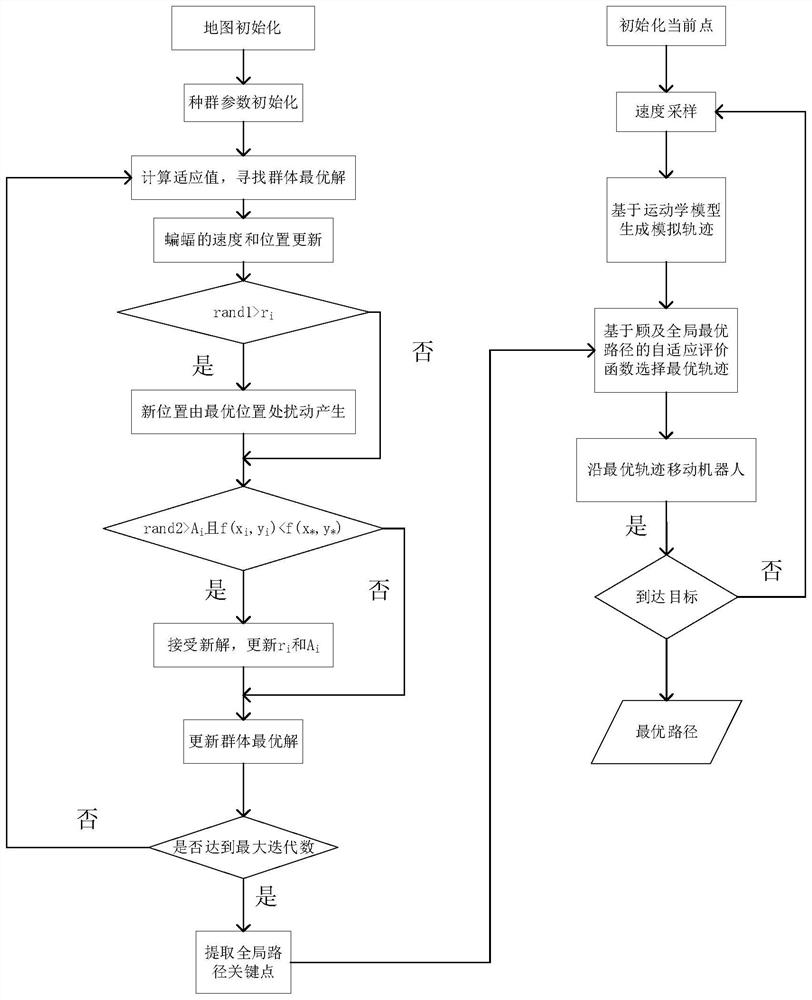
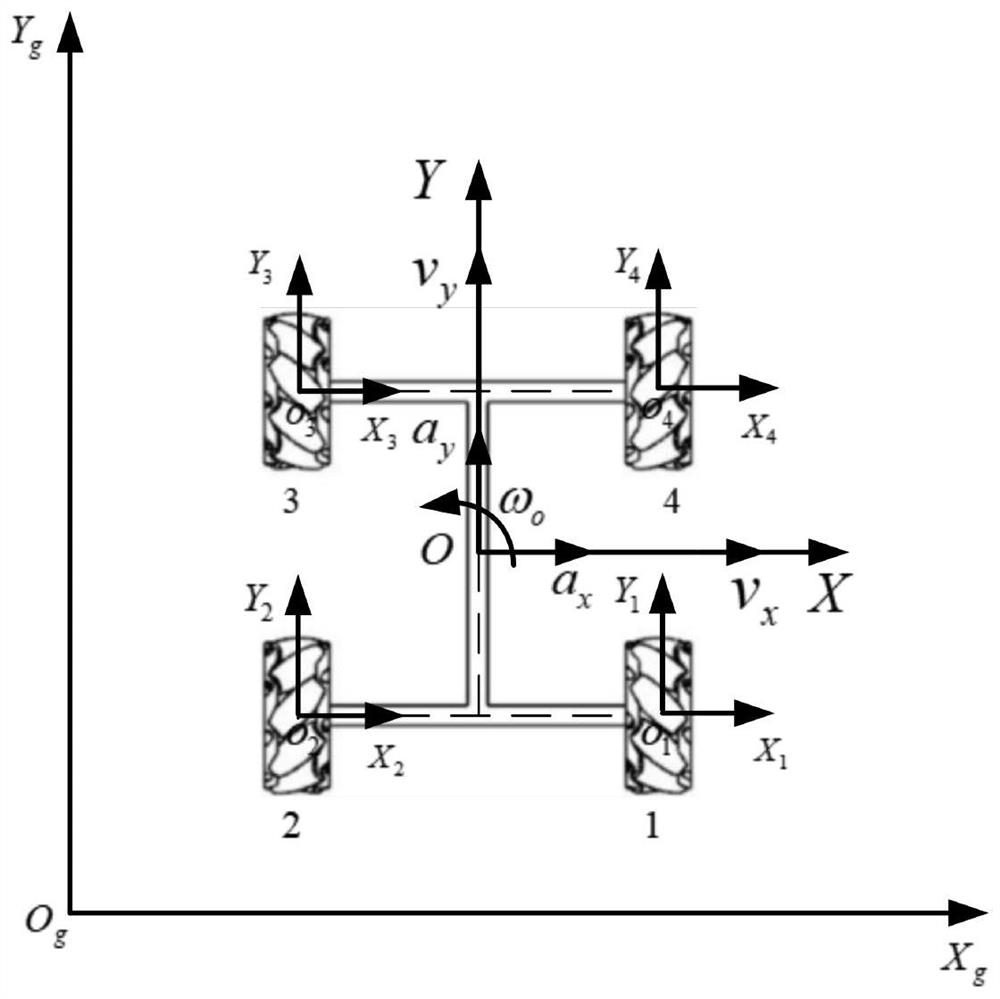
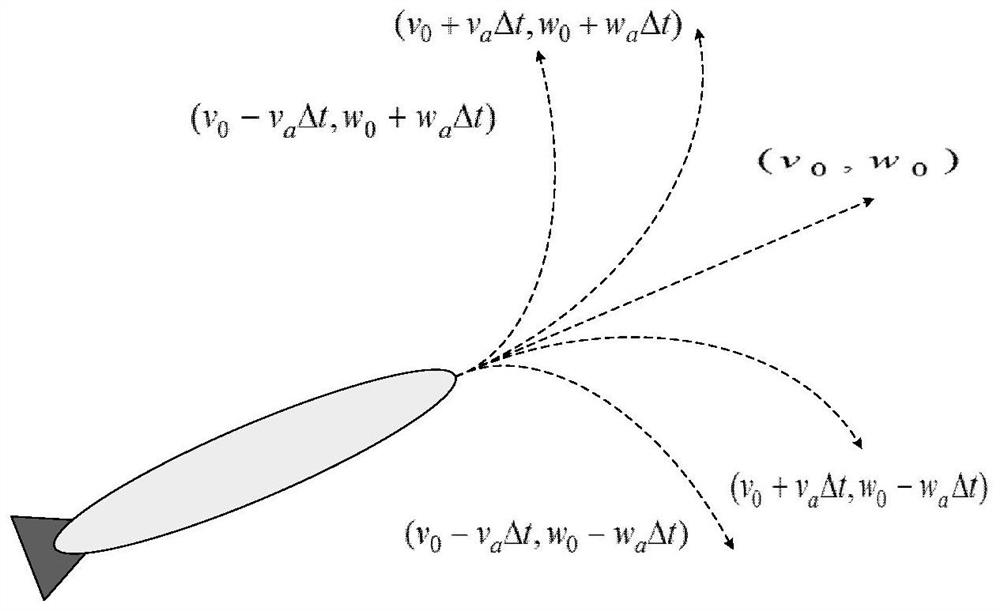
In robotics motion planning, the dynamic window approach is an online collision avoidance strategy for mobile robots developed by Dieter Fox, Wolfram Burgard, and Sebastian Thrun in 1997. Unlike other avoidance methods, the dynamic window approach is derived directly from the dynamics of the robot, and is especially designed to deal with the constraints imposed by limited velocities and accelerations of the robot.
Mobile robot intelligent path planning method
ActiveCN112631294AImprove real-time obstacle avoidance abilityImproved heuristic functionNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsGlobal planningSimulation
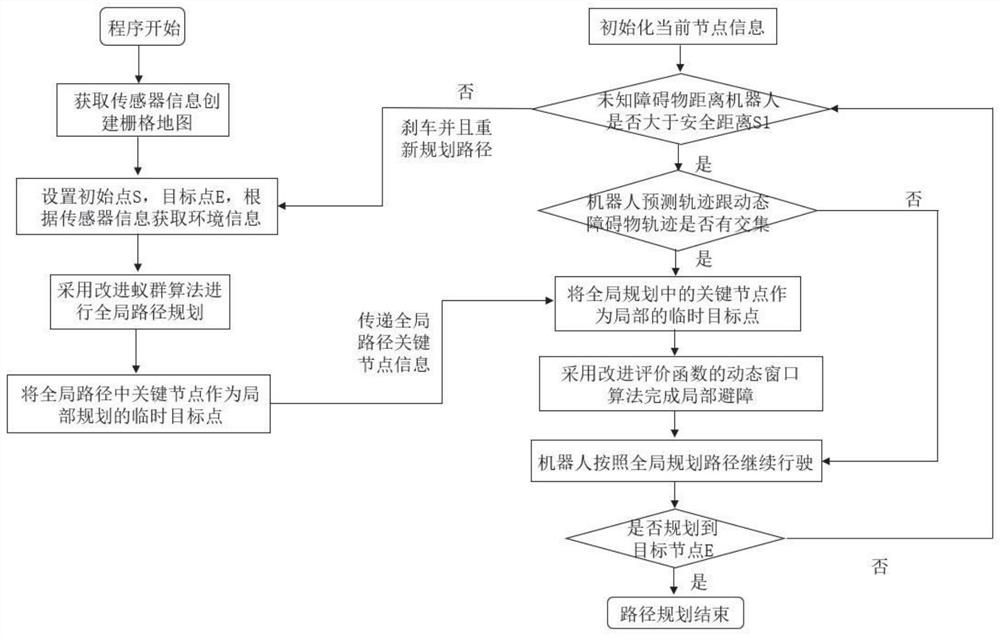
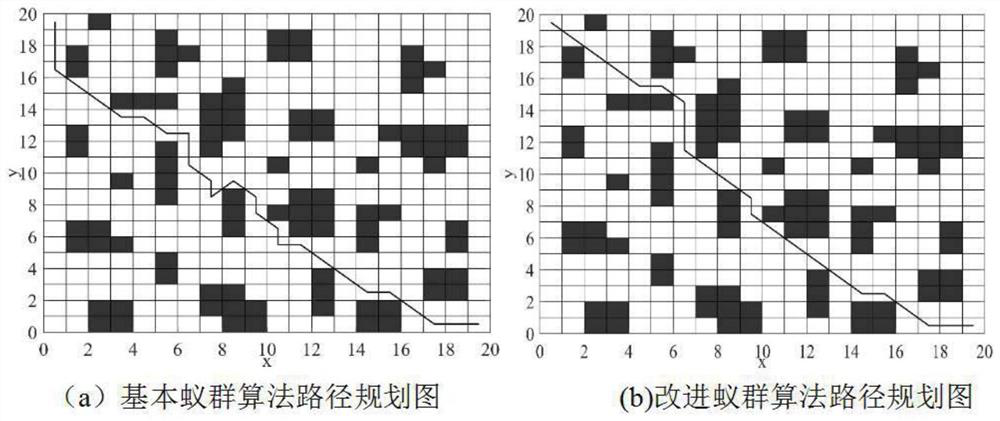
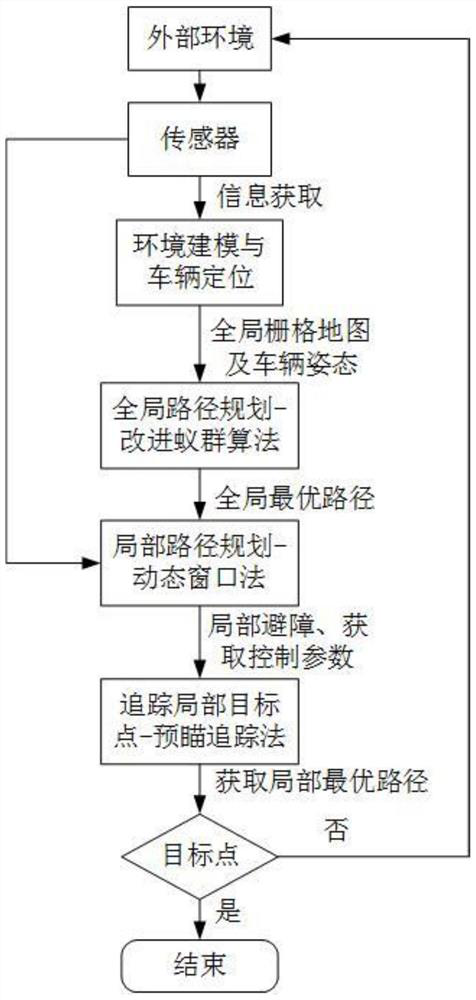
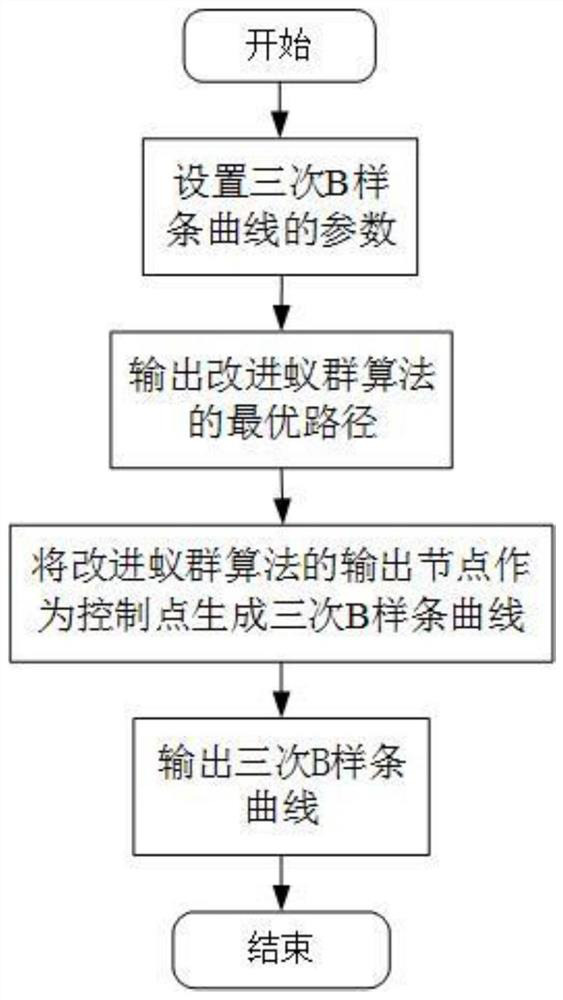
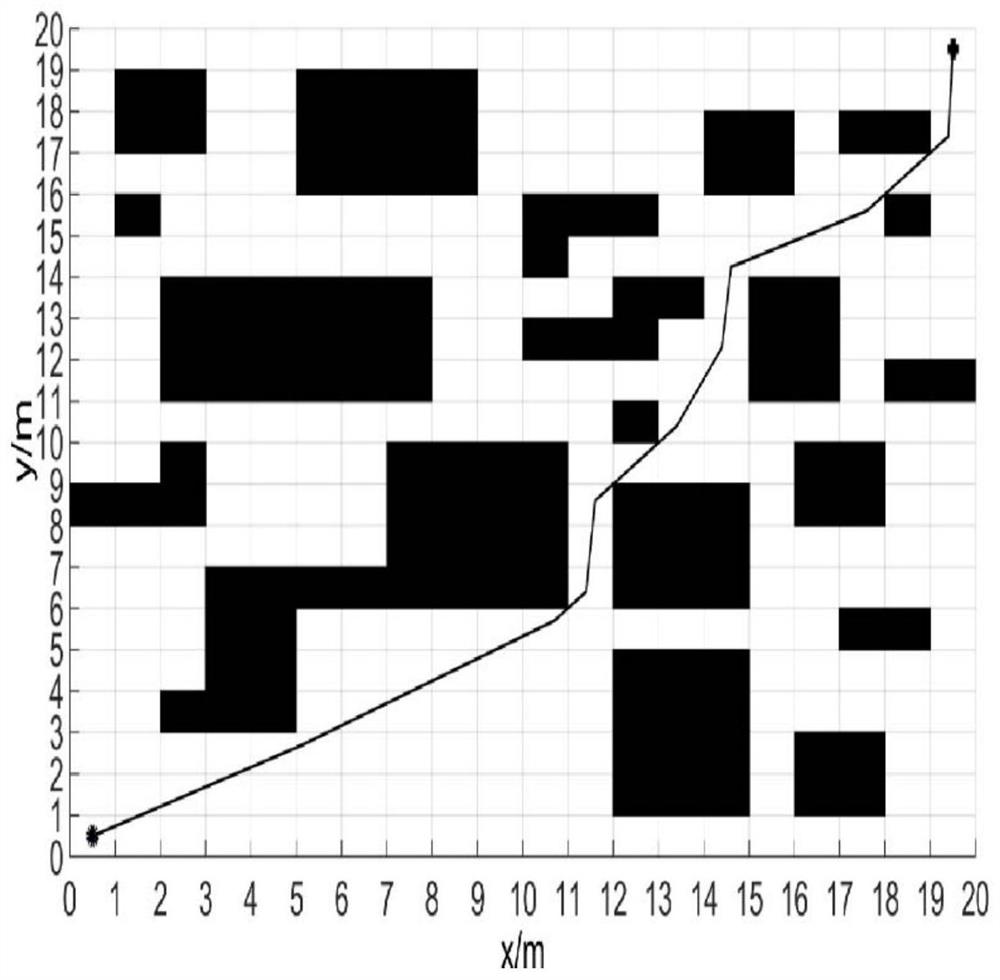
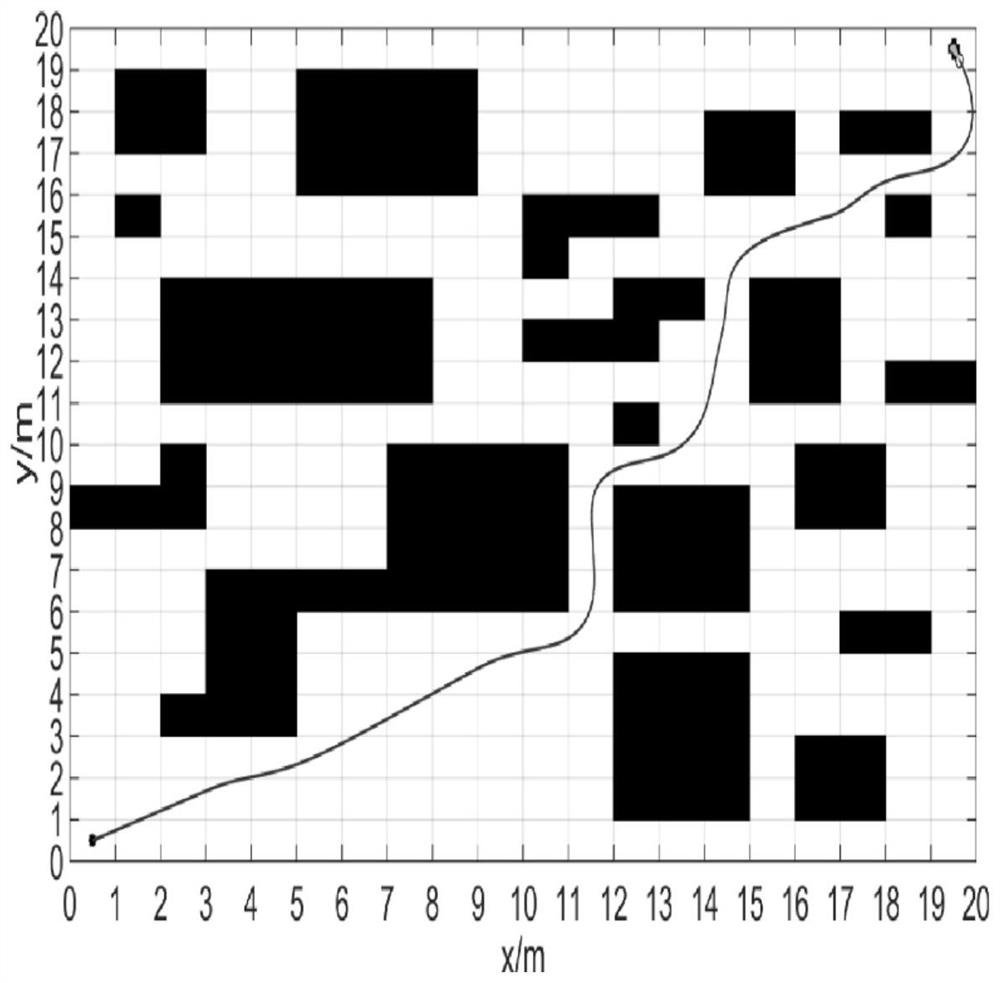
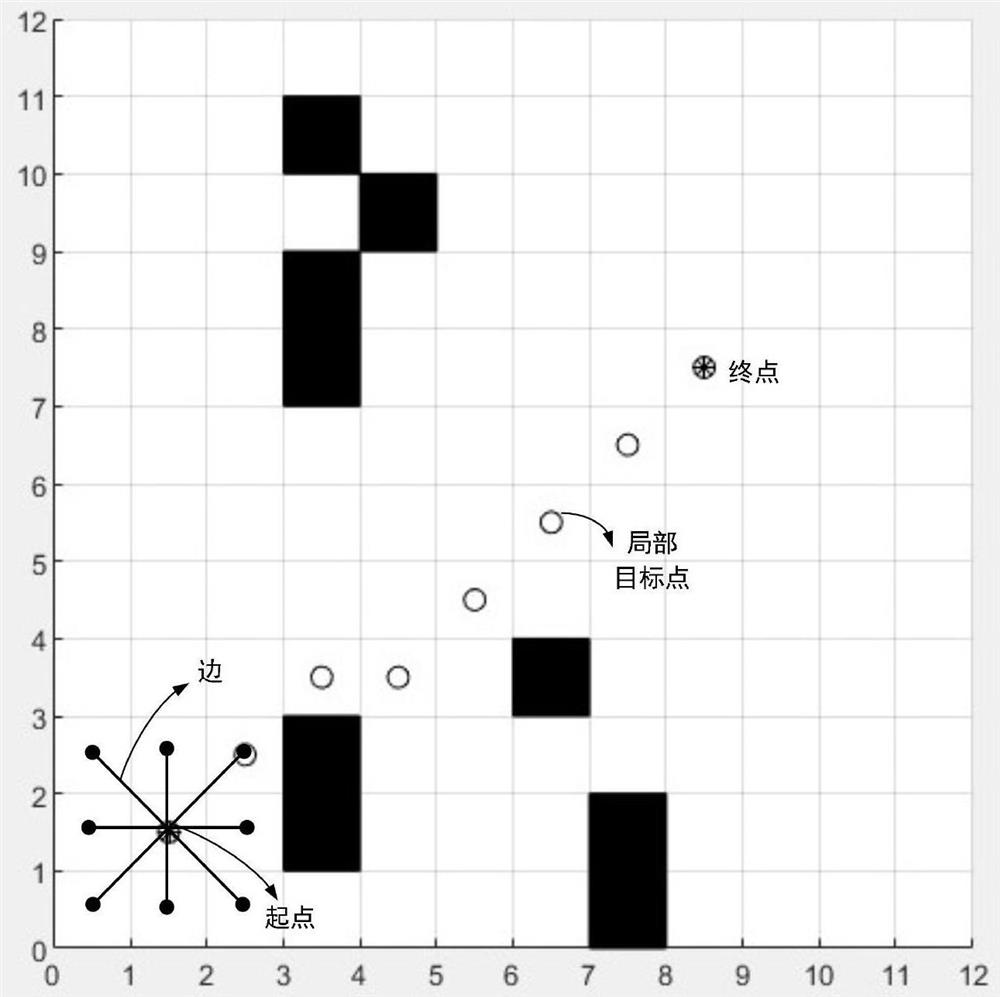
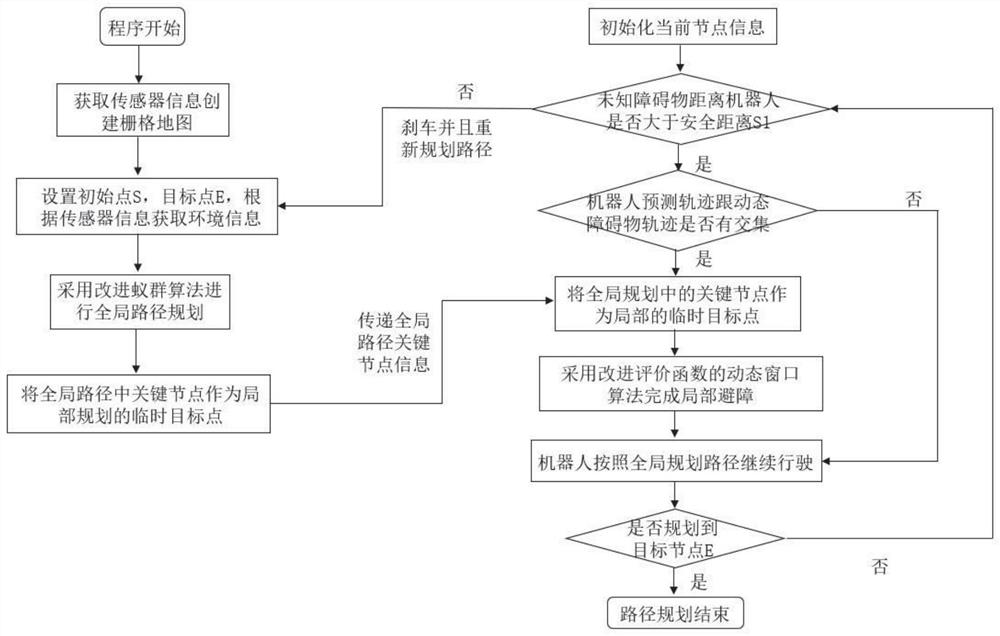
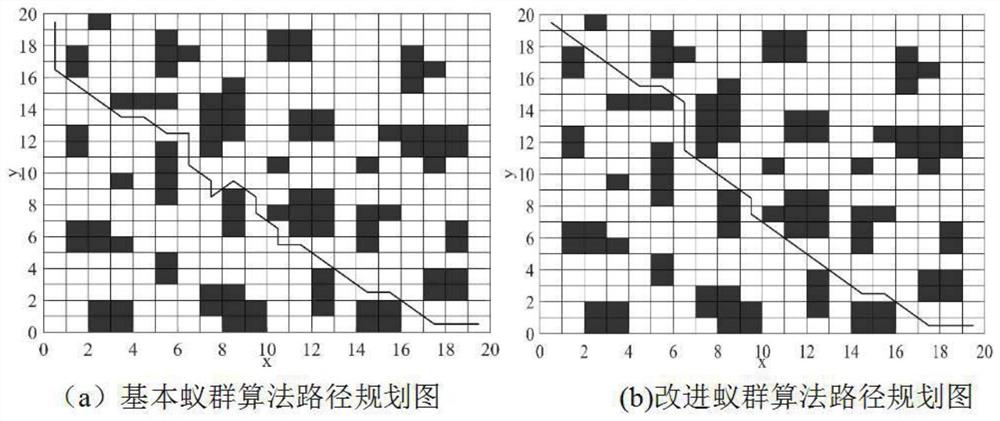
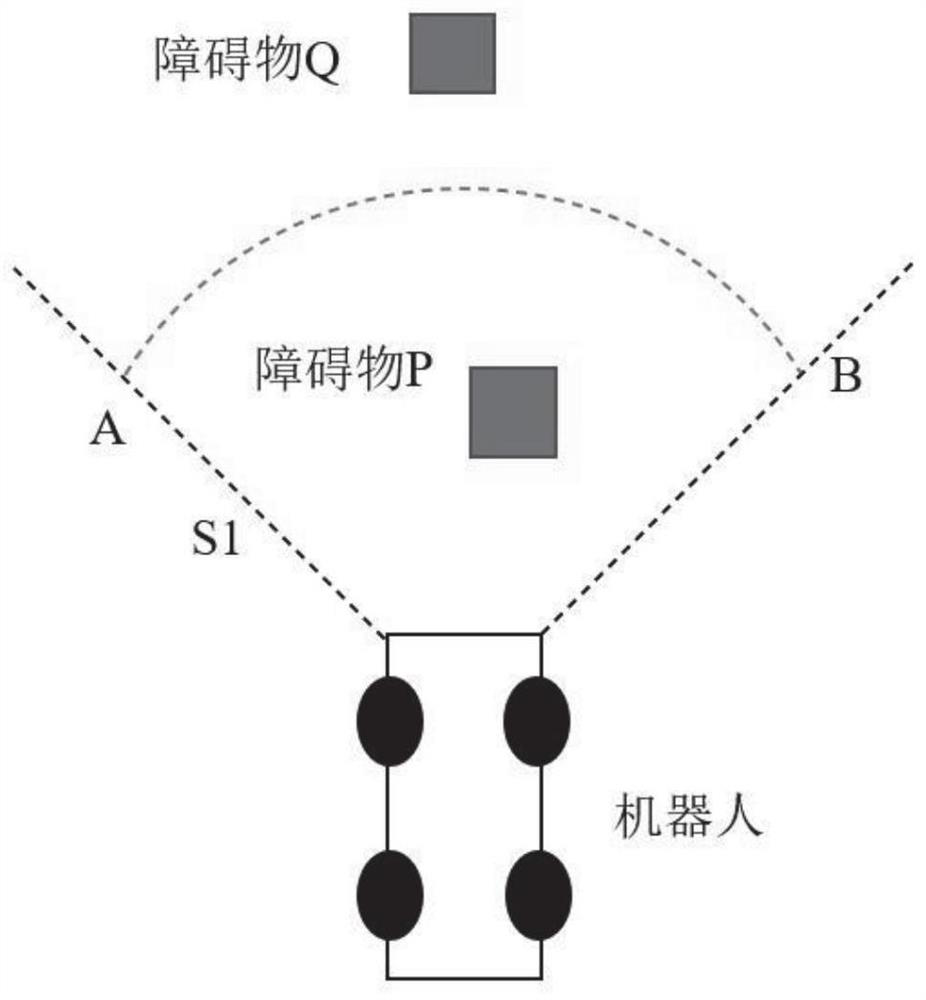
The invention discloses an intelligent path planning method for a mobile robot, and the method comprises the steps: building a static two-dimensional grid map, and carrying out the global path planning through an improved ant colony algorithm; enabling the mobile robot sensor module to detect unknown obstacle information, calculating an obstacle motion trail and a robot motion trail, adopts an optimized dynamic window method to carry out local dynamic obstacle avoidance, and taking the current position of the robot as a starting point and a closest key node on a global planning path as a temporary target point to carry out dynamic obstacle avoidance; and enabling the robot to travel along the planned path and safely reach the destination. According to the method, the actual problems of static obstacles and dynamic obstacles in the map environment are comprehensively considered, the heuristic function of the ant colony algorithm is improved, pheromone updating rules are adjusted for global path planning, the optimized dynamic window method is adopted for obstacle avoidance when the robot encounters the dynamic obstacles in the running process, and local path planning is completed; and the robot has higher practicability and research value in actual map operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Obstacle avoiding method based on dynamic window and virtual target points
ActiveCN107885209ASafe and efficient to avoidImprove work efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesVirtual targetSimulation
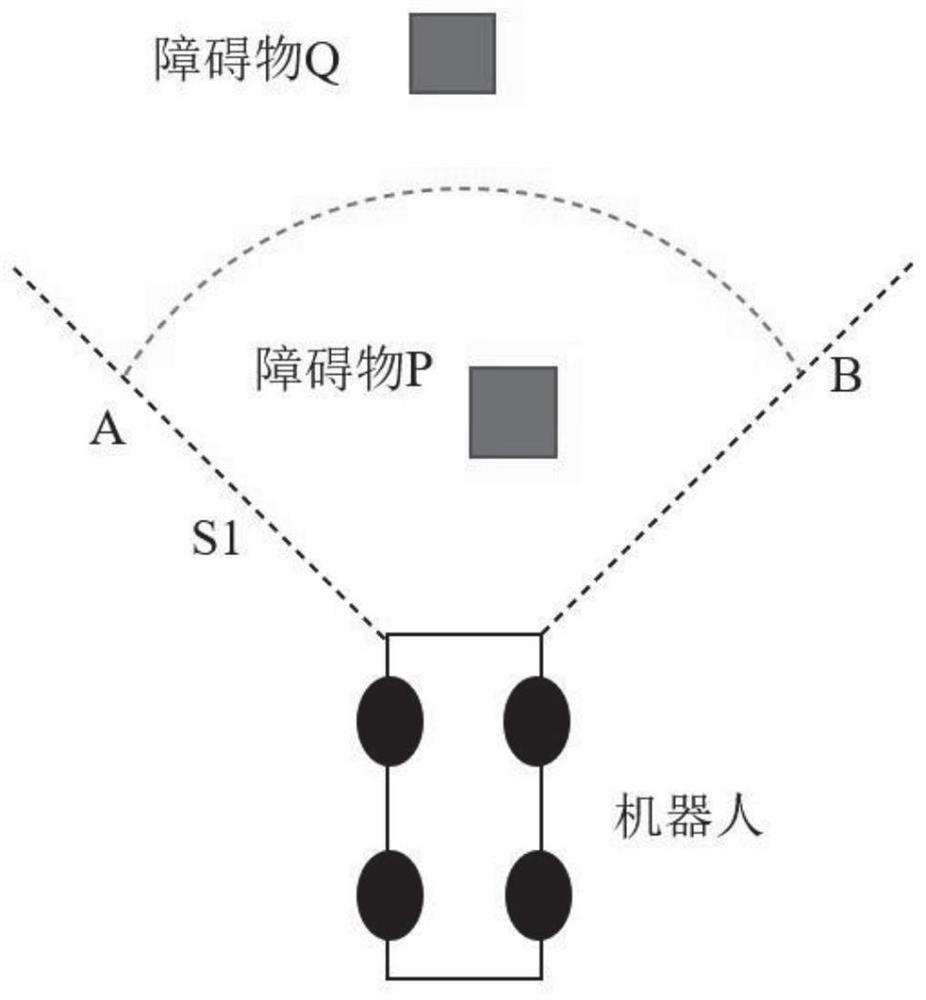
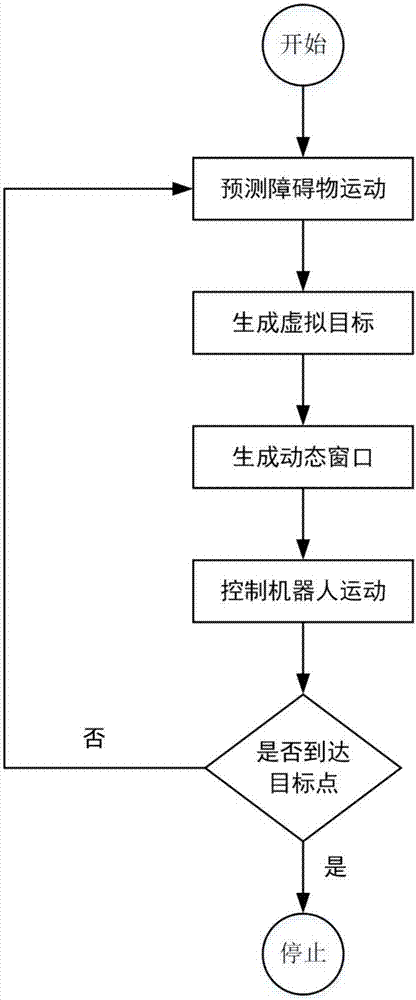
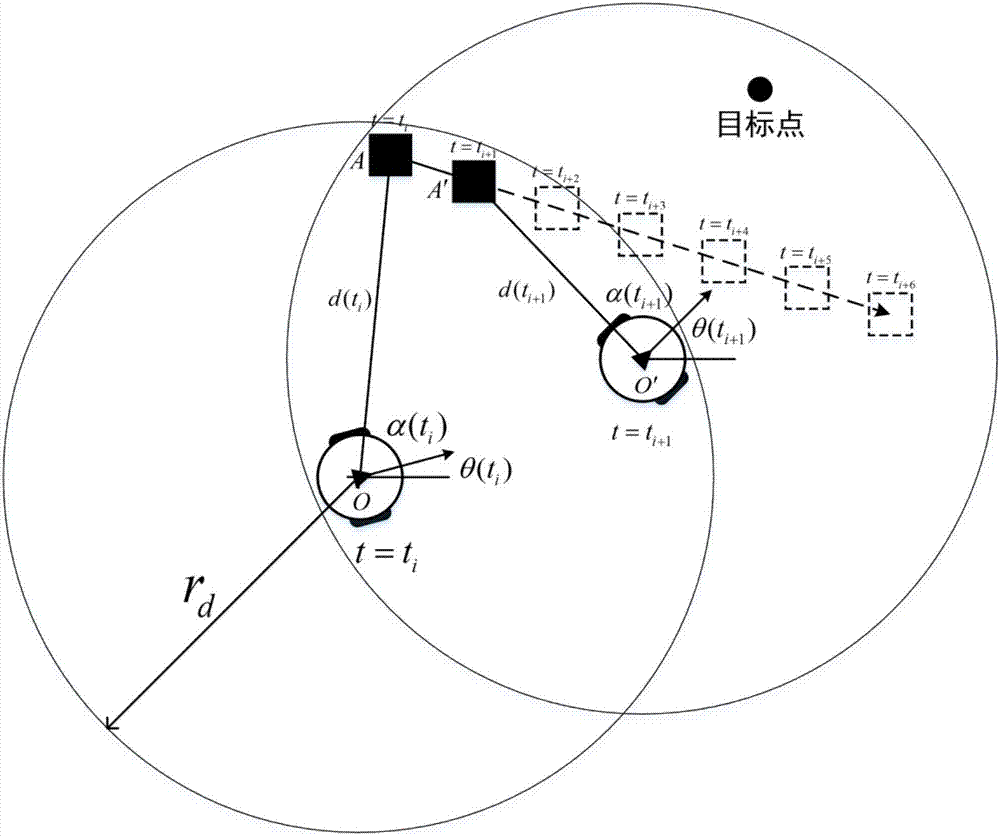
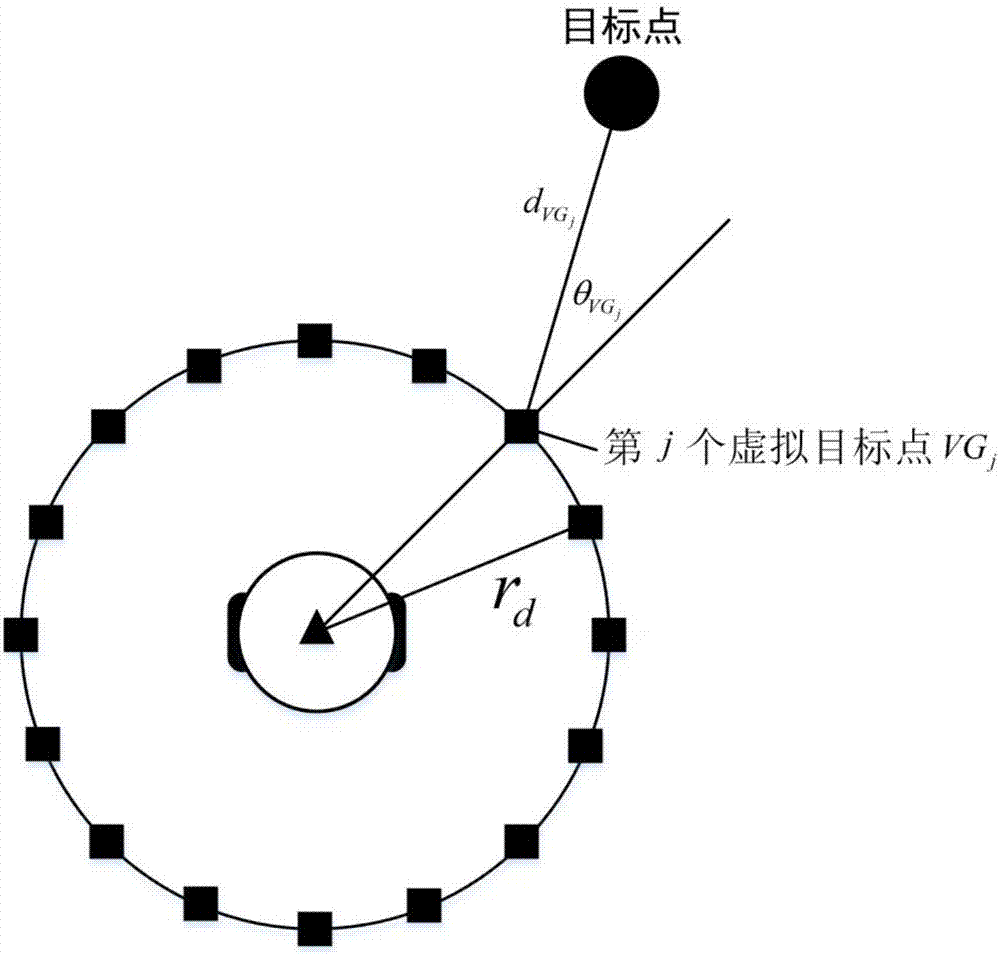
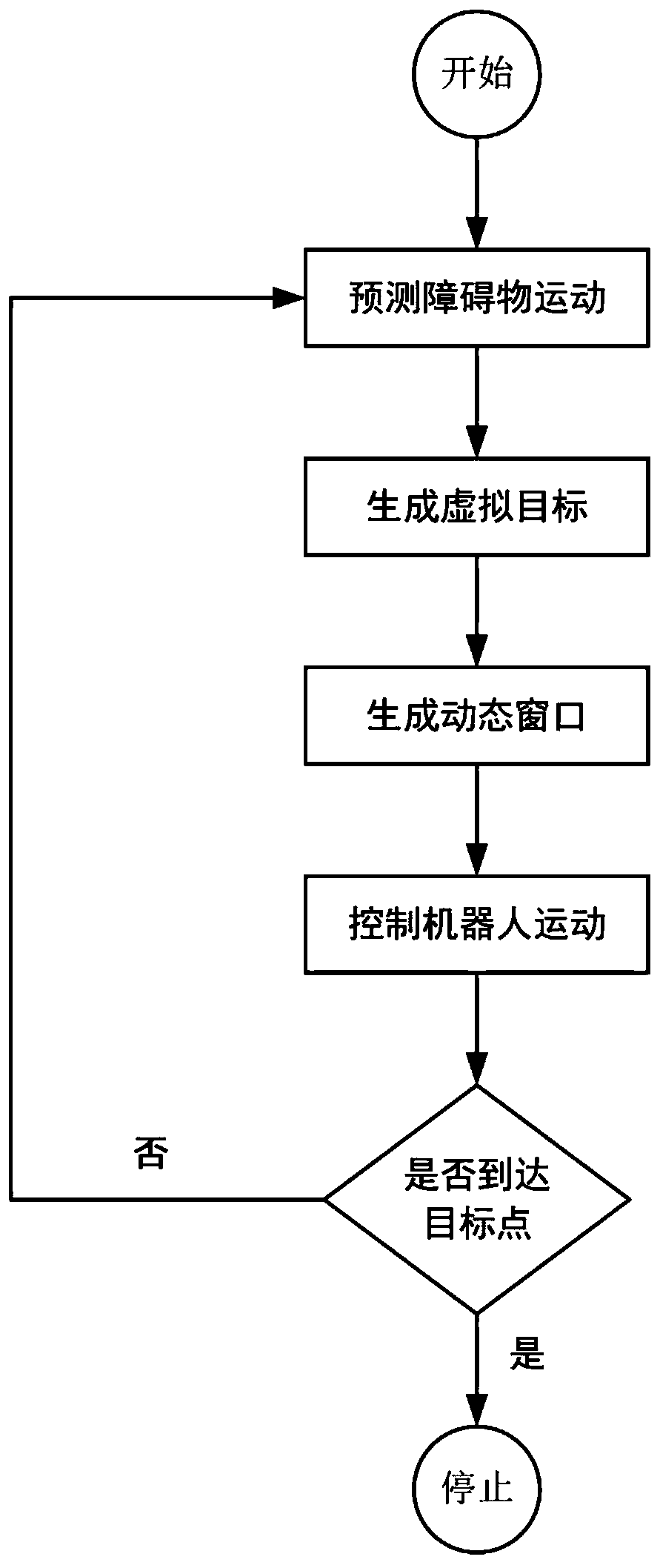
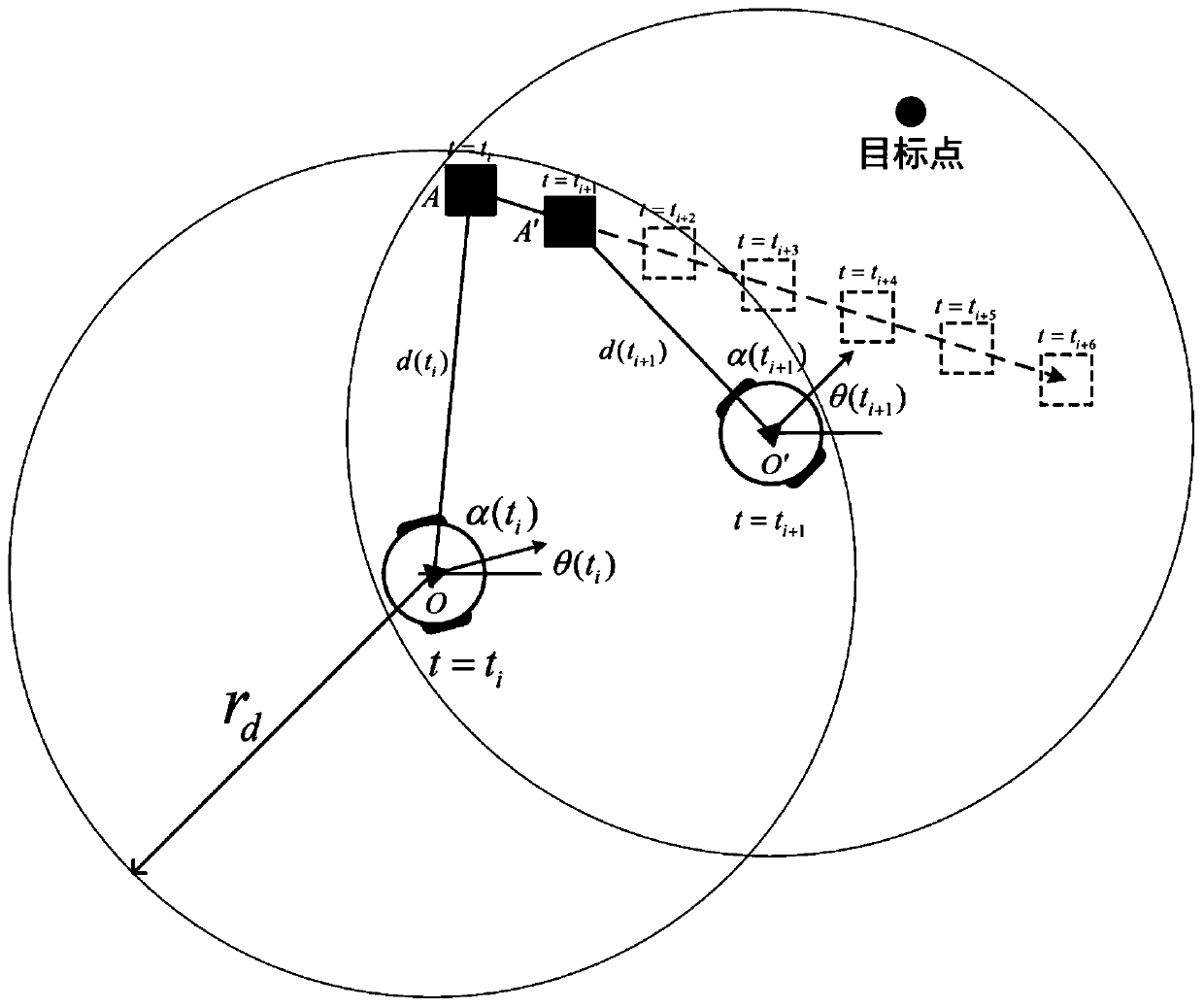
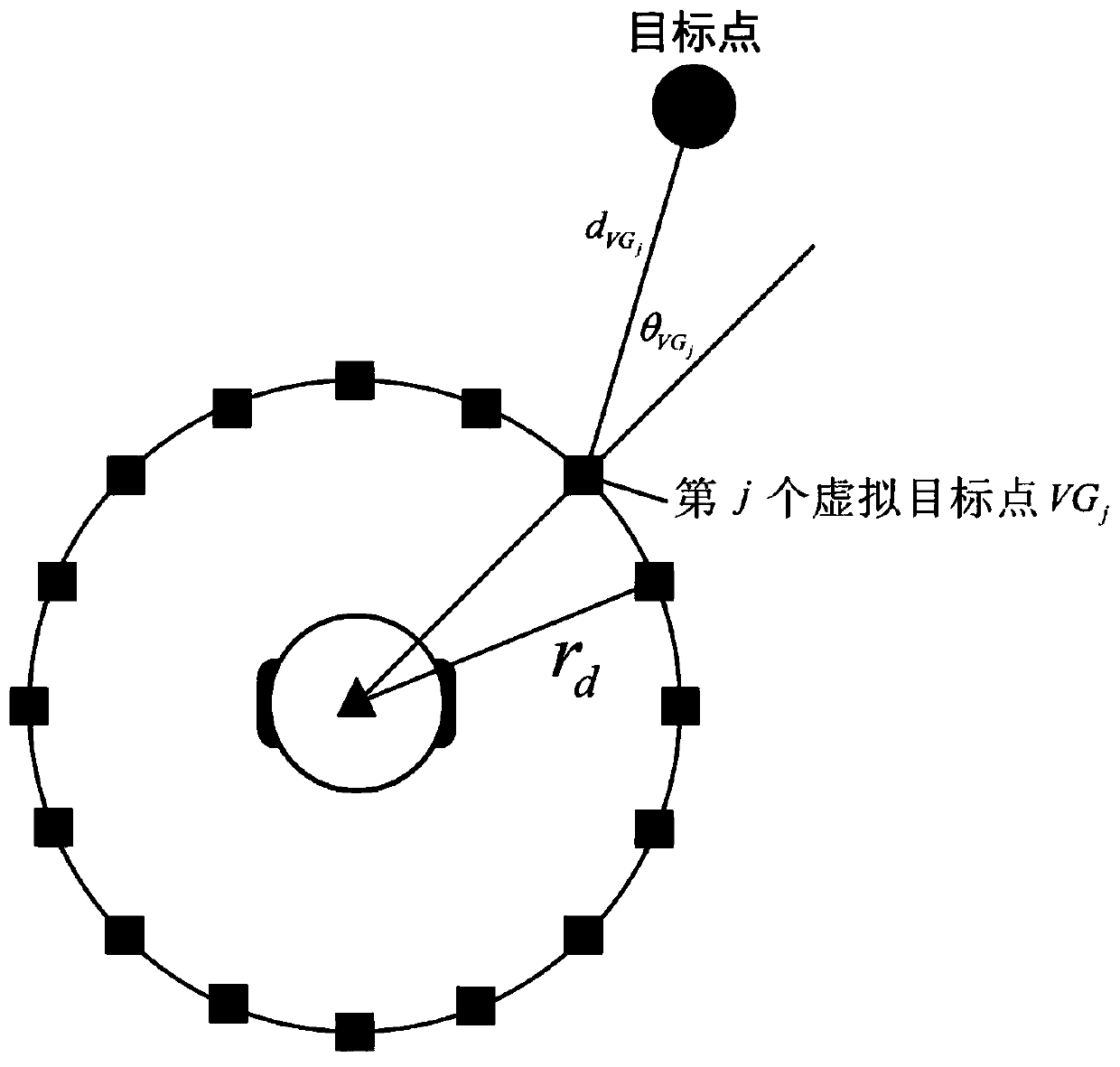
Provided is an obstacle avoiding method based on a dynamic window and virtual target points. A robot is guided by virtual target points to advance, and a motion instruction of the robot is issued through a dynamic window, and thus, the robot can avoid an obstacle to reach a target point. First, a robot predicts the motion track of an obstacle according to the angle and distance information of theobstacle fed back by a sensor on the robot; then, multiple virtual target points are generated according to the track prediction of the obstacle, the motion state of the robot and the position of a real target point, and an optimal virtual target is screened out by considering the direction of the robot and the distance between the virtual target points and the real target point through an evaluation function; and finally, the robot generates a control instruction set of the robot for the next moment through a dynamic window approach according to the track prediction of the obstacle and the positions of the virtual target points, and screens out an optimal control instruction of the robot for the next moment by considering the direction and motion speed of the robot and the distance between the robot and the target point through an evaluation function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Improved ant colony algorithm and dynamic window method-based hybrid algorithm applied to intelligent vehicle path planning
InactiveCN111694364AImprove environmental adaptabilityImprove accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesSimulationFeedback control
The invention discloses an improved ant colony algorithm and dynamic window method-based hybrid algorithm applied to intelligent vehicle path planning. The algorithm can realize real-time obstacle avoidance, improve the path planning efficiency and realize automatic feedback control of an intelligent vehicle. According to the algorithm, after the Matlab simulation platform and the ROS-based intelligent vehicle platform are used for specifying a starting point and a target point on the premise that the obstacle is known, global path planning of the intelligent vehicle is completed, meanwhile,unknown obstacles are set on the grid map, local moving target points are planned, the local target points are tracked in real time, and local real-time obstacle avoidance of the intelligent vehicle is completed. According to the intelligent vehicle path planning method based on the improved ant colony algorithm and the dynamic window method, the turning angle of the path is smoothened, the path planning efficiency is improved, real-time obstacle avoidance of the intelligent vehicle is achieved, and good robustness and accuracy are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Robot and navigation method thereof and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN106969770ANavigation implementationFix local navigation issuesNavigational calculation instrumentsControl signalSimulation
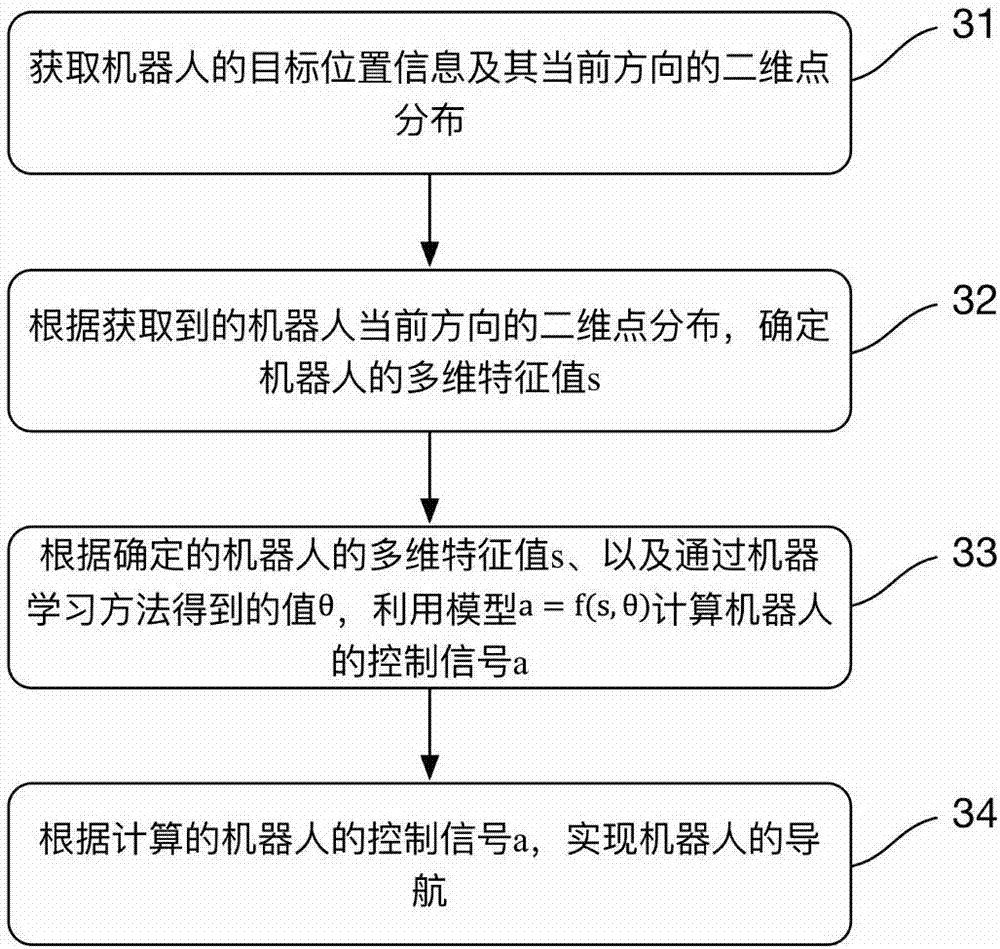
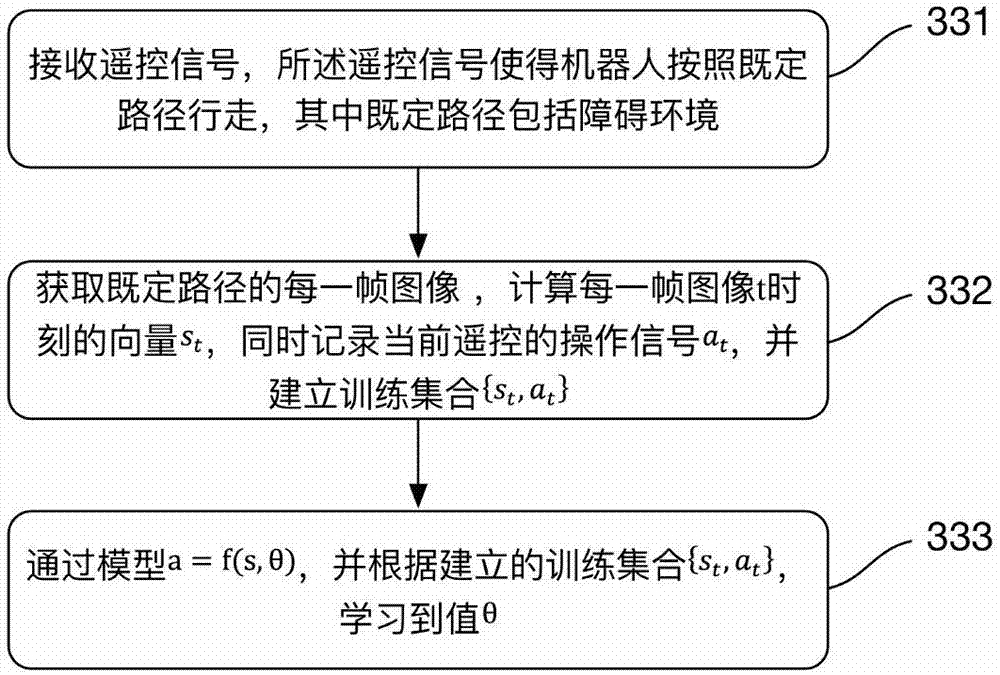
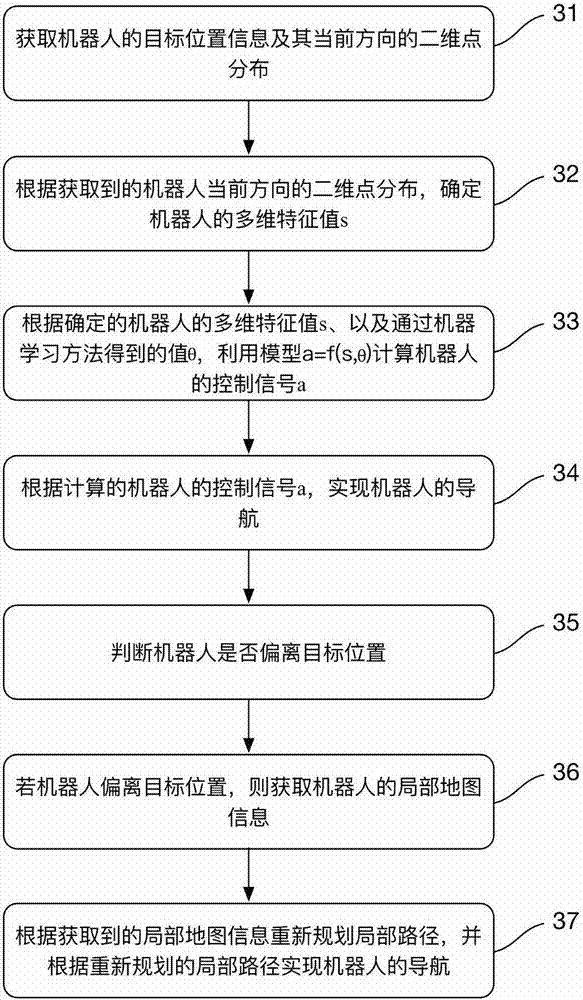
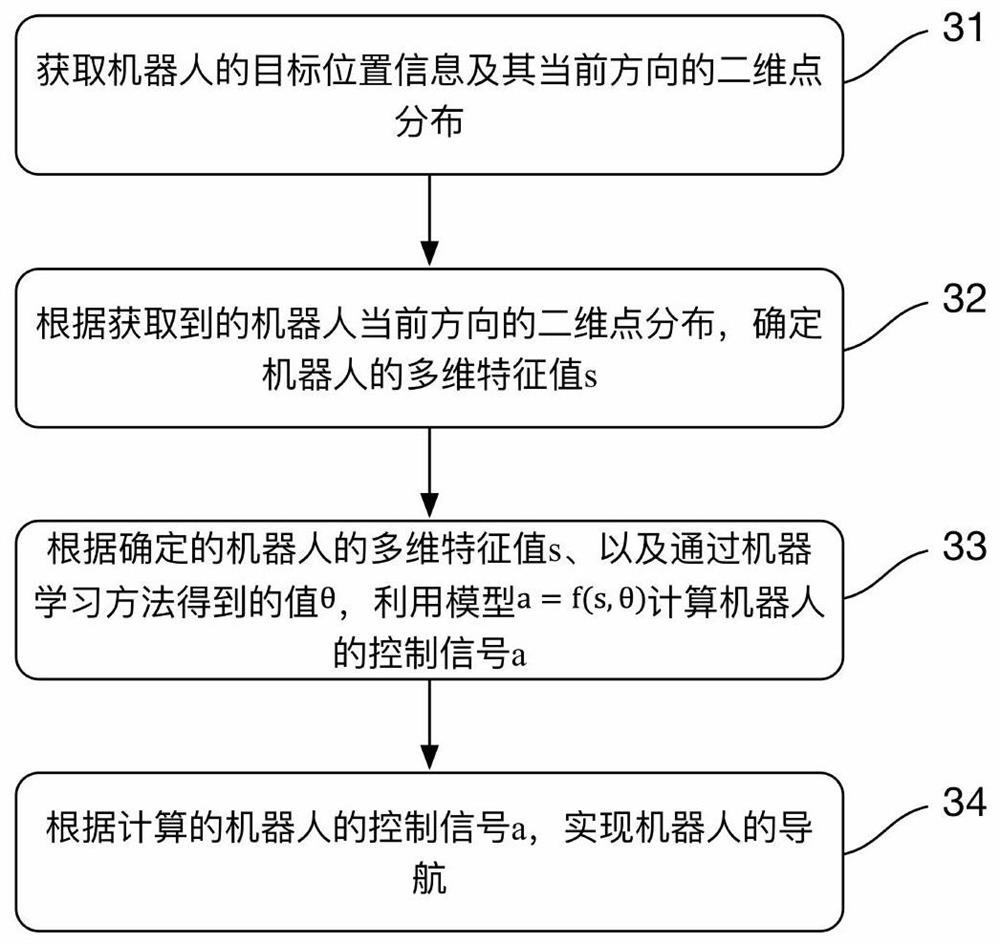
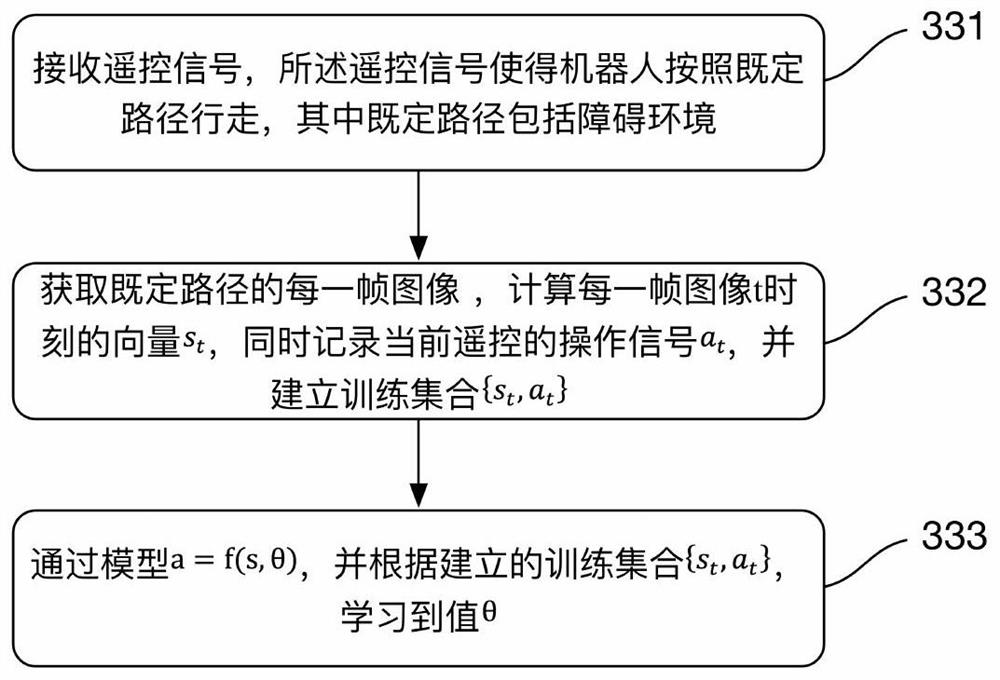
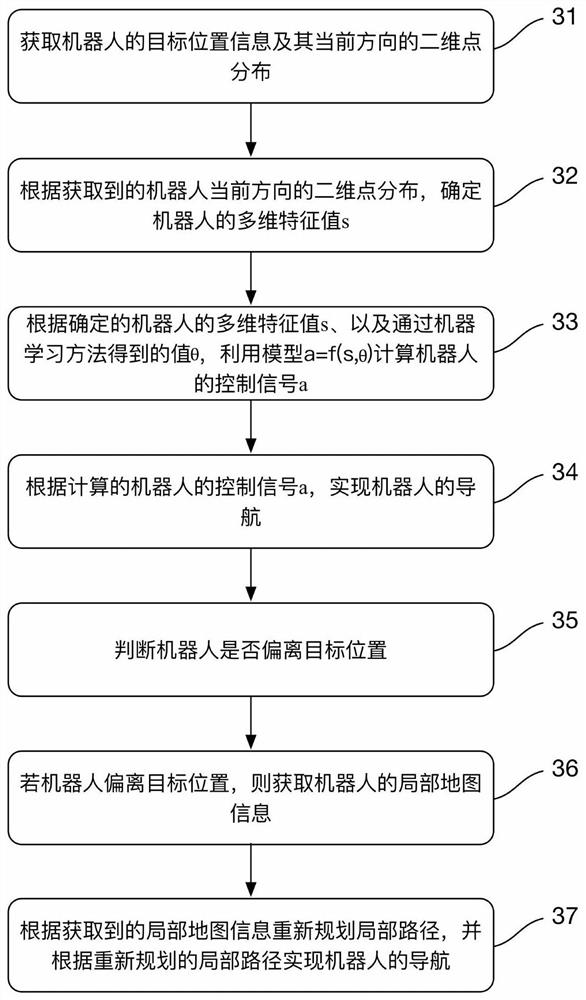
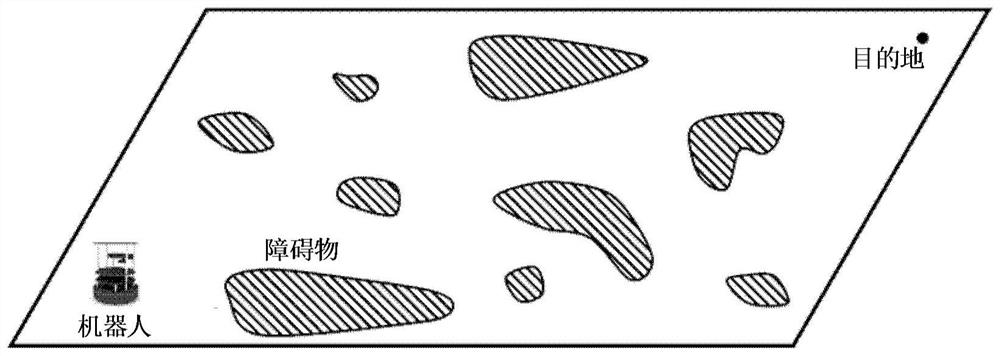
The invention discloses a robot and a navigation method thereof and a computer readable storage medium. The method includes the steps that target position information of the robot and two-dimensional point distribution of the current direction of the robot are obtained; the multi-dimensional feature value s of the robot is determined according to the obtained two-dimensional point distribution of the current direction of the robot; the control signal a of the robot is calculated through a model a equal to f (s, theta) according to the determined multi-dimensional feature value s of the robot and the theta value obtained through a machine learning method; navigation of the robot is achieved according to the calculated control signal a of the robot. According to the robot and the navigation method thereof and the computer readable storage medium, the control signal a of the robot is calculated through the model a equal to f (s, theta) through the theta value obtained through the machine learning method, and then navigation of the robot is achieved; relative to DWA (Dynamic Window Approach), TEB (Timed Elastic Band) and other local navigation algorithms in the prior art, the local navigation problem of the robot is effectively solved, the method is smooth in running, and efficiency is improved compared with an existing algorithm.
Owner:深圳中智卫安机器人技术有限公司
Hybrid path planning method for indoor mobile robot
ActiveCN111930121AShorten the lengthImprove dynamic obstacle avoidance abilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsGlobal planningBat algorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence and robot navigation, and particularly relates to a hybrid path planning method for an indoor mobile robot. According to the method, using a grid method for modeling the environment; searching a global path by using a bat algorithm as a global path planning method; optimizing the obtained global path, namely deleting redundantpath nodes, and reducing the length of the path and turning points of the path; designing an evaluation function of a dynamic window method, and bringing the global path into the evaluation functionof the dynamic window method to realize the combination of local planning and global planning; introducing an adaptive idea to dynamically adjust the coefficient of the evaluation function, and improving the dynamic obstacle avoidance capability of the fusion algorithm. The method can be applied to path planning of the indoor mobile robot, path planning and robot control are combined, and dynamicobstacle avoidance is considered under the condition that the global optimal path is guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
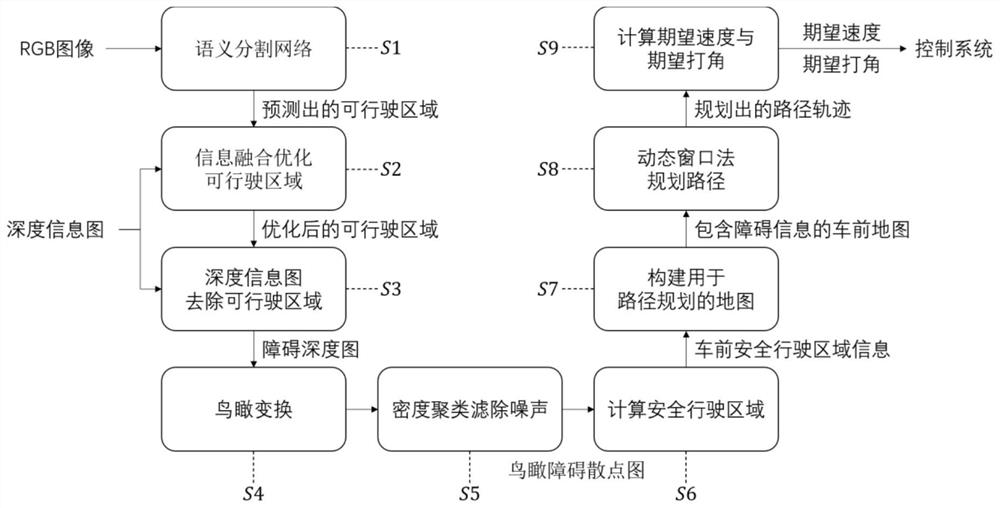
Vehicle obstacle avoidance method based on binocular vision and deep learning and electronic equipment
ActiveCN113255520ADrivabilitySignificant effect on obstacle detectionImage enhancementImage analysisRgb imageEngineering
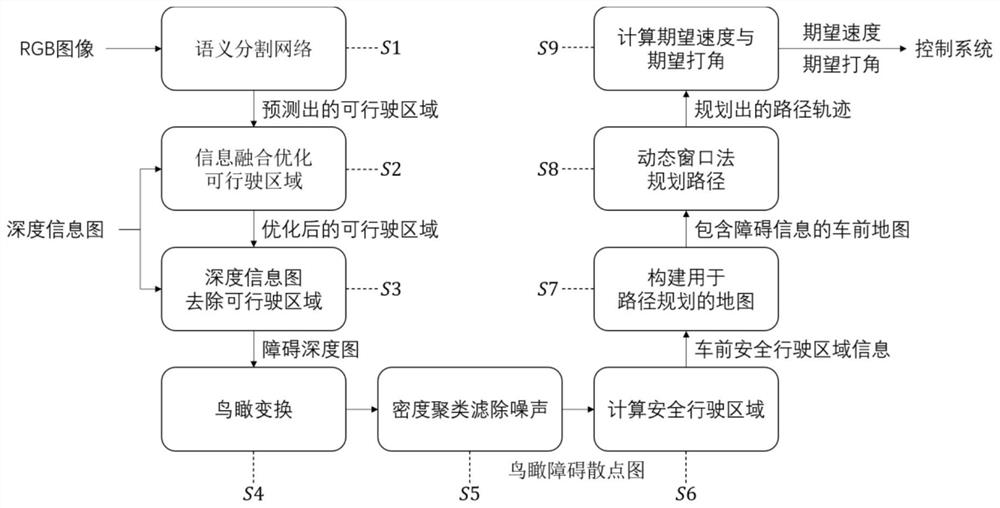
The invention discloses a vehicle obstacle avoidance method based on binocular vision and deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an RGB image in front of a vehicle; acquiring a depth information map in front of the vehicle; predicting a drivable area segmentation result; carrying out information fusion to optimize a drivable area; removing the depth information of a drivable area part, and generating a depth obstacle front view; acquiring an obstacle distribution condition in a three-dimensional space in front of the vehicle, and obtaining an aerial view obstacle scatter diagram according to the obstacle distribution condition; performing density clustering on the aerial view obstacle scatter diagram, and removing noise; performing euclidean distance transformation on the aerial view obstacle scatter diagram, setting an adaptive threshold value, and dividing a front map into a safe driving area and a dangerous area; constructing a map for path planning through the aerial view safe driving area map and the field angle boundary information; performing obstacle avoidance path planning by using a dynamic window method in combination with a map for path planning; and calculating an expected speed and an expected angle according to the obstacle avoidance path track and issuing the same to a control system. The invention further provides the corresponding electronic equipment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Indoor navigation method and system based on laser and vision fusion SLAM technology
PendingCN113238554AReduce storageSmall amount of calculationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGratingLaser data
The invention relates to an indoor navigation method and system based on a laser and vision fusion SLAM technology. The method comprises steps of laser data collected by an indoor robot laser sensor and vision data collected by an indoor robot camera being obtained; performing fusion processing on the laser data and the visual data by using a closed-loop detection algorithm based on multi-information fusion to obtain a two-dimensional SLAM semantic grating map; the sensing information collected by a sensor of the indoor robot being obtained, and according to the sensing information, a preset laser radar positioning method or a preset positioning method integrating a visual odometer and an IMU being selected to obtain the pose information of the indoor robot; and generating the navigation information for an indoor robot to execute by utilizing the pose information and the two-dimensional SLAM semantic grating map and based on a Voronoi global path planning technology and a dynamic window method local path planning technology extracted by a skeleton.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dynamic window approach using optimal reciprocal collision avoidance cost-critic
ActiveUS10429847B2Increase radiusNavigational calculation instrumentsAnti-collision systemsTime cyclesComputer vision
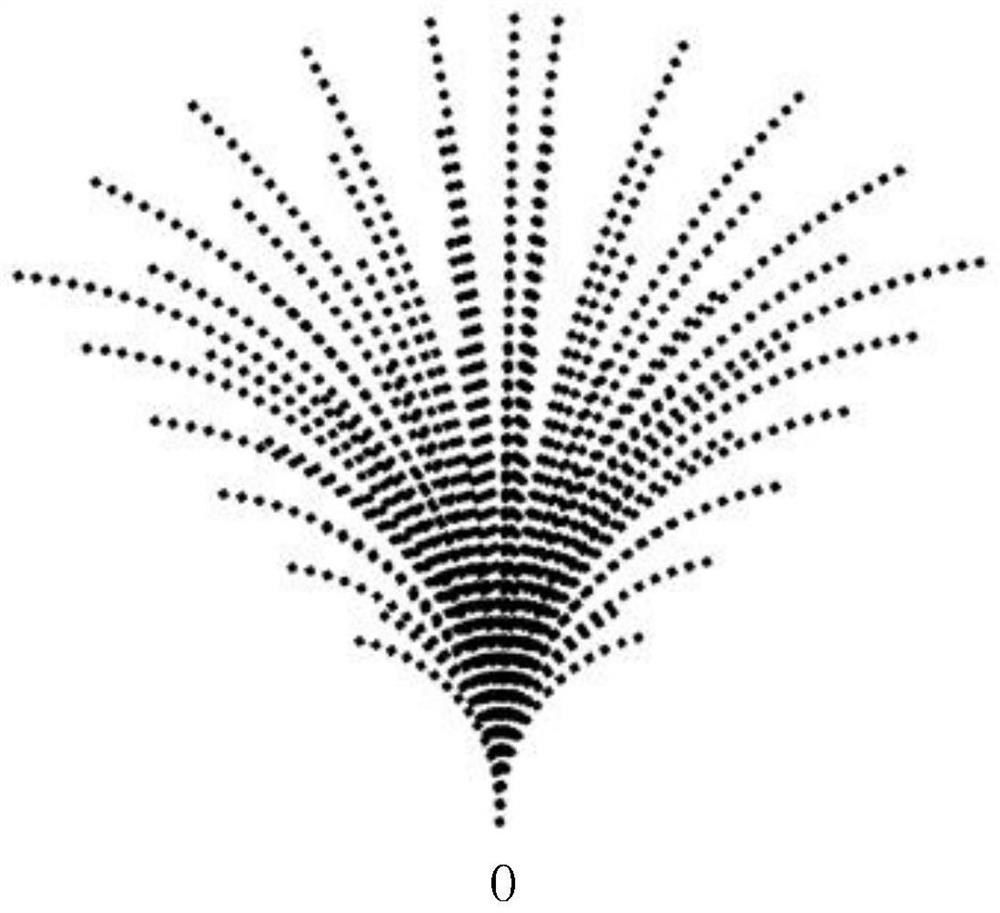
A method and system for navigation of a robot along a goal path and avoiding obstacles. The method includes receiving goal pose for one or more robots and determining a goal path for a first robot while avoiding moving and fixed obstacles of a received obstacle map. A first objective function is evaluated to select a preferred velocity from a generated set of candidate velocities, the selecting based on one or more weighted cost functions. A set of velocity obstacles created based on the poses of the one or more robots and the preferred velocity is used in evaluating a second objective function to determine the motion of the robot in the next time cycle. Creating the set of velocity objects includes converting the preferred velocity from a non-holonomic to a holonomic velocity.
Owner:LOCUS ROBOTICS CORP
Track evaluation method, track evaluation device and mobile robot
PendingCN111123934AImprove securityImprove adaptabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationComputer vision
A track evaluation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring N pieces of obstacle distance information; determining a target obstacle distance according to the N piecesof obstacle distance information; obtaining the distance between a terminal point of a preset path and the current position of a mobile robot, and taking the distance as a target point distance; forany to-be-evaluated track in a to-be-evaluated track set, determining a first weight corresponding to a first estimated distance and a second weight corresponding to a second estimated distance according to the target point distance and the target obstacle distance; according to the N pieces of obstacle distance information, determining a third weight corresponding to a target metric value, wherein the target metric value is used for indicating the distance between the to-be-evaluated track and an obstacle; and according to the first weight, the second weight and the third weight, obtaining anevaluation value corresponding to the to-be-evaluated track through a dynamic window method. Through the method, the evaluation accuracy of the to-be-evaluated track of the mobile robot in path planning can be improved.
Owner:深圳深岚视觉科技有限公司
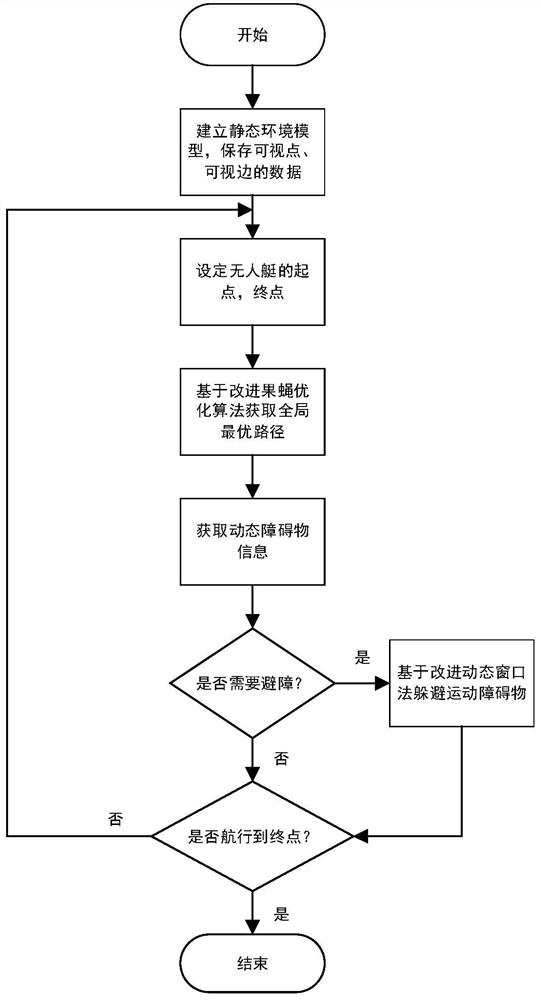
Unmanned vehicle real-time global path planning method based on dynamic window of safe A* guide point
PendingCN113608531AGuaranteed passabilityRealize the planPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesVirtual targetPathPing
The invention relates to an unmanned vehicle real-time global path planning method based on a dynamic window of a safety A* guide point. The method comprises steps that a node safety extension strategy and a path node quadratic optimization method are firstly provided on the basis of an A* algorithm, which are called as a safety A* algorithm, and an optimal safety virtual target point is rapidly found out through employing the safety A* algorithm; secondly, the virtual target point serves as a local target of a dynamic window method, speed sampling is conducted, path planning and obstacle avoidance are achieved, simulation is conducted in the MATLAB environment, the result shows that the unmanned vehicle can safely and stably avoid the obstacle under the guidance of the global path, and safety and stability of the method are verified.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Curvature consistency path planning algorithm based on adaptive dynamic window method in narrow channel environment
PendingCN112082555AGuaranteed Curvature ConsistencyImprove rationalityNavigational calculation instrumentsLocal optimumAlgorithm
The invention discloses a curvature consistency path planning algorithm based on an adaptive dynamic window method in a narrow channel environment, and belongs to the technical field of robot navigation. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the distance with a nearest obstacle, and if the distance D is smaller than a threshold value Dt, calculating a dynamic weight gamma of a speed item vel in a target function; calculating a curvature k of a track corresponding to each sampling speed, thereby calculating a curvature similarity factor Csim; and calculating values of a headingitem, a dis item and a vel item in the target function of a standard dynamic window method, and substituting the curvature similarity factor Csim and the dynamic weight gamma of the vel item to obtainan optimal motion trail and a corresponding execution speed at the next moment. According to the method, the problems that when the robot carries out local path planning in the narrow channel, the robot is prone to falling into local optimum, consequently, the terminal point cannot be reached, and the smoothness of the motion planning trajectory is poor are solved, and the reasonability and consistency of trajectory planning in the narrow channel environment are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
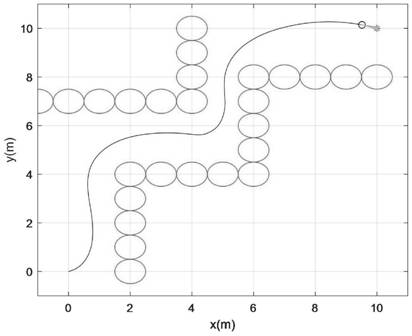
Unmanned ship layered obstacle avoidance method based on improved fruit fly optimization and dynamic window method
ActiveCN111580518AEffective dodgeHigh precisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocal optimumMaritime navigation
The invention relates to the field of autonomous navigation of unmanned ships, in particular to an unmanned ship layered obstacle avoidance method based on improved fruit fly optimization and a dynamic window method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an unmanned ship marine navigation geographical environment model based on an electronic chart; S2, completing global optimal path planning by adopting an improved fruit fly optimization algorithm; S3, establishing an environment model of the dynamic obstacle; and S4, using an improved dynamic window method to avoid the moving obstacle ship. According to the obstacle avoidance method for switching the dynamic obstacle avoidance mode and the static obstacle avoidance mode based on the judgment conditions, obstacles canbe effectively avoided during sailing, the algorithm is prevented from falling into a local optimal solution, the fuzzy control method is adopted for dynamically controlling the weight parameters of the optimal trajectory, and the trajectory prediction precision and efficiency are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Dynamic path planning method for improving particle swarm optimization
PendingCN114397896AShorten the lengthImprove smoothnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPathPingRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a dynamic path planning method for an improved particle swarm algorithm, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, generating a global path by adopting the improved particle swarm algorithm, and dividing the global path into n sections of local paths consisting of {S1G1, S2G2,... SnGn}; step 2, performing path planning on the local path S1G1 by using a dynamic window method DWA, including building a robot kinematics model, building a robot speed model, building an objective function of the dynamic window method DWA, selecting an optimal track according to the objective function, and performing path planning on the local path S1G1 by using the optimal track; step 3, performing local path planning on the local path S2G2 by using a dynamic window method DWA, and inheriting the course angle of the previous motion planning; 4, the dynamic window method DWA is repeatedly used for conducting local path planning on the paths S3G3,..., SnGn in sequence; and step 5, outputting a complete final path. The method has the characteristics of shortening the length of the planned path, improving the smoothness and real-time performance of the planned path and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Local path planning algorithm and device
ActiveCN111813100AReduce the situation of falling into local minimum pointsImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsPathPingAlgorithm
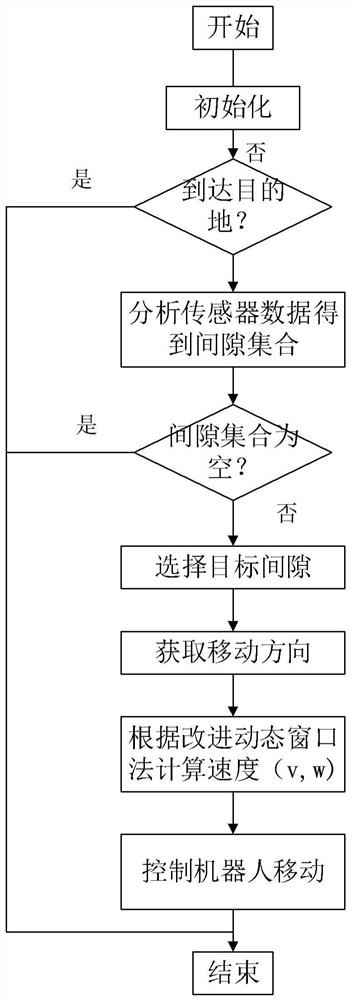
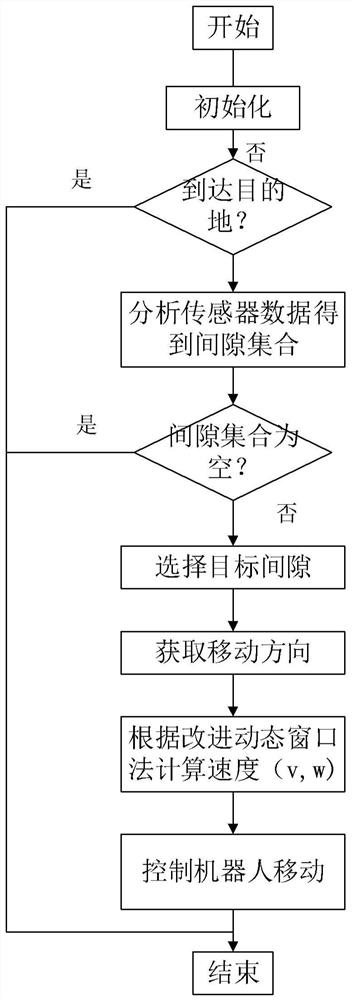
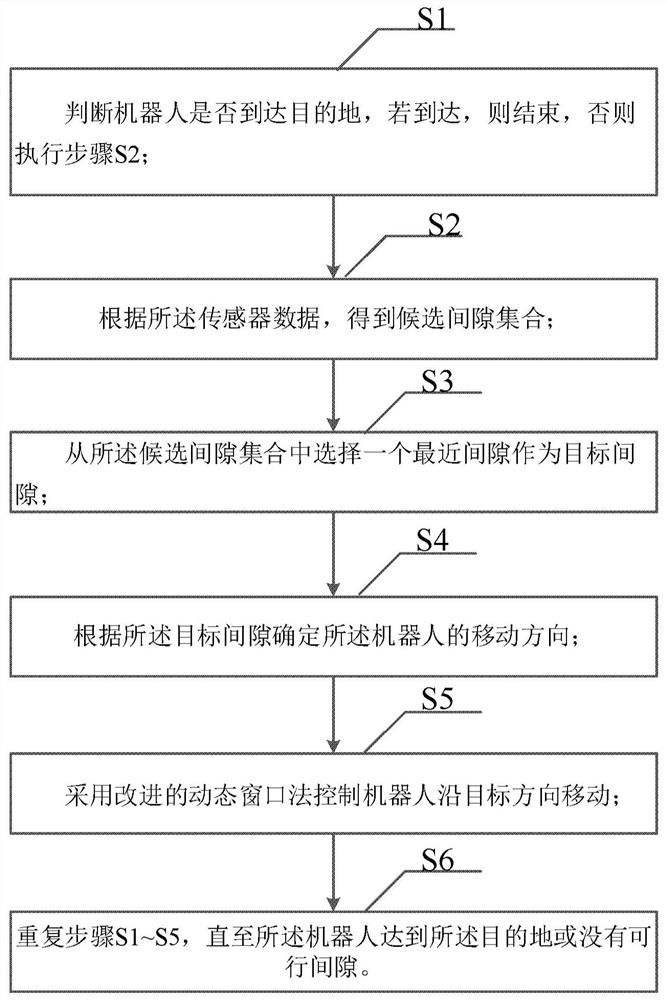
The invention provides a local path planning algorithm and device, which are used for path planning of mobile equipment that is provided with a sensor. The algorithm comprises the following steps: S1,judging whether the mobile equipment reaches a destination or not, and if so, ending a process, or if not, executing step S2; S2, acquiring a candidate gap set according to sensor data; S3, selectinga nearest gap from the candidate gap set as a target gap; S4, determining the moving direction of the mobile equipment according to the target gap; S5, controlling the mobile equipment to move alongthe target direction by adopting an improved dynamic window method; and S6, repeating the steps S1 to S5 until the mobile equipment reaches the destination or no feasible gap exists. The path of the mobile equipment is planned based on gaps and an improved dynamic window method so as to reduce the condition of local extreme value and improve obstacle avoidance performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Local path planning method based on dynamic window method and suitable for Ackerman model robot
ActiveCN112506199ASolve the problem that the Ackerman model robot is not applicablePosition/course control in two dimensionsControl theoryComputer science
The invention relates to a local path planning method based on a dynamic window method and suitable for an Ackerman model robot. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, acquiring the posture of the robot and the position of an obstacle according to a sensor carried by the robot, then calculating the coordinates of an obstacle avoidance starting point and coordinates and direction of a local target point, and determining a final speed space; meanwhile, segmenting the obstacle avoidance process of the robot to determine evaluation functions, judging the number of segments in segmented obstacle avoidance at present, and selecting the corresponding evaluation function for processing to obtain the speed corresponding to the minimum evaluation function value to serve as the optimal speed ofrobot operation, and repeatedly executing the obtained optimal speed, judging whether the robot reaches a local target point or not according to the current position of the robot, and if so, ending obstacle avoidance; conducting local path planning according to the size and position of the obstacle, the robot speed and the minimum turning radius, and promoting the robot to move in an optimal pathon the premise that the robot can avoid the obstacle and can return to a global path in a smooth direction after obstacle avoidance is finished.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
Path planning method for unmanned surface vehicle
PendingCN114839968AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove search capabilitiesPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocal optimumDynamic planning
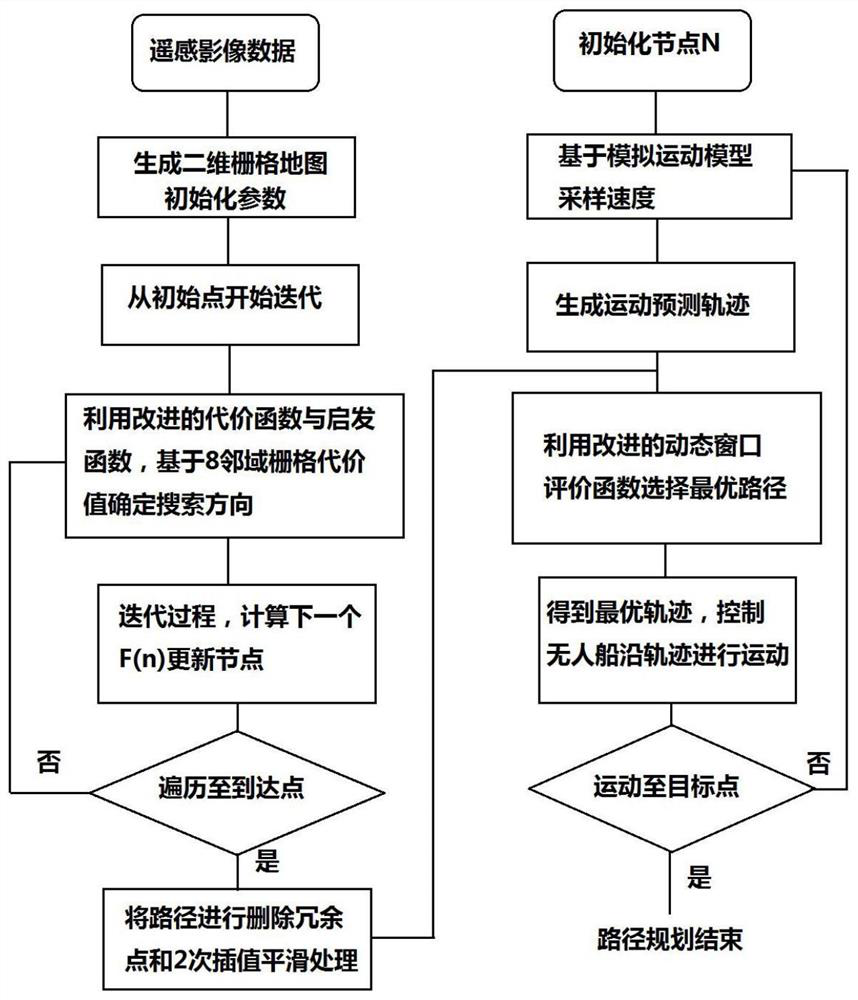
The invention provides an unmanned surface vehicle path planning method which is an unmanned surface vehicle path planning method based on a dynamic window method and an optimized LPA * algorithm in an environment with moving obstacles. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a global remote sensing image of a water surface environment through aerial photography of an aircraft, carrying out classification and binarization processing on the aerial photography image, converting the image into a grid map, carrying out global path planning by utilizing an LPA * algorithm of an optimized distance heuristic function based on the global grid map of the environment to obtain an initial path, and carrying out interpolation smoothing processing on the path; and based on a dynamic window method, constructing an evaluation function with a globally optimal path, and performing local path dynamic planning to achieve a local dynamic planning capability on the premise of the globally optimal path. Simulation results show that the method can obtain a smooth path better than a traditional heuristic A * algorithm, and can also realize good obstacle avoidance performance in a moving obstacle environment; moreover, the method is integrated with the structure of an LPA * global programming algorithm, and overcomes the defect that a dynamic window method is liable to fall into local optimum.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
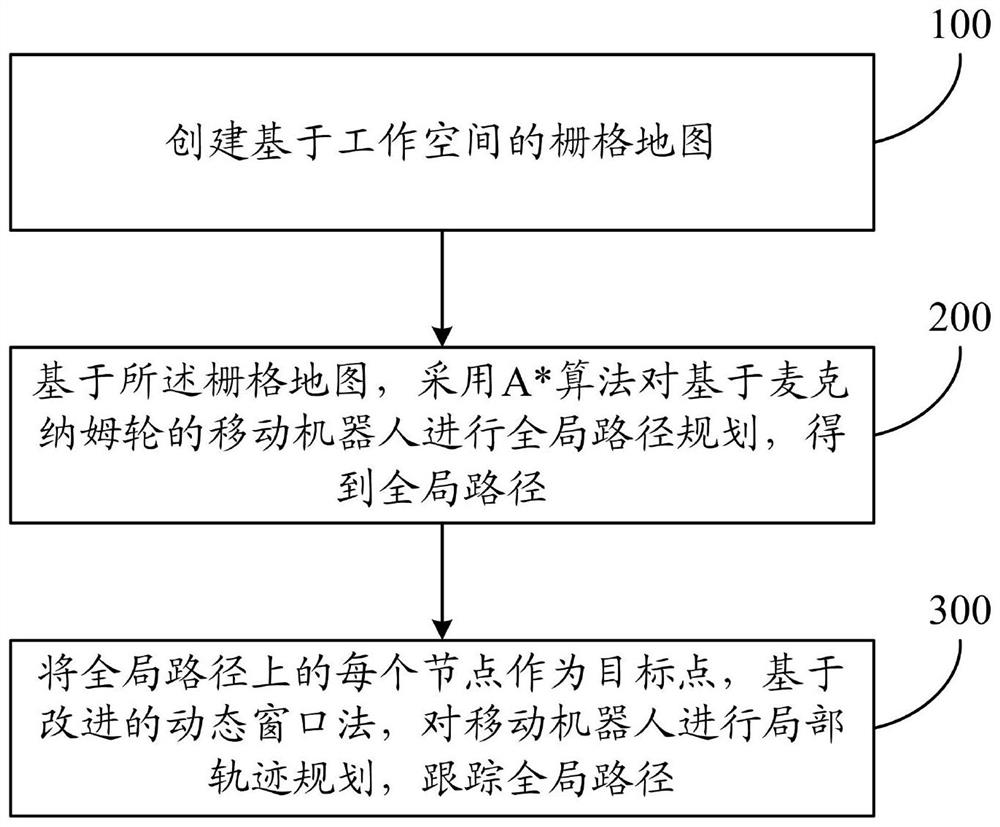
Mobile robot motion planning method and system based on Mecanum wheels
InactiveCN113296519ASolve the problem of unmanned autonomous movementGood local obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEngineeringPath plan
The invention relates to a mobile robot motion planning method and system based on Mecanum wheels. The method comprises the following steps of: creating a grid map based on a working space; based on the grid map, adopting an A * algorithm to carry out global path planning on the mobile robot based on Mecanum wheels to obtain a global path, wherein the global path is a path of the mobile robot from a starting point to an end point, and the global path comprises a plurality of nodes; by taking each node on the global path as a target point, performing local trajectory planning on the mobile robot based on an improved dynamic window method, and tracking the global path. The method is high in global path search efficiency, good in local obstacle avoidance effect and high in robustness, and can help the Mecanum wheel-based mobile robot to autonomously plan paths, flexibly avoid obstacles and safely and stably move based on the field environment, so that the flexibility of the movement is improved, and the autonomy of the movement is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
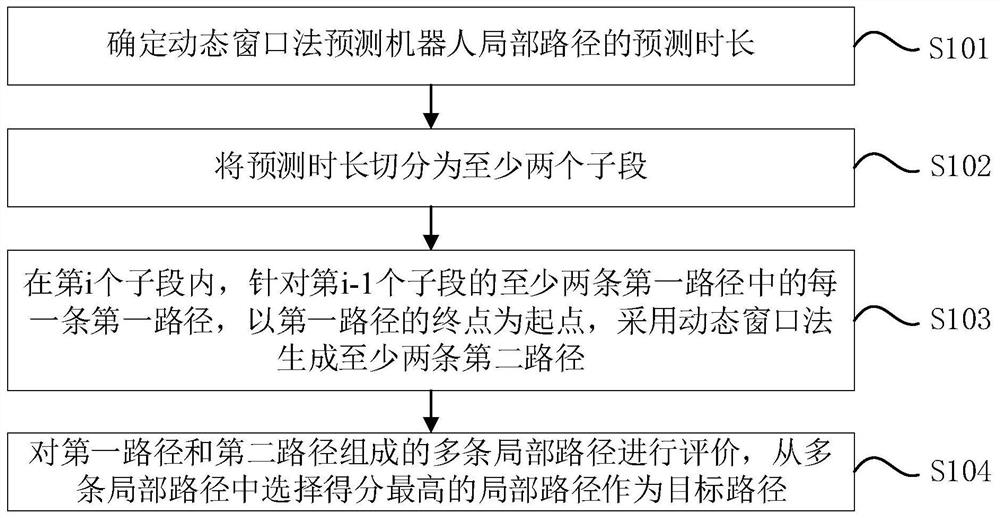
Local path planning method and device, robot and storage medium
PendingCN114415670AExpansion quantityImprove the effect of obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesSimulationOperation safety
The invention discloses a local path planning method and device, a robot and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting prediction duration of predicting local paths of a robot by using a dynamic window method into at least two sub-segments, generating at least two new paths by using the dynamic window method in each sub-segment by using an end point of each path in the previous sub-segment as a starting point, and evaluating a plurality of local paths formed by combining the paths of the sub-segments, and selecting the local path with the highest score from the plurality of local paths as a target path. According to the method, at least two new paths are generated by using the dynamic window method in each sub-segment by taking the end point of each path in the previous sub-segment as the starting point, the number of the paths in each sub-segment is multiplied relative to the number of the paths in the previous sub-segment, the total number of local paths in the prediction duration is increased, and the prediction accuracy is improved. The space coverage rate of the tail end of the path is increased, so that the optimal path which most conforms to the actual environment can be selected, the obstacle avoidance performance of the robot is improved, and the operation safety of the robot is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAITE INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
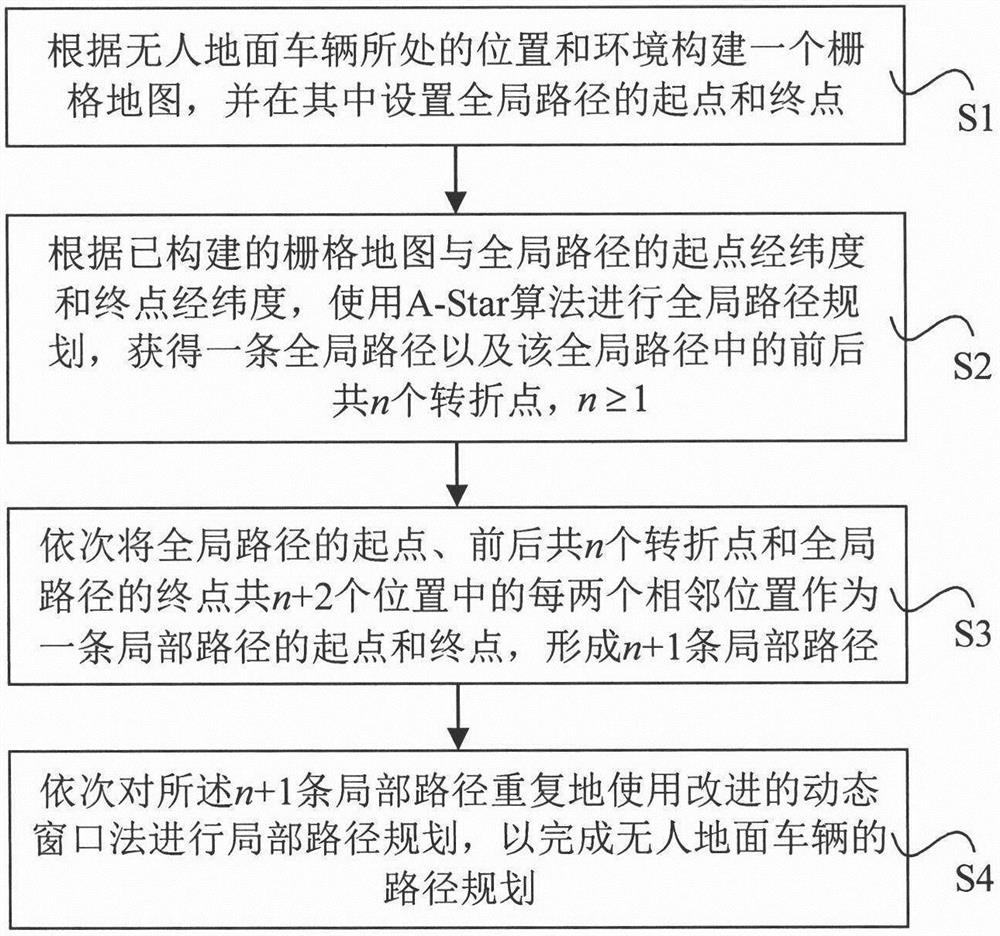
Unmanned ground vehicle path planning method based on improved dynamic window method
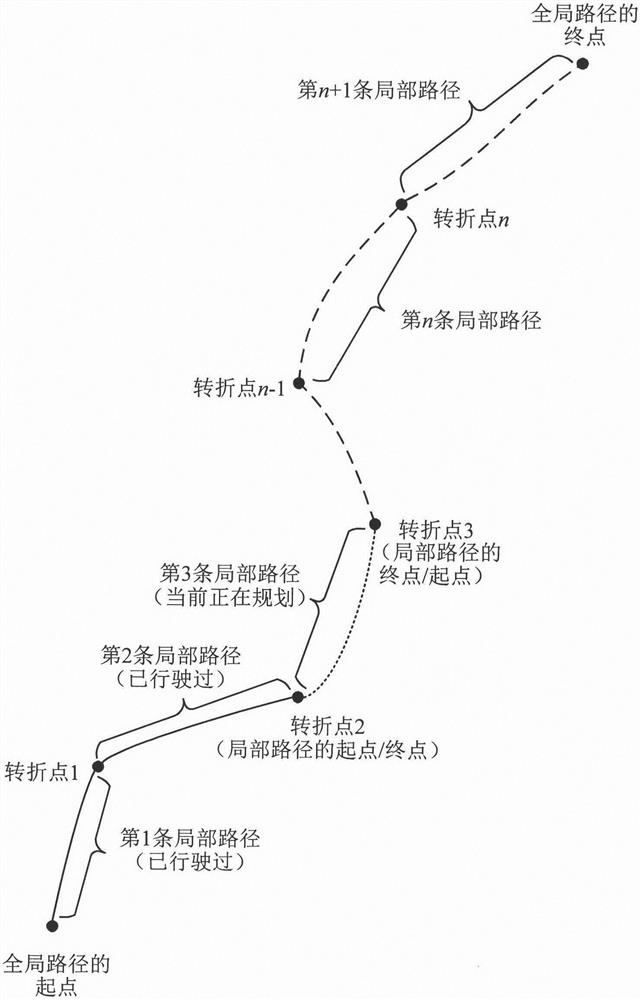
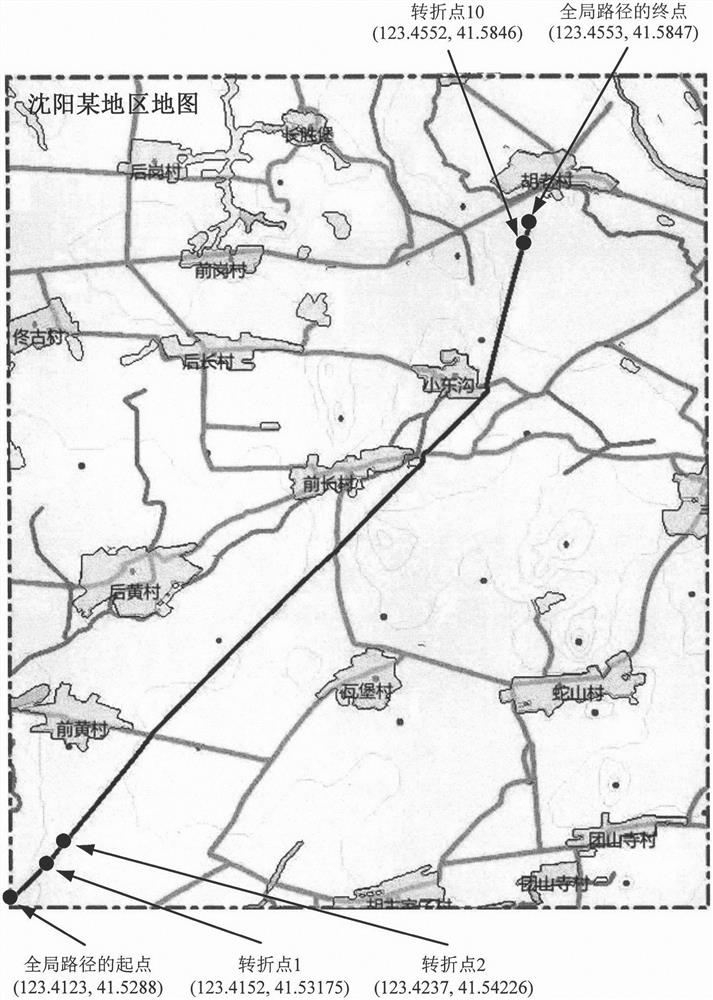
InactiveCN113156964AReduce path planning timeGlobal path smoothingPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesSimulationGround vehicles
The invention discloses an unmanned ground vehicle path planning method based on an improved dynamic window method, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a grid map according to the position and environment of an unmanned ground vehicle, and setting a starting point and an ending point of a global path in the grid map; according to the constructed grid map and the starting point longitude and latitude and the terminal point longitude and latitude of the global path, using an A-Star algorithm for global path planning, and obtaining a global path and n front and back turning points in the global path, wherein n is larger than or equal to 1; sequentially taking every two adjacent positions in n+2 positions including the starting point of the global path, the n front and back turning points and the ending point of the global path as the starting point and the ending point of one local path to form n+1 local paths; and repeatedly performing local path planning on the n+1 local paths in sequence by using an improved dynamic window method so as to complete path planning of the unmanned ground vehicle. According to the technical scheme, a short and smooth global path can be planned for the driving of the unmanned ground vehicle, the path planning time is short, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
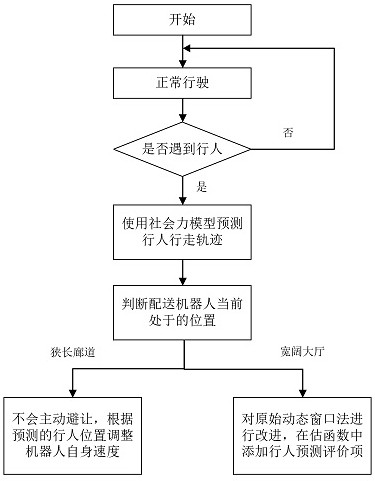
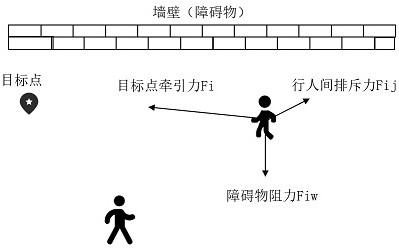
Mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on pedestrian prediction
PendingCN114296455AAvoid the pitfalls of local optimaImprove the effect of dynamic obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationReal-time computing
The invention discloses a mobile robot obstacle avoidance method based on pedestrian prediction, and the method refers to a thought that people can analyze the movement trend of moving obstacles when facing the moving obstacles, and then carry out the avoidance in advance. The moving robot is divided into a long and narrow corridor section and a wide hall section according to different scenes in the running process of the moving robot, when the robot encounters pedestrians in front, a social force model is used for predicting the walking track of the robot in the next period of time, an inactive avoiding mode is adopted in the long and narrow corridor section, and the speed of the robot is adjusted according to the predicted positions of the pedestrians; when the pedestrian is located in a hall section, an active avoidance strategy is adopted, a dynamic window method (DWA) is improved, and an evaluation item for predicting the direction of the pedestrian is newly added in an original evaluation function, so that the improved algorithm can avoid the position to which the pedestrian wants to walk in advance. According to the mobile robot obstacle avoidance method provided by the invention, the walking intention of the pedestrian is added to the obstacle avoidance decision of the robot, and the dynamic obstacle avoidance efficiency of the mobile robot is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A layered obstacle avoidance method for unmanned boats based on improved fruit fly optimization and dynamic window method
ActiveCN111580518BEffective dodgeAvoid local optimaPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocal optimumMaritime navigation
The invention relates to the field of autonomous navigation of unmanned boats, and in particular, to a layered obstacle avoidance method for unmanned boats based on improved fruit fly optimization and dynamic window methods. The invention includes: step S1: establishing a geographical environment model for maritime navigation of unmanned boats based on electronic charts; step S2: using an improved fruit fly optimization algorithm to complete global optimal path planning; step S3: establishing an environmental model of dynamic obstacles; Step S4: Use the improved dynamic window method to avoid moving obstacle ships. The present invention provides an obstacle avoidance method that switches between dynamic and static obstacle avoidance modes based on judgment conditions, which can effectively avoid obstacles during navigation, avoid the algorithm from falling into the local optimal solution, and adopt fuzzy control methods to determine the optimal trajectory. The weight parameters are dynamically controlled to improve the accuracy and efficiency of trajectory prediction.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A multi-AUV adaptive target search and obstacle avoidance method for unknown environments
ActiveCN108594834BEnsure positioning accuracyImprove search coverageAltitude or depth controlArtificial intelligenceControl theory
The invention discloses a multi-AUV self-adaptive target searching and obstacle avoidance method oriented to an unknown environment, and the method is suitable for multi-AUV target searching under anunknown complex underwater environment. The method is mainly divided into three modes including a target mode, a non-target mode, and an obstacle avoidance mode. In the target mode, the self-adaptivesearching is achieved through dynamic real-time prediction according to the target information for sensing the outside; in the non-target mode, full-area coverage searching and collaborative planningtasks are achieved through a sub-area strategy; and in the obstacle avoidance mode, the barrier threat is avoided in real time based on the improved dynamic window method. According to different underwater environment information, a multi-AUV target searching task is executed through alternate mode switching among the three modes, and the uncertain information under the unknown water can be dealtwith, the credible interval of the target state information is guaranteed, and environment adaptability and searching efficiency are achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Robot movement method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112526991BInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsSimulationComputer vision
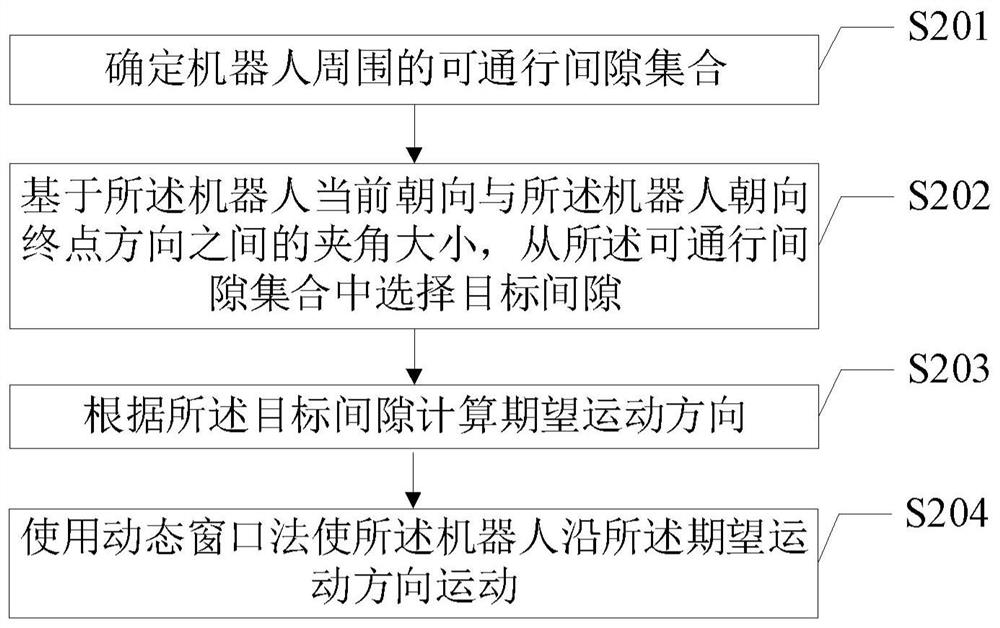
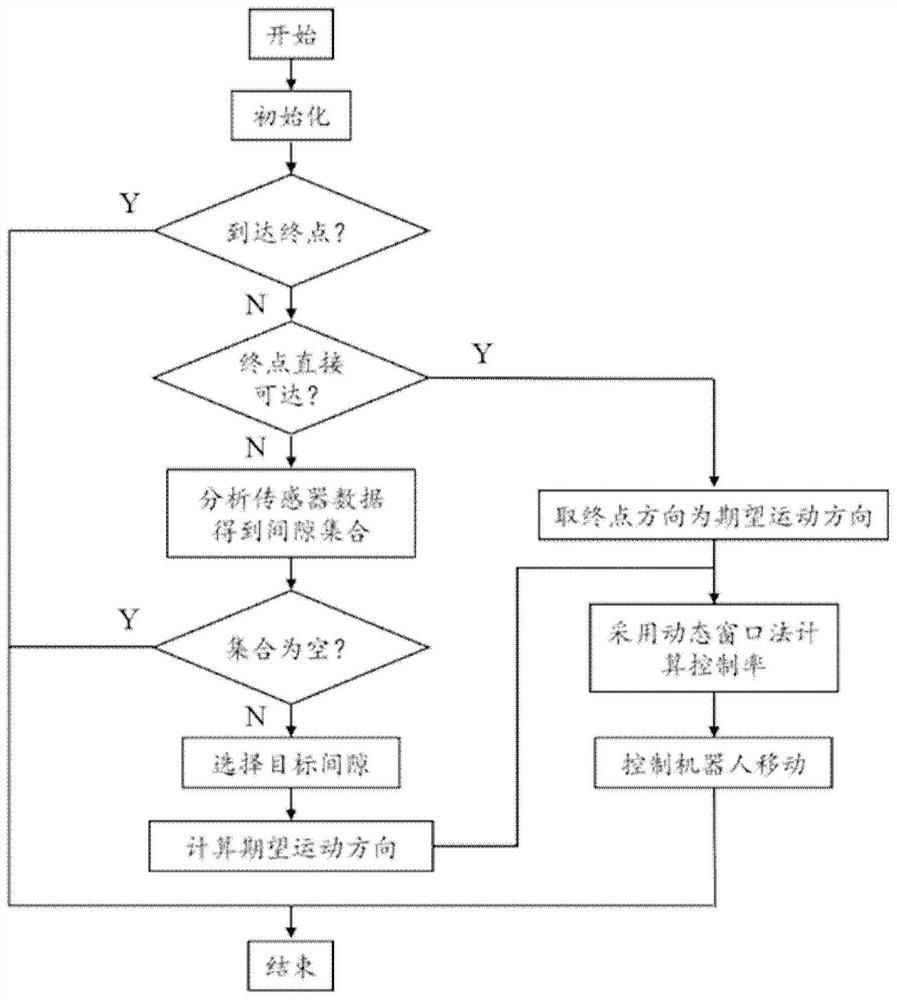
The present disclosure provides a robot movement method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium used in an unknown environment, which are applied in the field of robotics, including: determining a set of passable gaps around the robot; based on the current orientation of the robot and the robot Select the target gap from the set of passable gaps toward the angle between the end directions; calculate the expected motion direction according to the target gap; use the dynamic window method to make the robot move along the desired motion direction. Make the robot move along the edge of the obstacle, make the robot be guided by the obstacle, and get rid of the local minimum.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
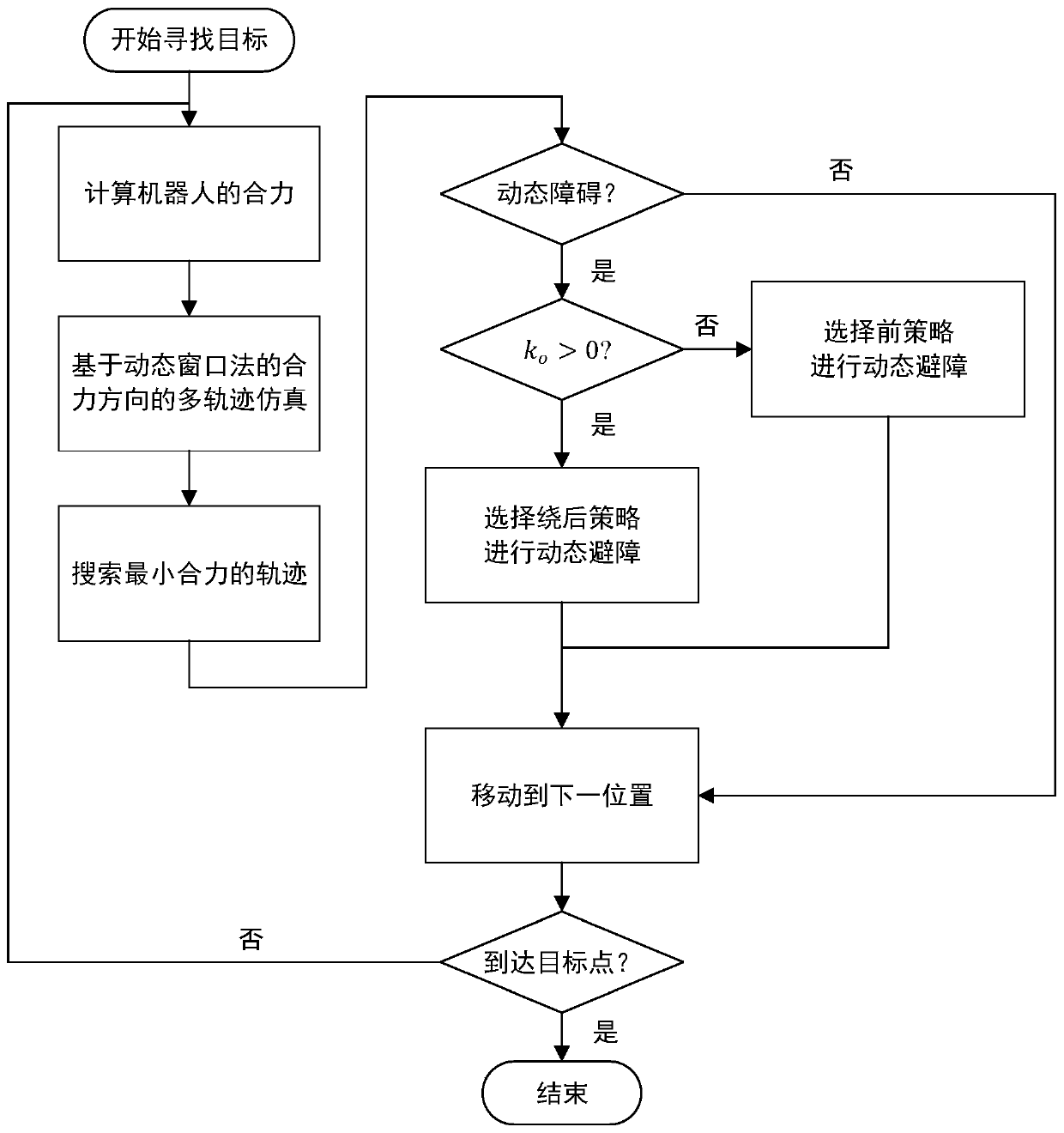
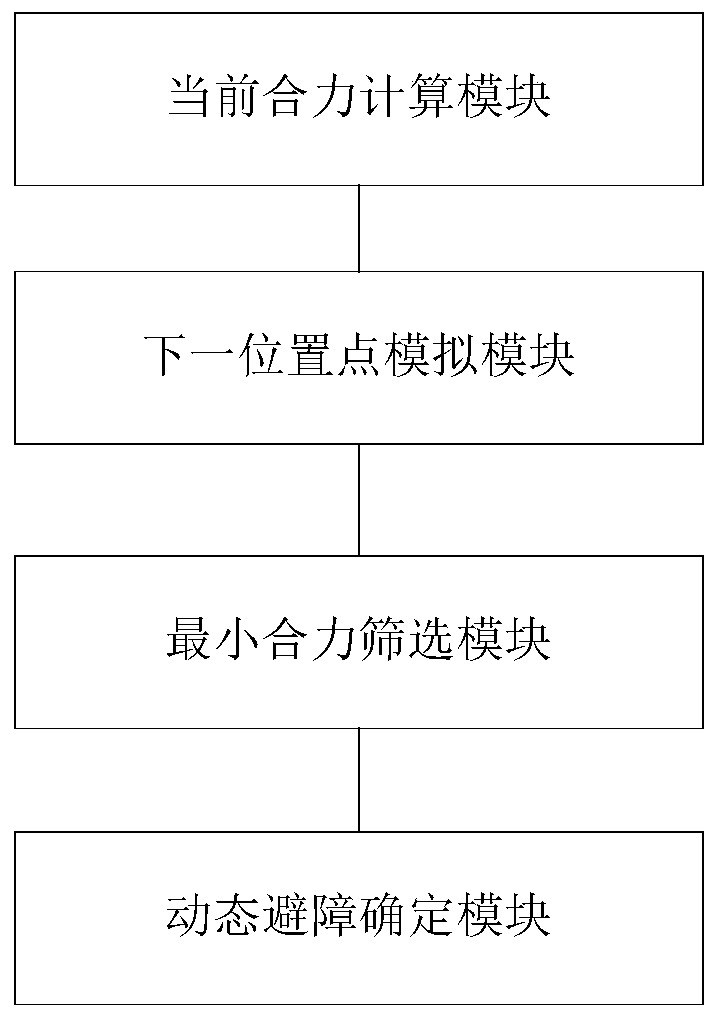
A dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method, controller and robot
ActiveCN109163728BImprove effectivenessProgramme-controlled manipulatorNavigational calculation instrumentsAnalog robotSimulation
The invention provides a dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method, a controller and a robot. The dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method comprises the steps of calculating a resultant forcesuffered by the robot at the current position, simulating next position points in multiple directions of the resultant force suffered by the robot at the current position based on a dynamic window method, determining the position point with the minimum resultant force from the next position points as a next movement position point of the robot, constructing a local map of the robot, controlling the robot to start dynamic obstacle avoidance if a dynamic obstacle enters the local map of the robot, or else, allowing the robot to move to the next position point till a target point is reached.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Vehicle obstacle avoidance method and electronic equipment based on binocular vision and deep learning
ActiveCN113255520BDrivabilitySignificant effect on obstacle detectionImage enhancementImage analysisRgb imageControl system
The invention discloses a vehicle obstacle avoidance method based on binocular vision and deep learning: obtain the RGB image in front of the vehicle; obtain the depth information map in front of the vehicle; predict and obtain the drivable area segmentation result; information fusion optimizes the drivable area; The depth information of the drivable area is used to generate the main view of depth obstacles; the distribution of obstacles in the three-dimensional space in front of the car is obtained, and the bird's-eye view obstacle scatter diagram is obtained accordingly; the bird's-eye view obstacle scatter diagram is density clustered to remove noise; The bird's-eye view obstacle scatter map performs Euclidean distance transformation and sets an adaptive threshold, and divides the front map into safe driving areas and dangerous areas; constructs a map for path planning through the bird's-eye view safe driving area map and field angle boundary information; uses dynamic The window method combines the map used for path planning to plan the obstacle avoidance path; calculate the expected speed and expected angle according to the obstacle avoidance path trajectory and send it to the control system. The invention also provides corresponding electronic equipment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A robot, navigation method thereof, and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveCN106969770BNavigation implementationFix local navigation issuesNavigational calculation instrumentsAlgorithmControl signal
The invention discloses a robot, its navigation method, and a computer-readable storage medium. The method includes the steps of: acquiring the target position information of the robot and the two-dimensional point distribution of its current direction; distribution, determine the multidimensional eigenvalue s of the robot; according to the determined multidimensional eigenvalue s of the robot and the θ value obtained by the machine learning method, use the model a=f(s,θ) to calculate the control signal a of the robot; according to the calculated The control signal a of the robot realizes the navigation of the robot. The robot, its navigation method, and computer-readable storage medium disclosed in the present invention use the model a=f(s,θ) to calculate the control signal a of the robot by using the value of θ obtained by the machine learning method, and then realize the navigation of the robot; compared with the current State-of-the-art local navigation algorithms such as DWA (Dynamic Window Approach) and TEB (Timed Elastic Band) can effectively solve the problem of robot local navigation, and the method runs smoothly and has improved efficiency compared with existing algorithms.
Owner:深圳中智卫安机器人技术有限公司
A local path planning algorithm and device
ActiveCN111813100BReduce the situation of falling into local minimum pointsImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsPathPingAlgorithm
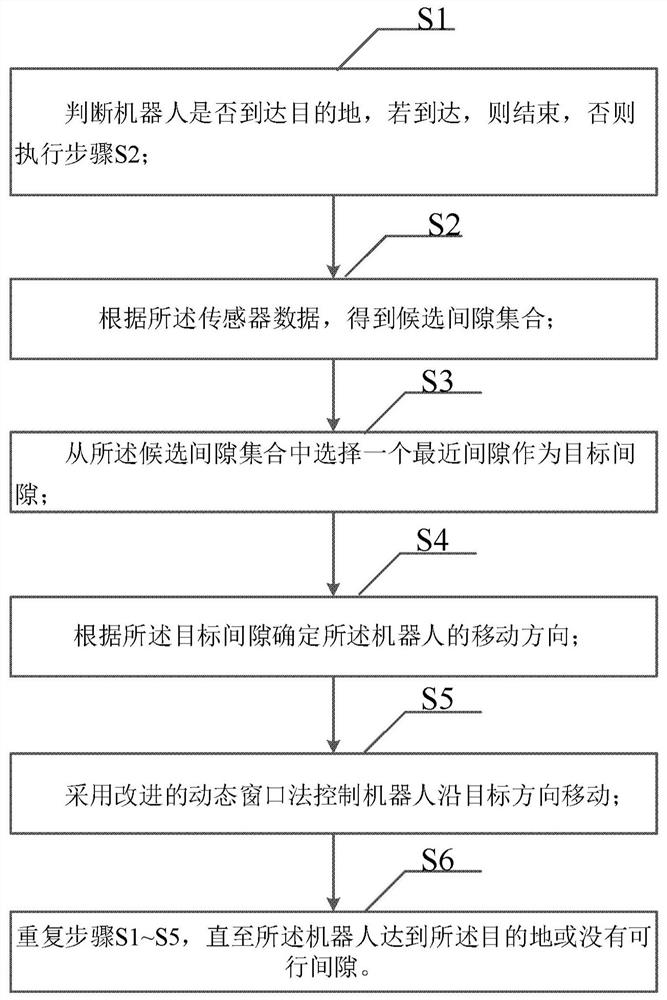
A local path planning algorithm and device, used for path planning of a mobile device, the mobile device is loaded with a sensor, the algorithm includes: S1, judging whether the mobile device has reached the destination, if it has reached the destination, end, otherwise, execute step S2; S2, according to Sensor data, get the candidate gap set; S3, select a nearest gap from the candidate gap set as the target gap; S4, determine the moving direction of the mobile device according to the target gap; S5, use the improved dynamic window method to control the mobile device to move along the target direction ; S6, repeating steps S1-S5 until the mobile device reaches the destination or there is no feasible gap. Gap-based and improved dynamic window methods are used to plan mobile device paths to reduce local extrema and improve obstacle avoidance performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
An Obstacle Avoidance Method Based on Dynamic Window and Virtual Target Point
ActiveCN107885209BSafe and efficient to avoidImprove work efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesVirtual targetSimulation
The obstacle avoidance method based on dynamic windows and virtual target points uses virtual target points to guide the robot forward, and combines the dynamic window to issue movement instructions to the robot, allowing the robot to avoid obstacles and reach the target point. First, the robot predicts the trajectory of the obstacle based on the angle and distance information about the obstacle fed back from its sensor; then, based on the trajectory prediction of the obstacle, it combines the robot's motion state with the location of the real target point to generate multiple virtual targets. point, and comprehensively considers the robot's orientation and the distance between the virtual target point and the real target point through the evaluation function to select the optimal virtual target; finally, the robot uses the dynamic window method based on the trajectory prediction of the obstacles and the position of the virtual target point. Generate the control instruction set for the robot at the next moment, and comprehensively consider the robot's orientation, running speed, and distance from the target point through the evaluation function to select the optimal control instruction for the robot at the next moment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
An Intelligent Path Planning Method for Mobile Robots
ActiveCN112631294BImprove real-time obstacle avoidance abilityImproved heuristic functionNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsGlobal planningEngineering
The invention discloses an intelligent path planning method for a mobile robot. A static two-dimensional grid map is established, and an improved ant colony algorithm is used for global path planning; a sensor module of a mobile robot detects unknown obstacle information, and calculates obstacle motion trajectories and robot motion trajectories. , using the optimized dynamic window method for local dynamic obstacle avoidance, with the current position of the robot as the starting point, and the nearest key node on the global planning path as the temporary target point for dynamic obstacle avoidance; the robot drives along the planned path and reaches the destination safely. The present invention comprehensively considers the actual problems of static obstacles and dynamic obstacles in the map environment, improves the heuristic function of the ant colony algorithm, adjusts the pheromone update rules for global path planning, and adopts optimized The dynamic window method is used to avoid obstacles and complete local path planning. The robot has relatively high practicality and research value when running on the actual map.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
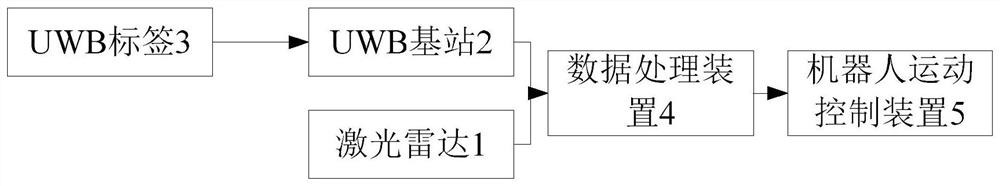
Pedestrian following system and method based on uwb and lidar hybrid positioning
ActiveCN107765220BFollow exactlyHigh precisionPosition fixationElectromagnetic wave reradiationMedicineComputer vision
The invention provides a pedestrian following system and method based on UWB and laser radar hybrid positioning. The method is characterized in that by carrying out initial positioning and identification on a pedestrian through UWB, and then, carrying out accurate positioning and identification on the pedestrian through laser radar, effective obstacle avoidance is achieved, and accurate tracking and positioning of the pedestrian under a complex environment are met; obstacle avoidance is realized through a dynamic window method, so that precision is higher; and movement of a robot is subjectedto filtering processing through Kalman filtering, so that stability is higher.
Owner:宁波科森智能装备有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com