A local path planning algorithm and device
A local path planning and algorithm technology, applied in two-dimensional position/course control, vehicle position/route/height control, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not directly eliminating speed, robot obstacle collision, robot falling into local minimum, etc. problem, to reduce the effect of falling into local minimum points
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clearly understood, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
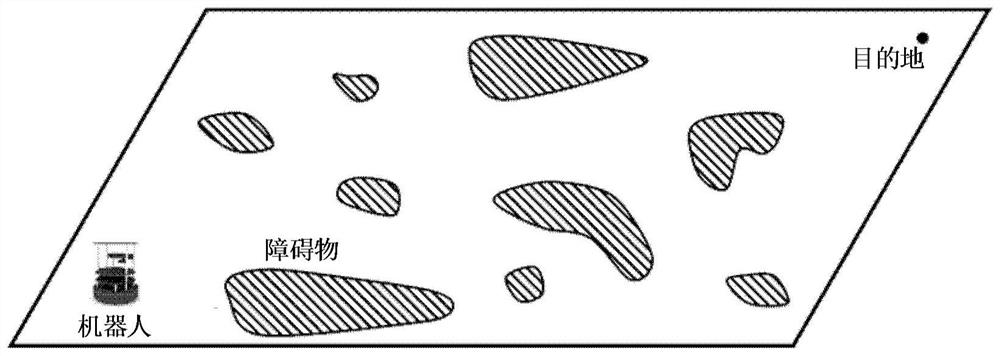
[0028] The mobile device will be loaded with 360-degree scanning sensors, such as lidar, to sense the local environment. In this embodiment of the present invention, the mobile device is a robot as an example to describe the solution in detail. When the robot moves on the ground, the surrounding environment Often there are many disjointed obstacles (such as figure 1shown), so the robot needs to effectively avoid these obstacles and reach the destination during the movement process.
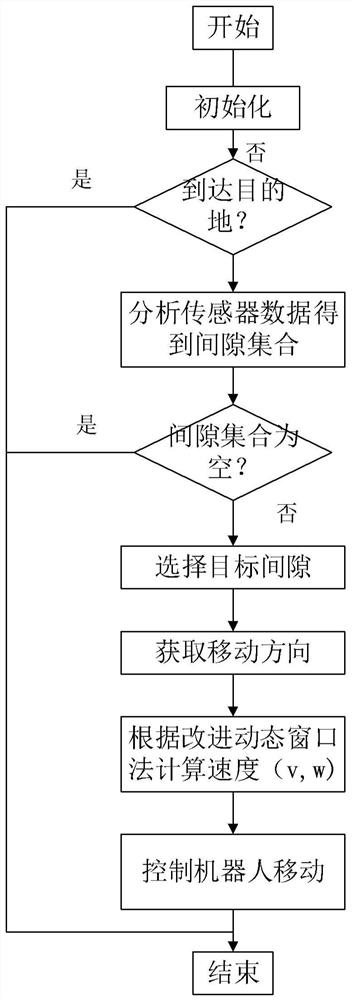
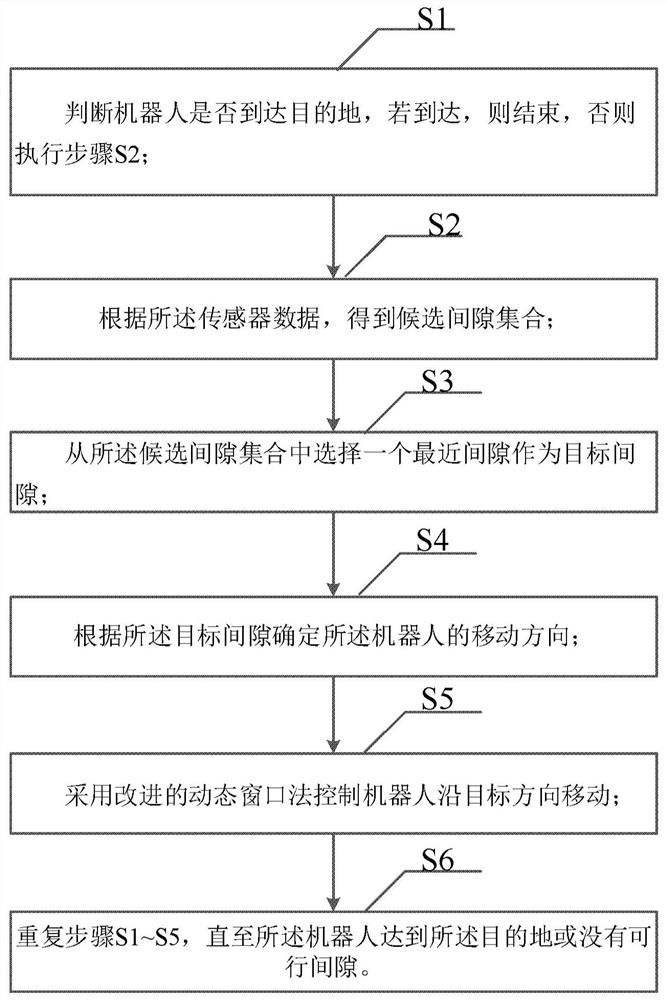
[0029] In a first aspect, the present invention provides a local path planning algorithm for path planning of a mobile device, the mobile device is loaded with sensors, see figure 2 and image 3 , the algorithm includes: S1, judging whether t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com