Automatic registration method for large scale three dimension scene multiple view point laser scanning data
A 3D scene and laser scanning technology, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of low accuracy of pose parameters, less memory usage, and large amount of calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] 1) Data acquisition
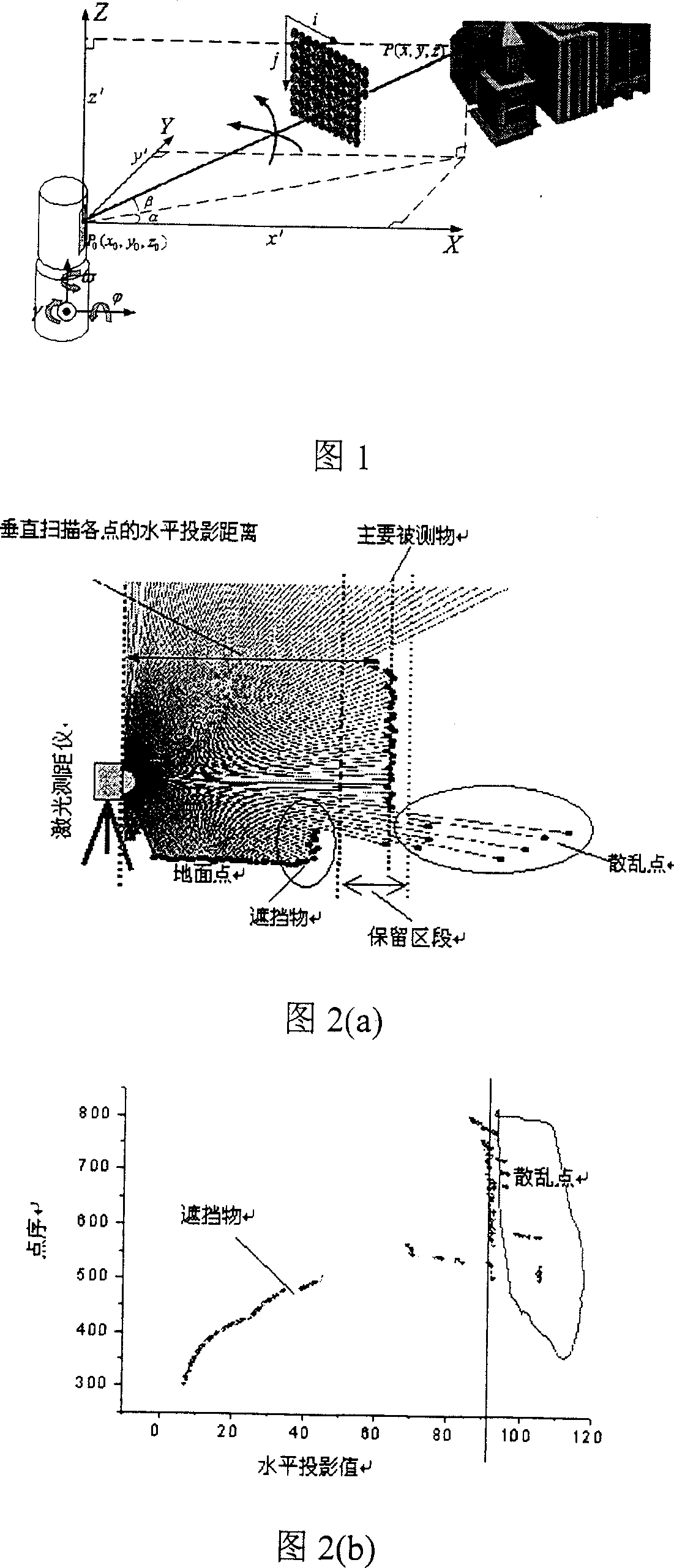
[0073] The laser rangefinder is placed 20-50 meters in front of the measured scene, adjust the rangefinder so that the Z axis is perpendicular to the ground, and the X and Y axes are parallel to the ground, and scan the measured scene row by row (as shown in Figure 1), and obtain The 3D data corresponding to the viewpoint In addition, the scanning data of adjacent viewpoints maintain an overlap of 10% to 20%, so that the 3D data of each viewpoint can be registered smoothly
[0074] 2) Extract the main building structure
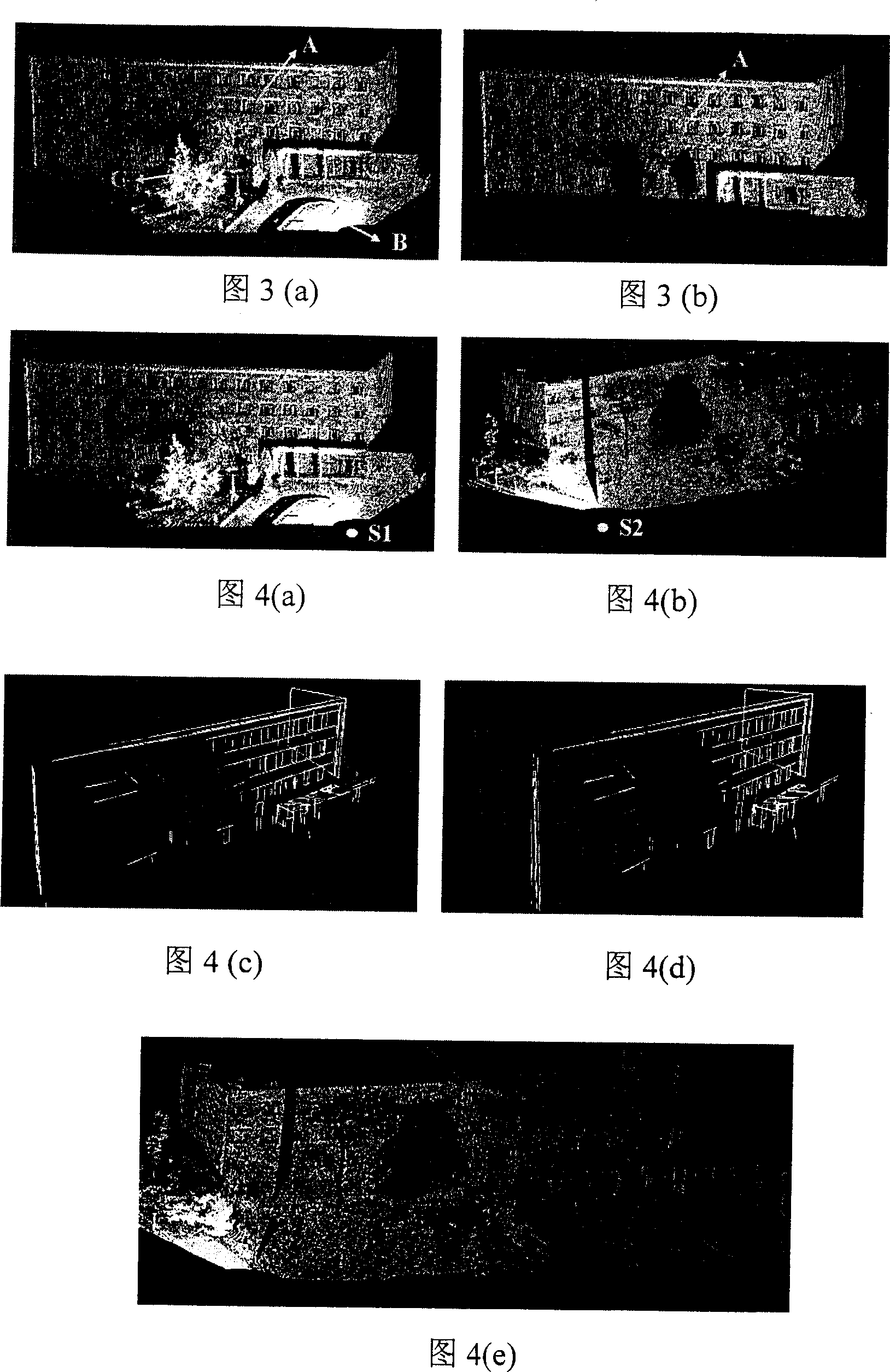
[0075] Input the laser scanning data corresponding to each viewpoint, calculate the horizontal distance between each point on each vertical scanning surface and the laser range finder, and use the Hough transform to detect the vertical line segment according to the horizontal distance (as shown in Figure 2(a) and Figure 2(b) )] Calculate the length of the vertical line based on the number of points it contains, and select the hor...
Embodiment 2
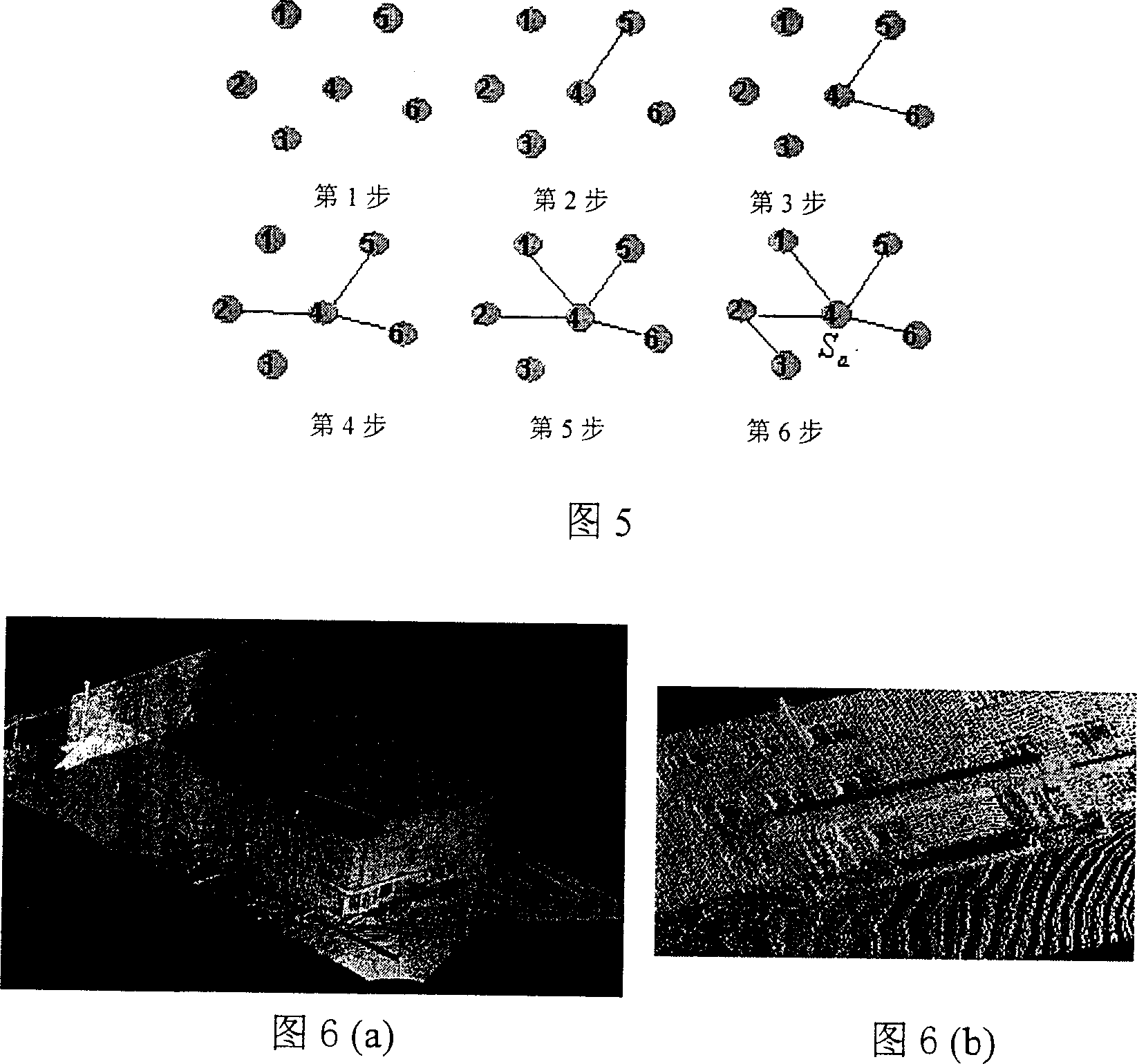
[0123] In order to use the method of the present invention to automatically register the laser scanning data of 8 viewpoints in a large-scale three-dimensional scene to the student restaurant, its steps 1)-5) are the same as in Embodiment 1, except that: since the number of viewpoints exceeds 2, it is necessary to Perform global registration;
[0124] First, all viewpoints (with overlapping areas) are pairwise registered, and a global registration model is established using the minimum spanning tree principle, and then a viewpoint S is selected according to the global registration model a Fixed, laser scan data conversion for other viewpoints in S a in the coordinate system
[0125] Specifically, the transformation matrix T can be calculated for each pair of two viewpoints with overlapping areas i =[R i , t i ] and local matching degree g(T i ) (counted by the number of registered points) with each viewpoint as a node, with g(T i ) is the connection weight of the node, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com