Self-tracking filter
A filter and self-tracking technology, applied in impedance networks, digital technology networks, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate zero-crossing detection, inaccurate counting of track crossings, and missed zero-crossings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] Embodiment of the invention
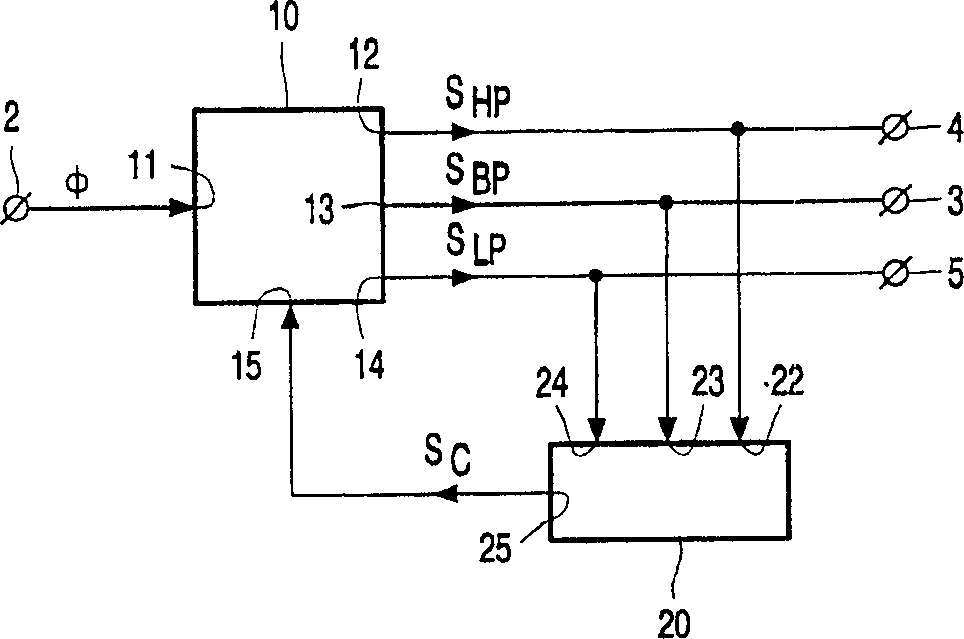
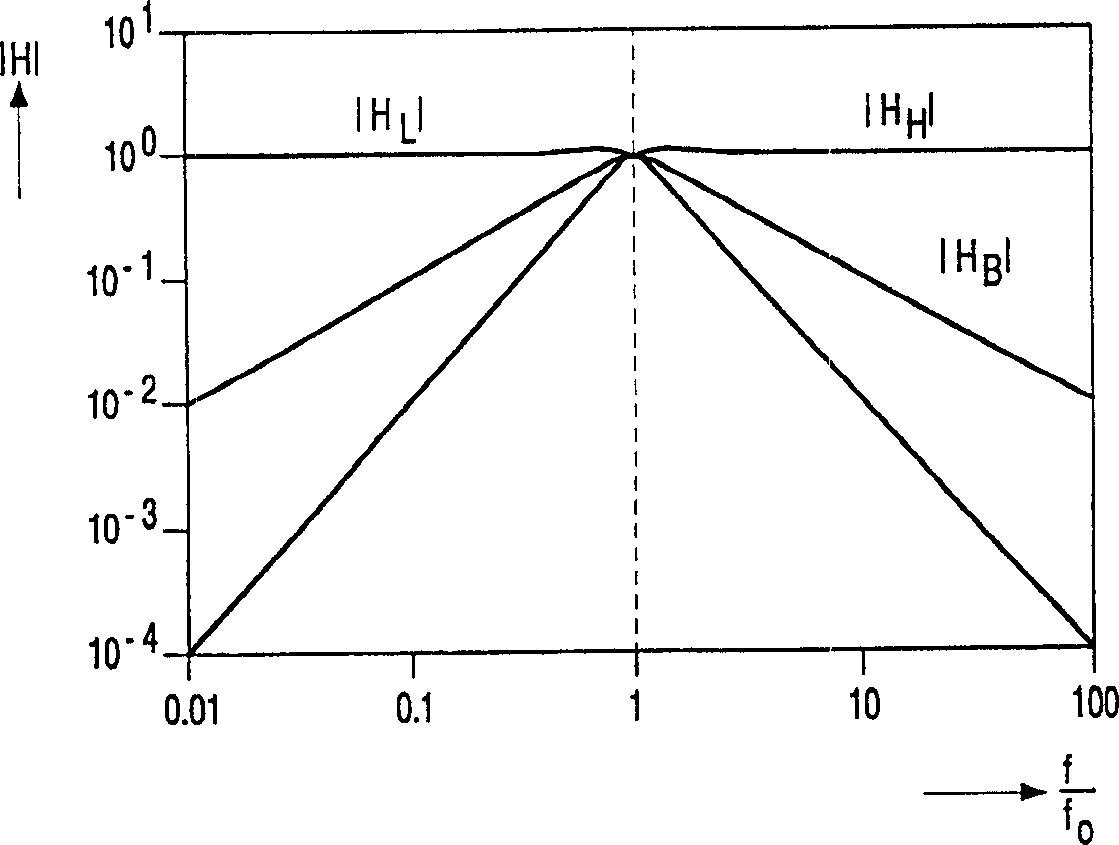
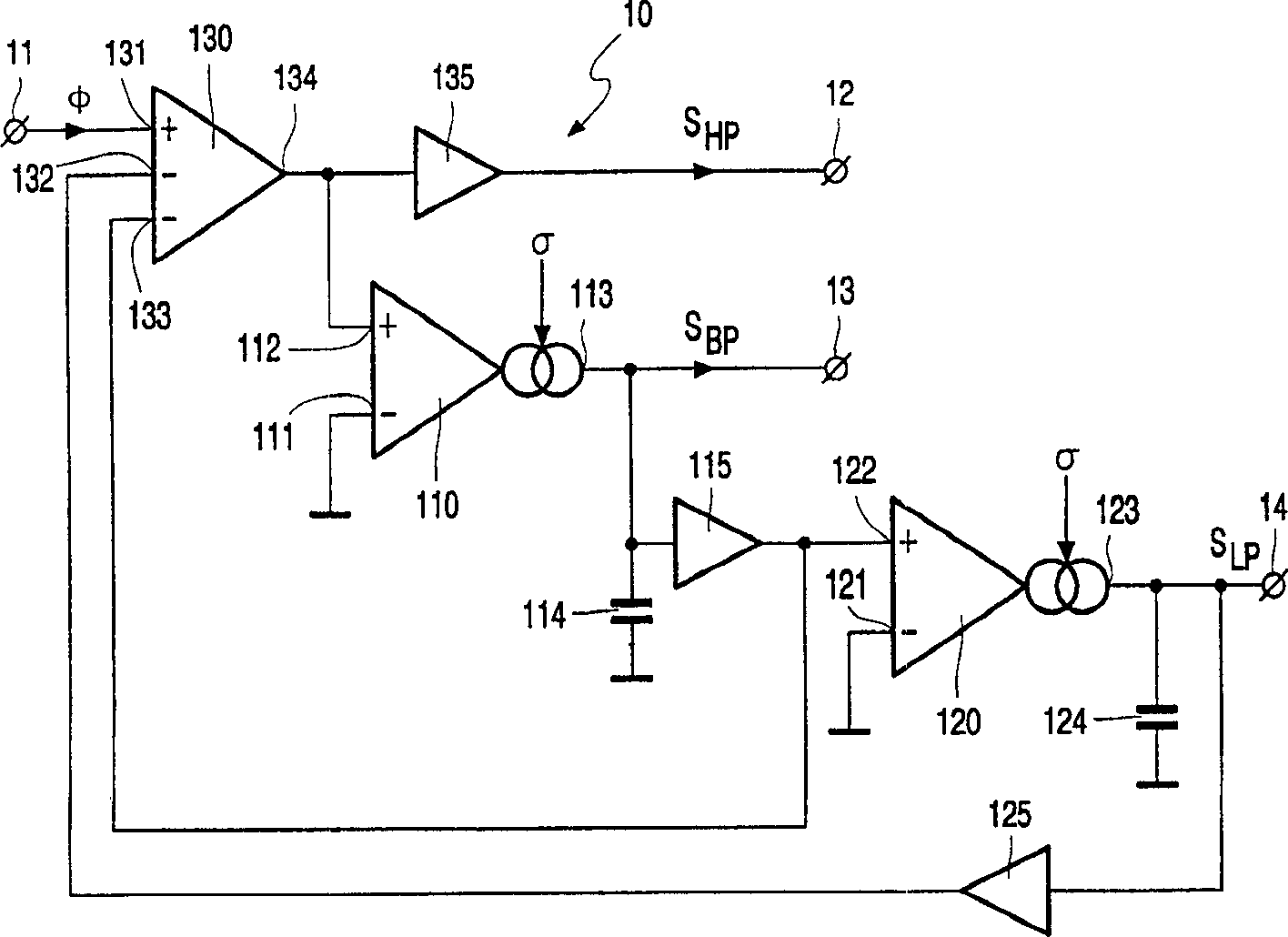
[0028] figure 1 A block diagram of a self-tracking bandpass filter 1 with a signal input 2 and a filtered signal output 3 according to the invention is schematically shown. A self-tracking band-pass filter 1 consists of a high-pass signal S HP , bandpass signal S BP and low-pass signal S LP A high-pass output 12, a band-pass output 13, and a low-pass output 14 of a controllable filter 10. The controllable filter 10 also comprises a signal input 11 coupled to the signal input 2 of the self-tracking bandpass filter 1 for receiving the signal φ to be filtered, and a control input 15 for receiving the control signal Sc. The self-tracking bandpass filter 1 also includes a control unit 20 whose signal inputs 22, 23, 24 receive the above-mentioned output signal S from the controllable filter 10 respectively. HP , S BP and S LP And on the basis of these received signals a control signal Sc for controlling the controllable filter 10 is genera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com