Photo transmitting device
An optical transmission and light source technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, time-division optical multiplexing systems, etc., can solve problems such as increased loss, increased cost, and difficulty in miniaturization, and achieve the effect of reducing optical loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
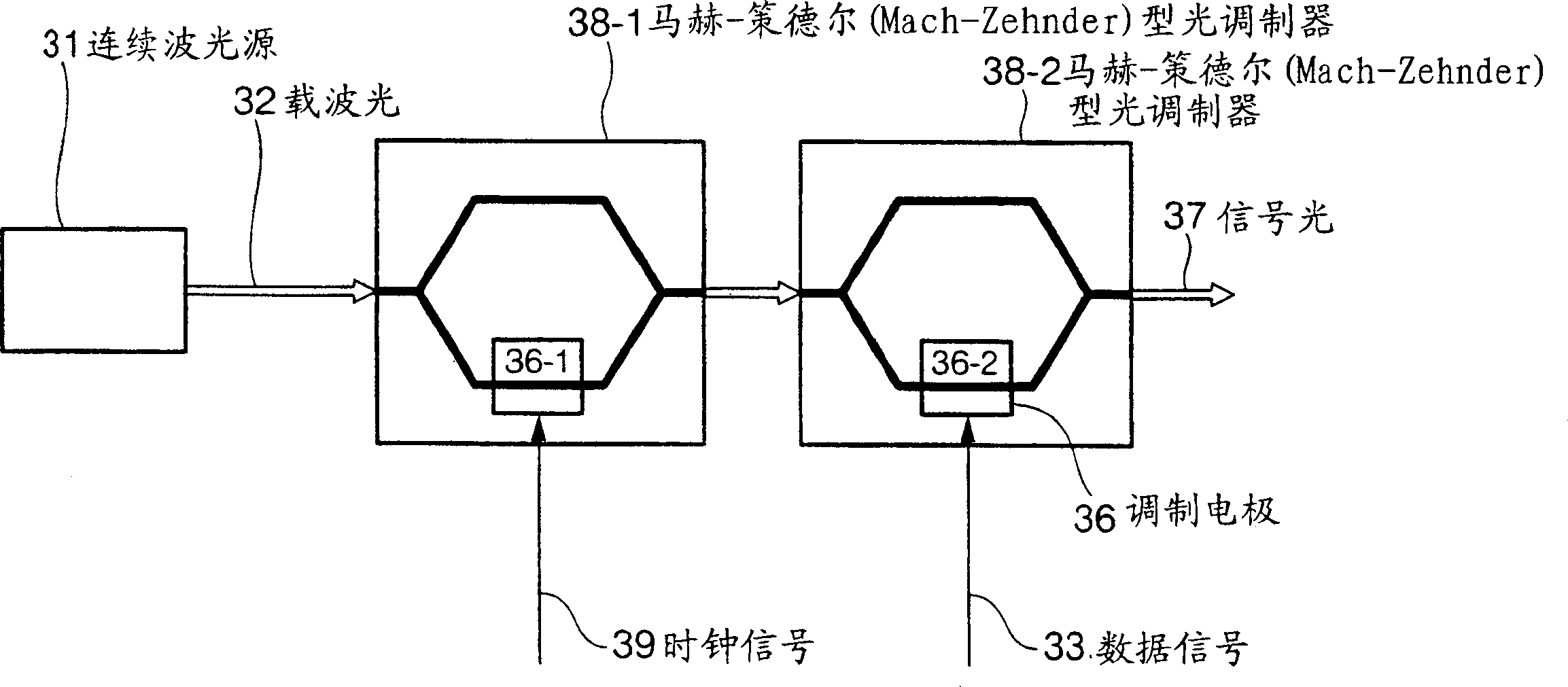
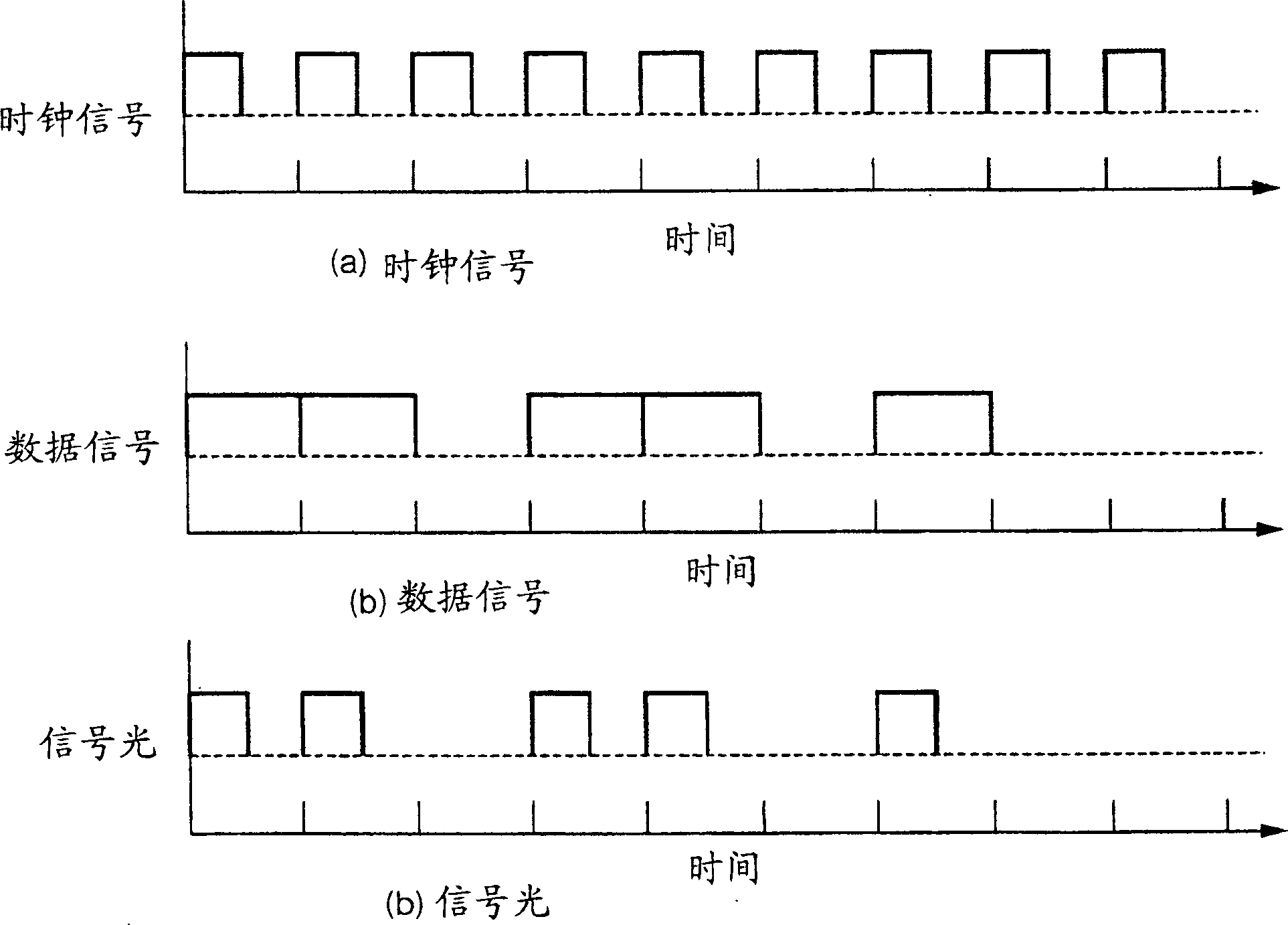
[0083] Figure 7An embodiment of the invention according to claim 1 is shown. The optical sending device includes: a continuous wave light source 11 outputting carrier light; a Mach-Zehnder optical modulator 18 with N (N is an integer greater than 2) modulation electrodes 16-1 to 16-N; The data signal is transformed into N return-to-zero transformation circuits 14-1~14-N of RZ encoding; the delay circuits 15-1~15-( N-1); As a component that provides a half-wavelength phase difference between the same arms to the input light of the interferometric light modulator, a bias of Vπ is applied to the arm of one side of the Mach-Zehnder type light modulator 18 Set circuit 10. Here, A is the frequency (Hz) of the signal velocity of the signal light 17, k is an integer from 1 to N-1, and Vπ is a driving voltage for shifting the phase of the input light by half a wavelength. Here, the bias circuit 10 is arranged on the arm on which the data signal is modulated, but it may also be arra...
Embodiment 2
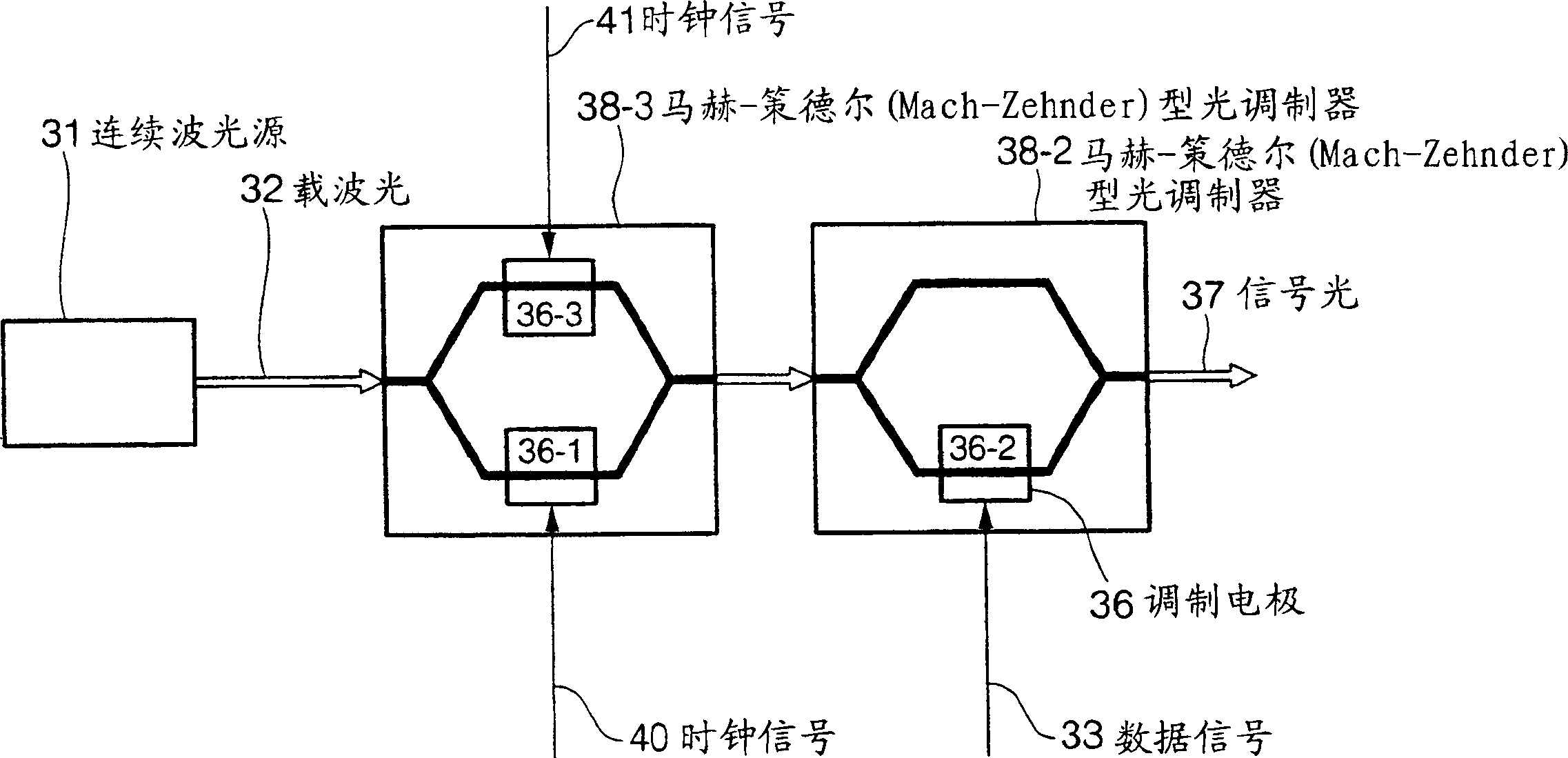
[0091] Figure 12 An embodiment of the invention according to claim 2 is shown. The optical sending device includes: a continuous wave light source 11 outputting carrier light; a Mach-Zehnder optical modulator 18 with N (N is an even number above 2) modulation electrodes 16-1 to 16-N; The data signal is transformed into N return-to-zero transformation circuits 14-1~14-N of RZ encoding; the delay circuits 15-1~15-( N-1); a signal polarity inversion circuit 19 for inverting the polarity of the even-numbered data signal. Here, A is the frequency (Hz) of the signal velocity of the signal light 17, and k is an integer from 1 to N-1. Here, the signal polarity inversion circuit 19 is arranged for even-numbered data signals, but may be arranged for odd-numbered data signals. The connection order of the signal polarity inversion circuit 19, the delay circuit 15, and the return-to-zero conversion circuit 14 can be interchanged.
[0092] Carrier light 12 from a continuous wave light ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] FIG. 15 shows an embodiment of the invention according to claim 3 . This optical transmission device comprises: a pulse light source 21 outputting pulsed light; a Mach-Zehnder type optical modulator 18 with N (N is an even number above 2) modulation electrodes 16-1 to 16-N; the data coded by NRZ The signal is converted into N return-to-zero conversion circuits 14-1~14-N of RZ code; the delay circuits 15-1~15-(N -1); a signal polarity inversion circuit 19 for inverting the polarity of the even-numbered data signal. Here, A is the frequency (Hz) of the signal velocity of the signal light 17, and k is an integer from 1 to N-1. Here, the signal polarity inversion circuit 19 is arranged for even-numbered data signals, but may be arranged for odd-numbered data signals. The connection order of the signal polarity inversion circuit 19, the delay circuit 15, and the return-to-zero conversion circuit 14 can be interchanged.
[0098] The pulsed light 26 from the pulsed light so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com