Adaptive variable length coding
An encoding and variable technology, applied in image encoding, code conversion, image data processing, etc., to solve the problems of encoder and decoder out-of-synchronization, high computational complexity, and impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
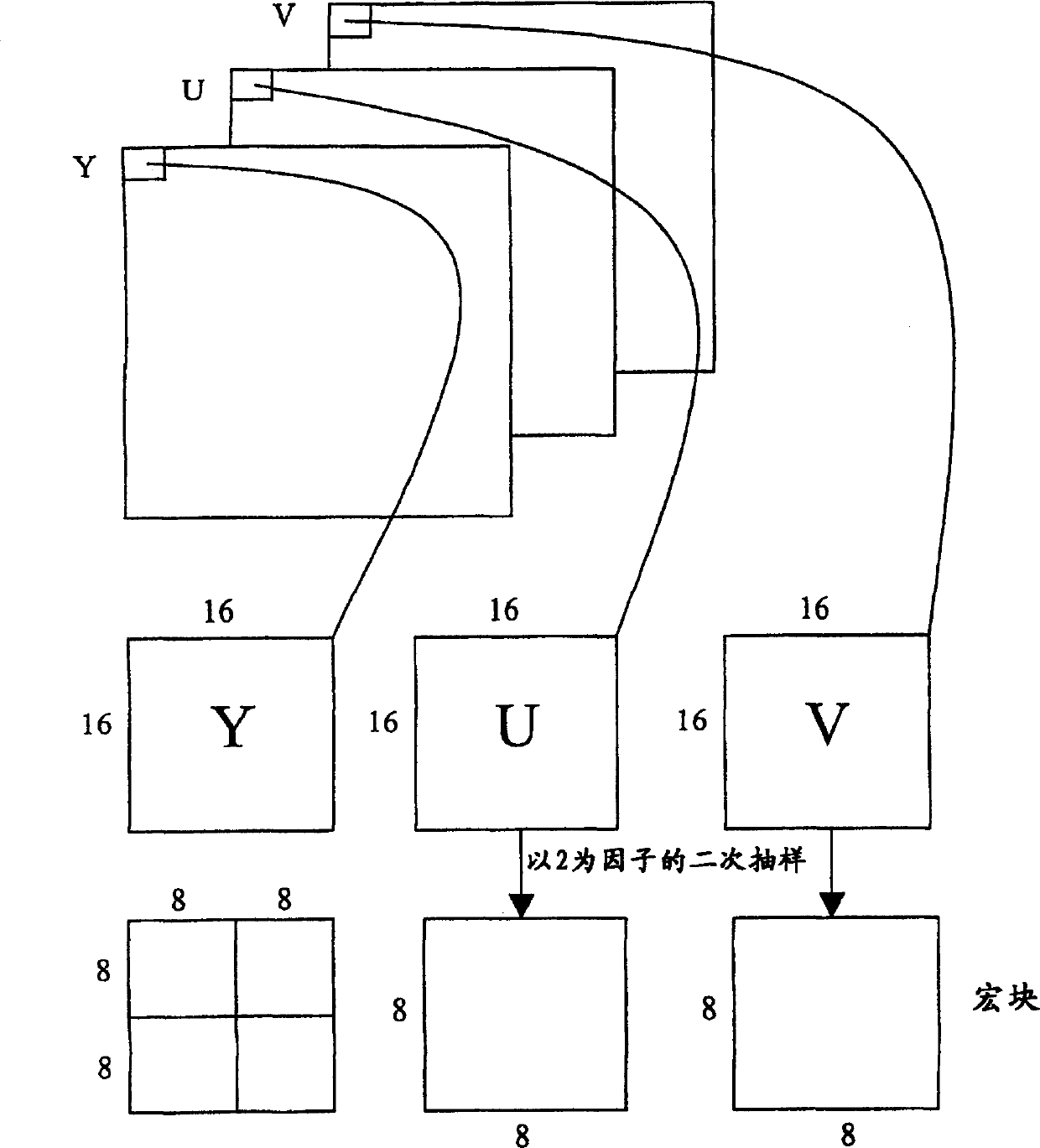
[0099] Exemplary embodiments of the method according to the invention will be presented in the following detailed description of the invention. The exemplary embodiments are concerned with variable length coding of (run, rank) pairs, where the pair denote the block-based transform coding in a video encoder and its subsequent decoding in a corresponding video decoder The resulting non-zero transform coefficients. It should be appreciated, however, that the variable length encoding and decoding method according to the present invention can be applied more generally to other types of data to be encoded.
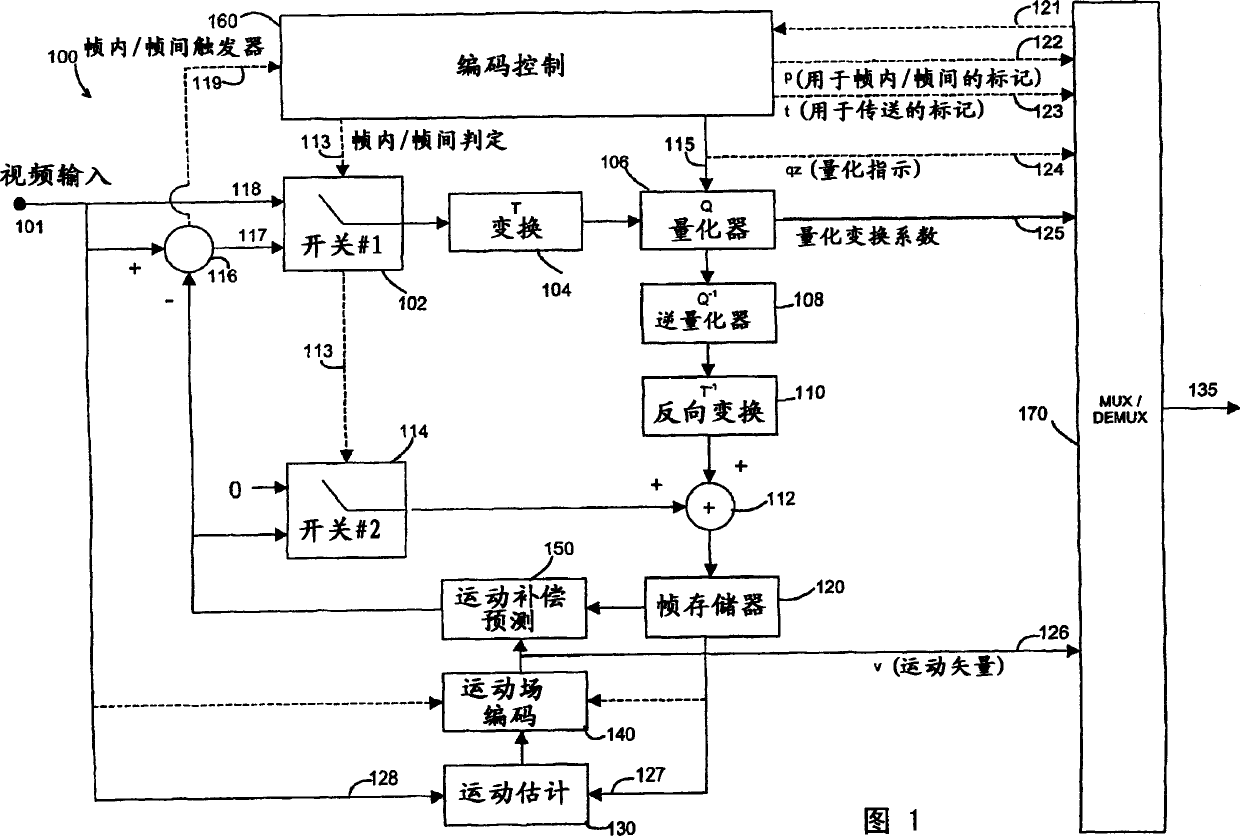
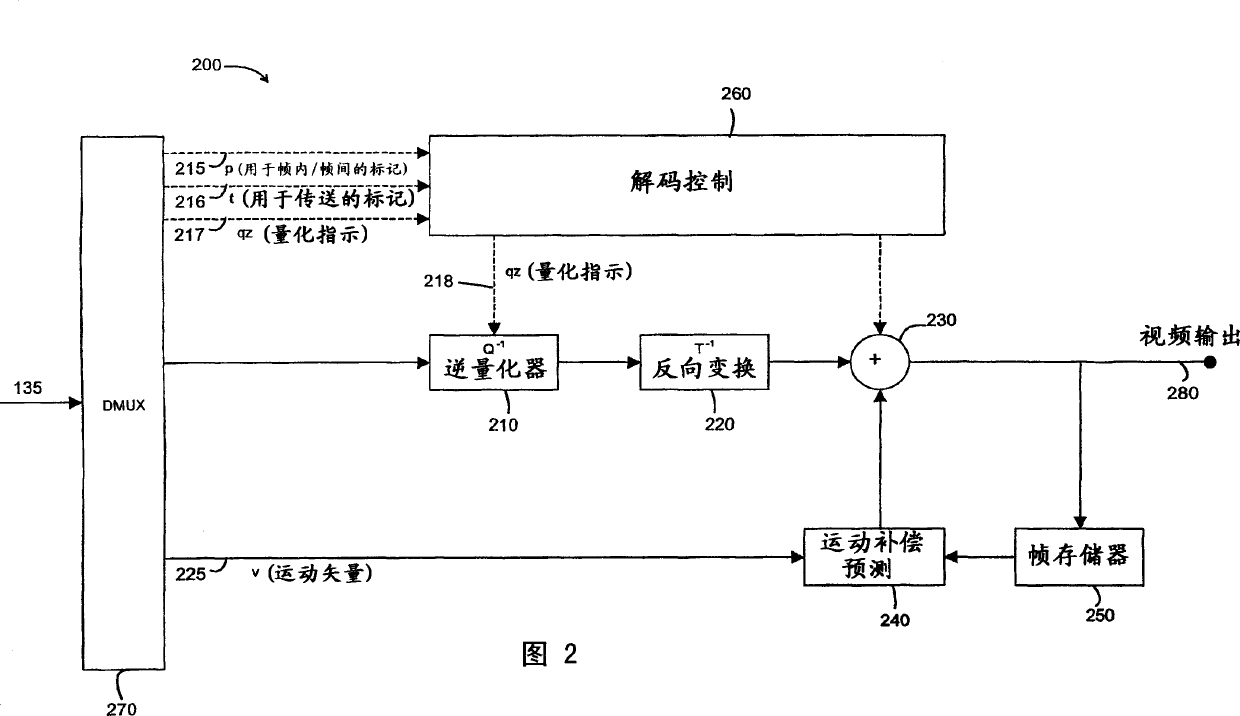
[0100] Fig. 6 is a schematic block diagram of a video encoder 600 to which the method according to this embodiment of the invention can be applied. Actually, the structure of the video encoder shown in FIG. 6 is the same as that of the prior art video encoder shown in FIG. 1, where only the part of the encoder that performs the variable length coding operation is appropriately ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com