Detection of impulse noise using unused spreading codes
A technology of impulse noise and spread spectrum, which is applied in the field of synchronous code division multiple access system, can solve the problems of wrong deletion indication, complex detection problem, recovery error, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
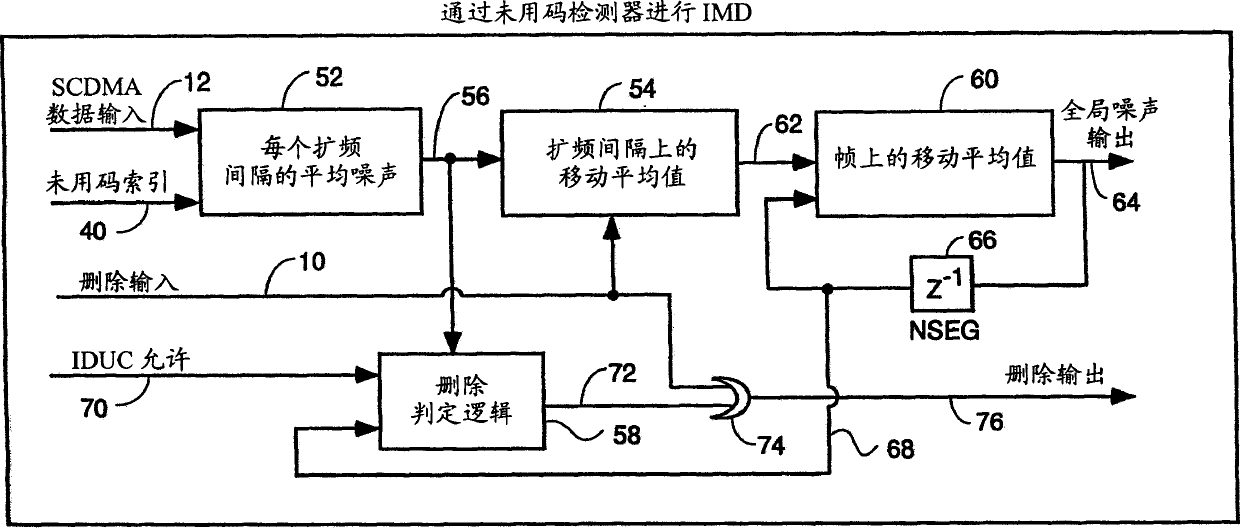
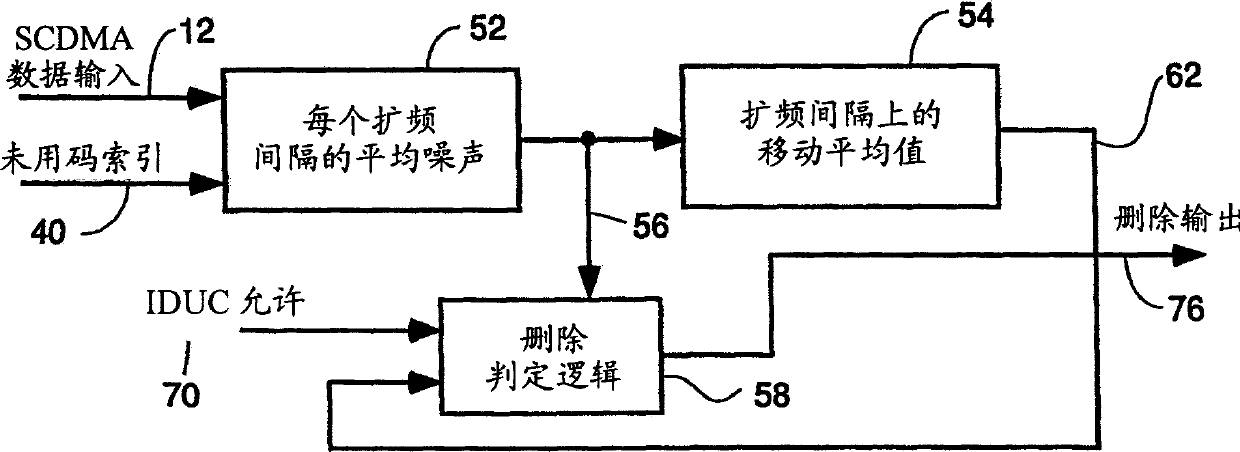
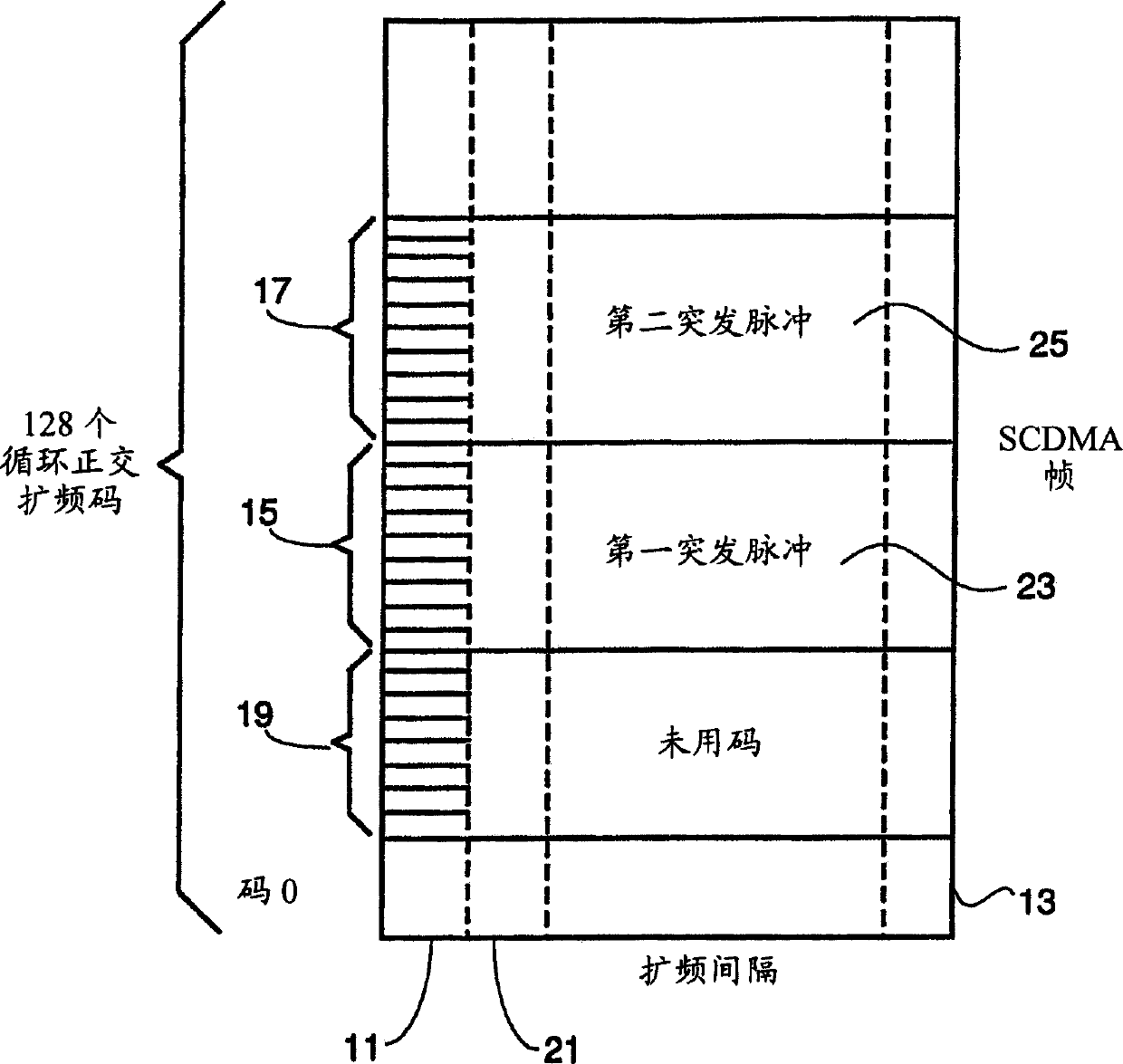
[0031] Spreading intervals exist in CMTS receivers in cable systems where cable modems (CMs) transmit upstream bursts using SCDMA techniques. For illustration, assume that there are 128 different cyclic or non-cyclic spreading codes. In each spreading interval, some or all of these codes are assigned to one or more CMs to transmit bursts (bursts). Each CM will use a different spreading code so that in cases where two or more bursts are transmitted simultaneously by different CMs, their transmissions can be distinguished by the CMTS. Referring to Figure 2, the concepts of spreading intervals, SCDMA frames and unused codes are understood.
[0032] Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a single SCDMA frame to illustrate the structure of a typical SCDMA frame with multiple bursts, showing unused codes. The present invention is equally applicable to any code division multiple access digital data transmission system with unused spreading codes, but here it is assumed to be a synchron...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com