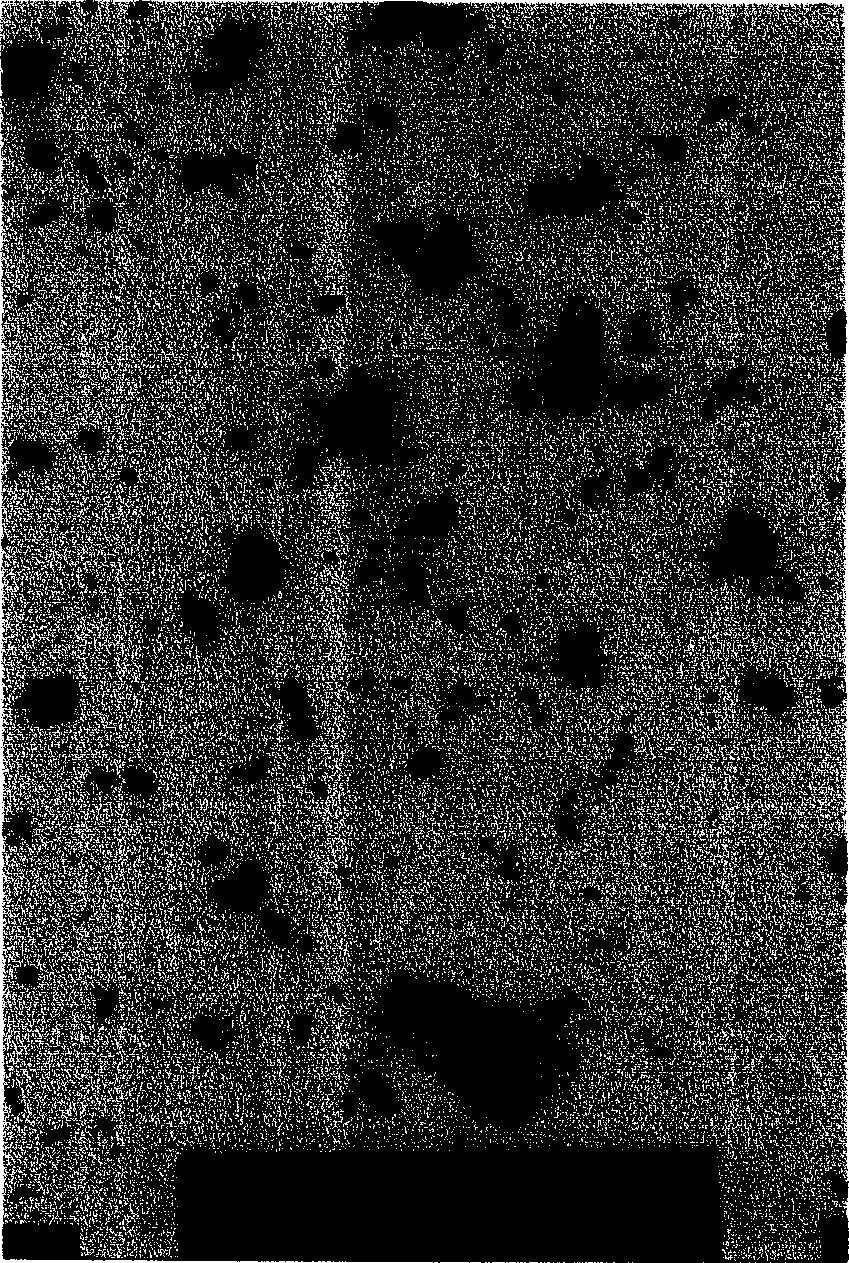
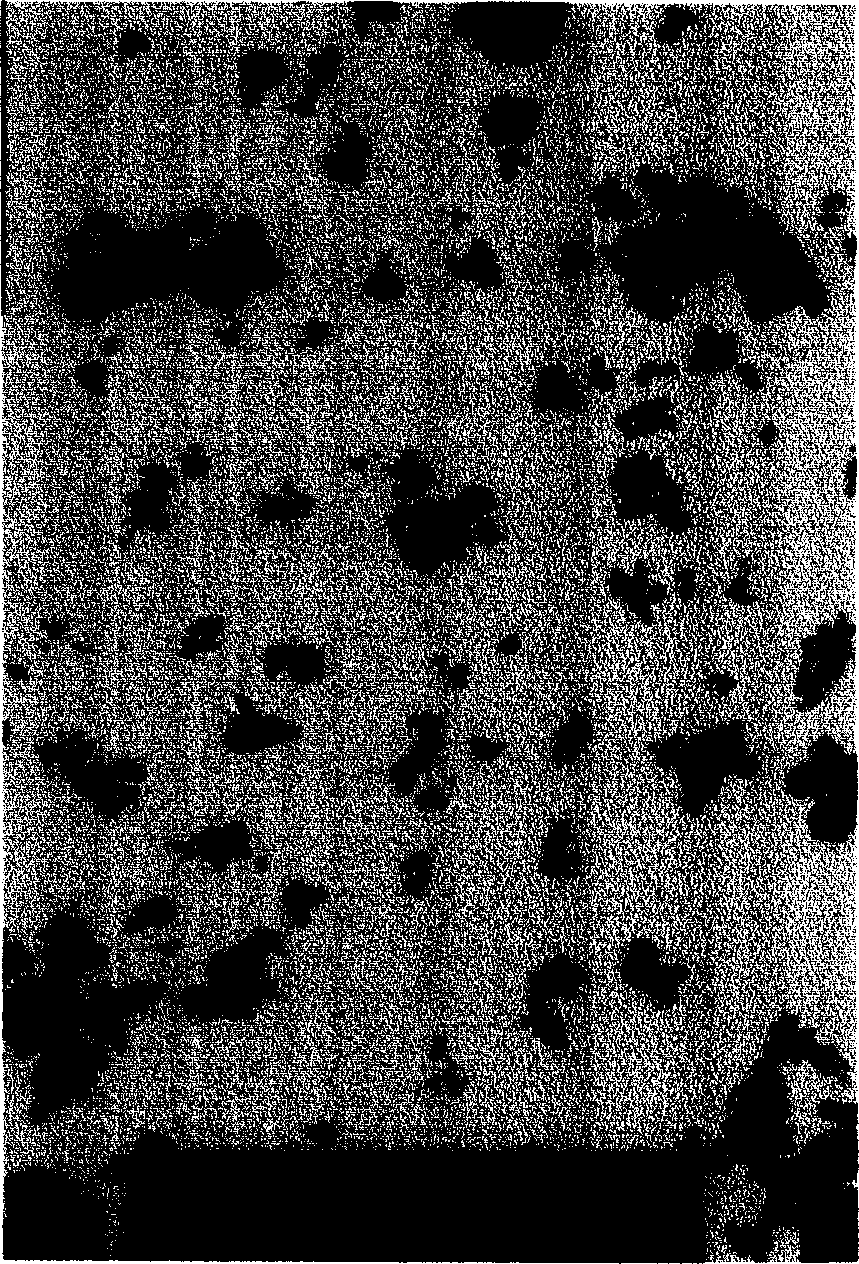
Nano composite anti-bacterial agent and preparation method
A technology of nanocomposite and antibacterial agents, applied in the field of nanocomposite antibacterial agents and their preparation, can solve the problems of high cost, achieve low cost, promote photocatalytic activity, and degrade organic pollutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] (1) Preparation of precursors
[0037] First, prepare a certain concentration of zinc sulfate or zinc nitrate, silver nitrate and ammonium bicarbonate aqueous solution as required. Take a certain amount of zinc sulfate or zinc nitrate solution with a concentration of 0.5 to 5 mol / L and place it in a container, at a temperature of 10 to 90 °C, keep stirring, and dropwise add the same volume of solution at a rate of 2 to 15 ml / s. 0.5~5mol / L ammonium bicarbonate solution, after the dropwise addition of ammonium bicarbonate is completed, continue to stir for 0.5~3 hours, and then dropwise add the same volume and concentration at the same time at a dropping speed of 2~15ml / s to Ag: ZnO=(1~50):(50~99) silver nitrate and ammonium bicarbonate, after the solution is added dropwise, the reaction is stopped after continuing to stir for 0.5~3 hours. The precursor mixture is then washed with doubly distilled water and / or absolute ethanol and centrifuged to separate out the precurso...
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0041] The first specific embodiment of the preparation method of the nanocomposite antibacterial agent of the present invention is as follows:
[0042] Take 200ml of zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 1~2mol / L in a three-necked flask, keep stirring at a temperature of 20~50℃, and add 200ml of 1~2mol / L carbonic acid dropwise at a dripping speed of 3~8ml / s Ammonia hydrogen solution, after the dropwise addition of ammonium bicarbonate, continue to stir for 0.5 hours, and then dropwise at a rate of 2 to 6ml / s at the same time. 100ml each of L silver nitrate and 0.1-1mol / L ammonium bicarbonate. After the solution was added dropwise, the reaction was stopped after continuing to stir for 0.5 to 1 hour. The precipitate was then washed with double distilled water and absolute ethanol and centrifuged to isolate the precursor, followed by vacuum drying. The dried precursor is placed in a box-type resistance furnace, heated to 430-460 ° C at a certain speed under the air, an...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0043] The second specific embodiment of the preparation method of the nanocomposite antibacterial agent of the present invention is as follows:
[0044] Take 200ml of zinc sulfate solution with a concentration of 0.5~1.5mol / L in a three-necked flask, under the temperature of 20~50℃, keep stirring, and add 200ml of 0.5~1.5mol / L dropwise at a dripping speed of 3~8ml / s. L ammonium bicarbonate solution, after the dropwise addition of ammonium bicarbonate is completed, continue to stir for 1 hour, and then at the same time dropwise at a rate of 2~6ml / s, the concentration of Ag:ZnO=10:90 by mass ratio is 0.1~ 1 mol / L silver nitrate and 100 ml each of 0.1-1 mol / L ammonium bicarbonate. After the solution was added dropwise, the reaction was stopped after continuing to stir for 0.5 to 1.5 hours. The precipitate was then washed with doubly distilled water and / or absolute ethanol and centrifuged to isolate the precursor, followed by vacuum drying. The dried precursor is placed in a va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com