K-ras oligonucleotide microarray and method for detecting K-ras mutations employing the same
An oligonucleotide, microarray technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: the manufacture of K-ras oligonucleotide microarray
[0056] Eighteen oligonucleotides were designed to include all possible substitutions at the two mutant hotspot codons (codons 11 and 12) of the K-ras gene, while 2 oligonucleotides were used as wild type. All oligonucleotides are 21 base pairs, and each mismatch sequence is located in the center of the oligonucleotide, as shown in Table 1. Oligonucleotides with missense mutations at a hotspot codon are: oligonucleotides described by SEQ ID NOs.2-10 at codon 12; oligonucleotides described by SEQ ID NOs.12-20 at codon 13 Nucleotides. The oligonucleotides described by SEQ ID NOs. 1 and 11 are wild type.
[0057] SEQ ID NO.
Oligonucleotides
Sequence (5'-3')
1
12W a
GTTGGAGCTGGTGGCGTAGGC
2
12M b 1
AGTTGGAGCT TGT GGCGTAGG
3
12M2
AGTTGGAGCT AGT GGCGTAGG
4
12M3
AGTTGGAGCT CGT GGCGTAGG
5
12M4 ...
Embodiment 2
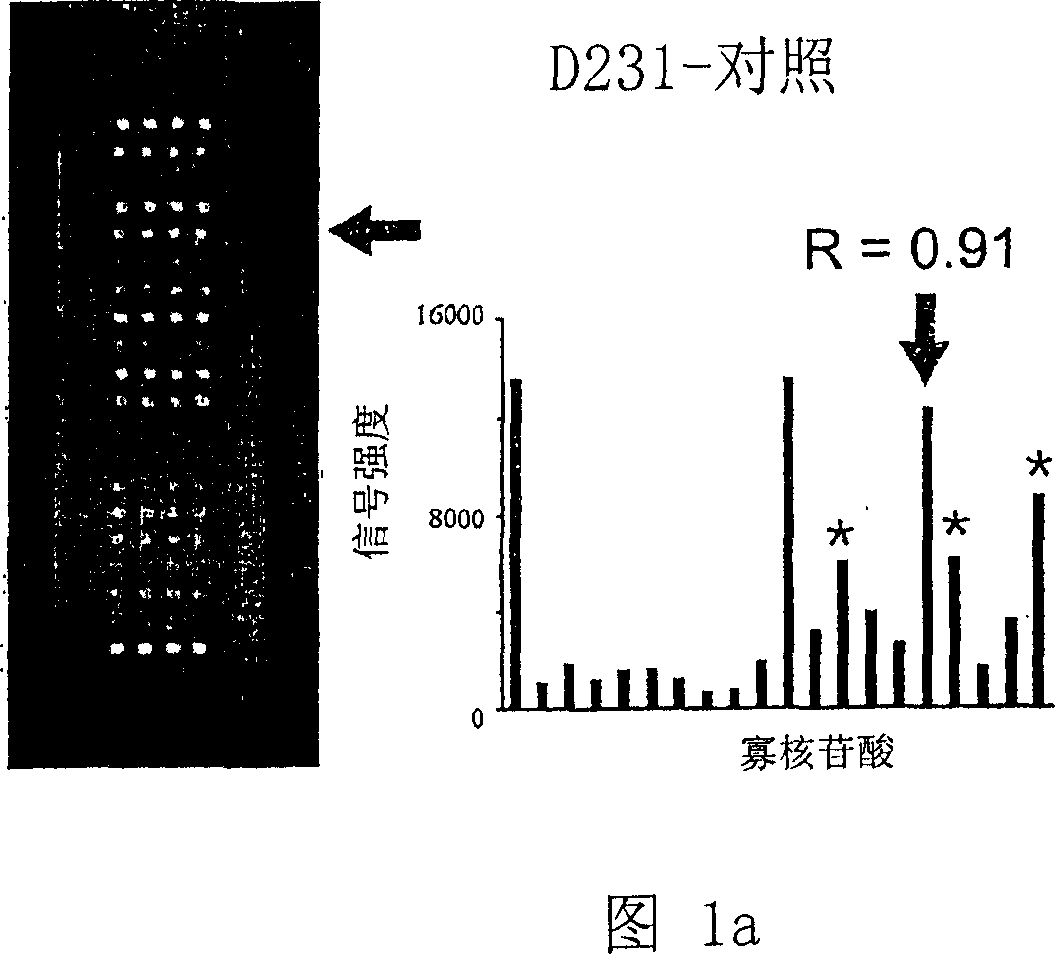
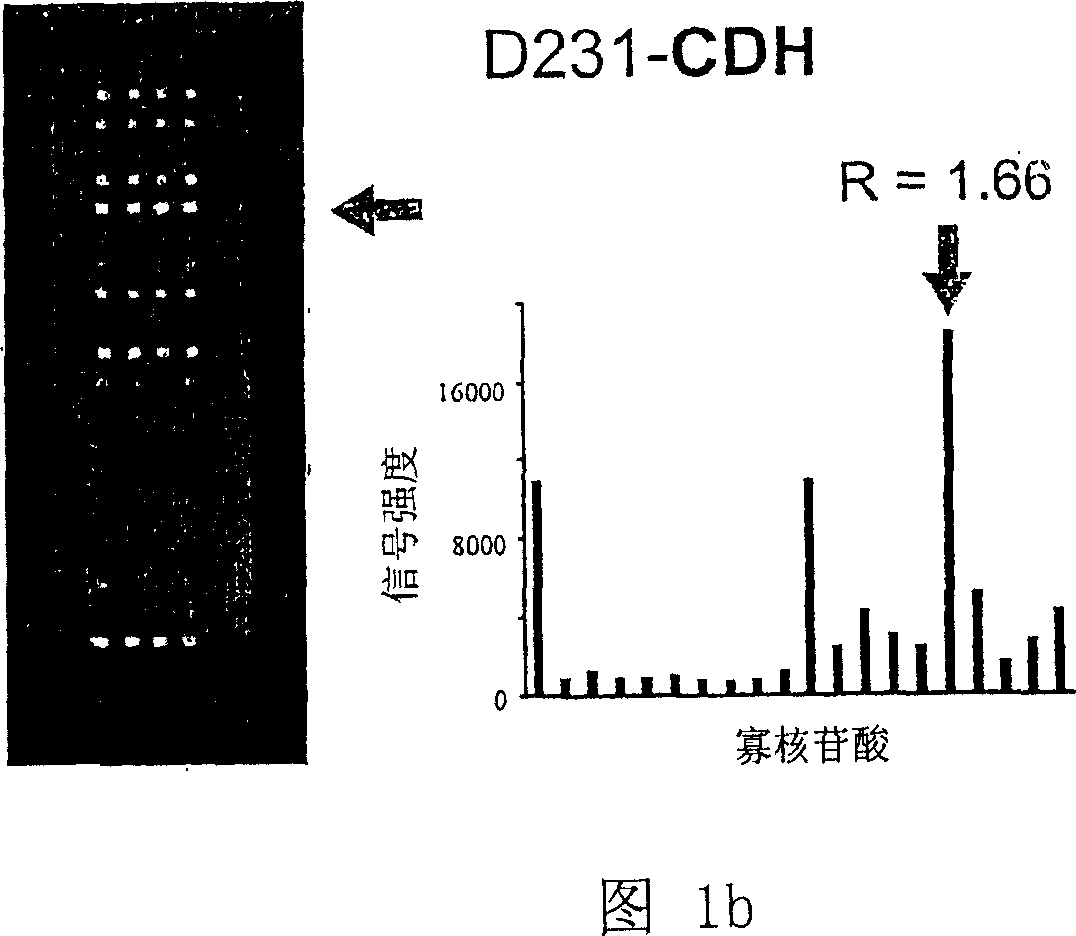
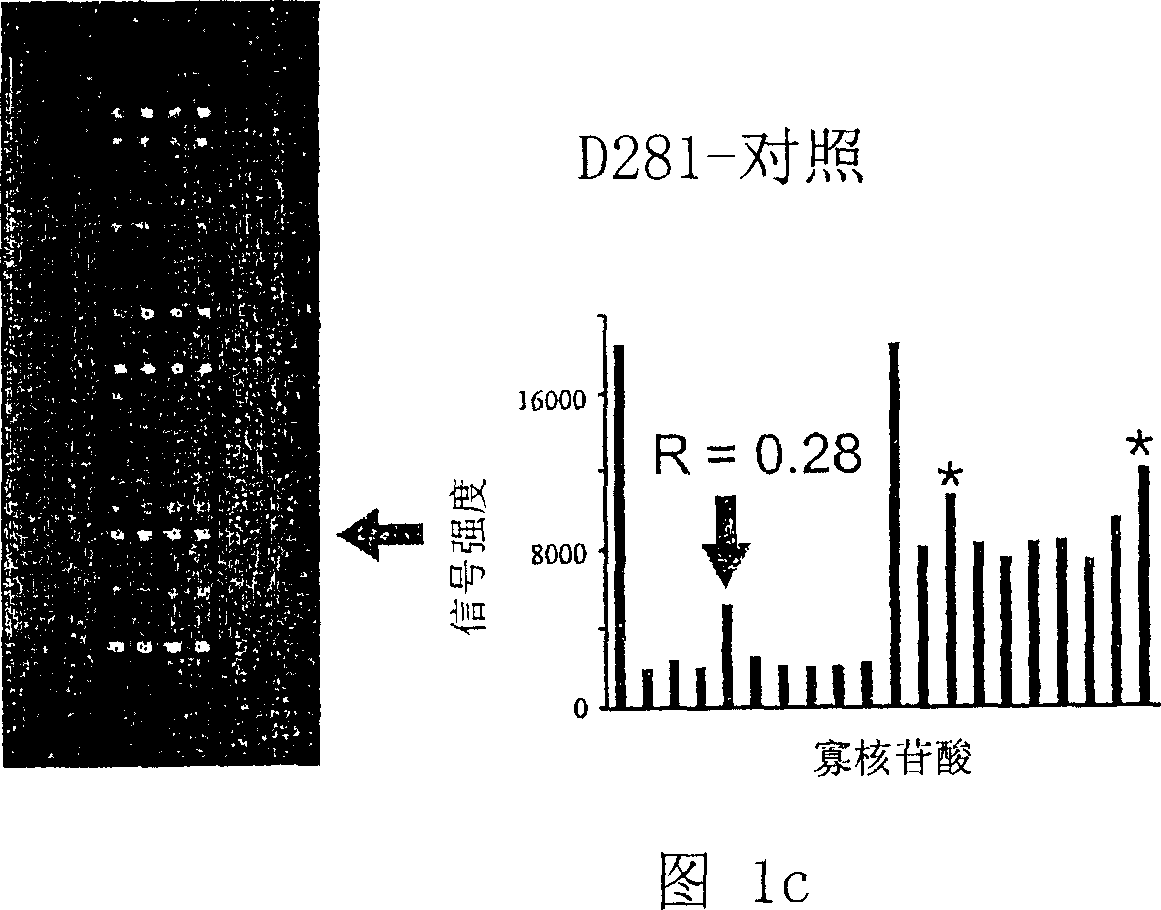
[0061] Example 2: Study of K-ras mutations with K-ras oligonucleotide microarray
[0062] (Step 1) DNA sample preparation
[0063] A total of 204 colorectal cancer patients from Seoul National University Hospital and Korea National Cancer Center were investigated for the presence of K-ras in somatic cells. Written consent was obtained from all patients. Of the 204 colorectal cancers, 103 were from the proximal colon (cecum to splenic flexure) and 101 from the distal colon (splenic flexure to rectum). Again, normal tissues from colorectal cancer patients were used as negative controls.
[0064] Genomic DNA was extracted from frozen samples using TRI reagent (Center for Molecular Research, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA) as previously described (Kim IJ et al., Clin. Cancer Res. 9:2920-2925, 2003). To generate fluorochrome-labeled DNA samples, the extracted DNA was used as a template for PCR amplification using the two pairs of primers SEQ ID NOs 21 and 22 (Metabion, Germany) as previo...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3: The K-ras mutation detected by the K-ras oligonucleotide microarray is indeed
[0076]In order to confirm the K-ras mutation detected by the K-ras oligonucleotide microarray of the present invention, 205 colorectal cancer samples were subjected to bidirectional sequencing analysis as previously described (Park, JH et al., Clin. Genet .64:48-53, 2003). For sequencing, previously reported primers of SEQ ID NOs: 23 and 24 were used (Lagarda H et al., J. Pathol. 193: 193-199, 2001). PCR was carried out in the same manner as described in step (1) of Example 2, but using a conventional dNTP mixture.
[0077] Bidirectional sequencing was performed using Taq dideoxy terminator cycle sequencing kit (Taq dideoxy terminator cycle sequencing kit) and ABI 3100 DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Forster City, CA).
[0078] As a result, the mutation results were 100% consistent with direct sequencing, indicating that there were neither false positives nor false negativ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com