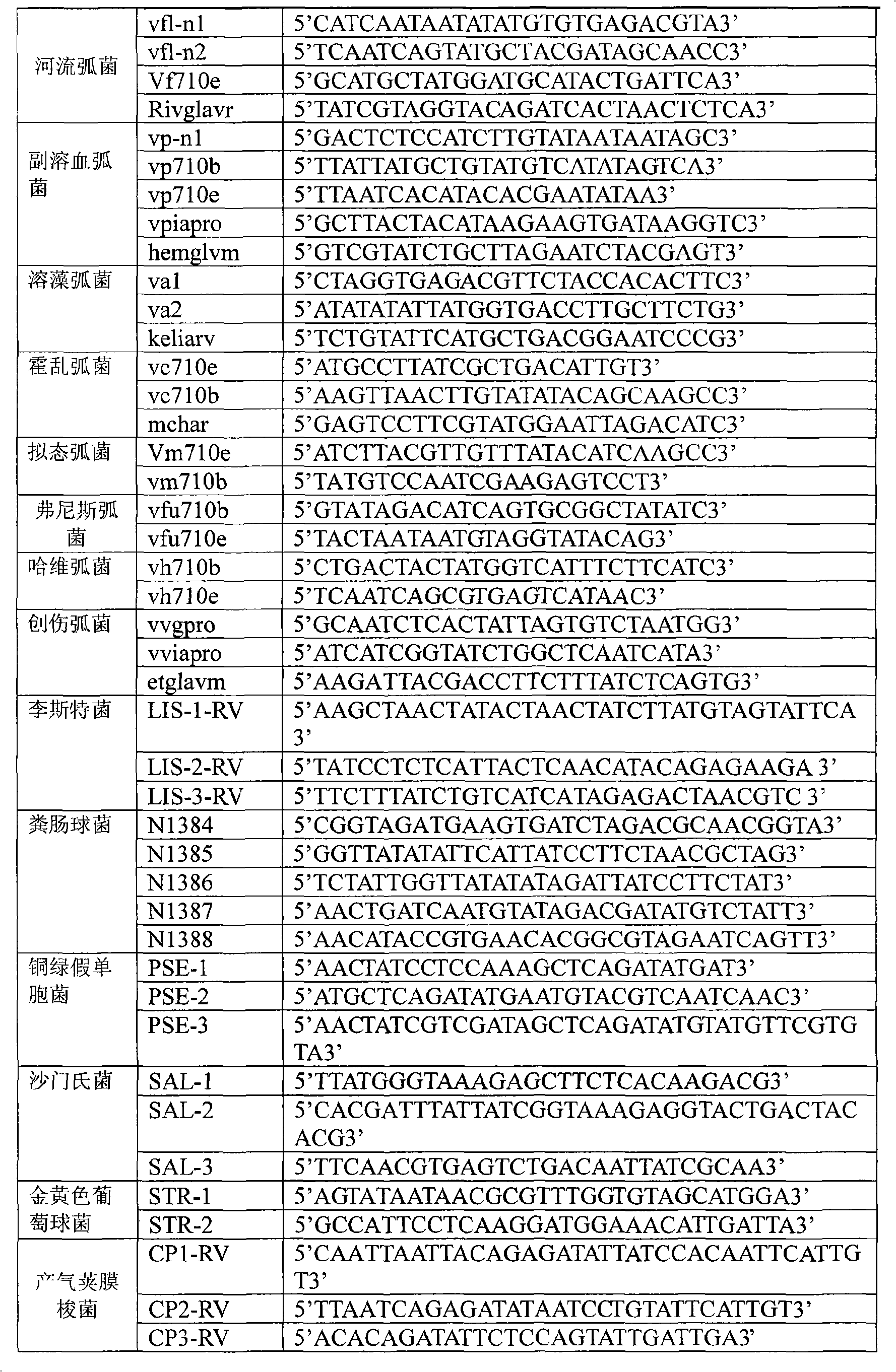
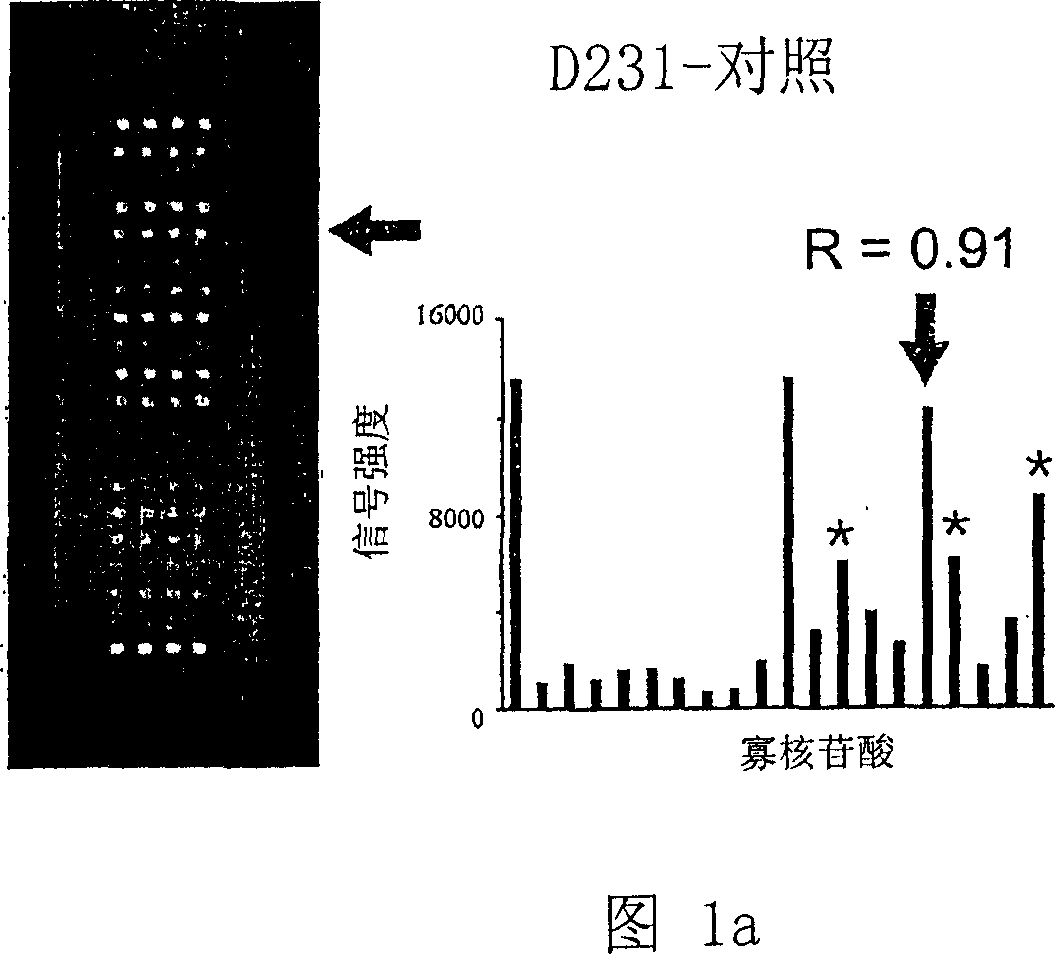
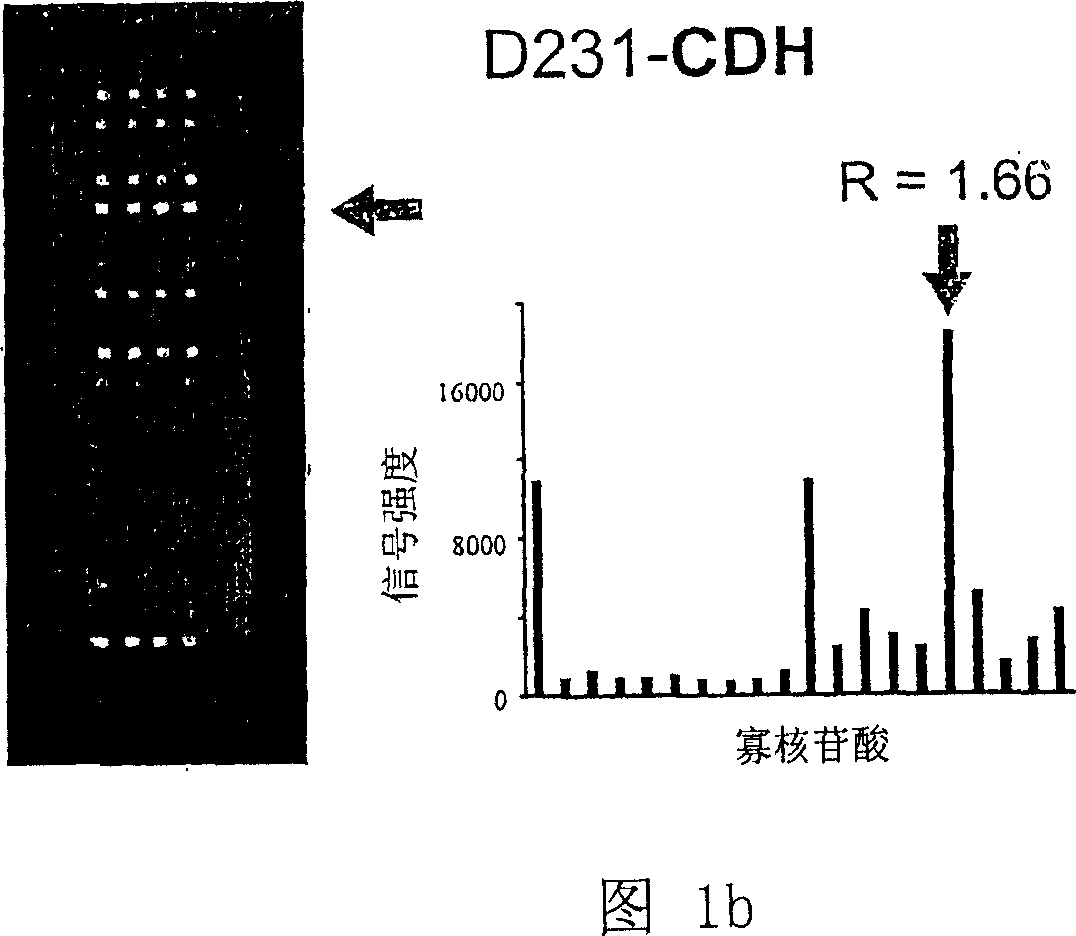
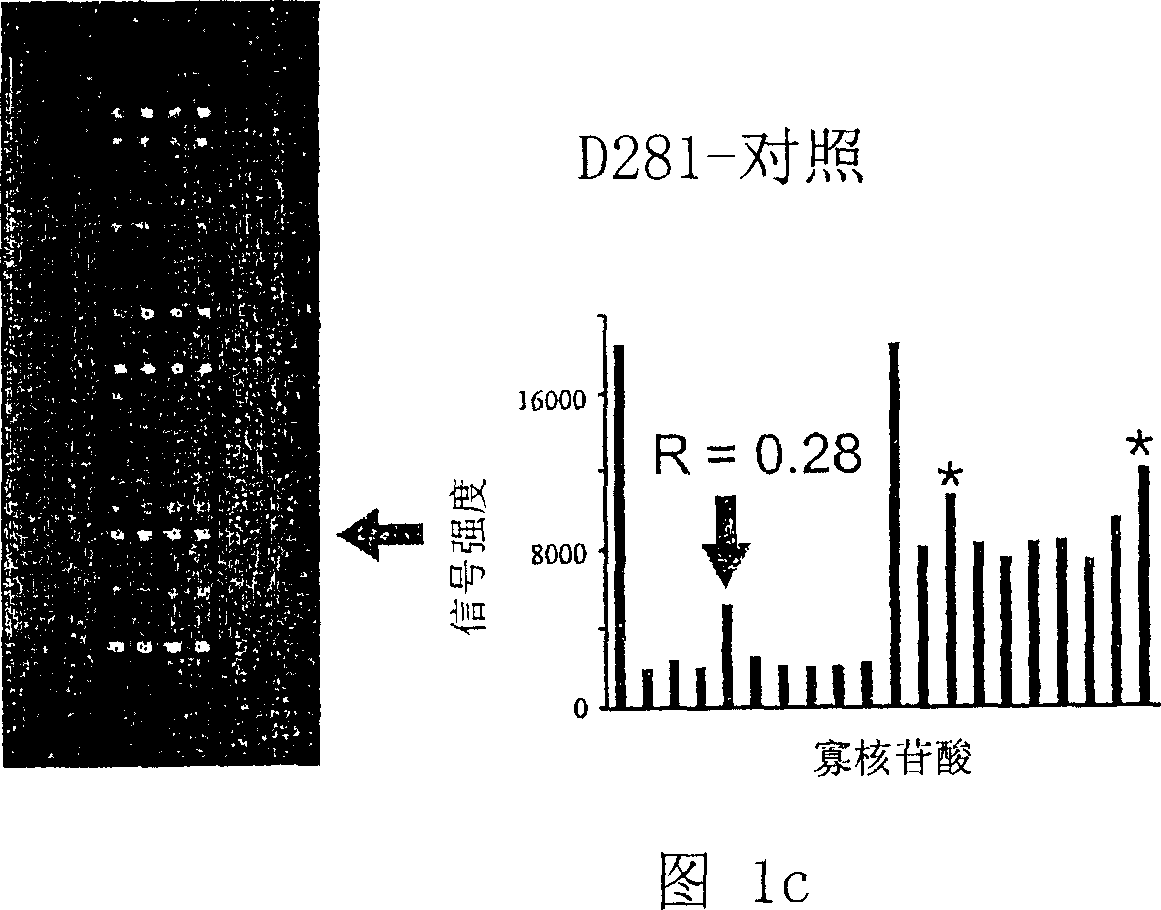
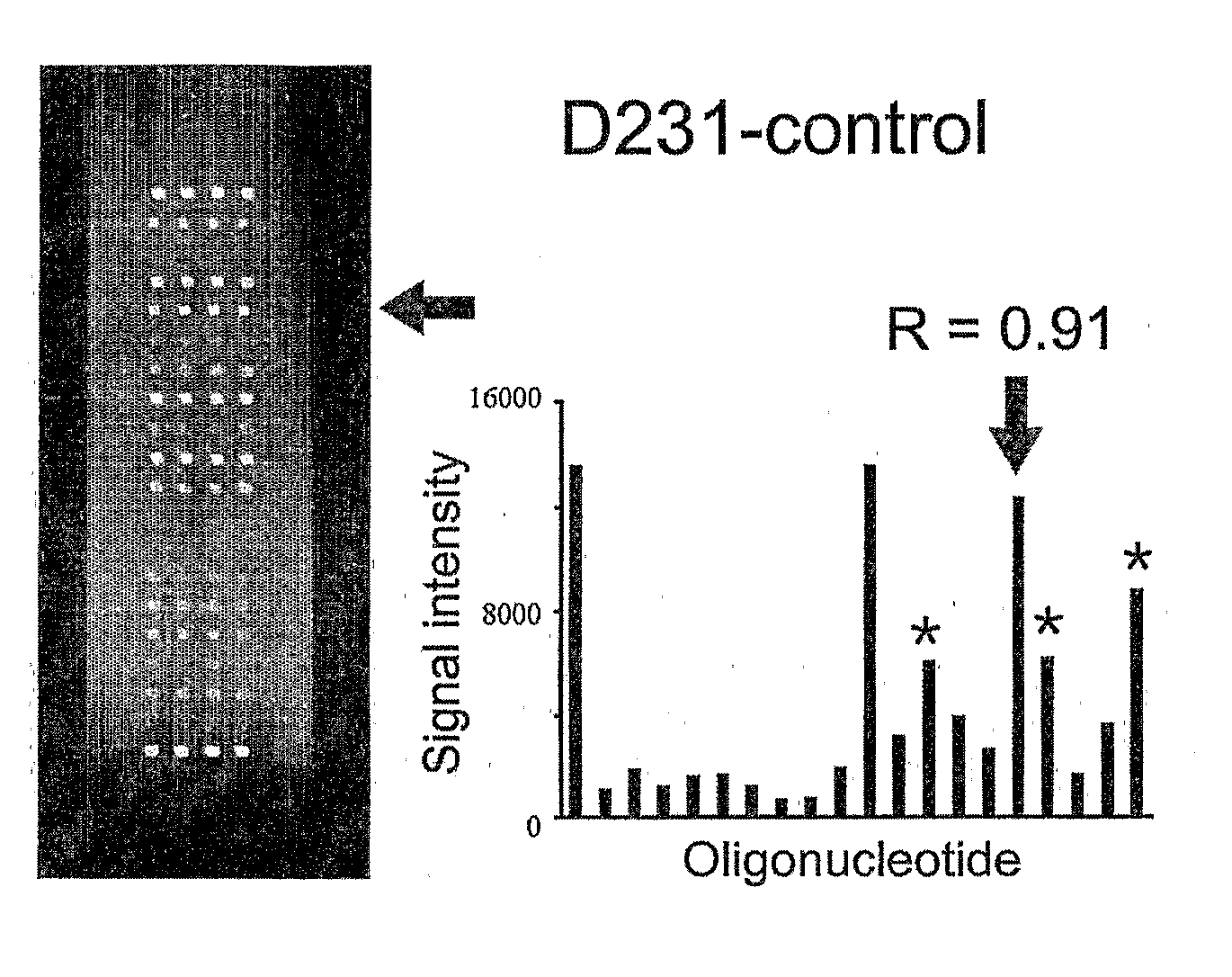
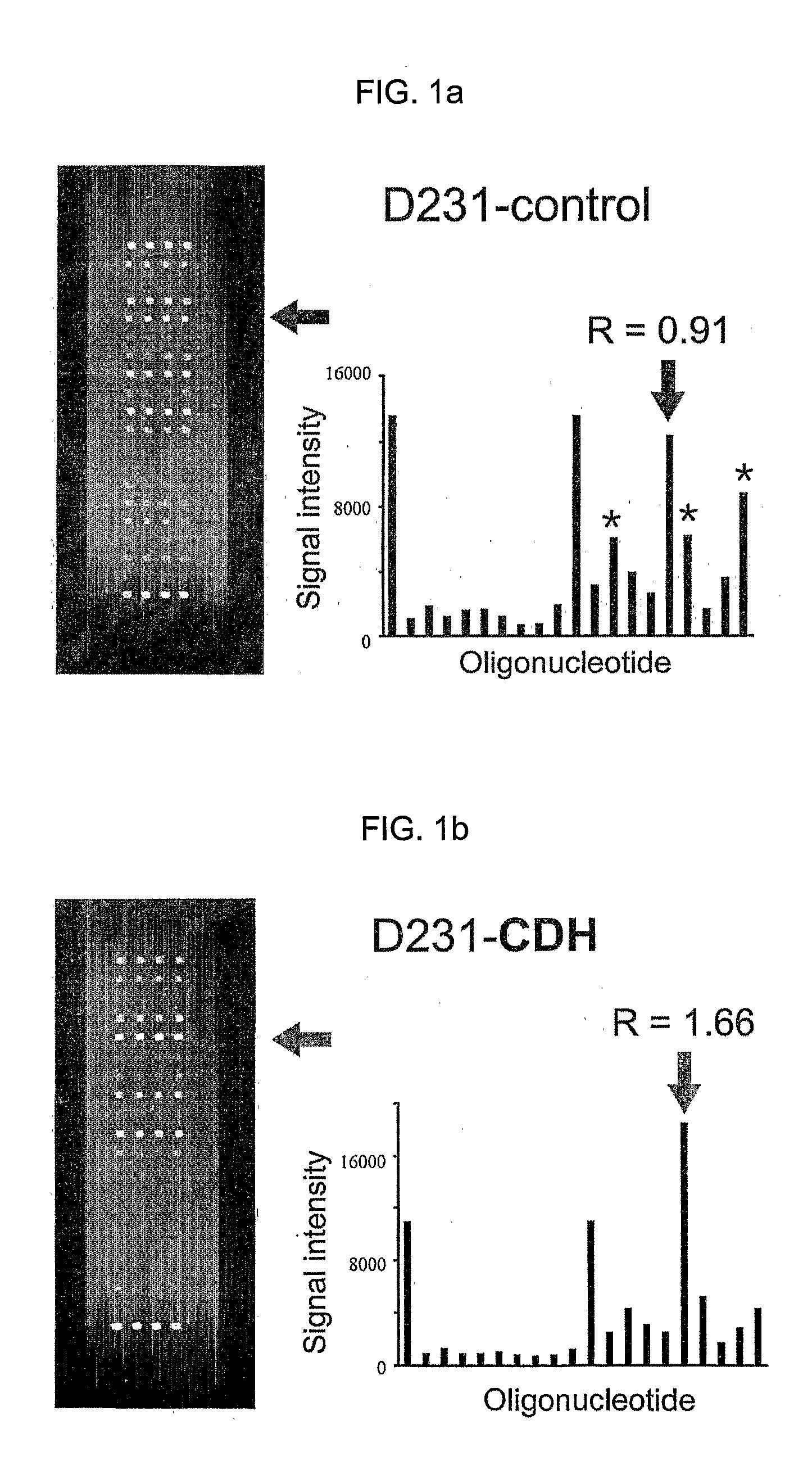
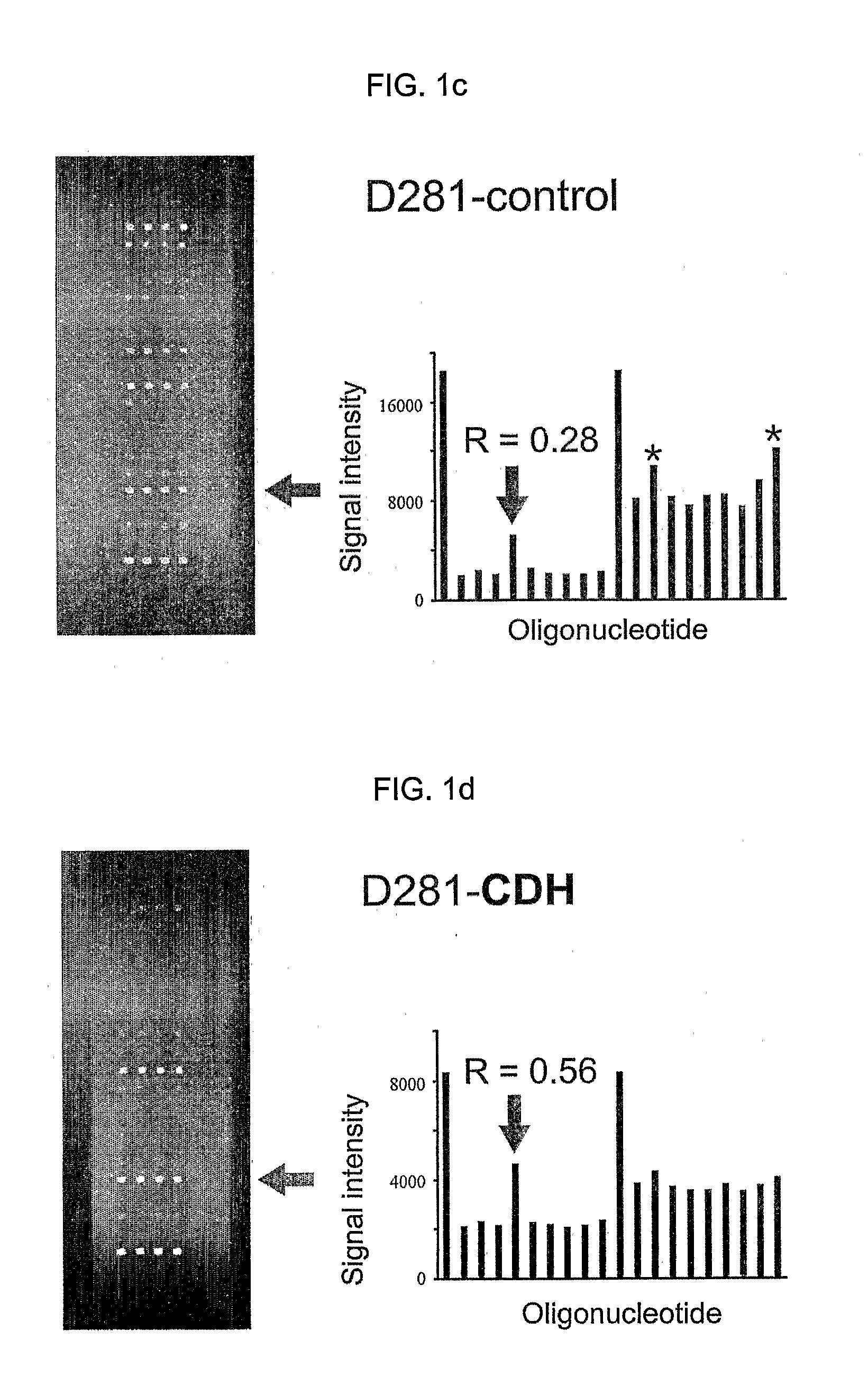
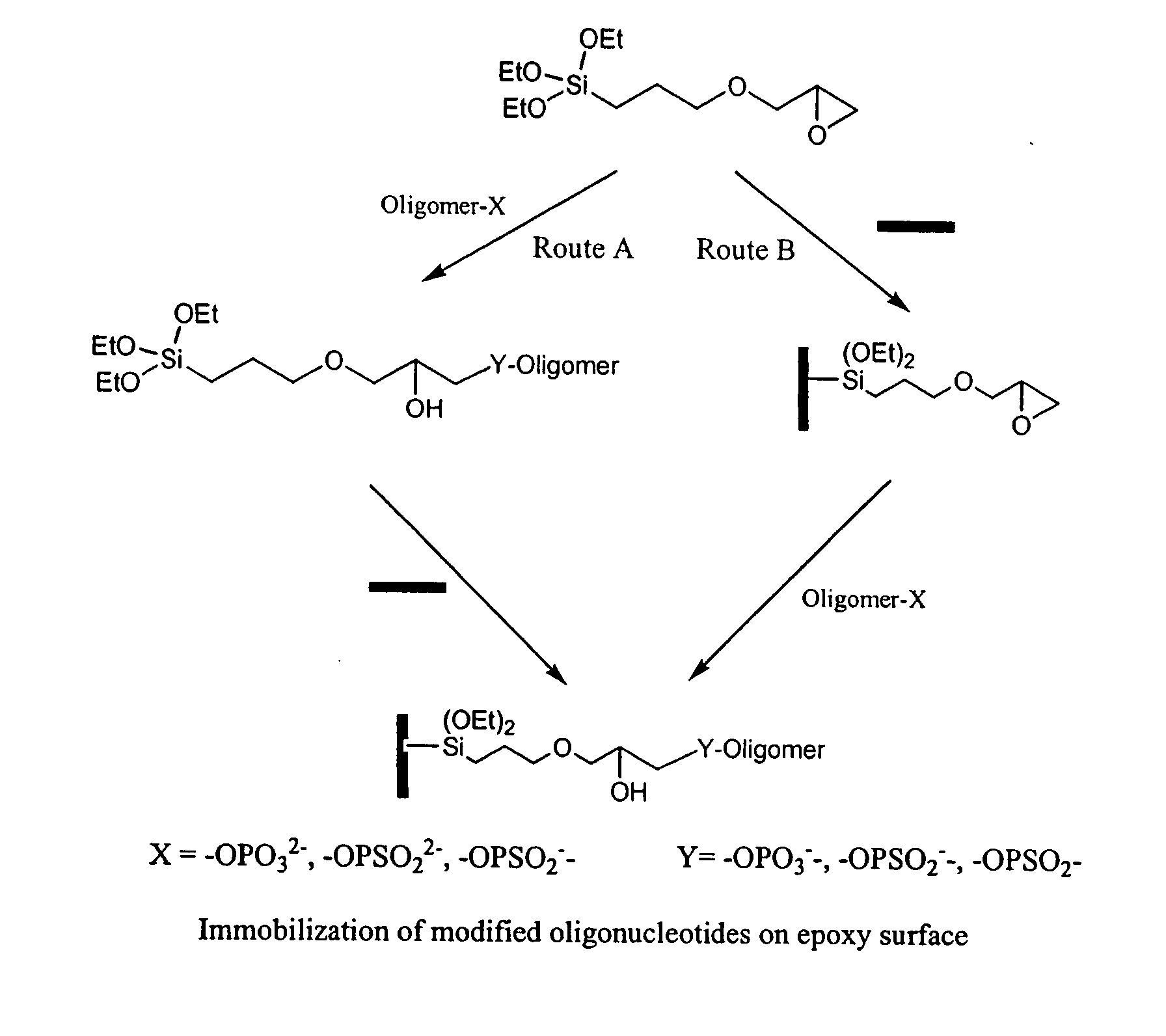
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Oligonucleotide Microarray" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
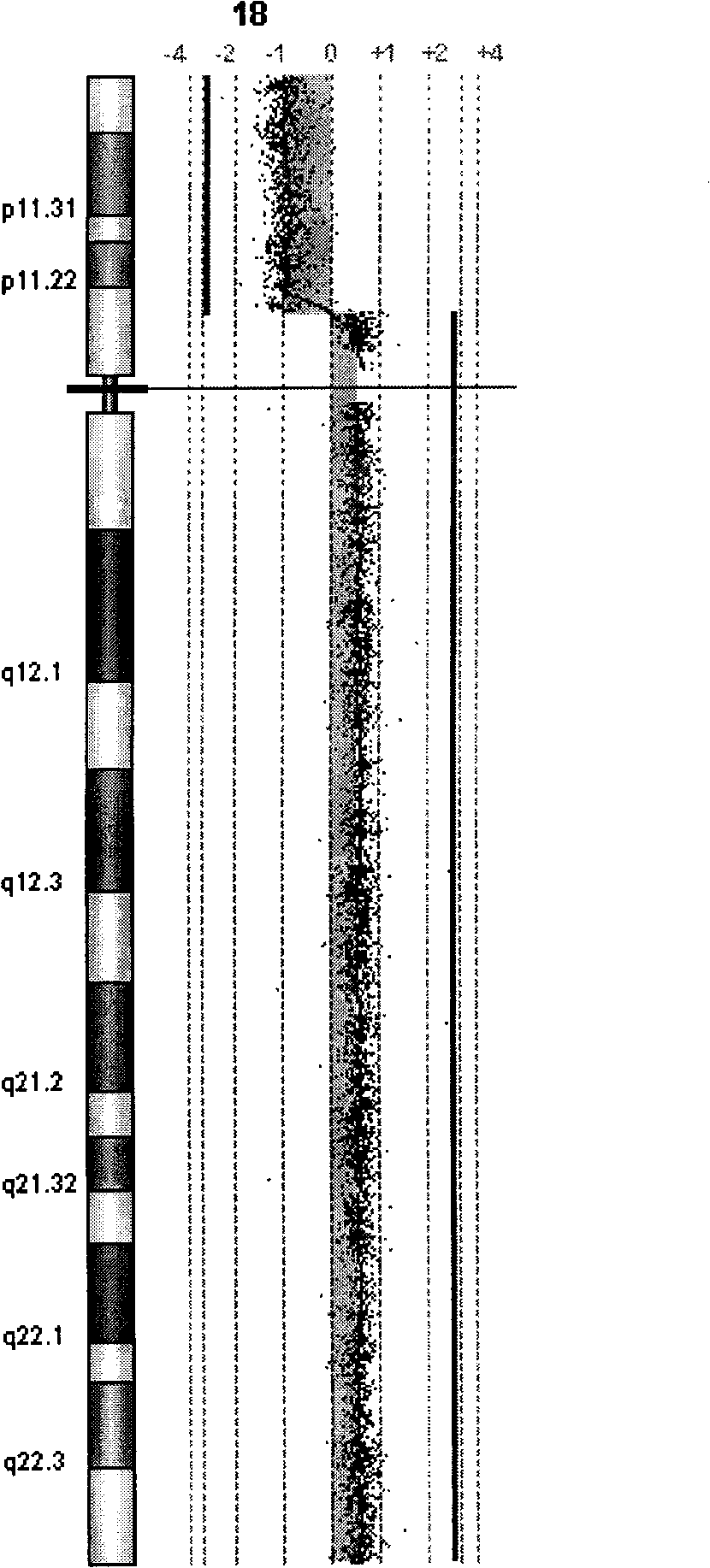
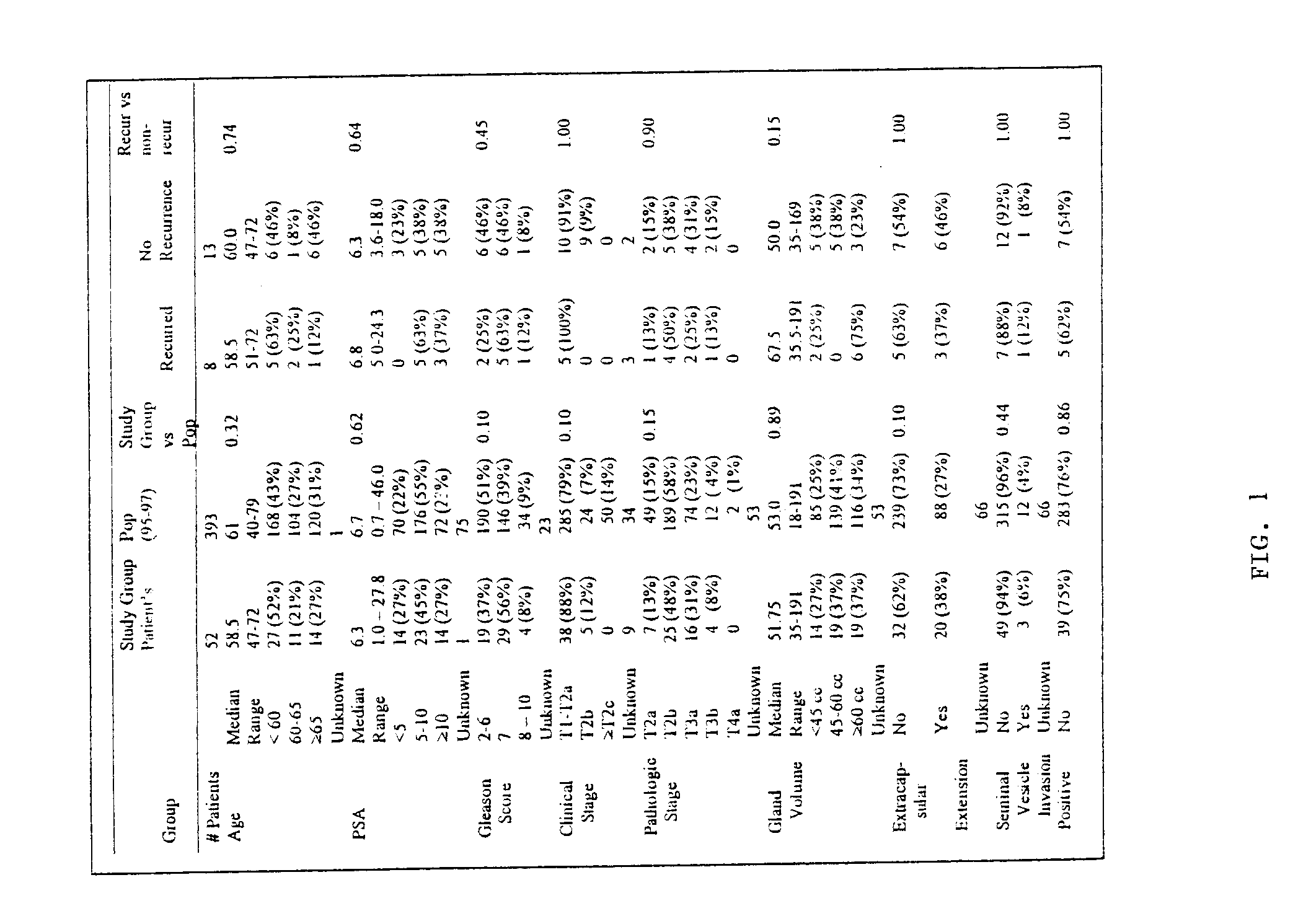
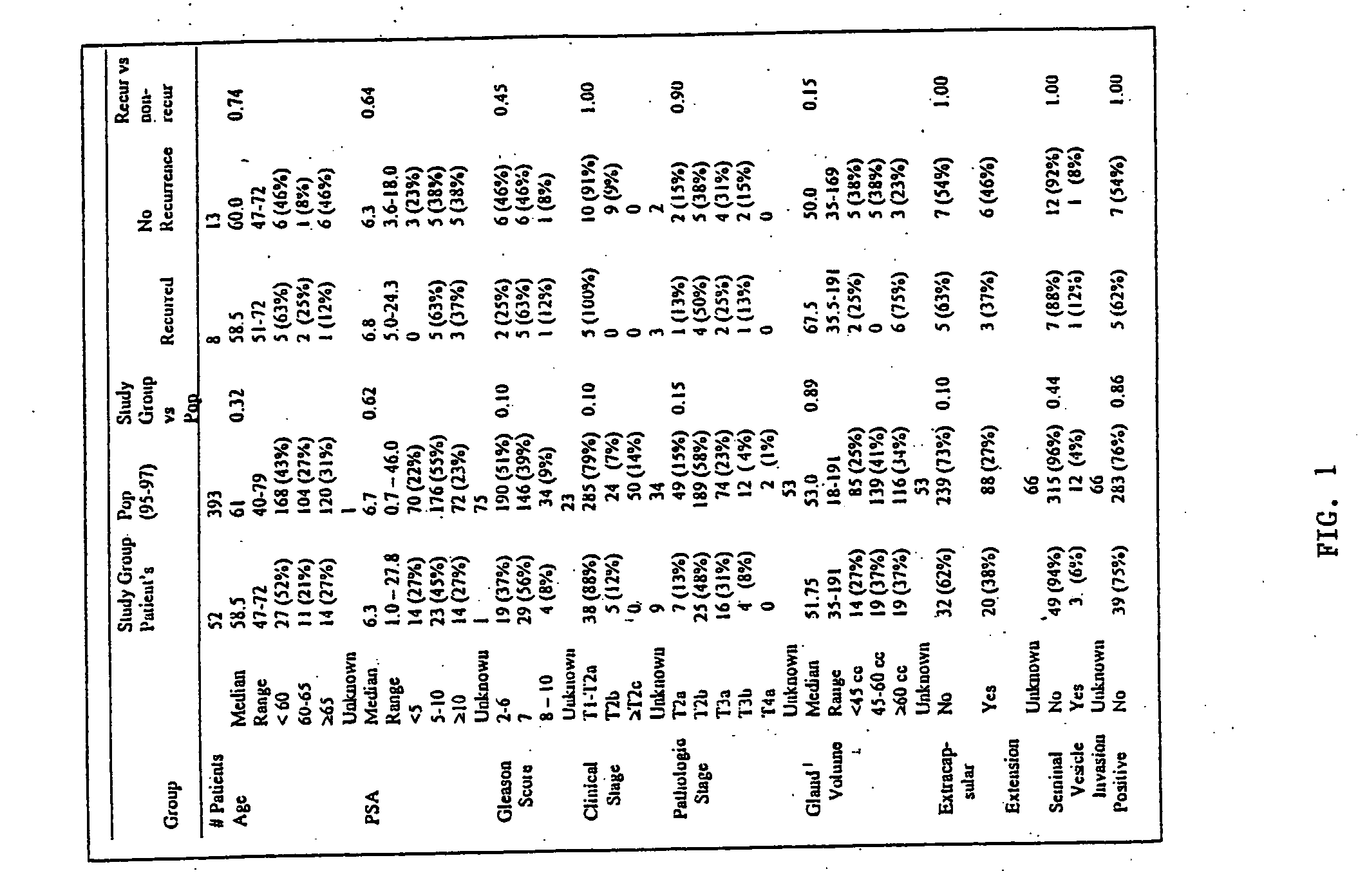
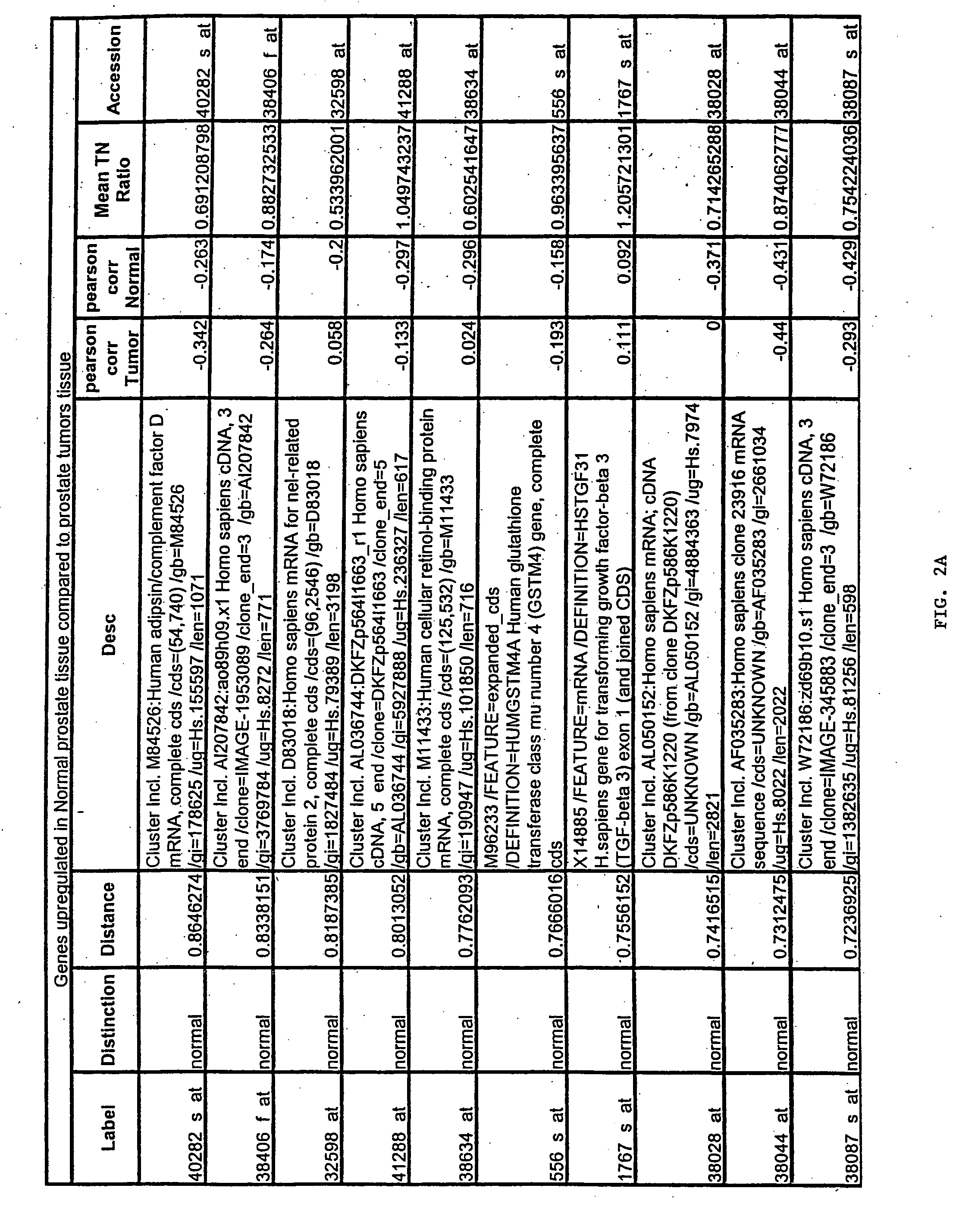
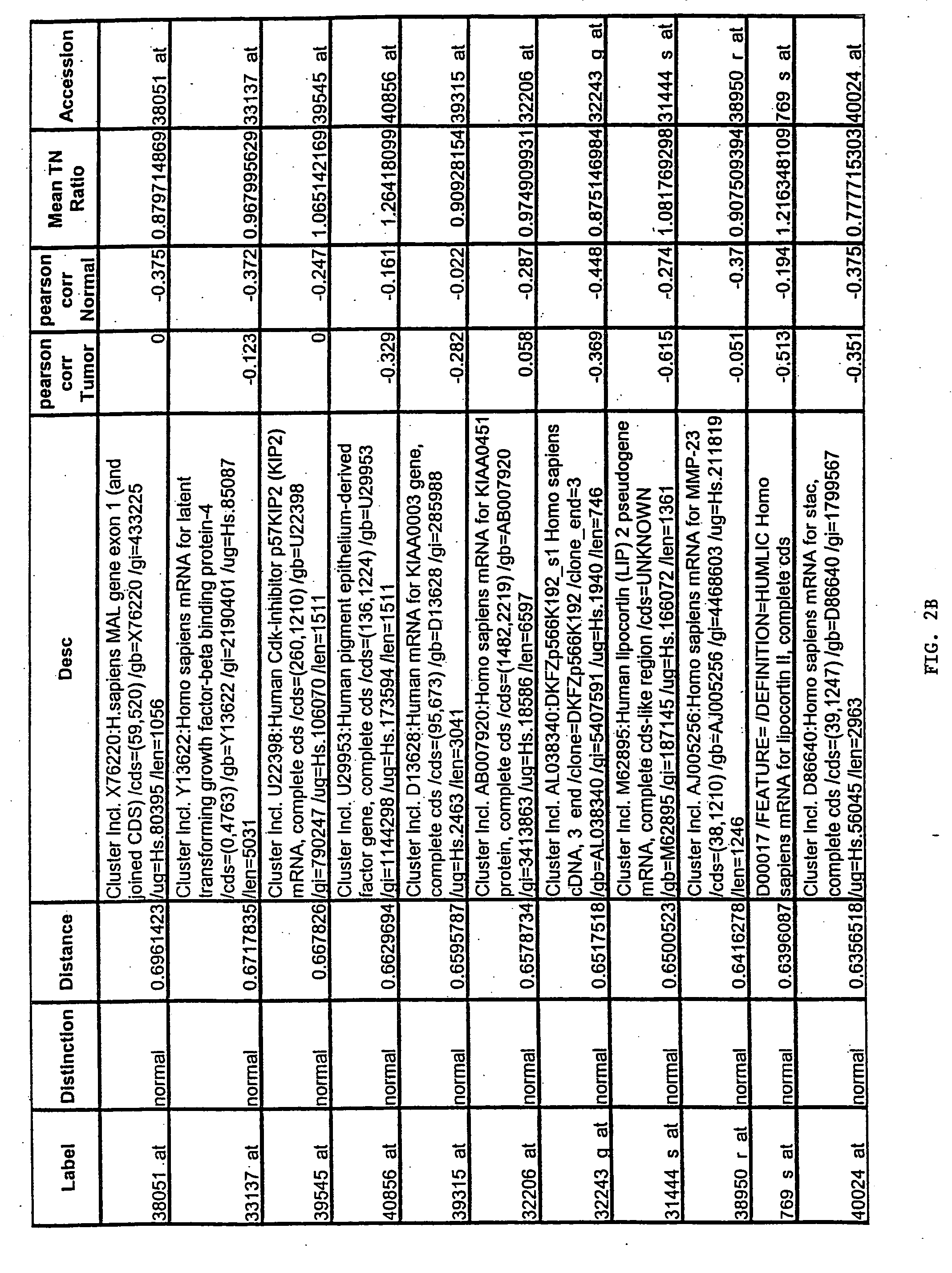
Prostate cancer diagnosis and outcome prediction by expression analysis
InactiveUS6949342B2Lower Level RequirementsEffective treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisOligonucleotide MicroarrayProstate cancer
Methods identifying prostate cancer, methods for prognosing and diagnosing prostate cancer, methods for identifying a compound that modulates prostate cancer development, methods for determining the efficacy of a prostate cancer therapy, and oligonucleotide microarrays containing probes for genes involved in prostate cancer development are described.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
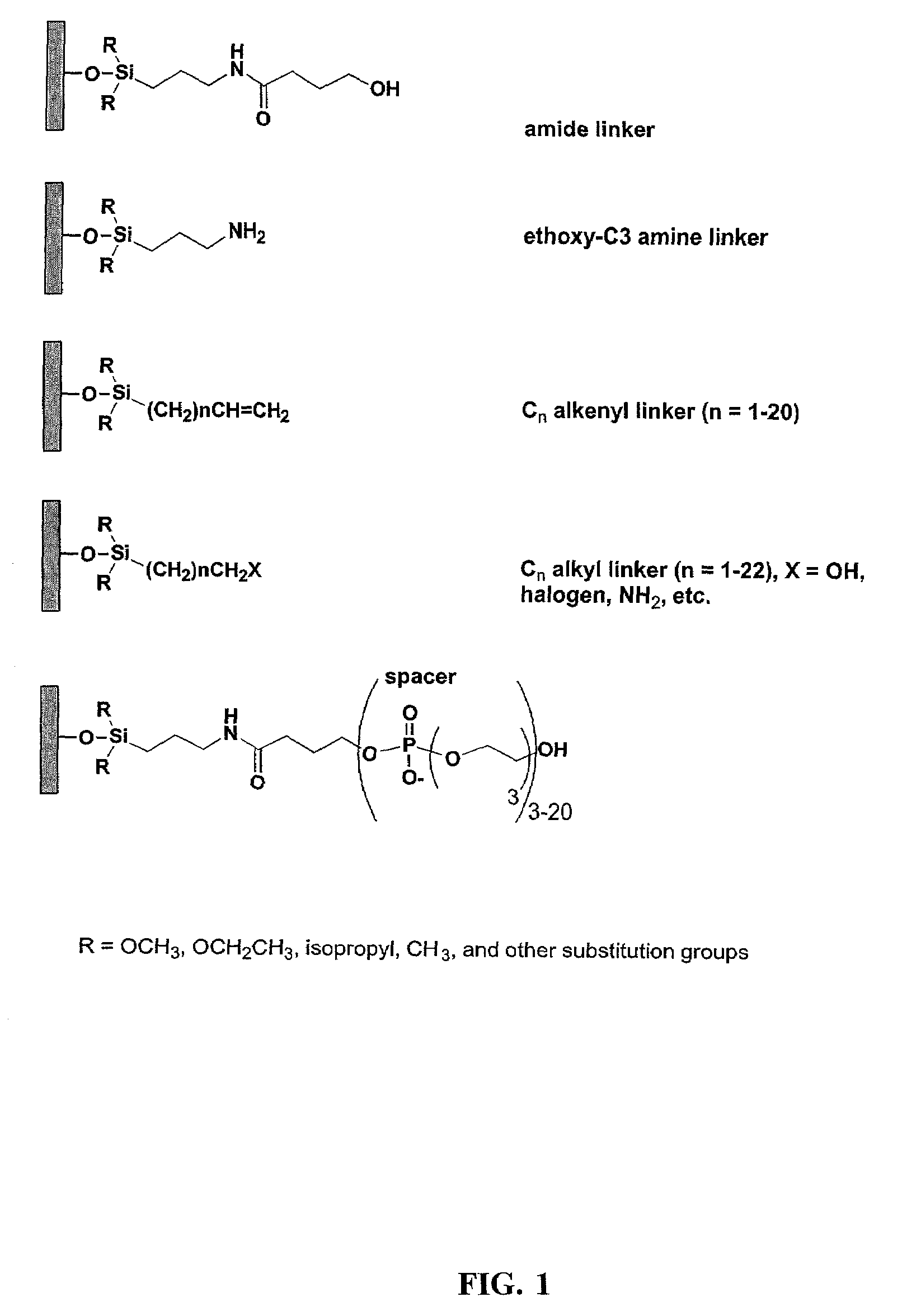
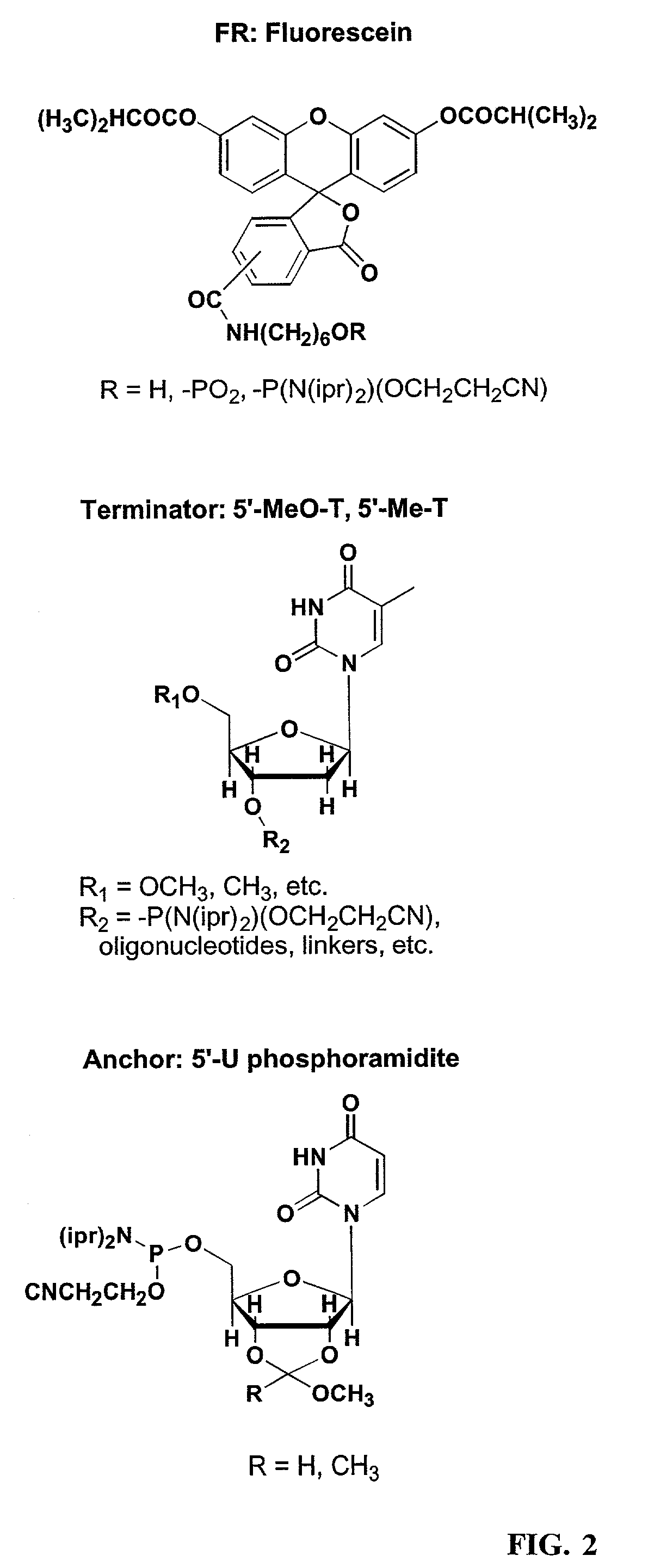
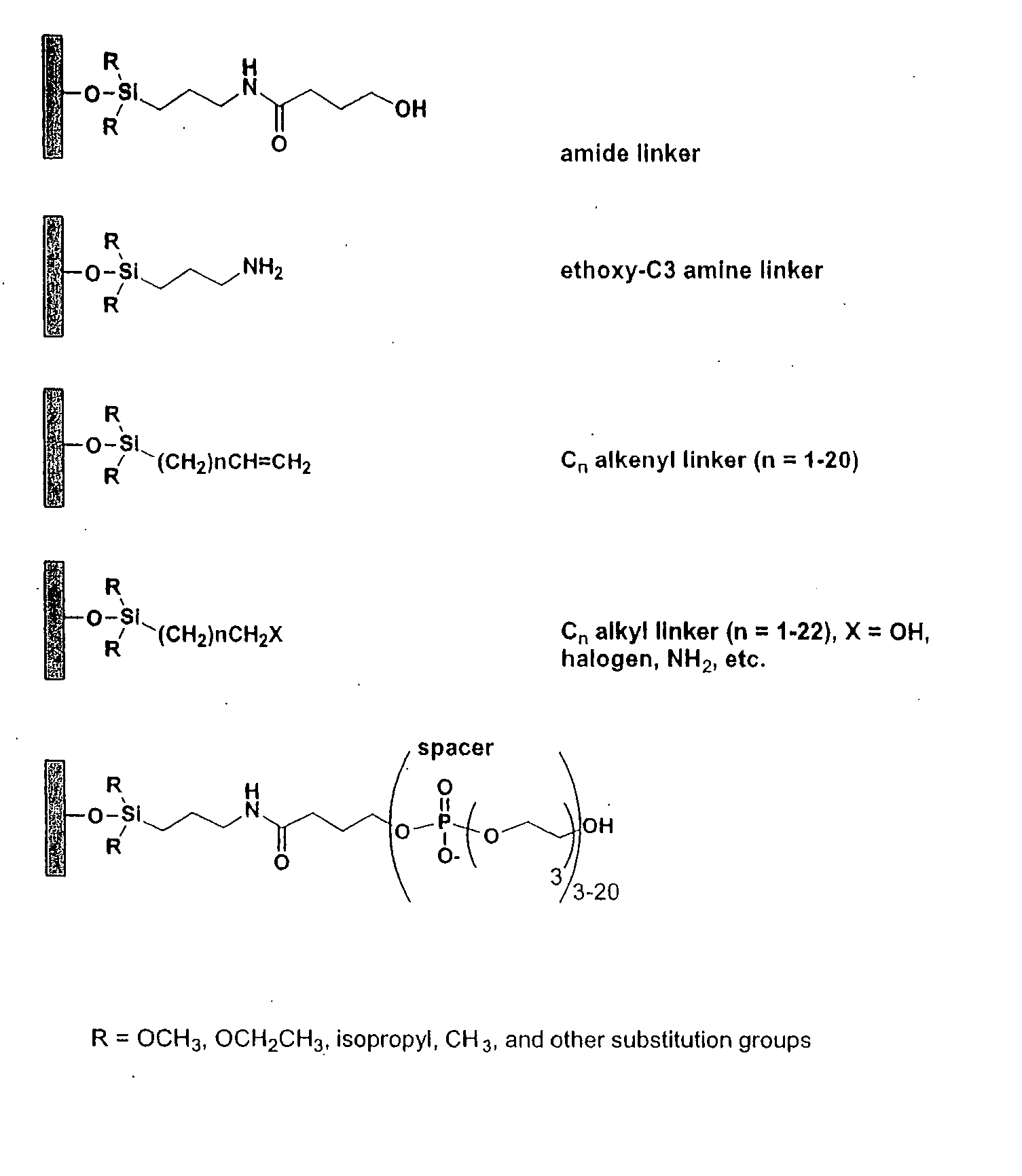
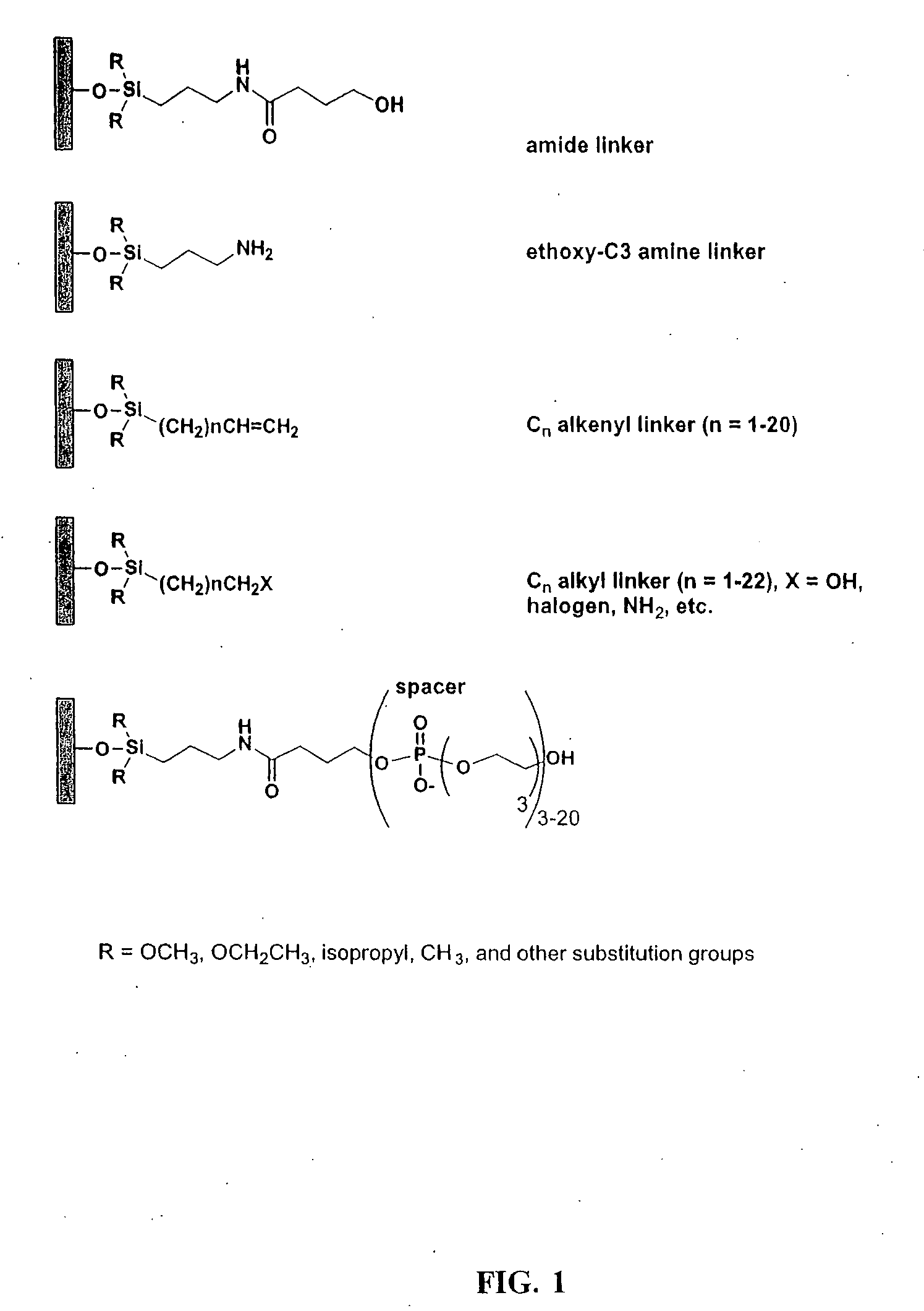
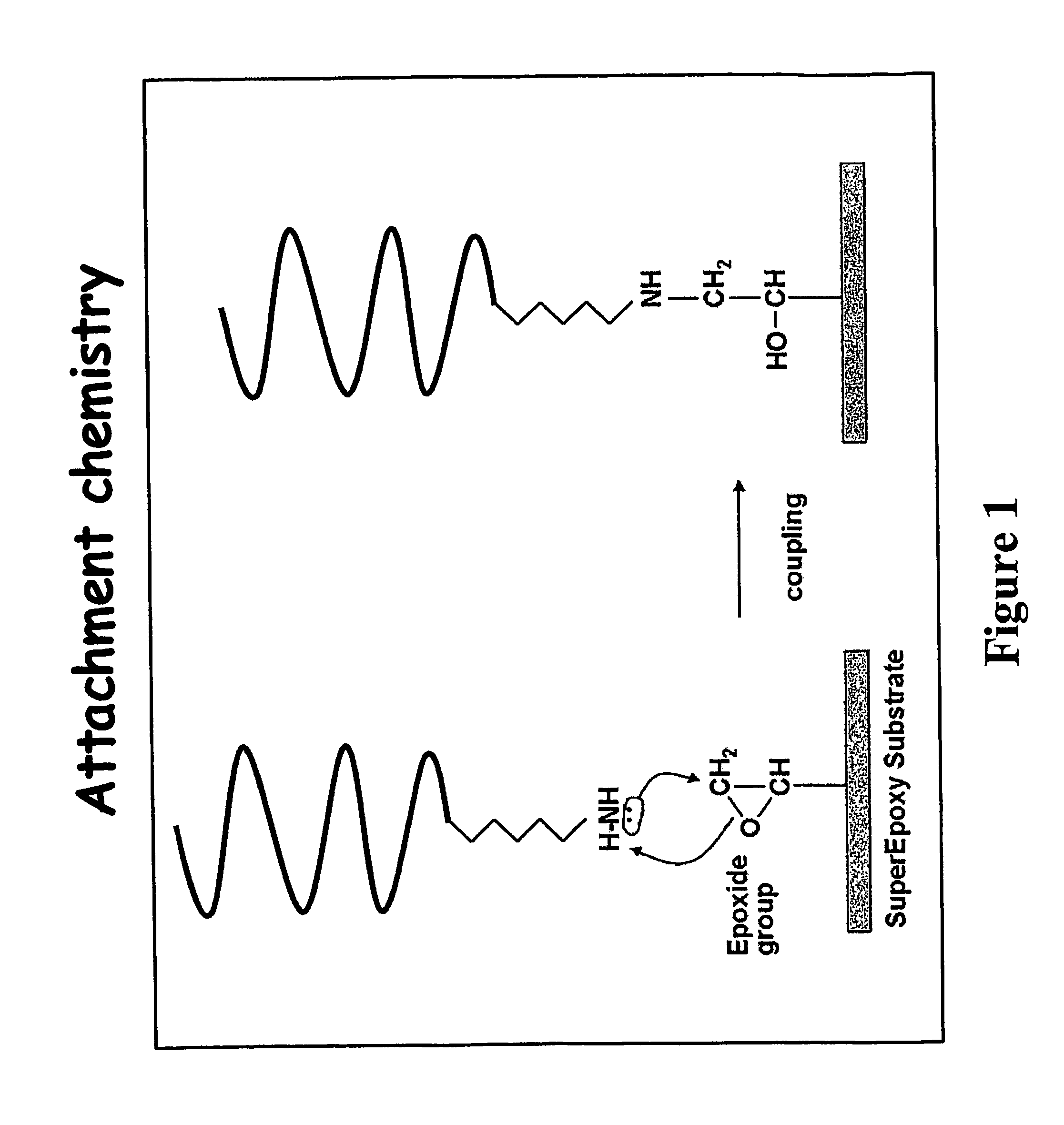
Linkers and co-coupling agents for optimization of oligonucleotide synthesis and purification on solid supports
InactiveUS7211654B2Promote hydrolysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid surfaceTime-Consuming
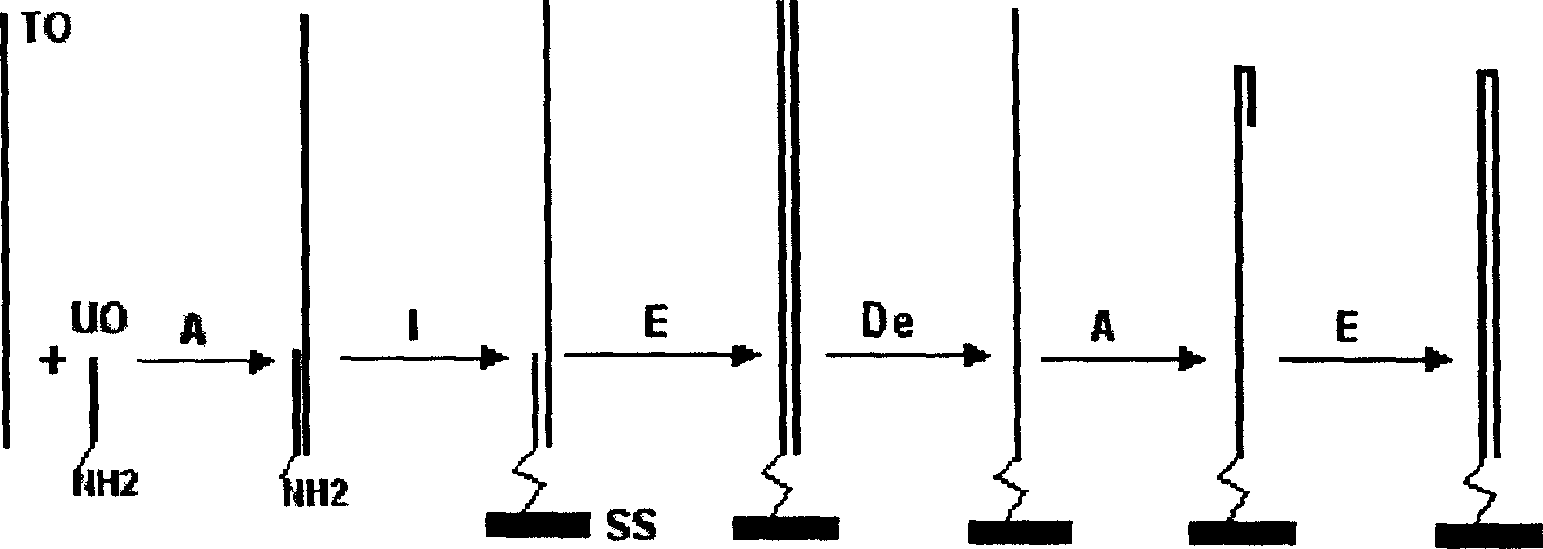
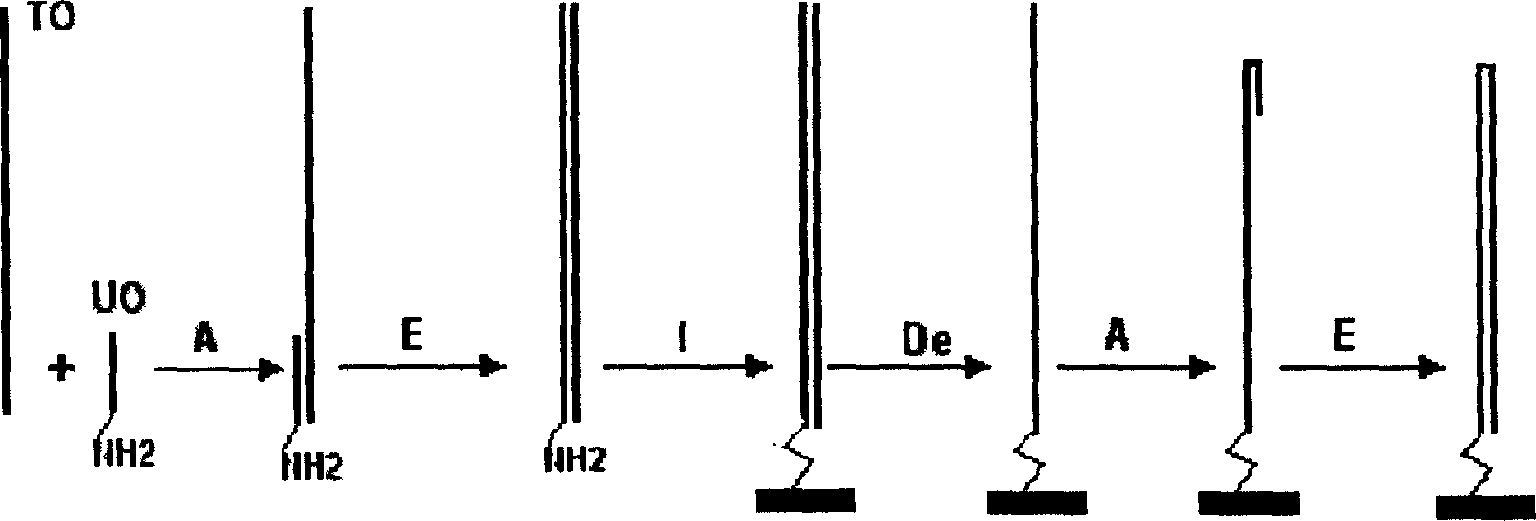
A method of modulation of synthesis capacity on and cleavage properties of synthetic oligomers from solid support is described. The method utilizes linker molecules attached to a solid surface and co-coupling agents that have similar reactivities to the coupling compounds with the surface functional groups. The preferred linker molecules provide an increased density of polymers and more resistance to cleavage from the support surface. The method is particularly useful for synthesis of oligonucleotides, oligonucleotides microarrays, peptides, and peptide microarrays. The stable linkers are also coupled to anchor molecules for synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides using on support purification, eliminating time-consuming chromatography and metal cation presence. Oligonucleotides thus obtained can be directly used for mass analysis, DNA amplification and ligation, hybridization, and many other applications.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
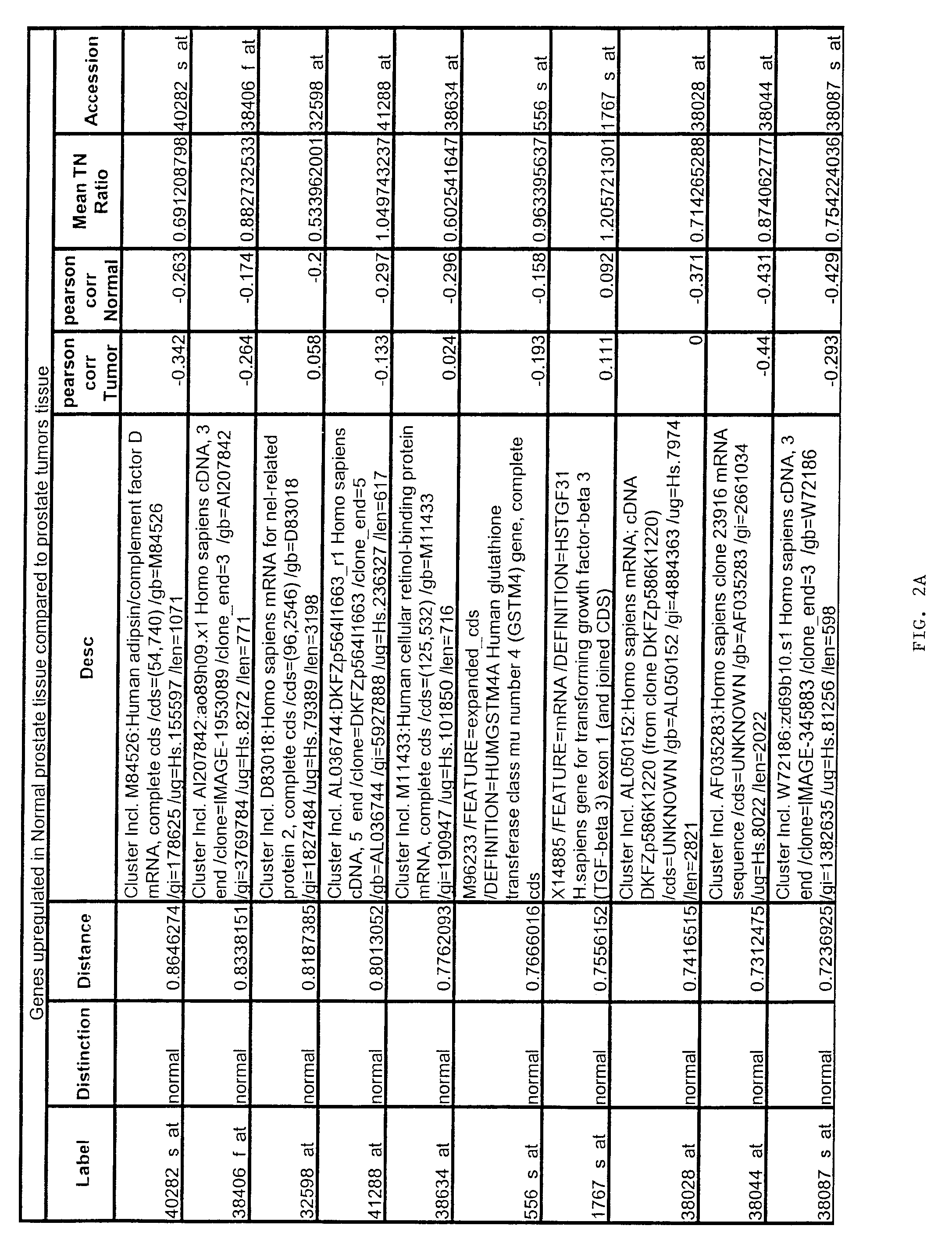
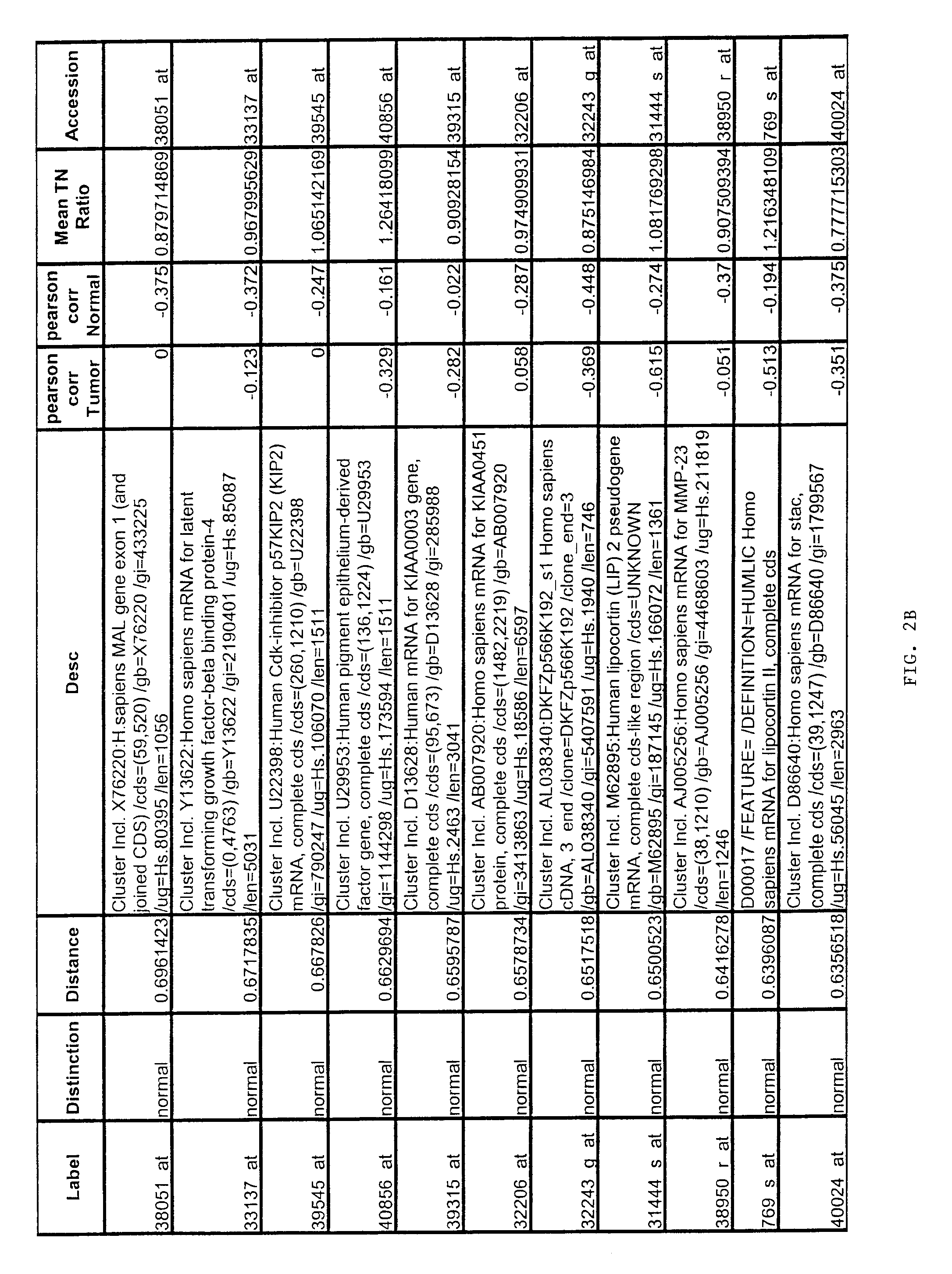
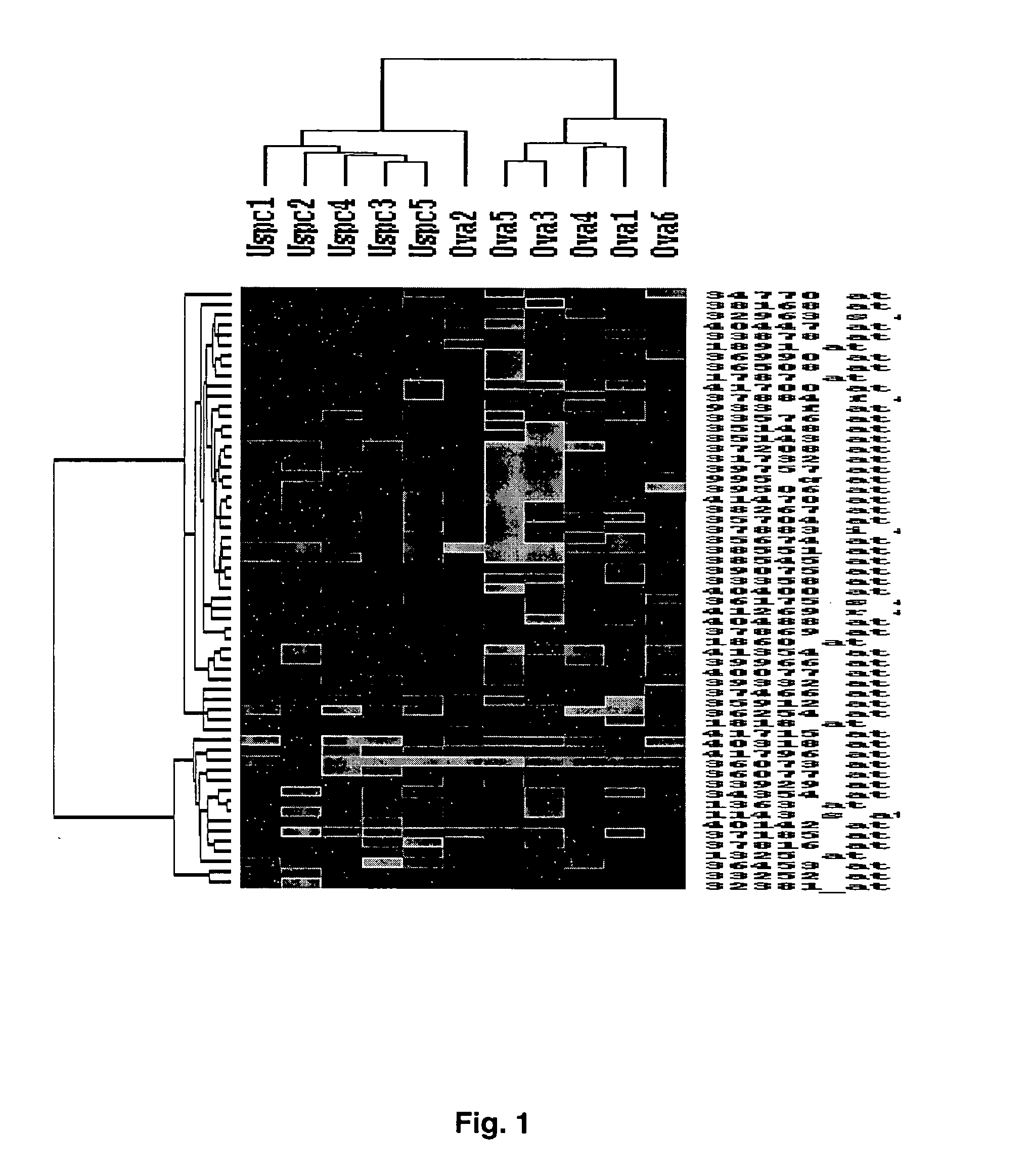
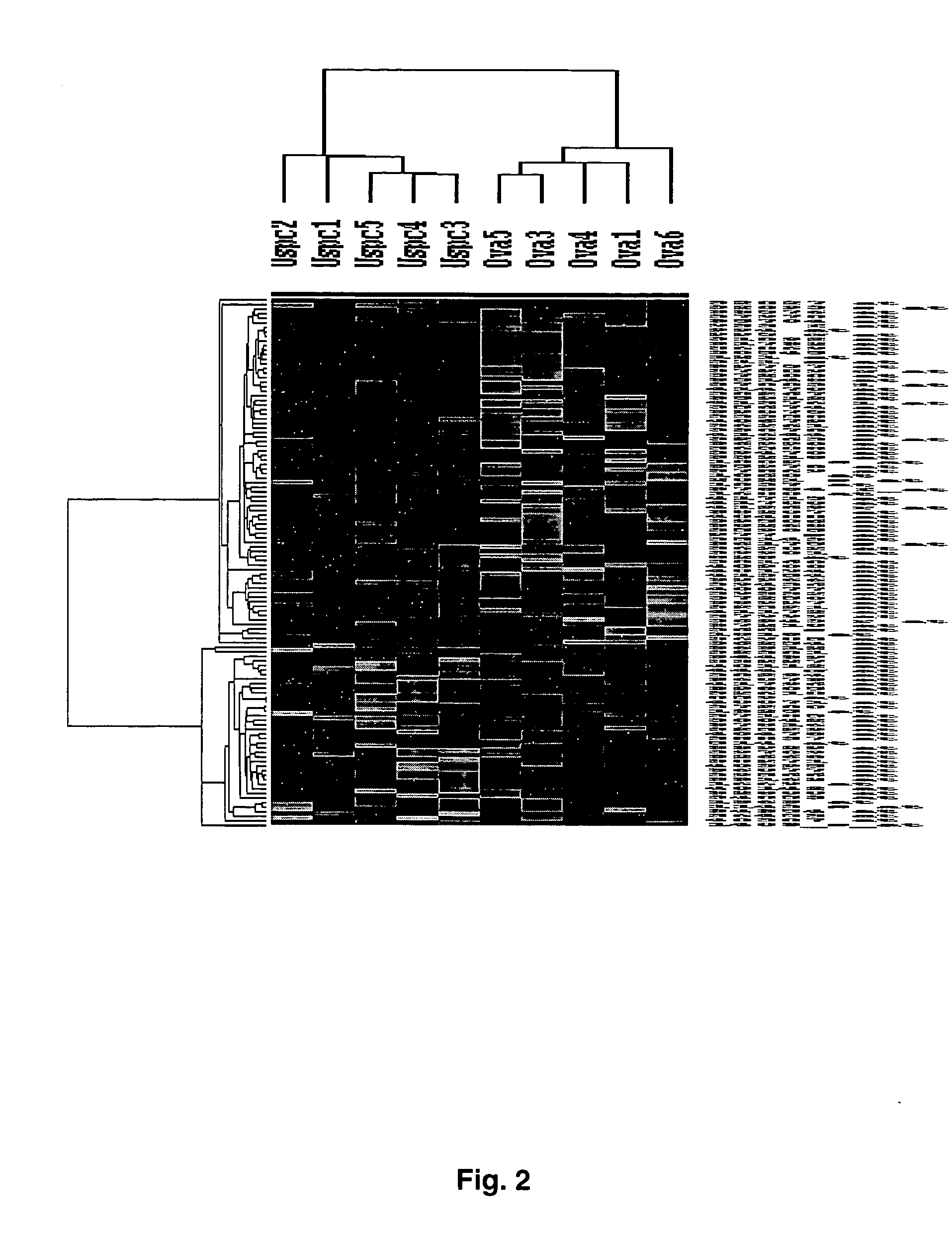
Gene expression profiling of uterine serous papillary carcinomas and ovarian serous papillary tumors
InactiveUS20050037389A1Different responseAccelerated differential diagnosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPapillary carcinomaEndometrial epithelium
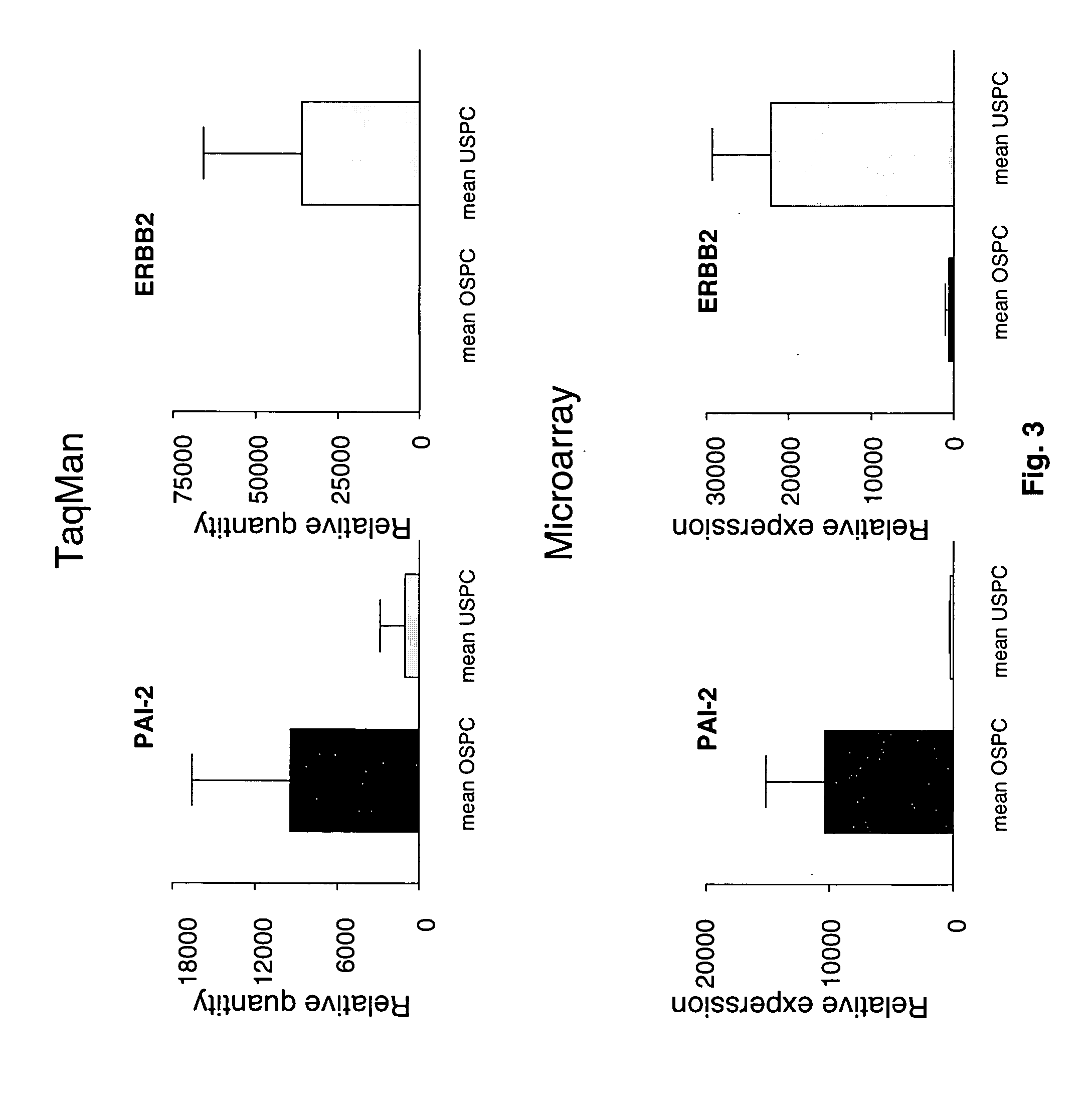
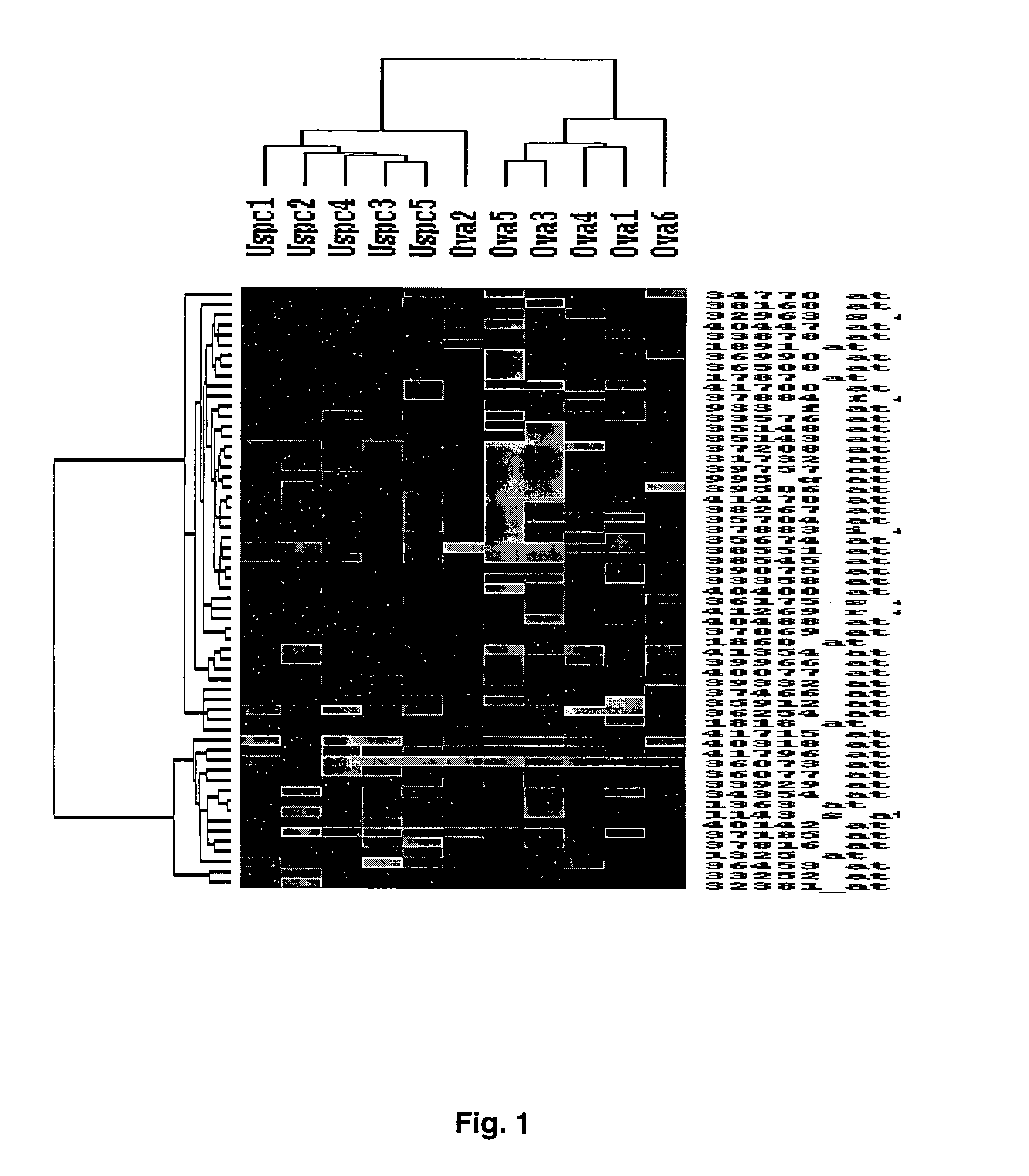
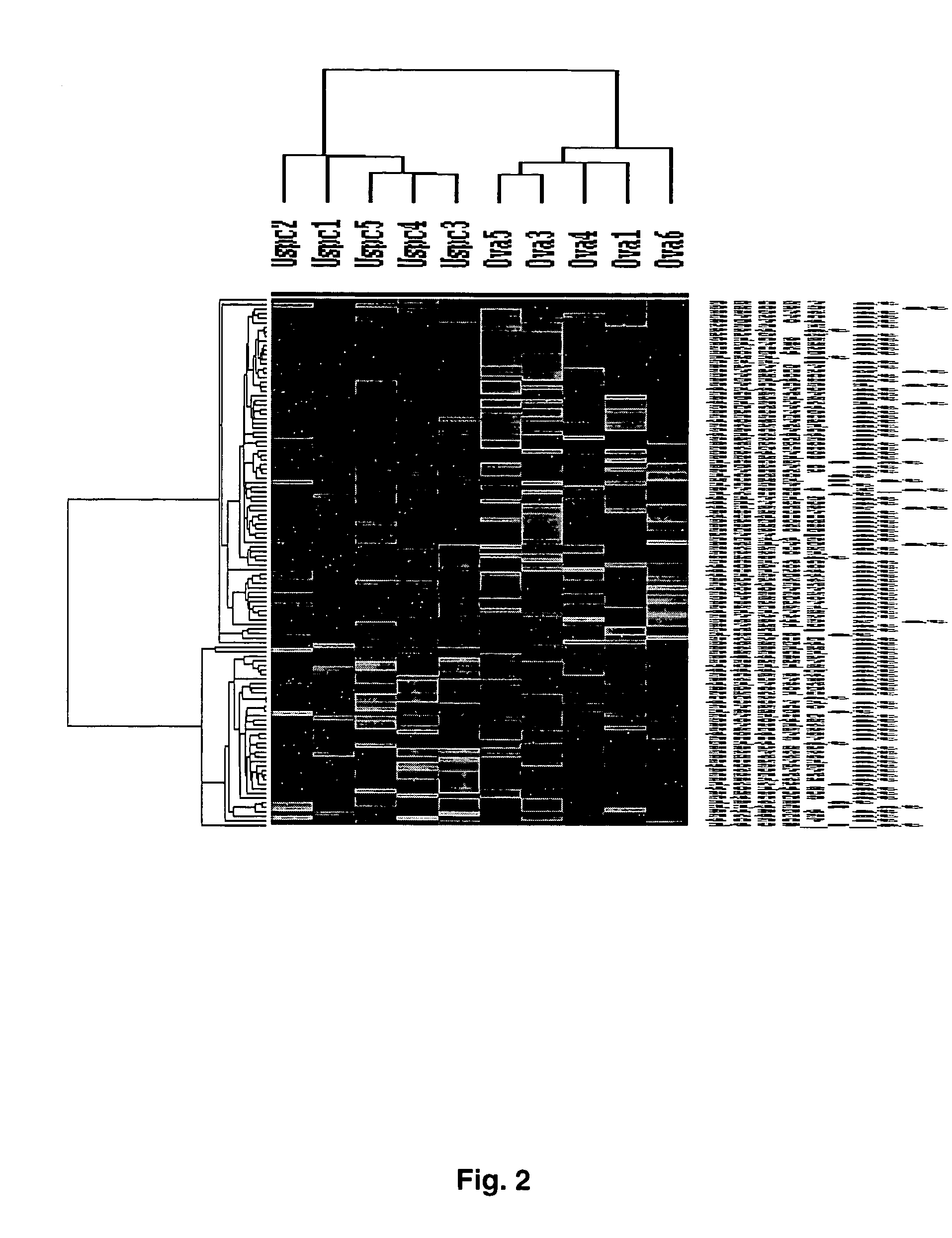
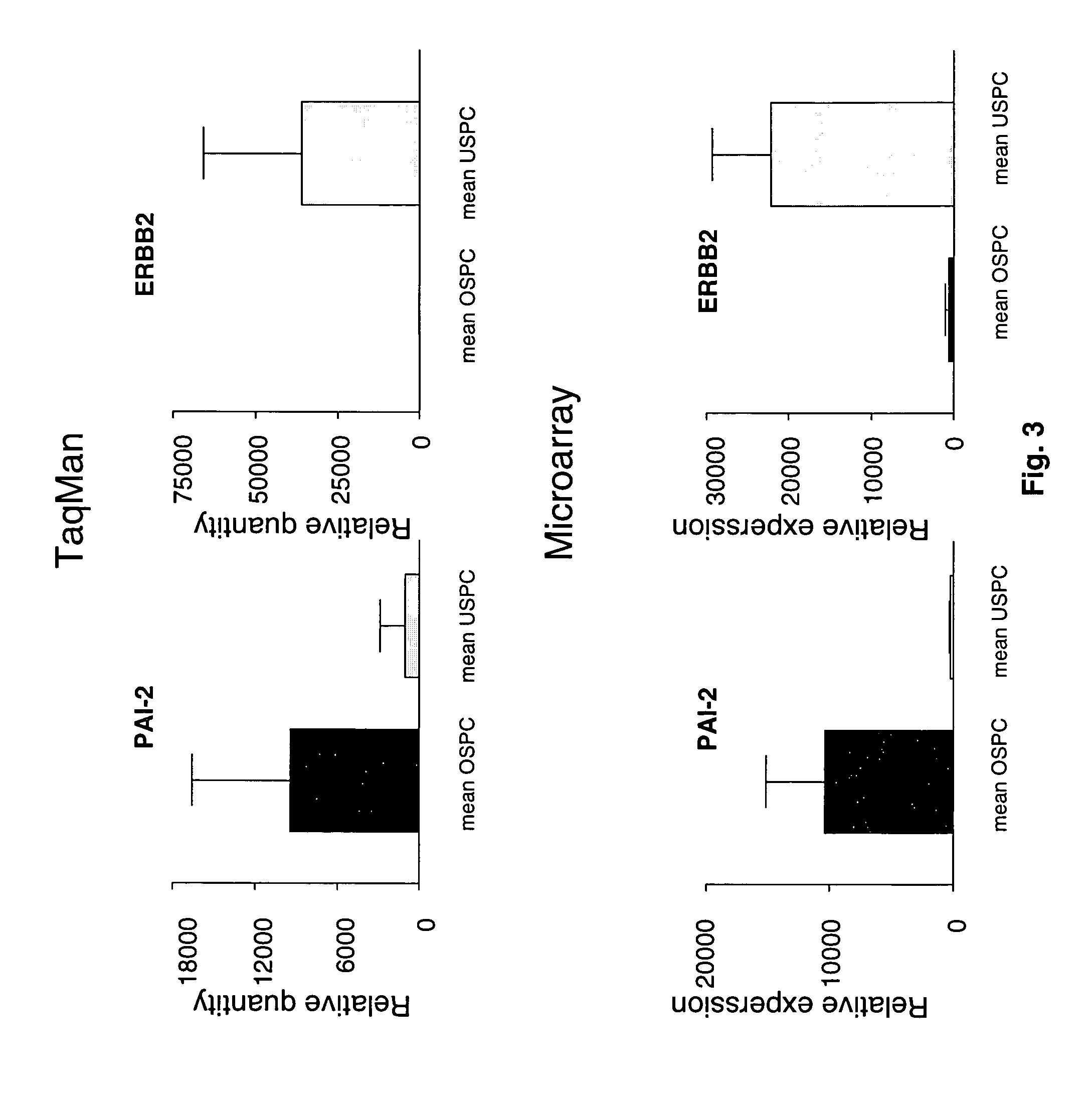
Oligonucleotide microarrays were used to profile and compare gene expression patterns between uterine serous papillary carcinoma and ovarian serous papillary carcinoma or normal endometrial epithelial cells. mRNA fingerprints readily distinguish the more biologically aggressive and chemotherapy resistant USPC from OSPC or NEC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is the most highly up-regulated gene in OSPC relative to USPC, whereas the c-erbB2 gene product (HER-2 / neu) is strikingly overexpressed in USPC relative to OSPC and may therefore represent a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker for this highly aggressive subset of endometrial tumors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060172325A1Enabling detectionImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligonucleotide MicroarrayBioinformatics
Disclosed herein are oligonucleotide microarrays, wherein the microarrays comprise a plurality of target-specific oligonucleotide probes, including both sense and antisense probe pairs for each target nucleic acid. Such arrays are useful for high throughput detection of target nucleic acids in a sample, particularly when coupled to multiplex PCR. Also disclosed herein are methods of using the disclosed microarrays.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating mental retardation
InactiveUS20070015194A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementINFANTILE BILATERAL STRIATAL NECROSISNucleic acid sequencing
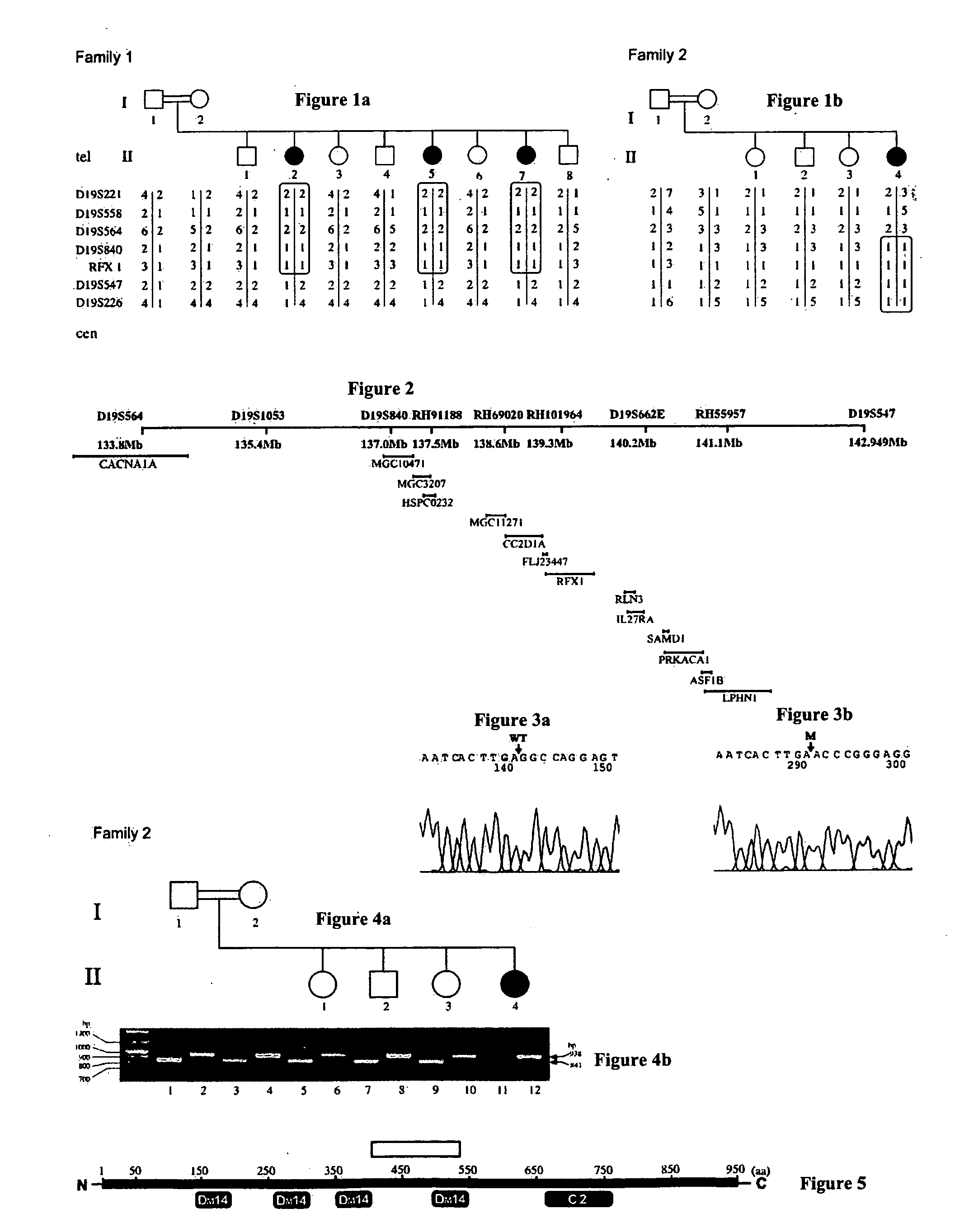
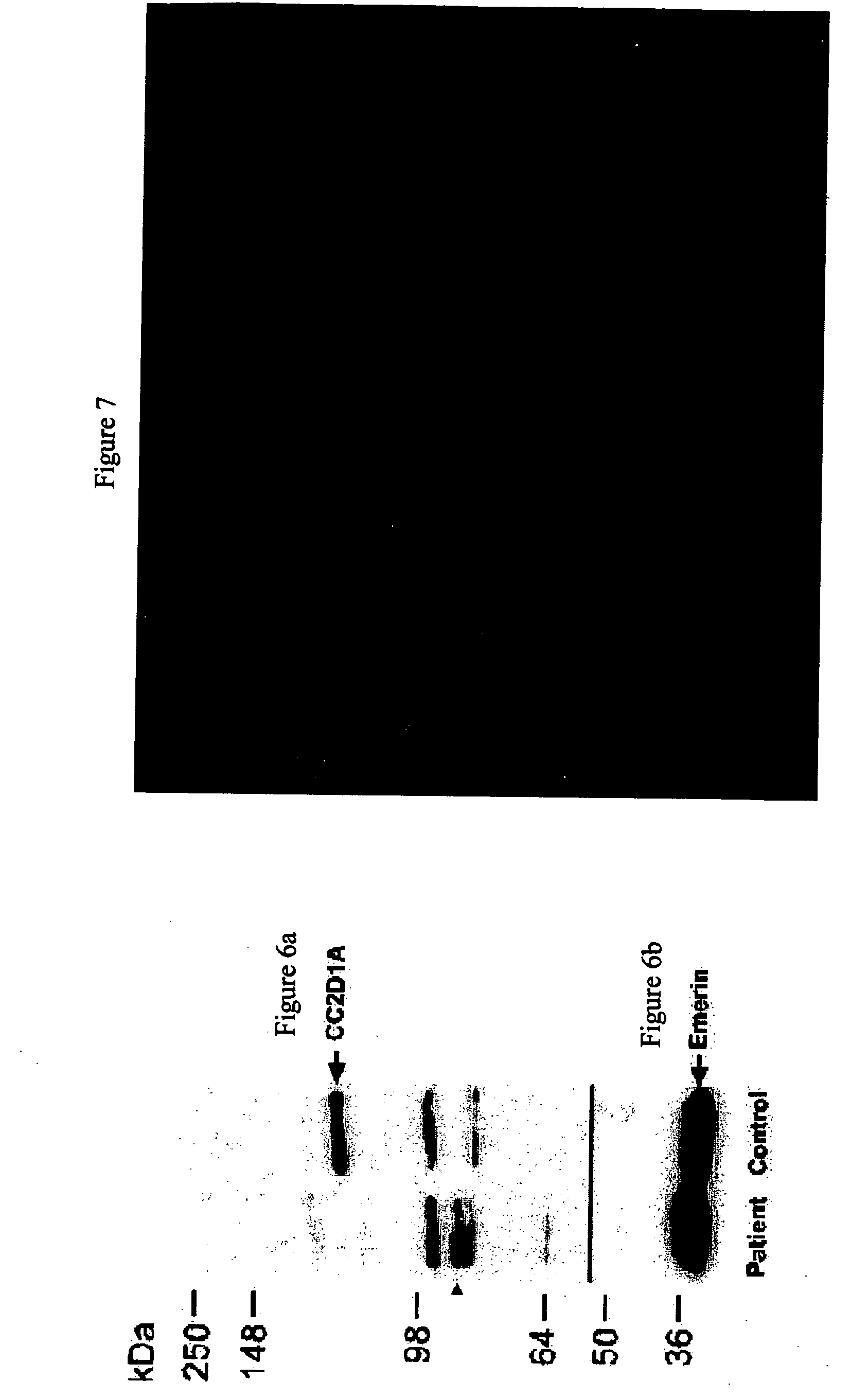
The present invention provides methods, kits, isolated nucleic acid sequences, antibodies and addressable oligonucleotides microarrays which can be for analyzing sequence alterations and detecting the expression level of CC2D1A or nup62 in cells of an individual and thus diagnose nonsyndromic mental retardation (NSMR) and / or infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (IBSN) in the individual. In addition, the present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions which can be used to treat pathologies associated with mental retardation such as NSMR or IBS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Prostate cancer diagnosis and outcome prediction by expression analysis
InactiveUS20060008838A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisProstate cancerOutcome prediction
Methods identifying prostate cancer, methods for prognosing and diagnosing prostate cancer, methods for identifying a compound that modulates prostate cancer development, methods for determining the efficacy of a prostate cancer therapy, and oligonucleotide microarrays containing probes for genes involved in prostate cancer development are described.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
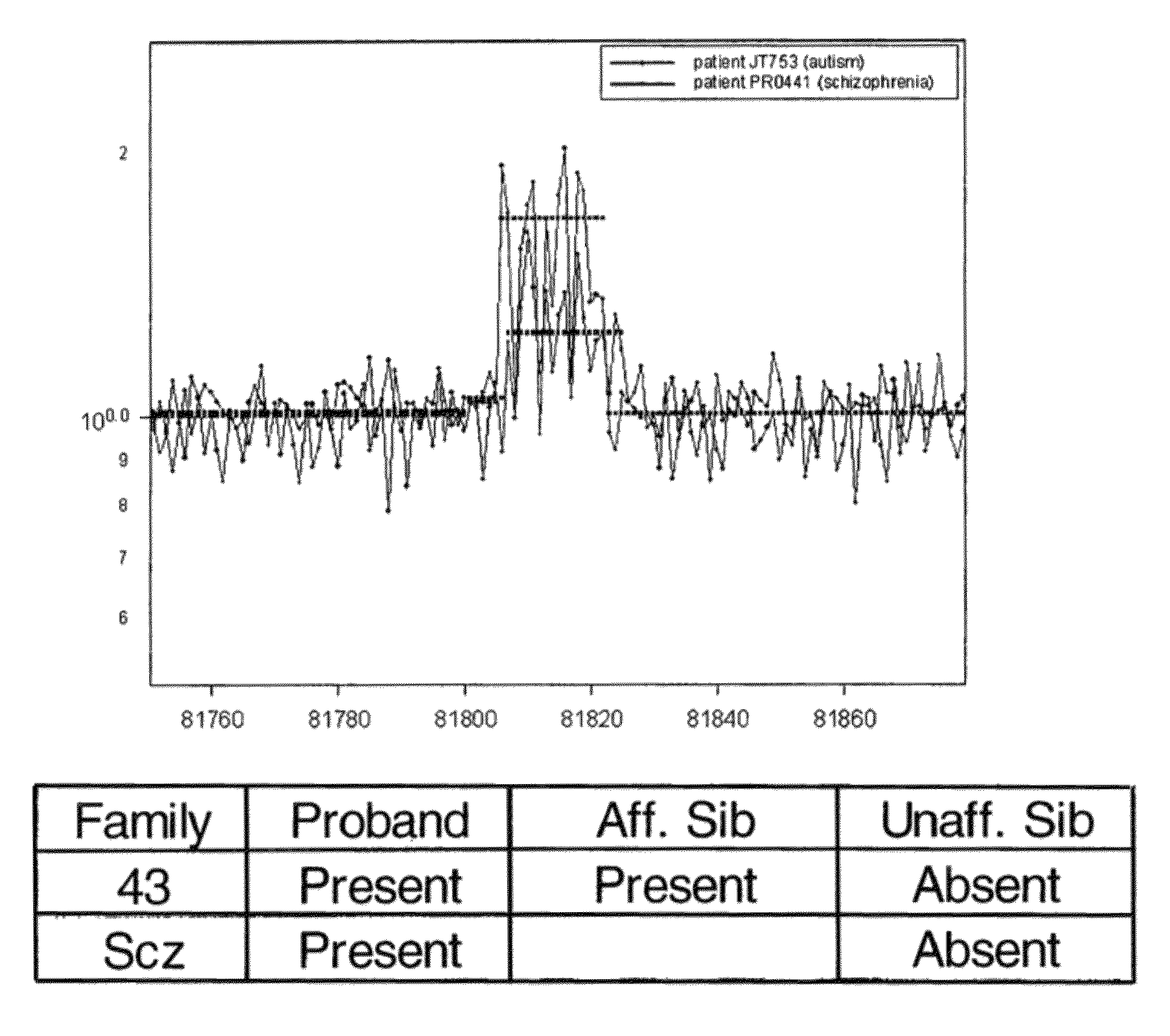
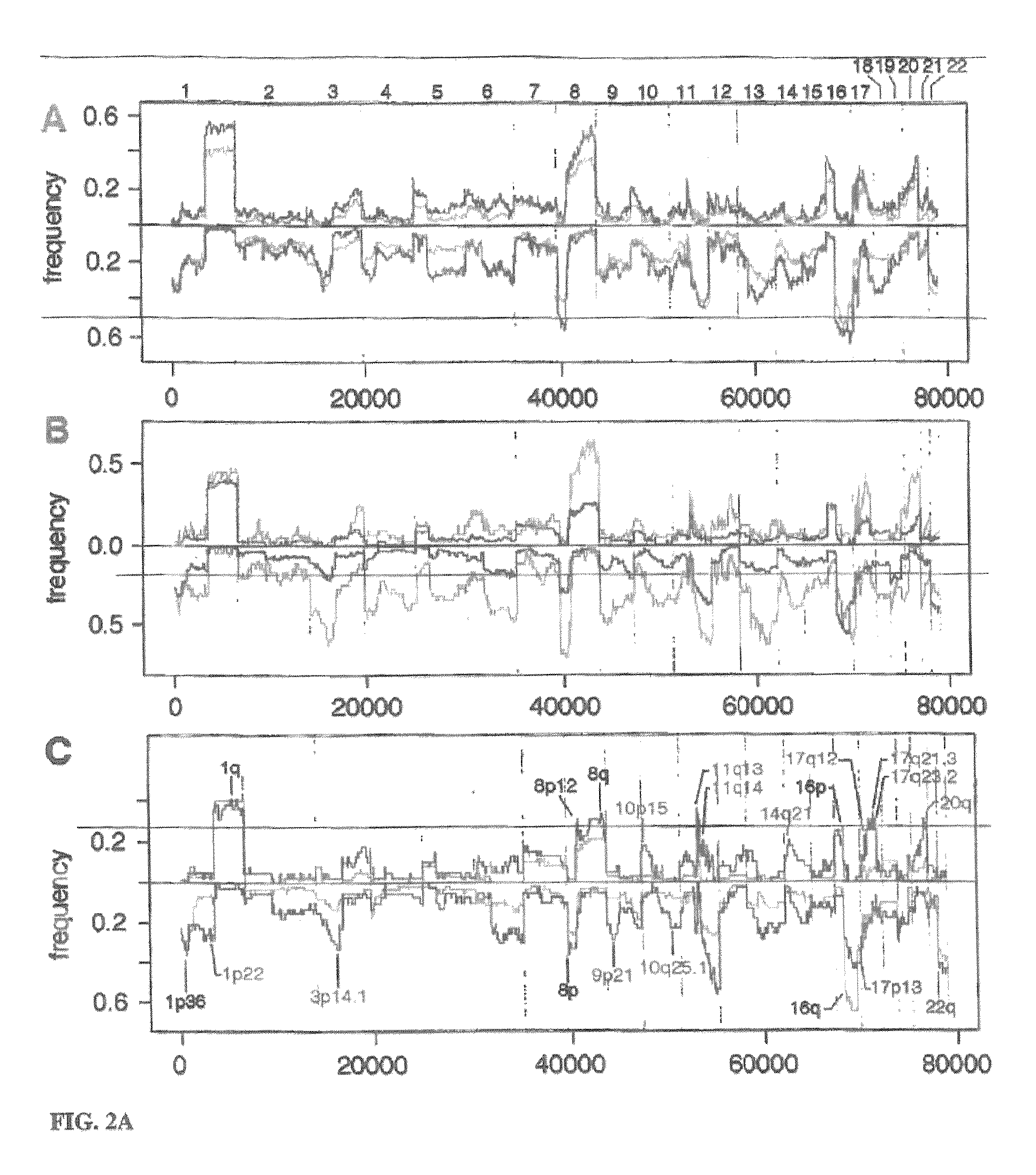
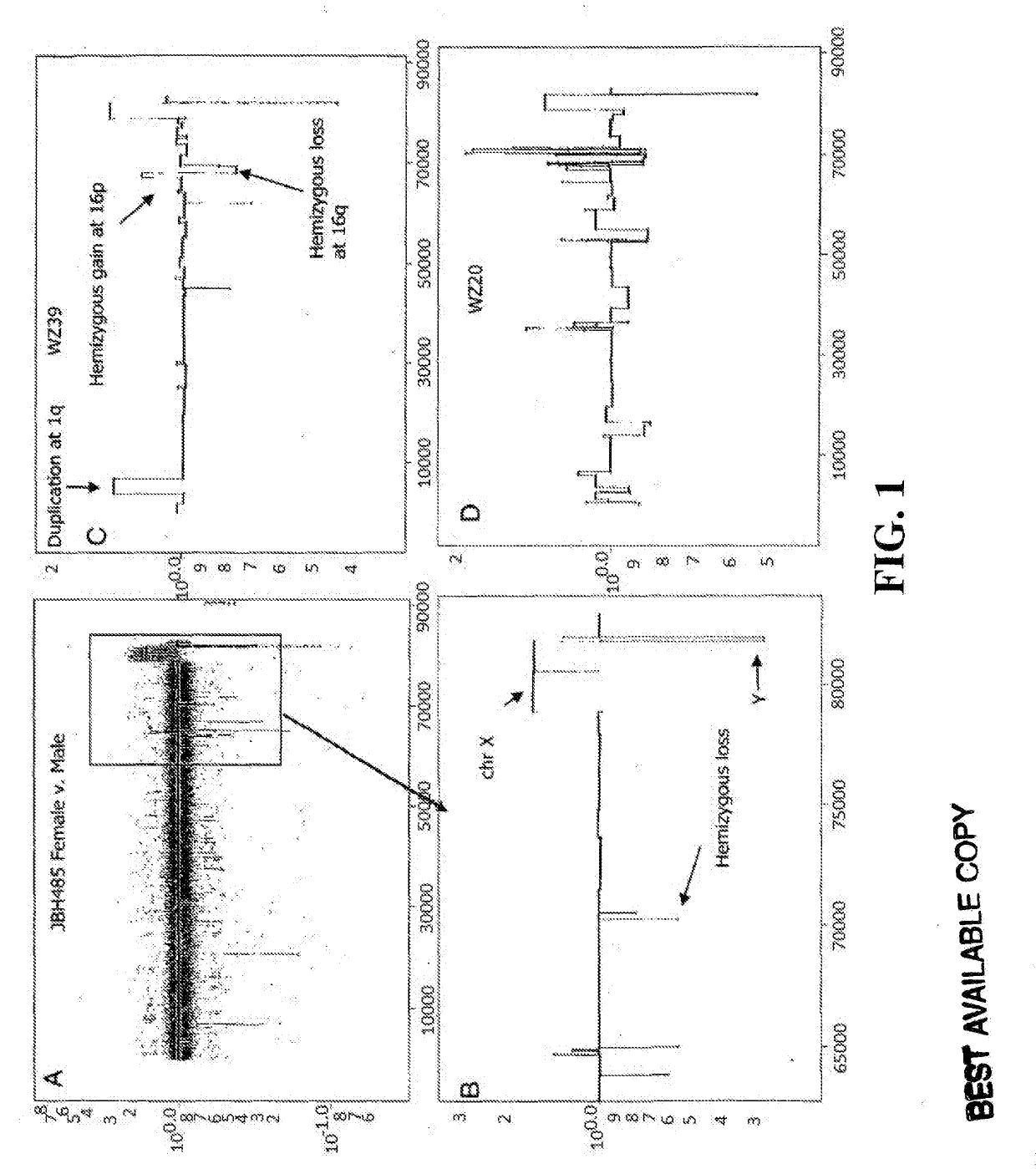
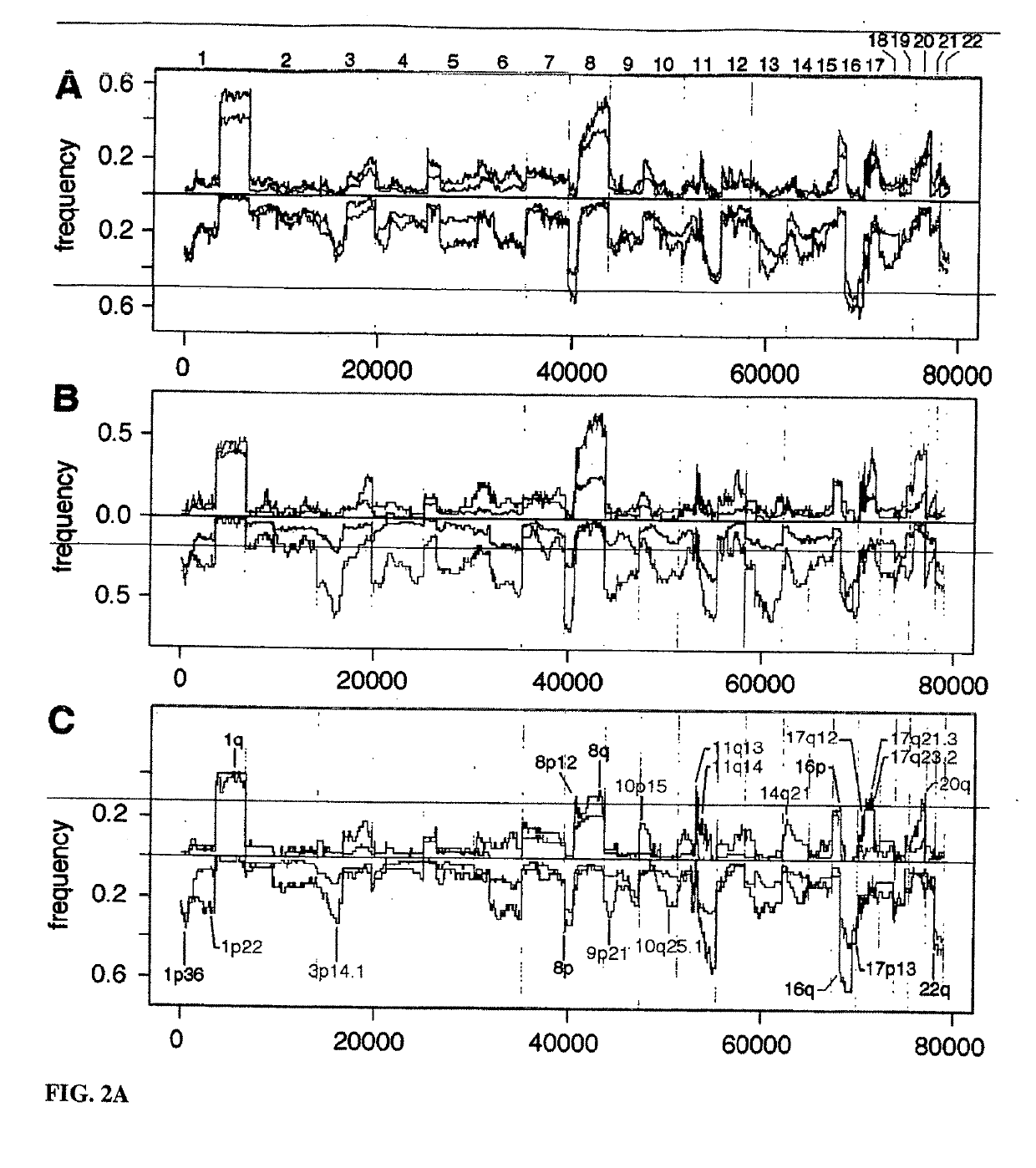
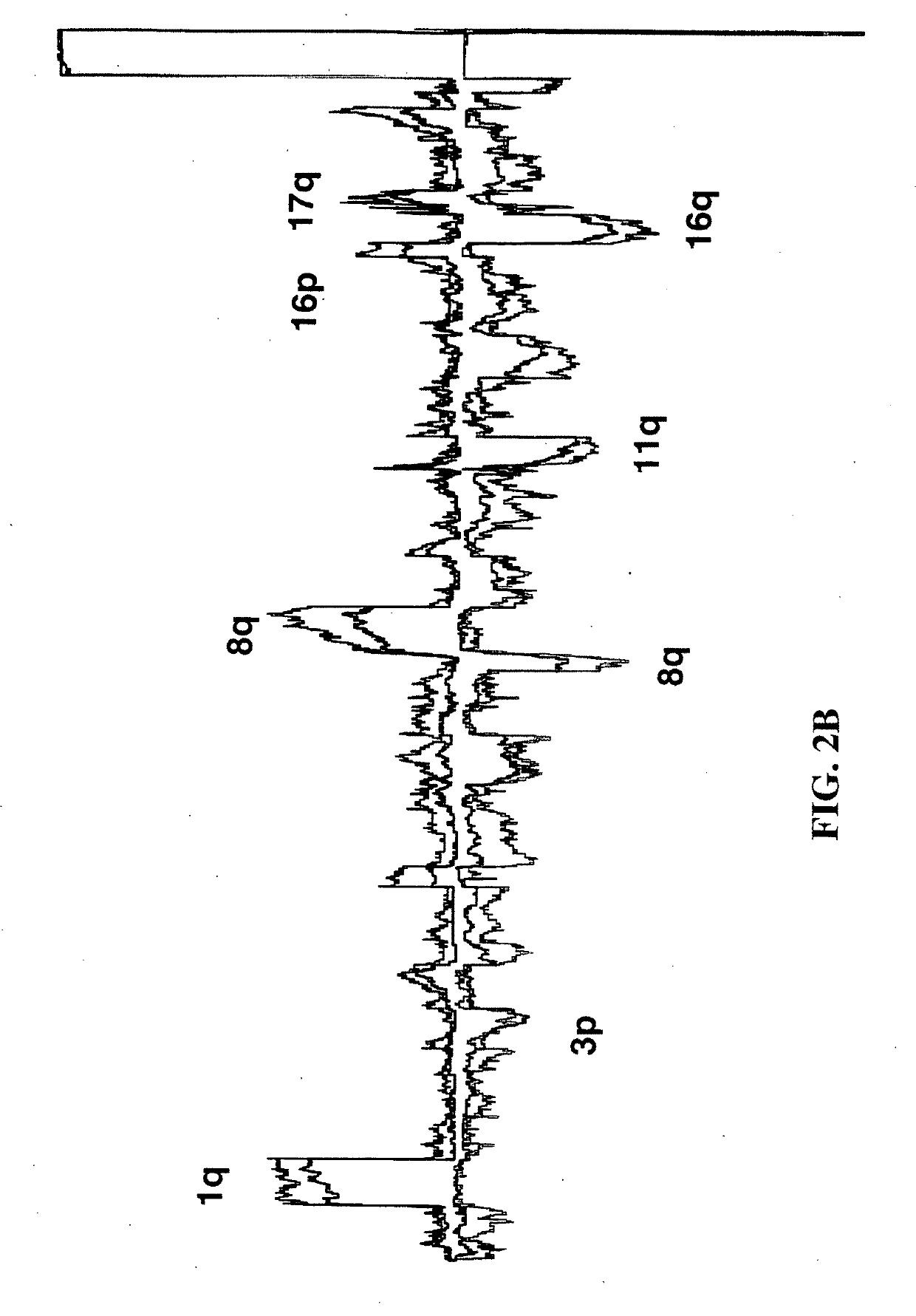
Determining a probabilistic diagnosis of autism by analysis of genomic copy number variations
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to genomic profiling, and in particular, to assigning probabilistic measure of clinical outcome for a patient having a disease or a tumor using segmented genomic profiles such as those produced by representational oligonucleotide microarray analysis (ROMA).
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Single molecule dsDNA microarray chip preparation method
InactiveCN1590559APromote commercial applicationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological studiesPolymerase L
A process for preparing the unimolecular ds DNA microarray on the surface of solid carrier includes chemically synthesizing target oligonucleotide and universal oligonucleotide, renaturation of them, linking them to the surface of solid carrier to become oligonucleotide microarray, on-chip polymerase elongation reaction to become bimolecular dsDNA microarray, modifying to become ssDNA microarray, renaturation to form hairpin structure, and on-chip polymerase elongation reaction.
Owner:王进科 +2
Oligonucleotide microarray technique for detecting pathogen contamination in seawater
InactiveCN101580877AStrong specificityThe detection operation process is shortNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDigoxinEnrichment culture
The invention relates to an oligonucleotide microarray technique for detecting pathogen contamination in seawater, belonging to the field of seawater contamination monitoring. The technique comprises the main technical schemes that a 16S-23S rRNA gene transcription interval sequence is used as a detection target and is amplified by a one-step polymerase chain reaction, a digoxin mark is obtained simultaneously, and then oligonucleotide hybridization is carried out; and the obtained monitoring result is interpreted in a manner that an enzyme-labeled antibody catalyzes the substrate colour development. Compared with the traditional product for detecting seawater contamination, the invention utilizes microarray detection to obtain the distribution situation of large numbers of pathogens and contamination index bacteria, and has the advantage of high flux; the invention can directly utilize seawater as a sample and truly obtain the contamination situation information of target bacteria under a condition of keeping the natural proportion of the flora number in the seawater; however, most existing detection techniques need the step of enrichment culture, destroy the original proportion of a flora composition, have lower reliability of the result and have longer detection procedure; and the oligonucleotide microarray detection operation has short procedure and is comparatively sensitive and fast.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
K-ras oligonucleotide microarray and method for detecting K-ras mutations employing the same
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
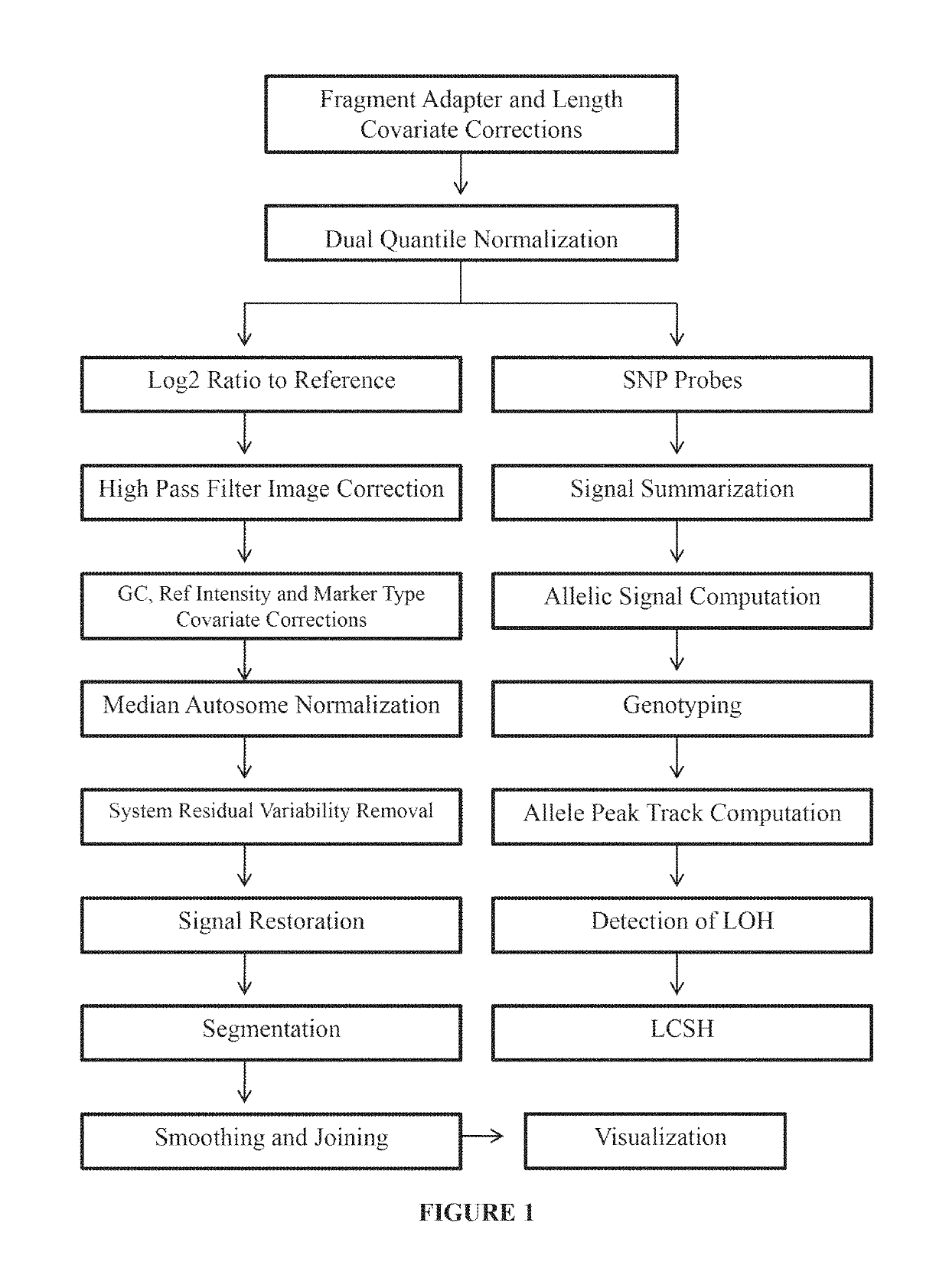
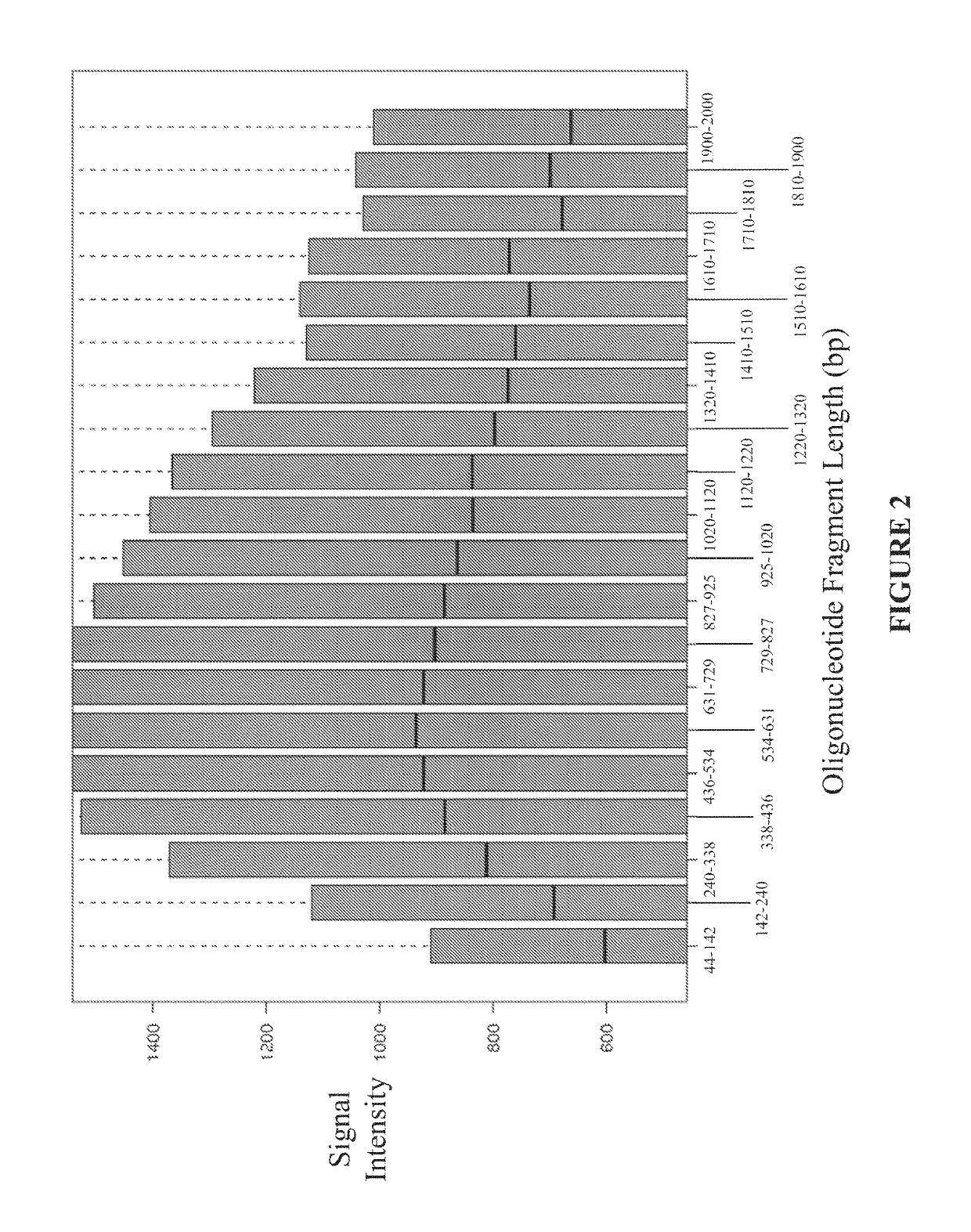
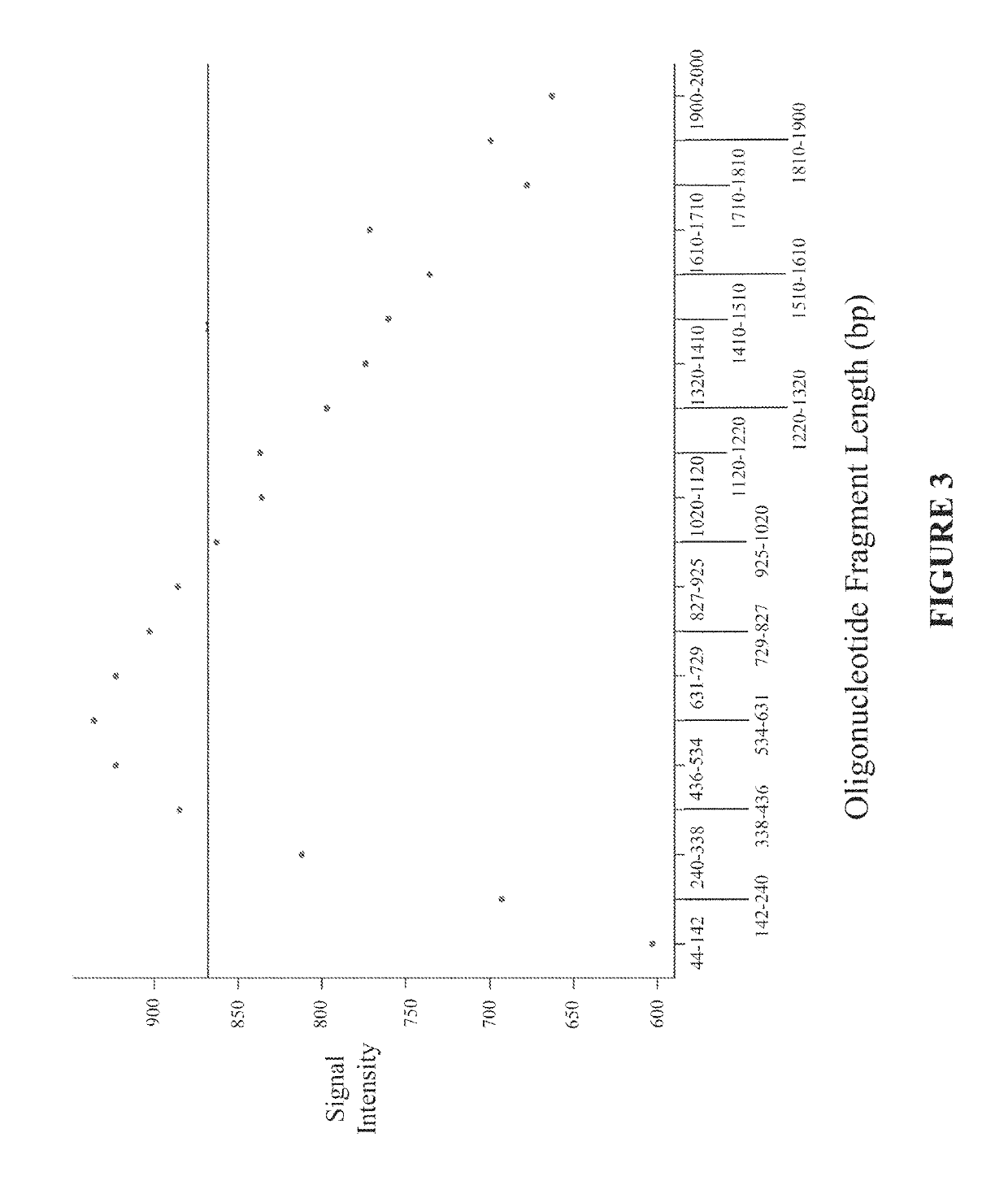
Analysis of Data Obtained from Microarrays
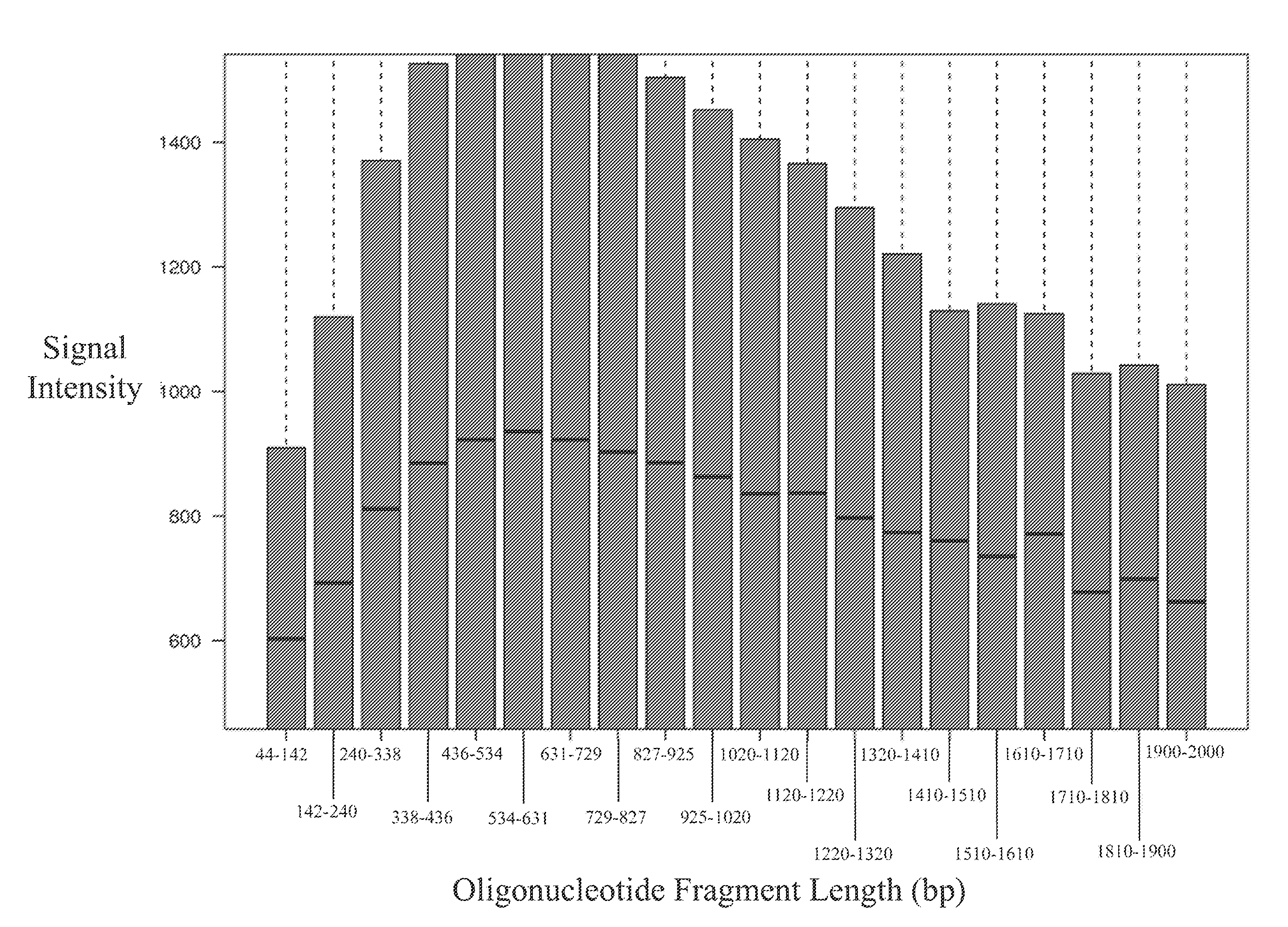
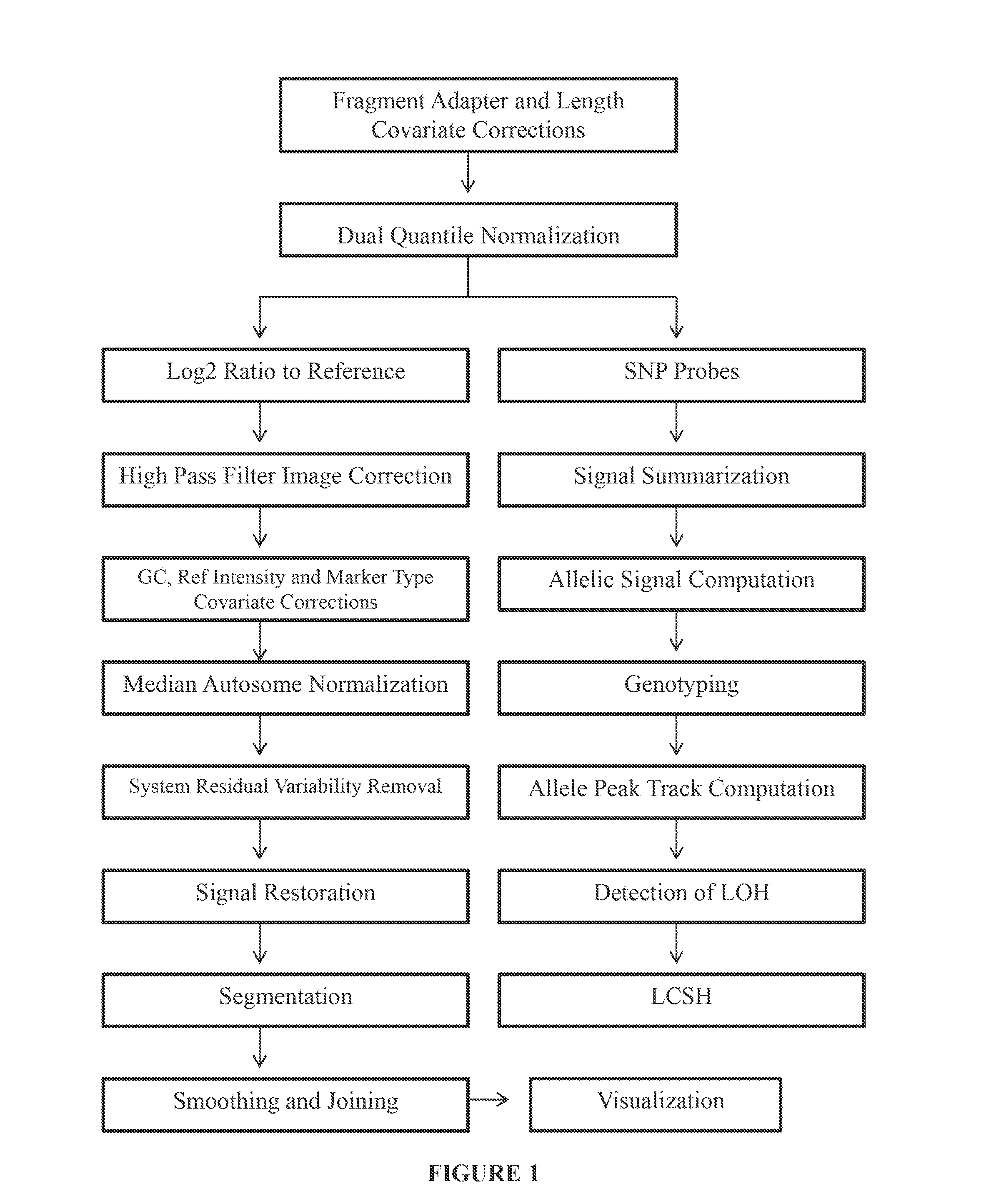
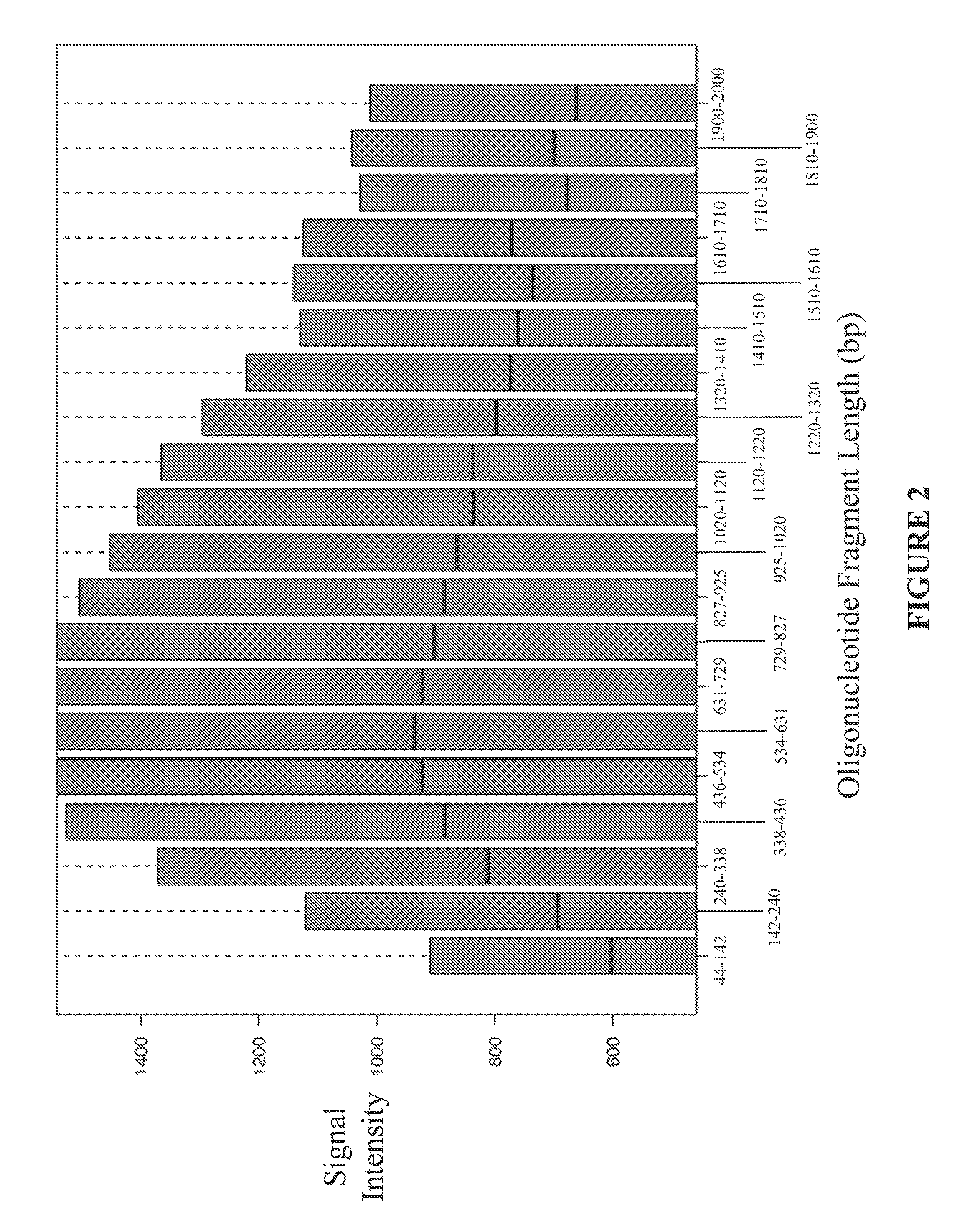
Disclosed are methods and software for biological data analysis. Specifically, provided are methods, computer programs and systems for analyzing data in the form of various intensity measurements obtained from an oligonucleotides microarray experiment. Such data may be microarray data obtained from an experiment conducted to determine copy number of a human genetic sample. The data are corrected by application of one or more covariate adjusters which may be applied simultaneously and which may be selected by a user. Further, the present application provides methods of filtering image data and signal restoration of image data using log2 ratio data.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Quantifying method for oligonucleotide microarray
InactiveCN101586156ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesLength wave
The invention relates to a quantifying method for an oligonucleotide microarray, and in particular provides a method and a device for simultaneously quantitatively measuring multiple nucleic acids from one or more pathogens in a sample in real time. Amplicons of target nucleic acids and internal nucleic acid contrast labeled by fluorescence are positioned on the matrix surface by hybridizing with target nucleic acid probes which are arranged in a predetermined two-dimensional mode and bound on the matrix surface and internal nucleic acid contrast probes. The hybridized amplicons can be detected by exciting fluorescence labels of the amplicons by using evanescent wave of proper wavelength light. By measuring fluorescence intensity on different positions of the matrix surface, abundance of hybridized amplicons of each target nucleic acid and the internal nucleic acid contrast can be determined.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Oligonucleotide microarray for identification of pathogens
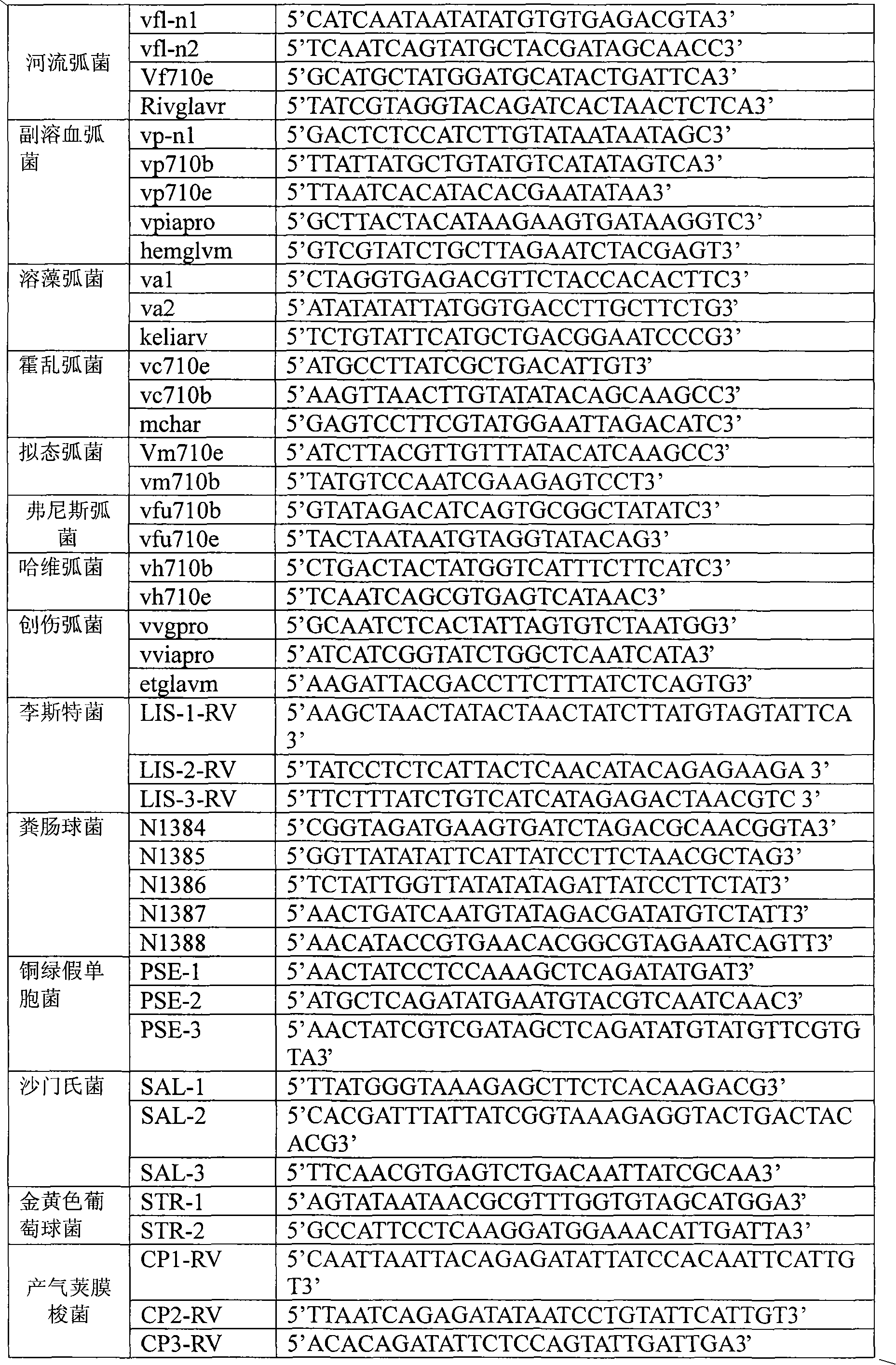
ActiveUS8741565B2Rapidly and easily determinedSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesNucleic acid detectionTest sample
A method for detecting a target nucleic acid of a pathogen in a test sample, the method comprising preparing a target nucleic acid detecting reagent and contacting the target nucleic acid detecting reagent with an oligonucleotide microarray. A kit for detecting a target nucleic acid of a pathogen in a test sample is also described. The kit comprises at least one primer pair and an oligonucleotide microarray comprising at least one probe.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for preparing birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip
InactiveCN101514372AGuaranteed check outReduce detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationComparative genomic hybridizationGenome
The present invention relates to the field of diagnostic reagent and provides a method for preparing birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip. The birth defect target oligonucleotide microarray comparative genomic hybridization hybrid chip prepared by the method of the invention is constructed by the probes of specifically targeted chromosome or chromosome area. Not only can the detection of pathological CNVs be guaranteed, but also the detection of CNVs which have indefinite clinical meaning can be greatly reduced.
Owner:戴勇
Gene expression profiling of uterine serous papillary carcinomas and ovarian serous papillary tumors
InactiveUS7659062B2Different responseEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPapillary carcinomaEndometrial epithelium
Oligonucleotide microarrays were used to profile and compare gene expression patterns between uterine serous papillary carcinoma and ovarian serous papillary carcinoma or normal endometrial epithelial cells. mRNA fingerprints readily distinguish the more biologically aggressive and chemotherapy resistant USPC from OSPC or NEC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor is the most highly up-regulated gene in OSPC relative to USPC, whereas the c-erbB2 gene product (HER-2 / neu) is strikingly overexpressed in USPC relative to OSPC and may therefore represent a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker for this highly aggressive subset of endometrial tumors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Linkers and co-coupling agents for optimization of oligonucleotide synthesis and purification on solid supports
InactiveUS20070287832A1Promote hydrolysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid surfaceTime-Consuming
A method of modulation of synthesis capacity on and cleavage properties of synthetic oligomers from solid support is described. The method utilizes linker molecules attached to a solid surface and co-coupling agents that have similar reactivities to the coupling compounds with the surface functional groups. The preferred linker molecules provide an increased density of polymers and more resistance to cleavage from the support surface. The method is particularly useful for synthesis of oligonucleotides, oligonucleotides microarrays, peptides, and peptide microarrays. The stable linkers are also coupled to anchor molecules for synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides using on support purification, eliminating time-consuming chromatography and metal cation presence. Oligonucleotides thus obtained can be directly used for mass analysis, DNA amplification and ligation, hybridization, and many other applications.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
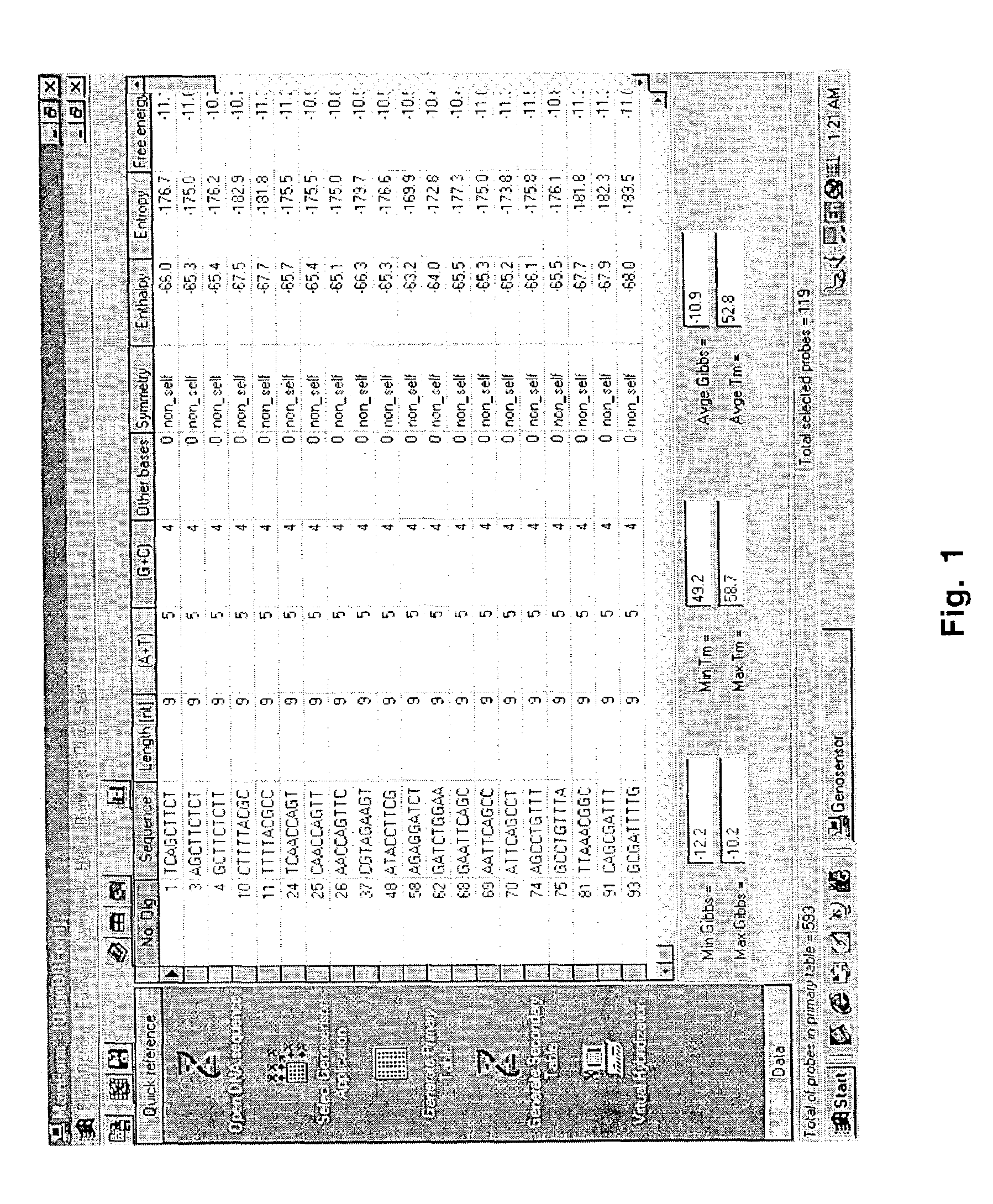
Oligonucleotide probes for genosensor chips
InactiveUS7539579B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein secondary structureMultiple criteria
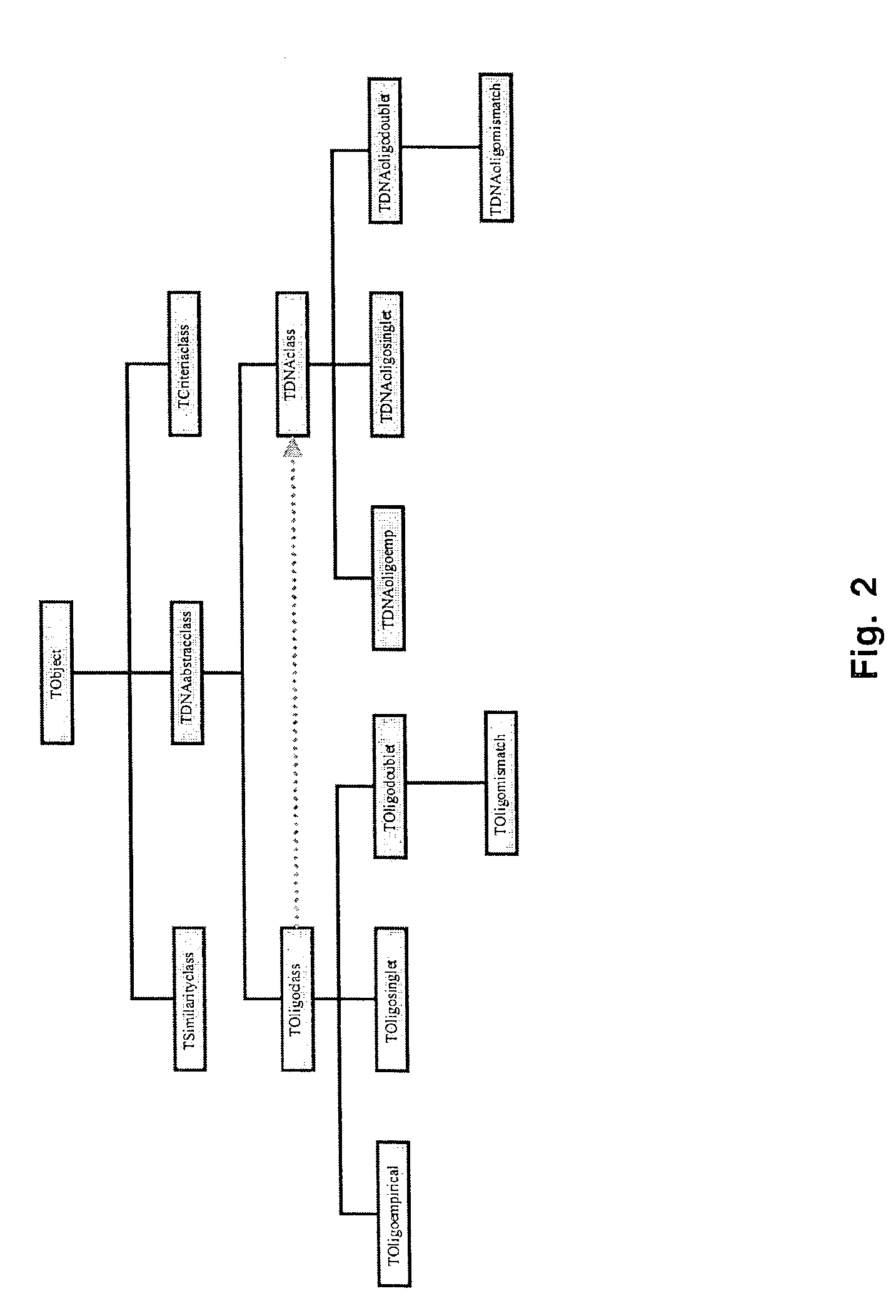
Software for designing optimized sets of oligonucleotide probes for use in genosensors (oligonucleotide microarrays) is disclosed. The selection of probe sequences is based on multiple criteria including thermal stability of the probe-target pairs, similarity degree of the probes with respect to other DNA sequences, and evaluation of the secondary structure of target molecules. The programs were written in the programming language Borland Delphi by means of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) techniques. The Genosensor Probe Design computer program disclosed herein facilitates the design of optimized arrays of probes which accurately represents the characteristics of the nucleic acid molecule under study, such as its identity or its differences in sequence or abundance with respect to other molecules.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Nucleic acid test method for oligonucleotide microarray by fluorescence resonance energy transferring
InactiveCN1358867AReduce distractionsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide MicroarrayFörster resonance energy transfer
The nucleic acid detection method is characterized by that the nucleic acid sample to be detected and oligonucleotide microarray are hybridized and eluted to make the nucteic acid capable of completely pairing with oligonucleotide probe combine on the gene chip, and the sequence characteristics of oligonucleotide fragment on the oligonucleotide microarray are that the sequence of 5'0terminal and 3'-sequence of target area of nucleic acid sample to be detected are paired, sequence of 3'-terminal and 5'-sequence of target area are paired and middle sequence is oligomeric thymonucleic acid. The terminals are modified by different fluorescence groups respectively, and its middle is modified by using biotin. According to the wavelength of excitation light of fluorescence donor group and wavelength of emtting light of fluorescence receptor group it can detect the fluorescence signal and its position of microarray so as to can define the structural characteristics of said nucleic acid sample and its content.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Oligonucleotide Microarray
The present invention relates to oligonucleotide microarrays comprising short chemically modified RNA oligonucleotides and uses of such microarrays in genomics applications. More specifically, the invention provides an oligonucleotide array comprising a surface and a plurality of oligonucleotide, wherein at least one oligonucleotide has at least one modified sugar moiety at the 2'OH position. The microarrays of the invention are more specifically useful to detect small RNAs.
Owner:WEILER JAN +5
Method and kit for classifying a patient
InactiveUS20130203623A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPersonalized medicineTreatment response
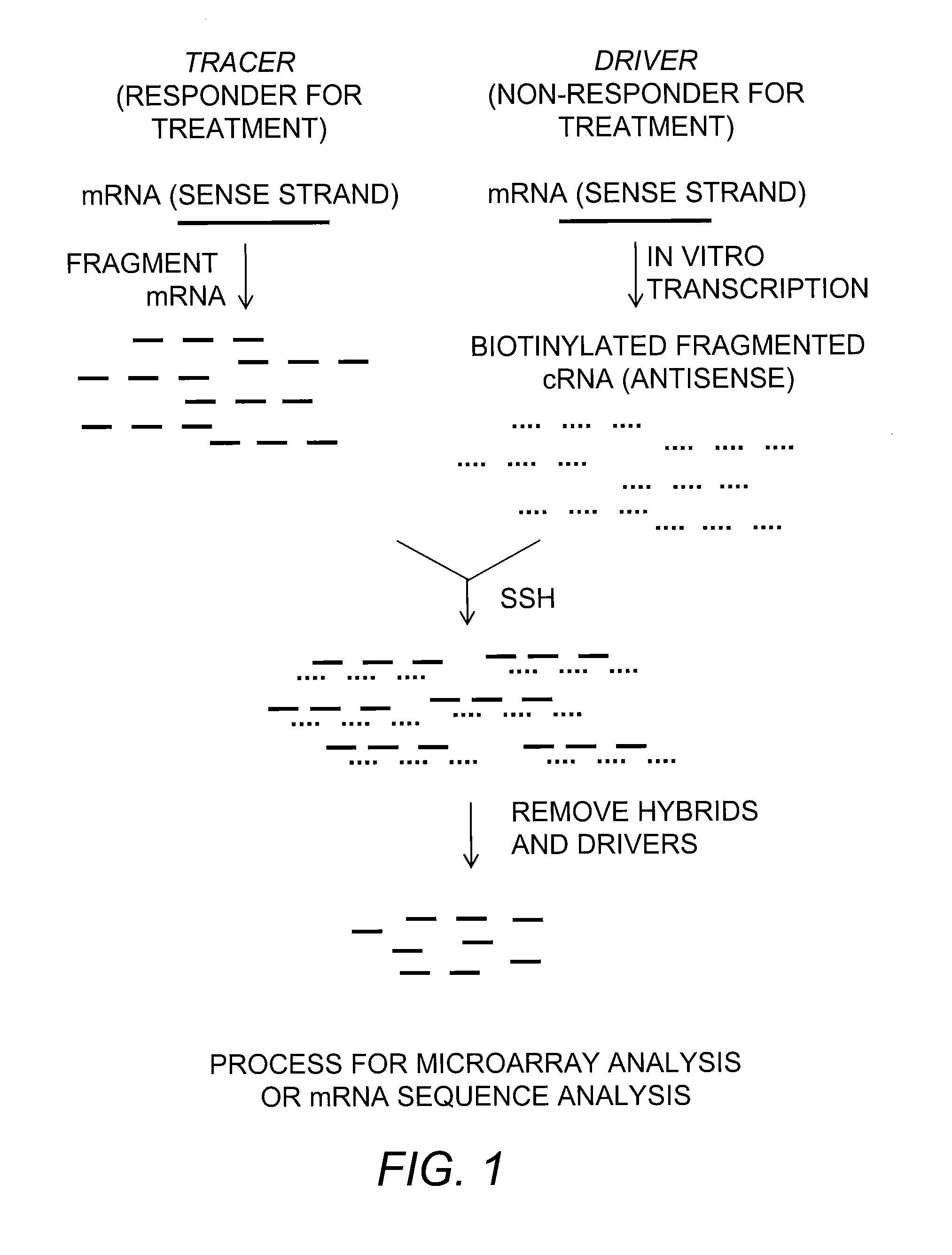
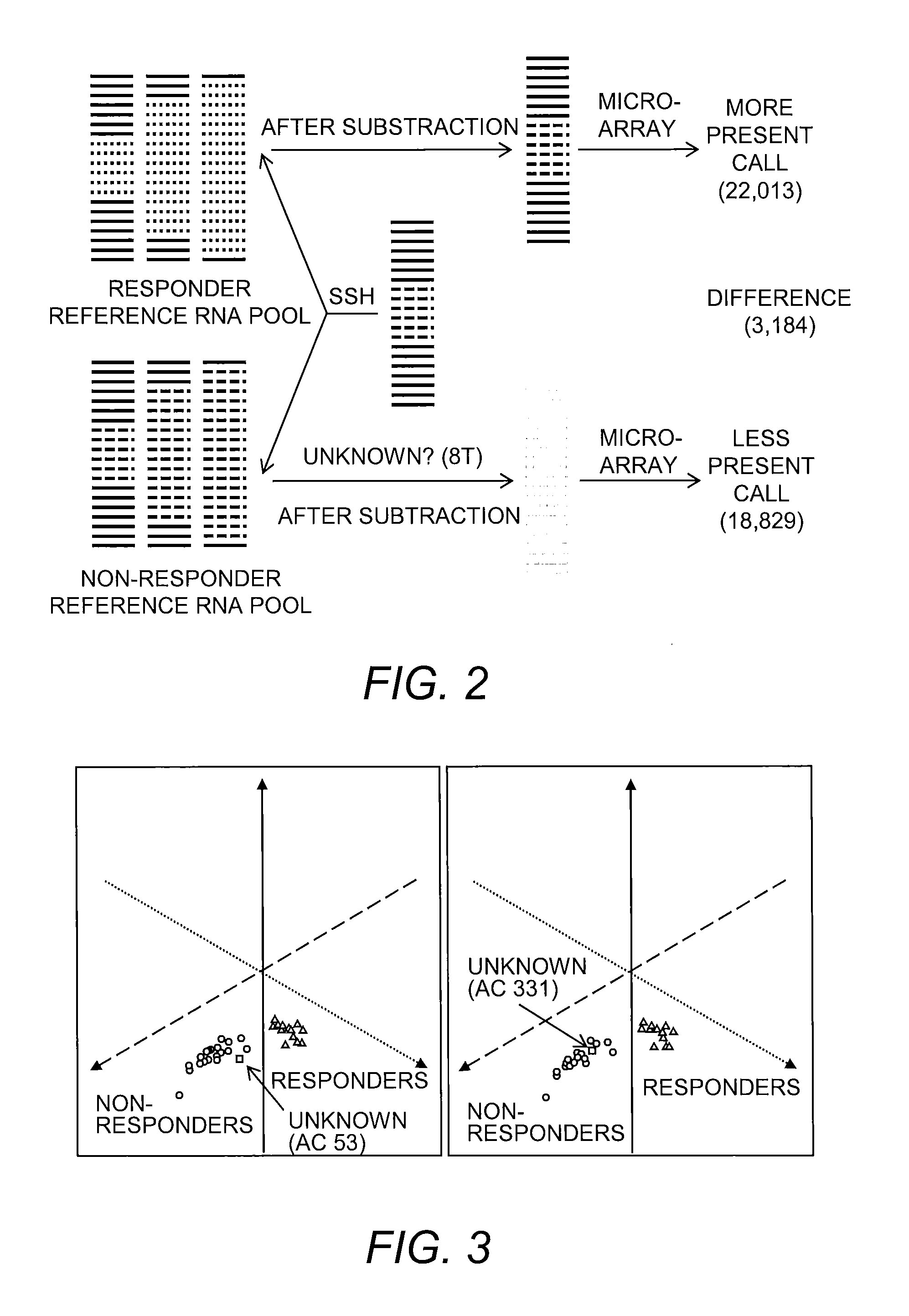
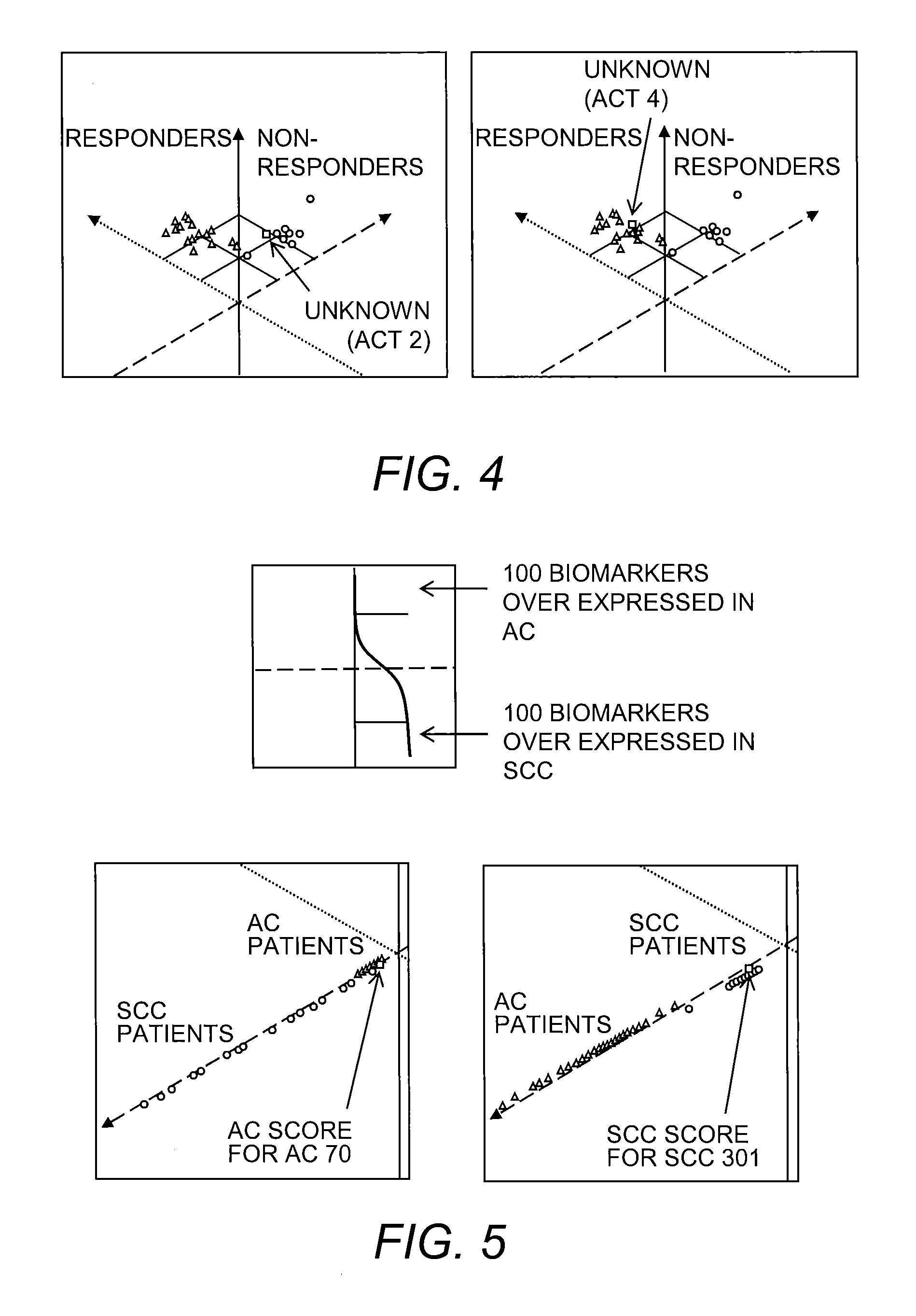
Provided is a Suppressive Subtractive Hybridization-Oligonucleotide Microarray (SSH-OM) method for the prediction of treatment response for personalized medicine applications and for the prediction of cancer classes and subclasses.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Test probes, common oligonucleotide chips, nucleic acid detection method, and their uses
ActiveUS20110218115A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligonucleotide chipDna polymerasen
High-throughput detection for the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample can be achieved by the linear test probe pairs P1 and P2. The test probe pairs P1 and P2 respectively comprise either of the flanking complementary sequences which are adjacent to the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample. When the test probe pairs P1, P2 are annealed and hybridized to the nucleic acid sample, a gap will be generated at the interesting base or the mutation site position between the probe pairs and the sample. Divide the annealed hybrid sample into four equal reaction systems to which add dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP, respectively. The test probe pairs P1 and P2 will be ligated into one single probe when adding the complementary nucleotide system under the DNA polymerase or ligase. After purified and amplified, the generated single probes are hybridized to the corresponding area in a common oligonucleotide microarray. The generated single probe will give a signal in the hybrid area, and therefore detect and analyze the hybrid signal to determine the base type or the mutation genotype at the detection position. The invention can be applied to the re-sequencing the target nucleic acid sequence, the detection and analysis for the mutation, insertion, or deletion sites of a known nucleic acid sequence, and the genotyping of the pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
Determining a probabilistic diagnosis of cancer by analysis of genomic copy number variations
InactiveUS20190325113A1Increase probabilityMedical data miningHealth-index calculationDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to genomic profiling, and in particular, to assigning probabilistic measure of clinical outcome for a patient having a disease or a tumor using segmented genomic profiles such as those produced by representational oligonucleotide microarray analysis (ROMA).
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
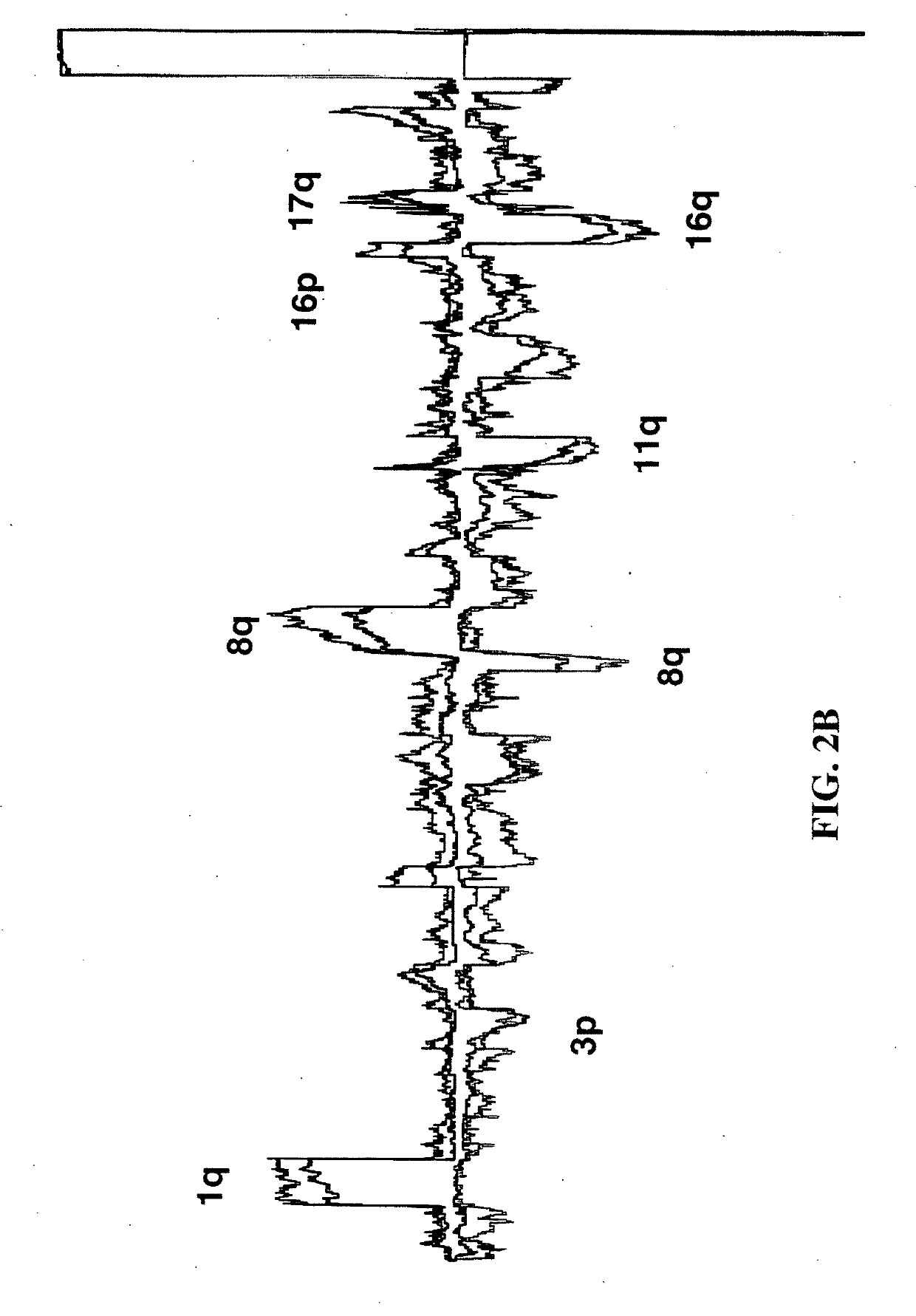
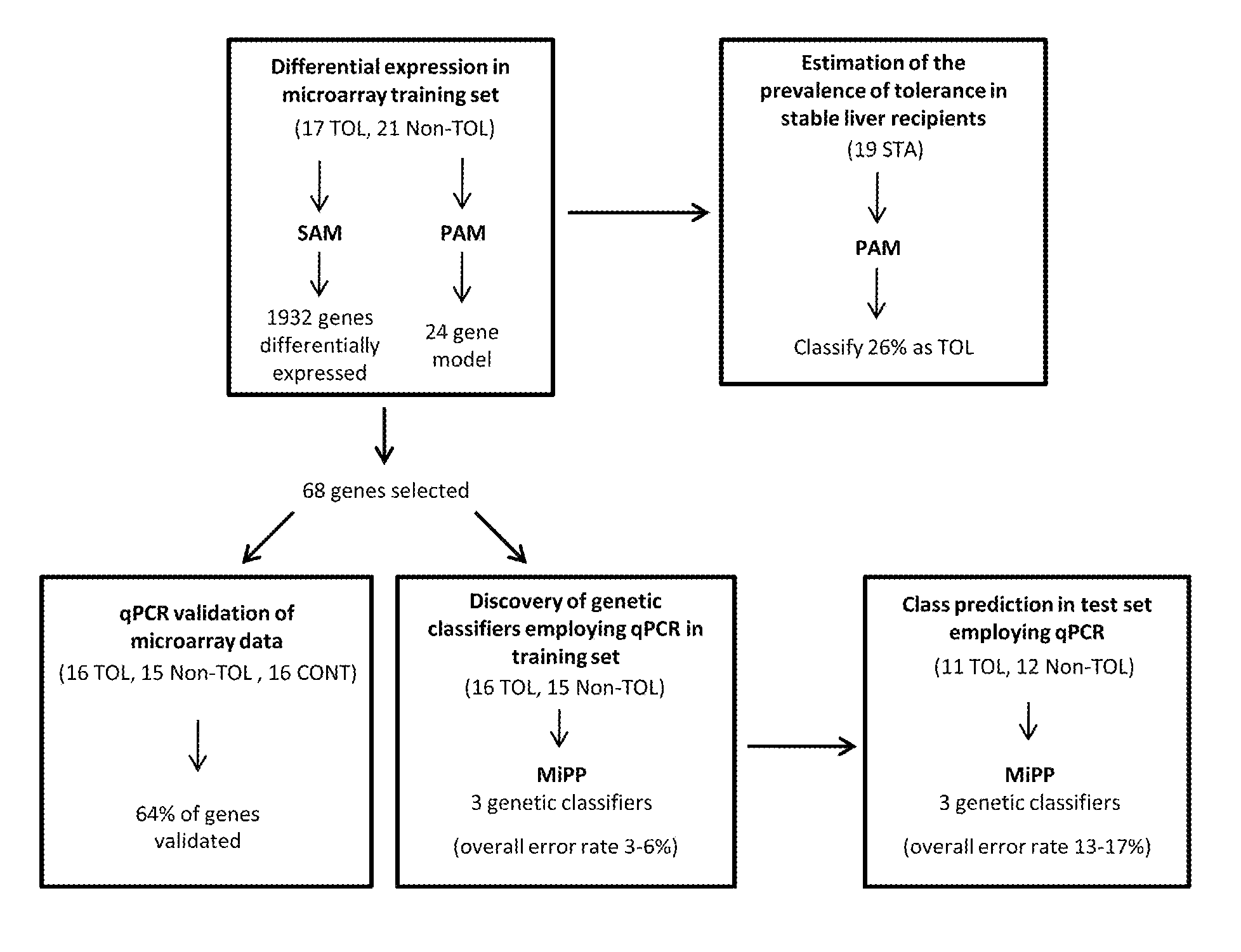
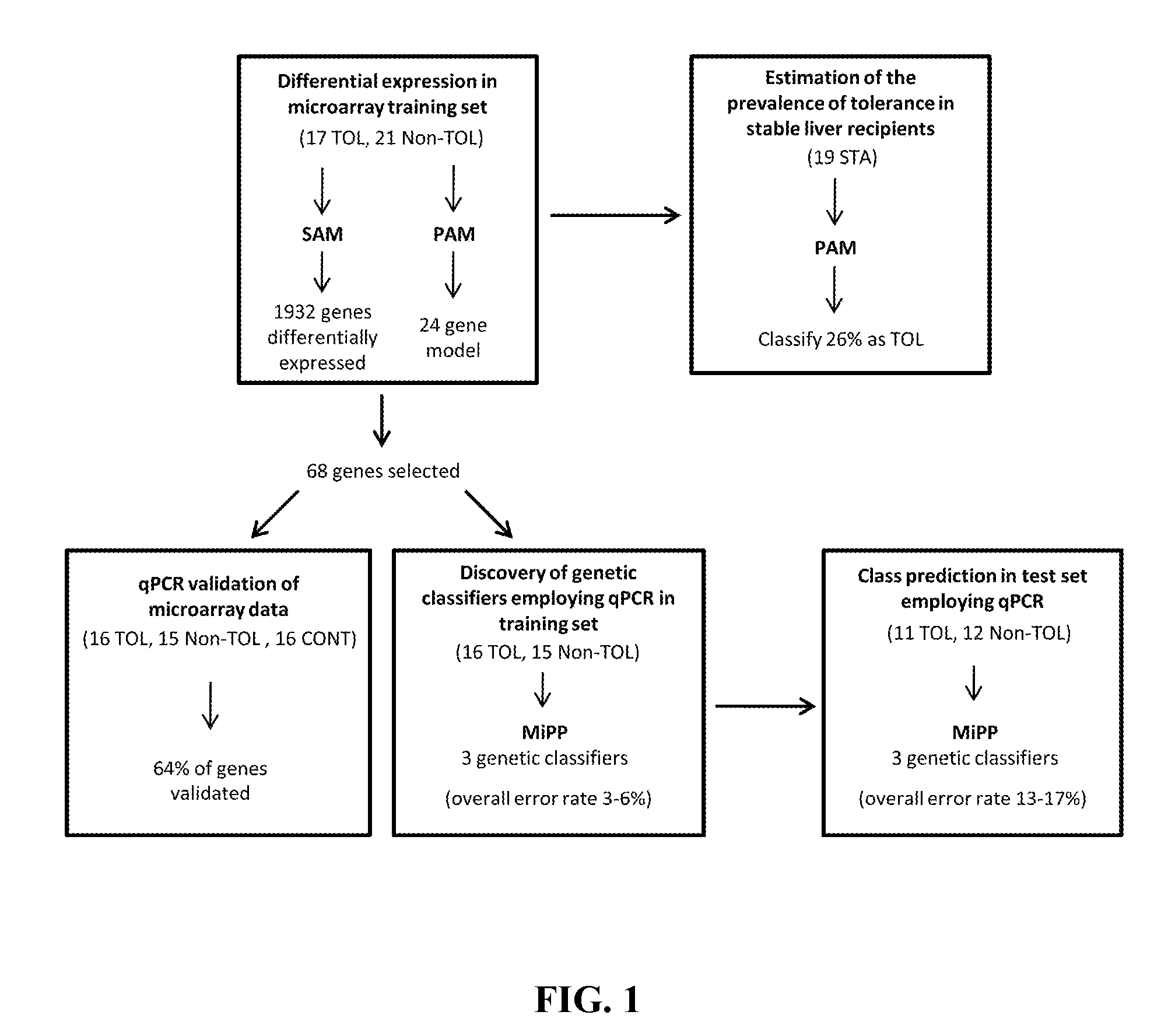
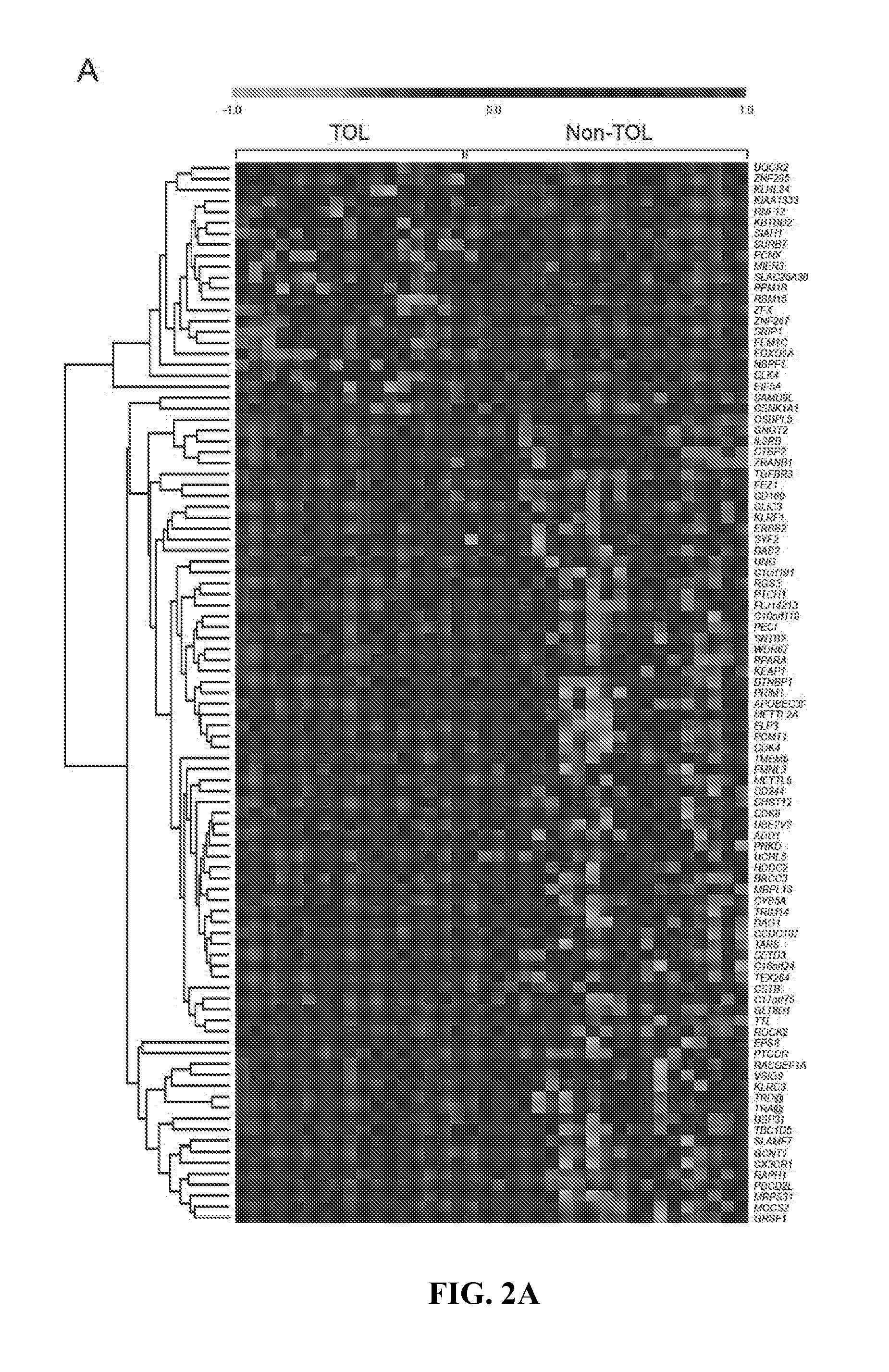
In vitro diagnosis/prognosis method and kit for assessment of tolerance in liver transplantation
InactiveUS20110130303A1Improve diagnostic accuracyImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesQuantitative Real Time PCRLiver transplant recipient
In vitro diagnosis / prognosis method and kit, for assessment of tolerance in liver transplantation. The present invention refers to the study of peripheral blood transcriptional patterns from 80 liver transplant recipients and 16 non-transplanted healthy individuals employing either oligonucleotide microarrays and / or quantitative real-time PCR to design a clinically applicable molecular test. This has resulted in the discovery and validation of several gene signatures comprising a modest number of genes capable of identifying tolerant and non-tolerant recipients with high accuracy. The marker genes are KLRF1, SLAMF7, NKG7, IL2RB, KLRB1, FANCG, GNPTAB, CLIC3, PSMD14, ALG8, CX3CR1, RGS 3. Multiple peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets contribute to the tolerance-associated transcriptional patterns with NK and γdelta T cells exerting a predominant influence. The invention concludes that transcriptional profiling of peripheral blood can be employed to identify liver transplant recipients who can discontinue immunosuppressive therapy and that innate immune cells are likely to play a major role in the maintenance of operational tolerance in liver transplantation.
Owner:INST DINVESTIGACIONS BIOMEDIQUES AUGUST PI I SUNYER IDIBAPS
K-Ras Oligonucleotide Microarray and Method for Detecting K-Ras Mutations Employing the Same
InactiveUS20070298419A1Fast and reliableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsK-ras GenesBiology
Since the K-ras oligonucleotide microarray of the present invention can detect K-ras mutations by applying a competitive DNA hybridization method to the oligonucleotides spotted on a solid matrix different from the previously reported method for detecting a mutation, it makes the more precise analysis and can reduce experimental cost and time. Accordingly, the K-ras oligonucleotide microarray of the present invention can be used in studies to detect K-ras mutations and unravel the signal transduction mechanism and tumorigenesis related to K-ras gene. Further, since the microarray of the present invention can be applied to other genes having mutational hot spot regions such as K-ras, it has wide applicable range.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
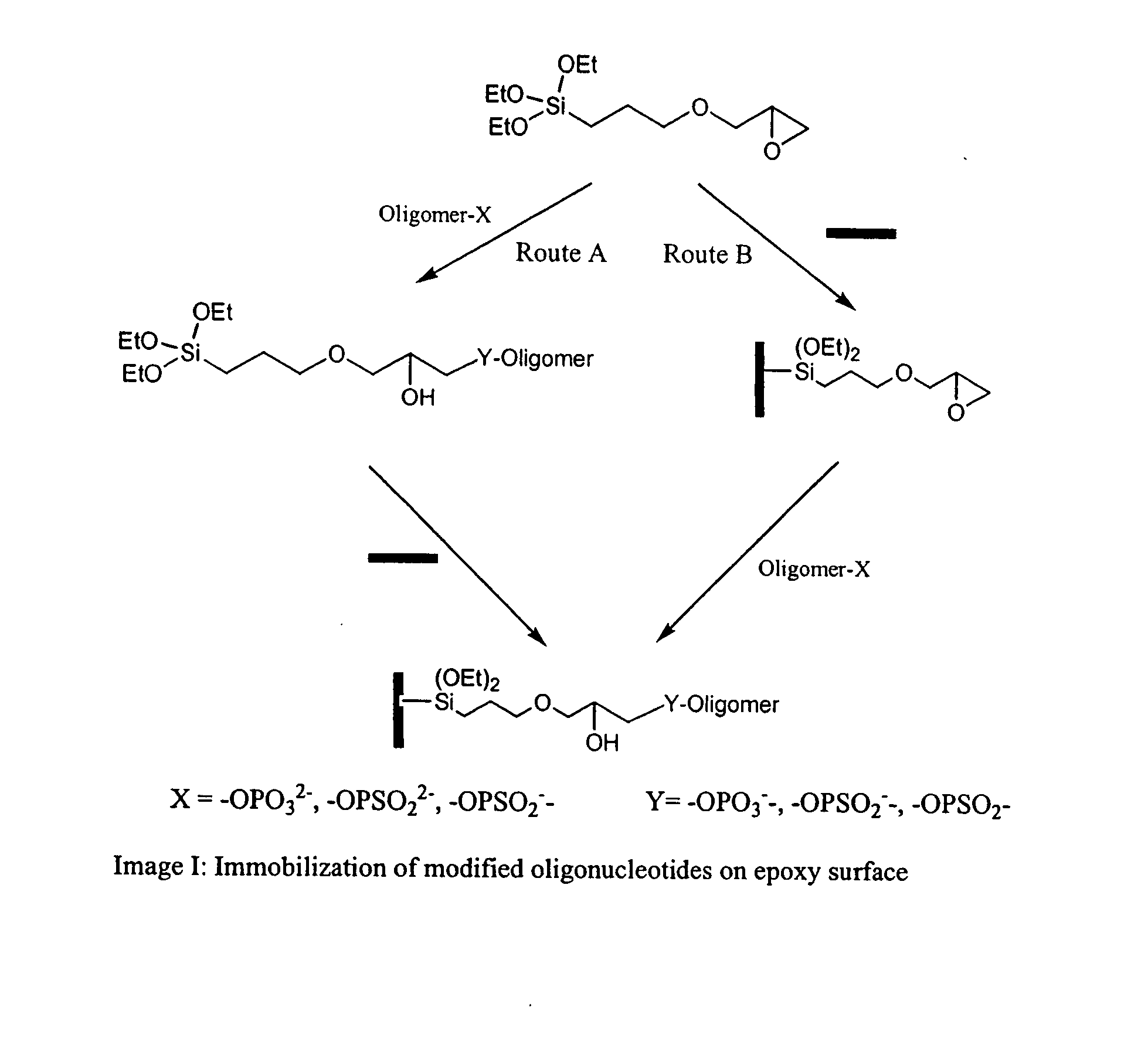
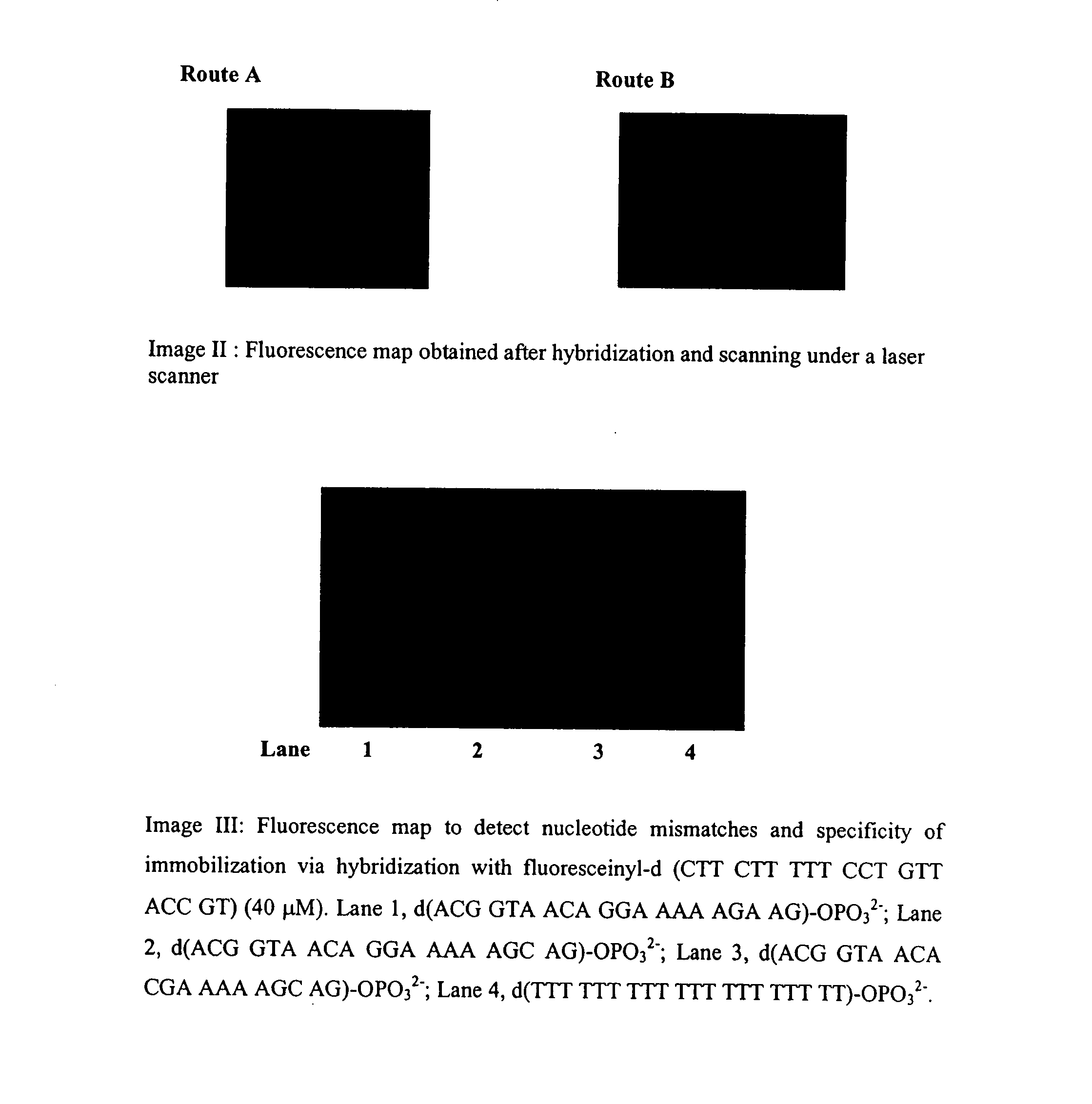
Novel method for construction of oligonucleotide microarrays
InactiveUS20080146462A1Simple and rapidImproved and rapid and simple methodSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Chemistry
The present invention lies in developing a novel method for the preparation of oligonucleotide microarrays obviating the drawbacks to an extent, such as time consuming complex chemical reactions, preparation of modified supports / oligomer modifying reagents, use of activating / condensing reagent, low signal to noise ratio, poor immobilization and hybridization efficiencies, etc. Further, the prepared arrays can be used to detect single or multiple nucleotide mismatches using hybridization assay.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating mental retardation
InactiveUS7776551B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementINFANTILE BILATERAL STRIATAL NECROSISNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods, kits, isolated nucleic acid sequences, antibodies and addressable oligonucleotides microarrays which can be for analyzing sequence alterations and detecting the expression level of CC2D1A or nup62 in cells of an individual and thus diagnose nonsyndromic mental retardation (NSMR) and / or infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (IBSN) in the individual. In addition, the present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions which can be used to treat pathologies associated with mental retardation such as NSMR or IBS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Analysis of data obtained from microarrays
Disclosed are methods and software for biological data analysis. Specifically, provided are methods, computer programs and systems for analyzing data in the form of various intensity measurements obtained from an oligonucleotides microarray experiment. Such data may be microarray data obtained from an experiment conducted to determine copy number of a human genetic sample. The data are corrected by application of one or more covariate adjusters which may be applied simultaneously and which may be selected by a user. Further, the present application provides methods of filtering image data and signal restoration of image data using log2 ratio data.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Determining a probabilistic diagnosis of cancer by analysis of genomic copy number variations
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
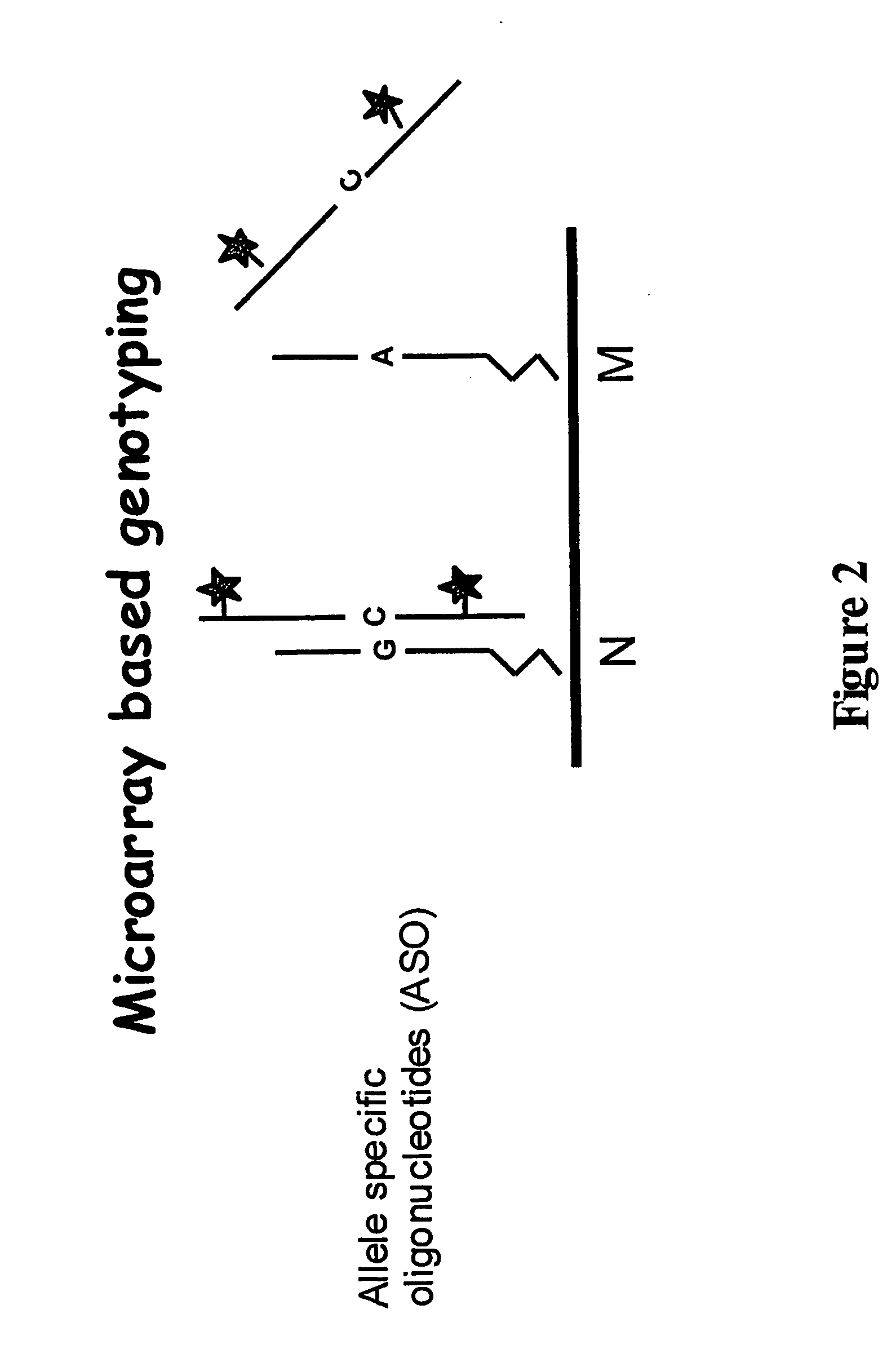
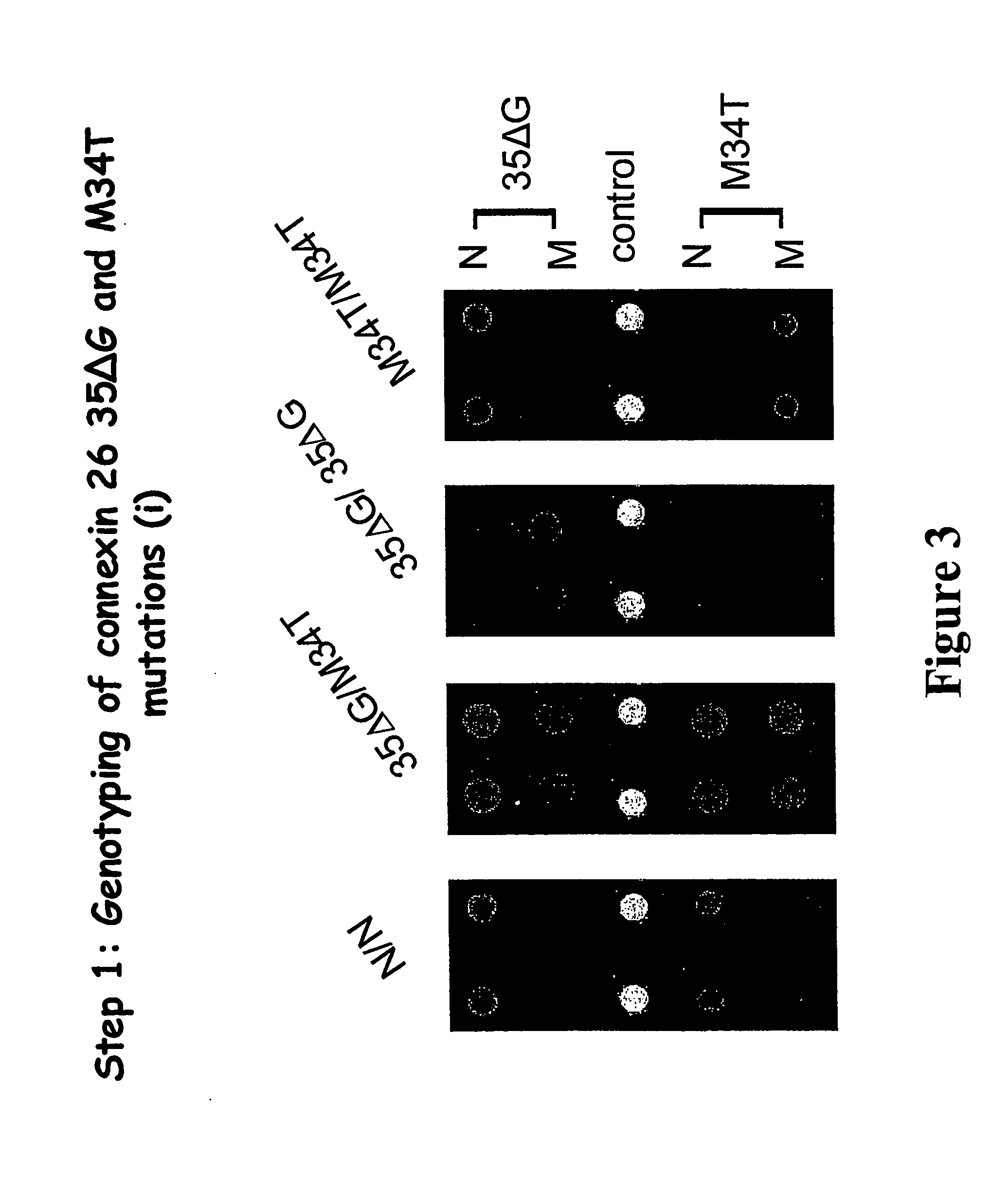
Genotyping of deafness by oligonucleotide microarray analysis
InactiveUS20070009887A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-Stranded RNATotal Deafness
A method for genotyping a subject with respect to a gene or target nucleic acid sequence associated with a pathological condition, said method comprising contacting an allele specific oligonucleotide immobilized to a solid support with a single-stranded from of RNA or DNA from a subject to be tested labeled directly or indirectly with a reporter molecule capable of giving an identifiable signal under conditions which permit hybridization of single stranded RNA or DNA which is exactly complementary to the immobilized allele specific oligonucleotide but substantially less or no hybridization of non-complementary single-stranded RNA or DNA molecules and then screening for the presence or absence or level of reporter molecule which provides an indicator of the genetic identity of the single-stranded RNA or DNA molecule which in turn provides the genotype of the subject.
Owner:MURDOCH CHILDRENS RES INST
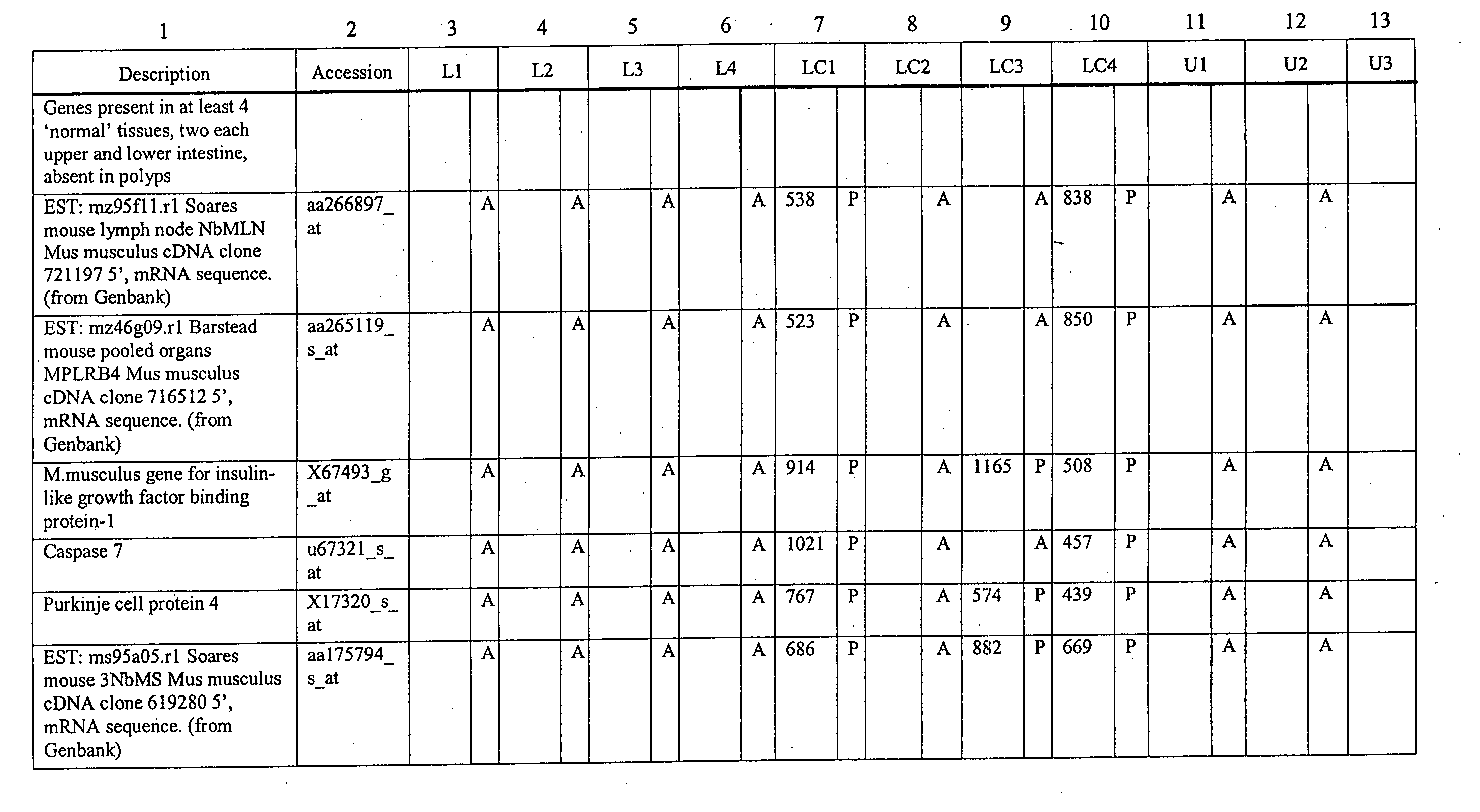
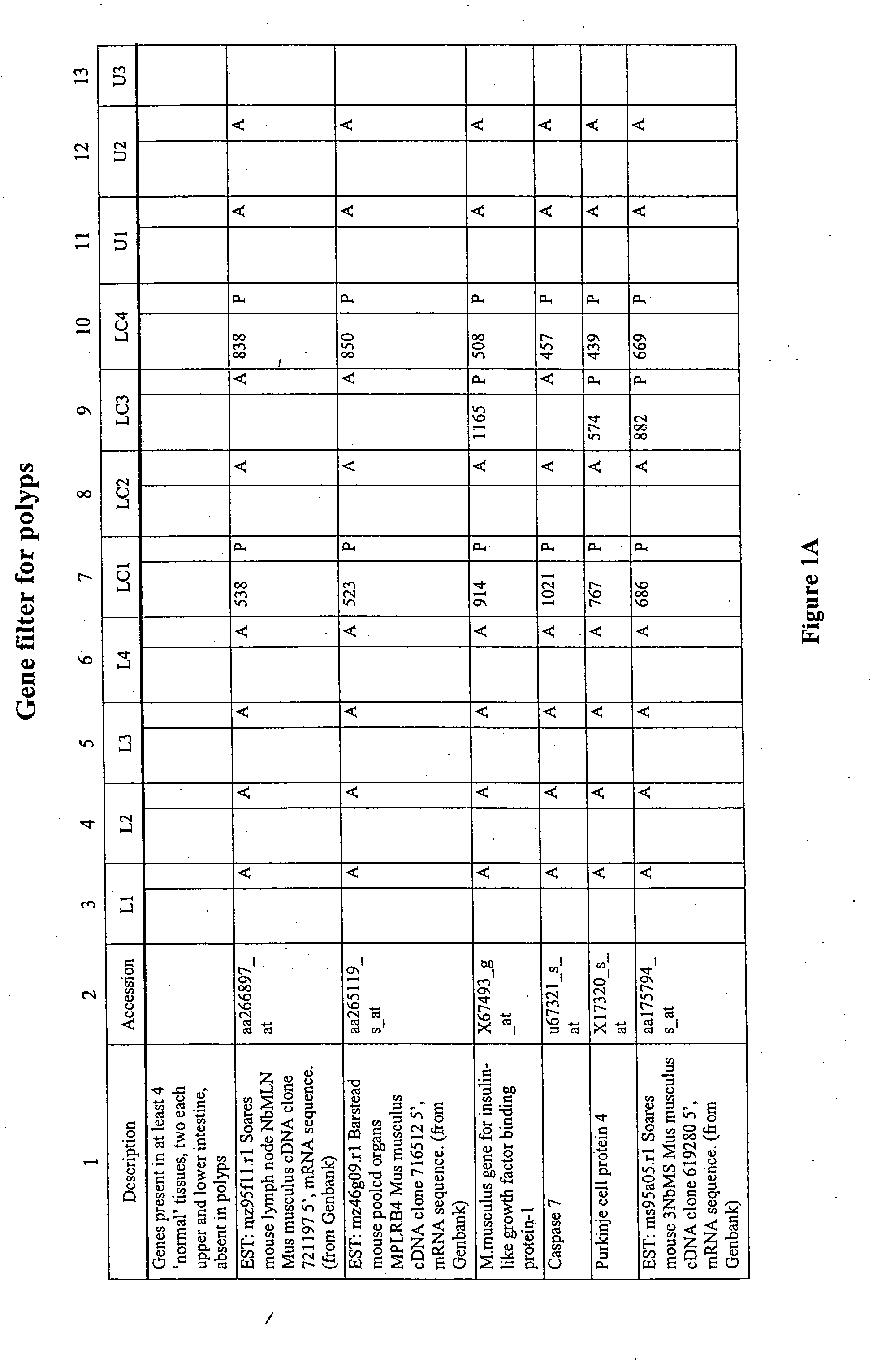
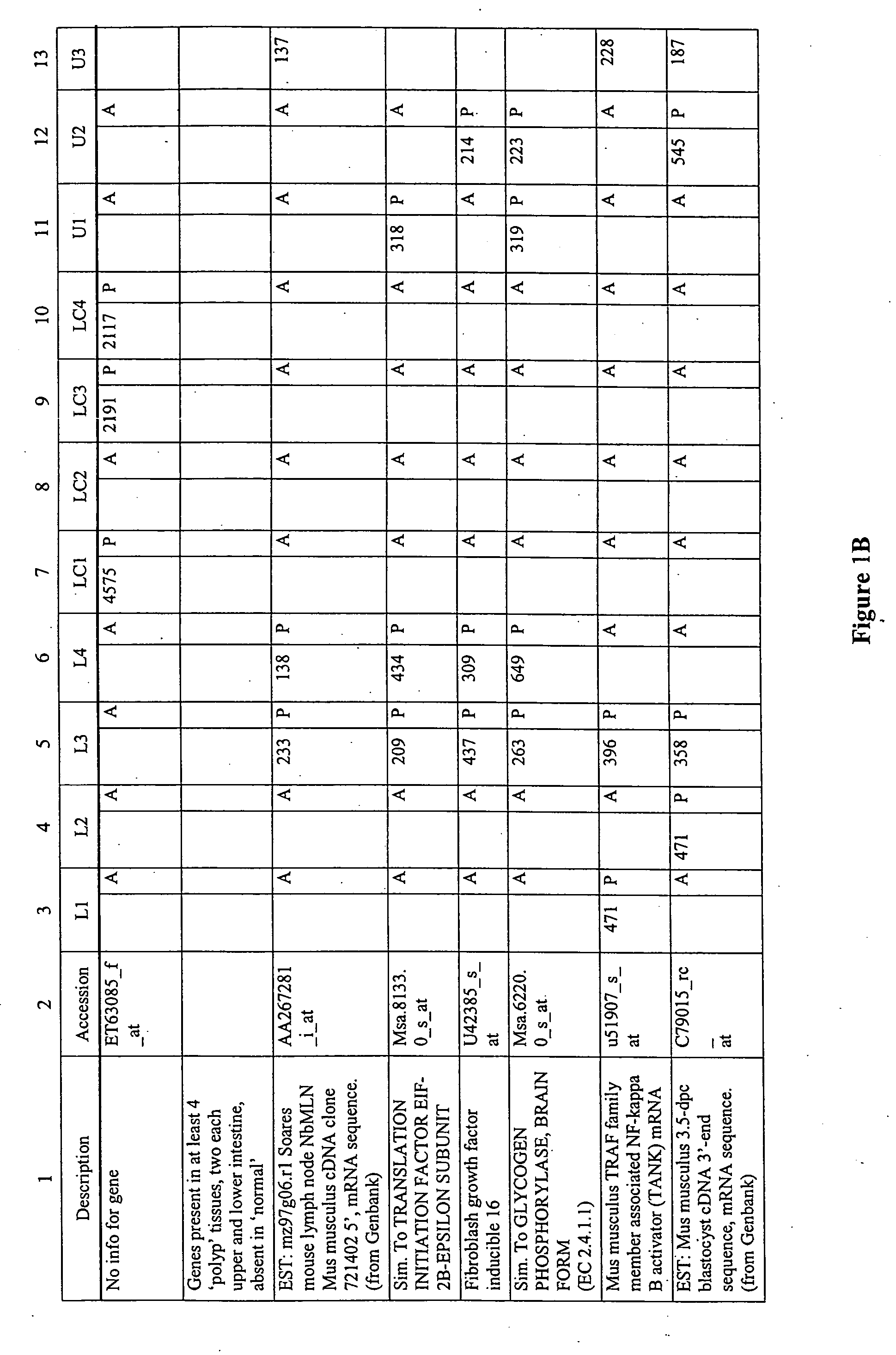
Differential gene expression in intestinal polyps
The present invention features method for identifying an intestinal polyp according to the gen expression profile obtained from intestinal tissue. The present invention also features methods for identifying a compound that modulates intestinal polyp development, as well as oligonucleotide microarrays having genes involved in intestinal polyp development immobilized thereon.
Owner:GRAAF DAVID DE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com