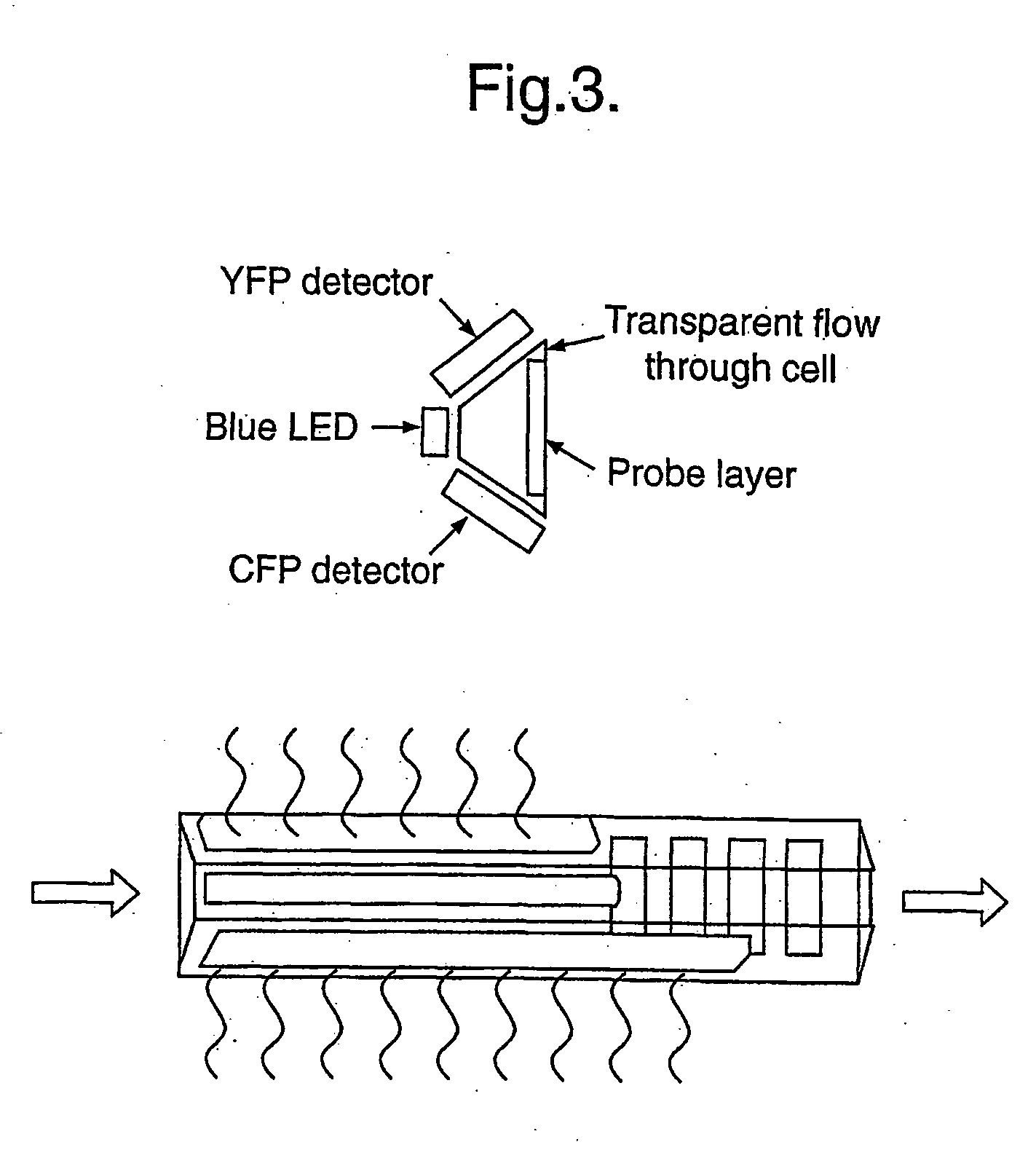
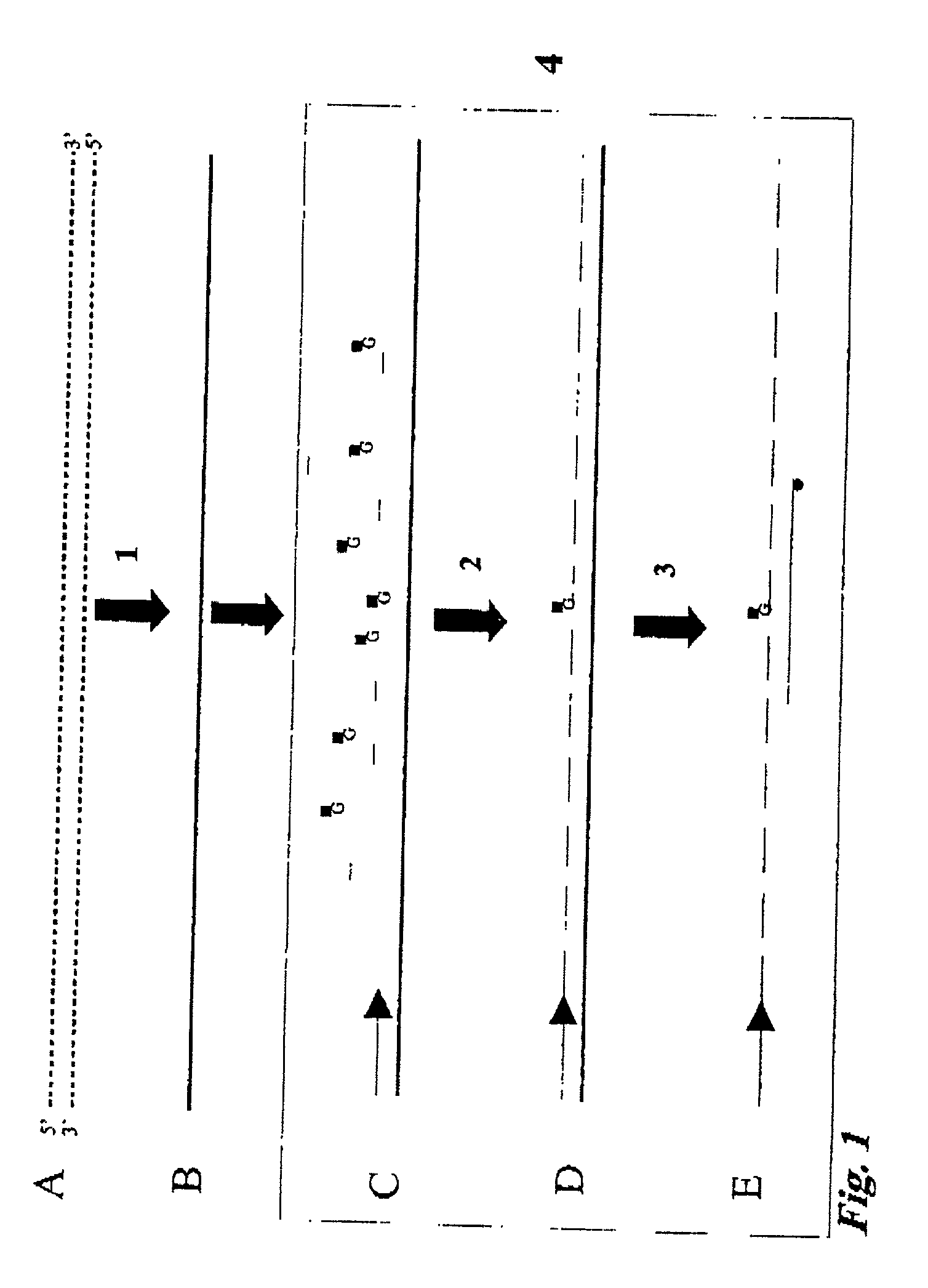
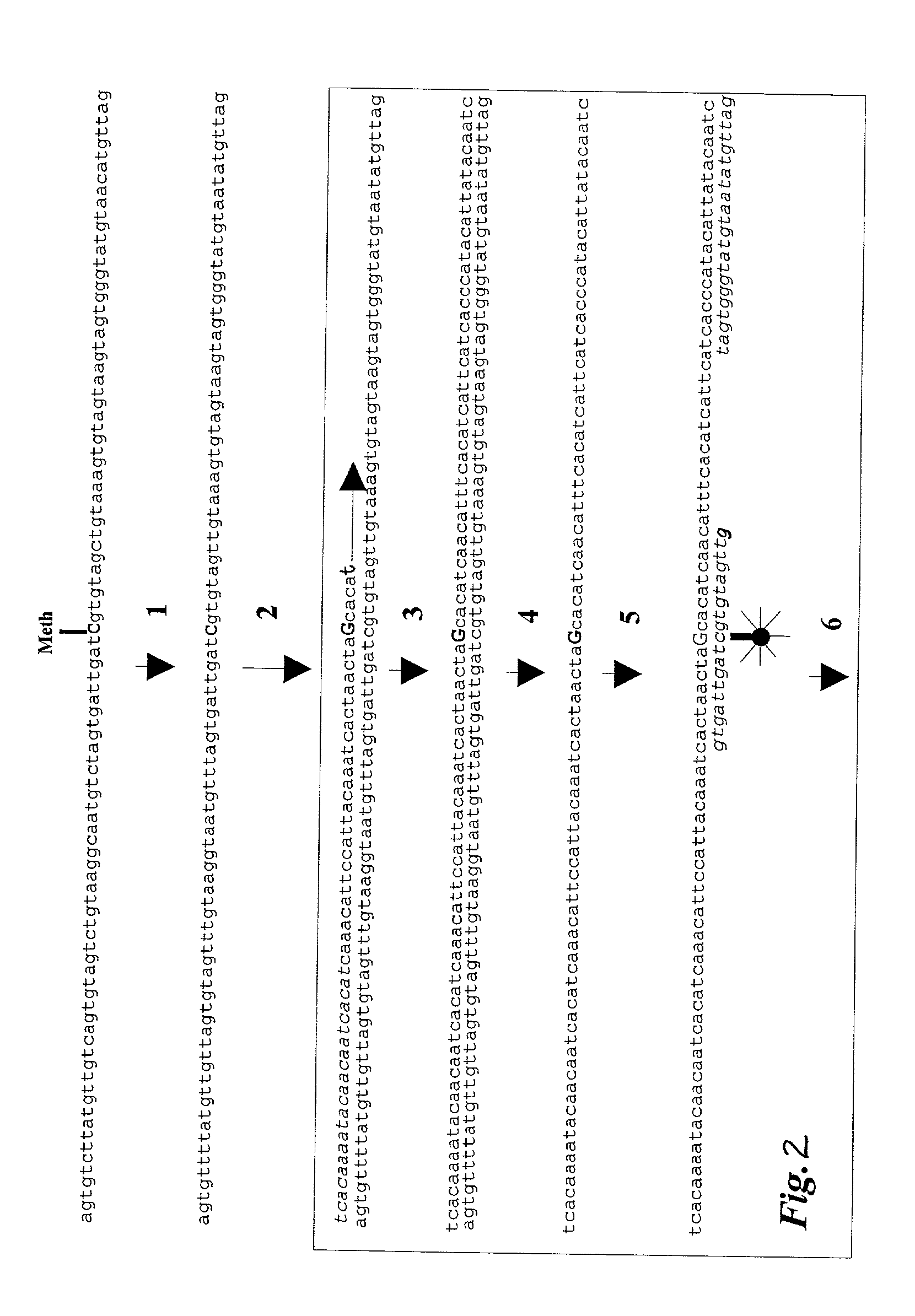
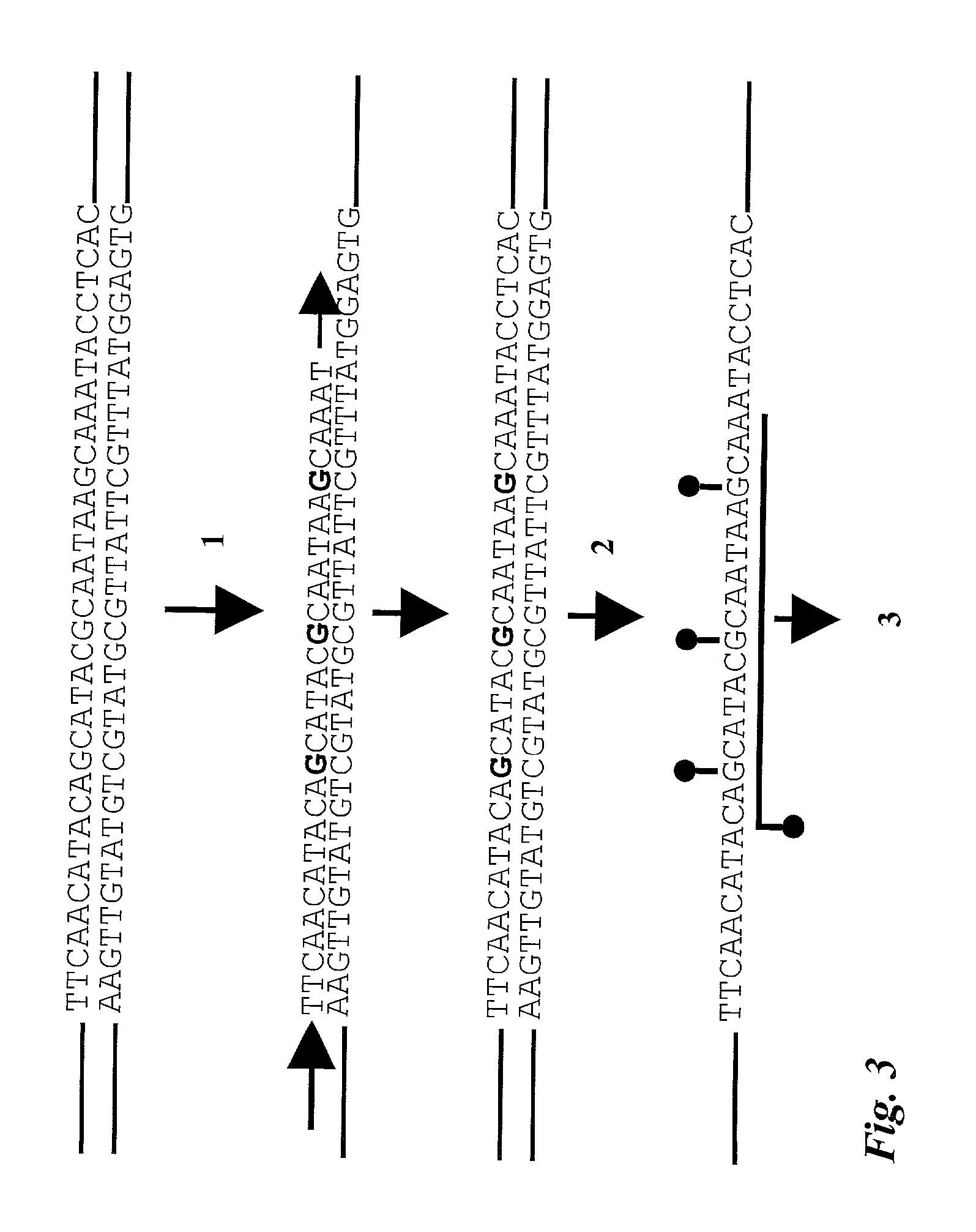
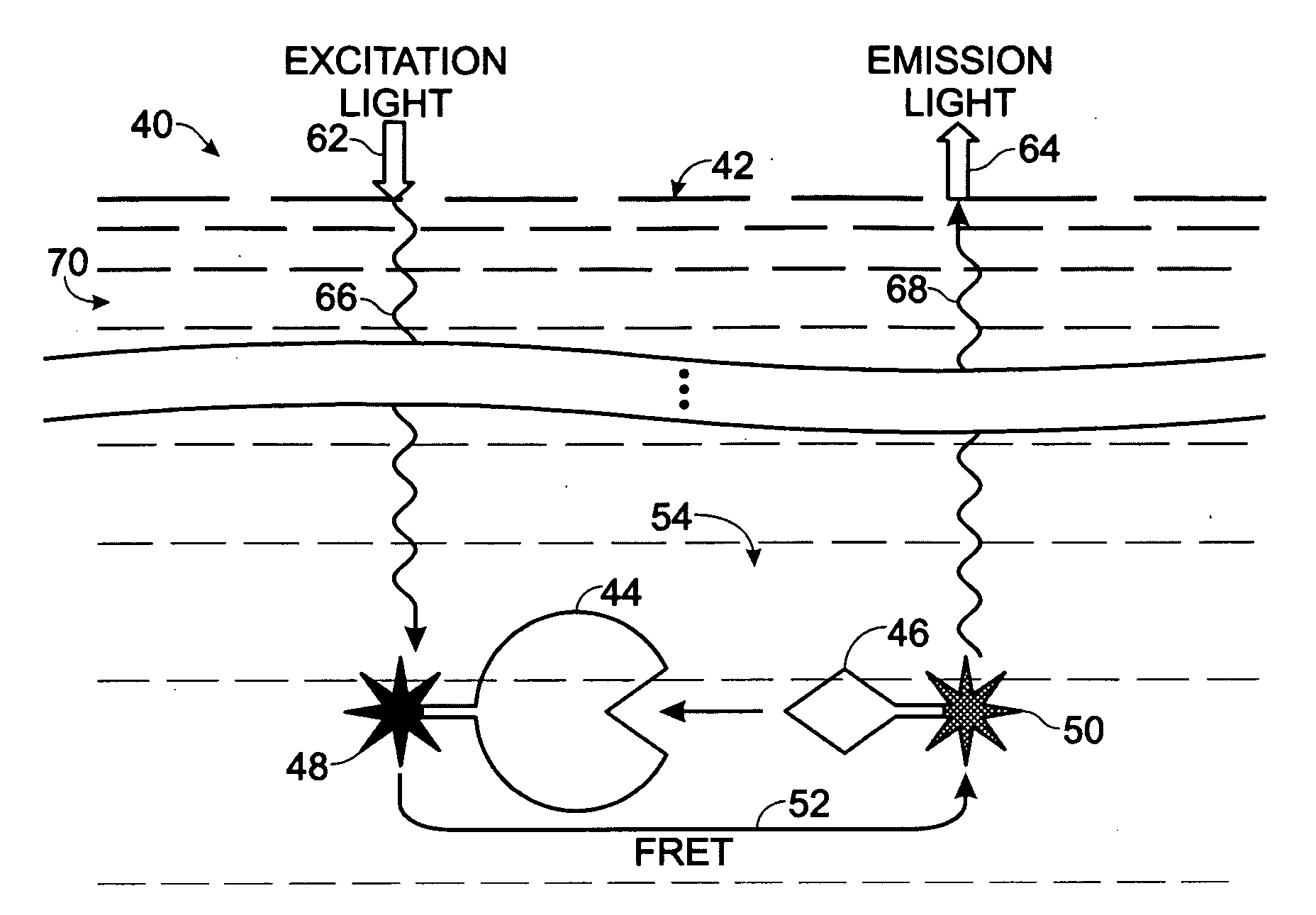
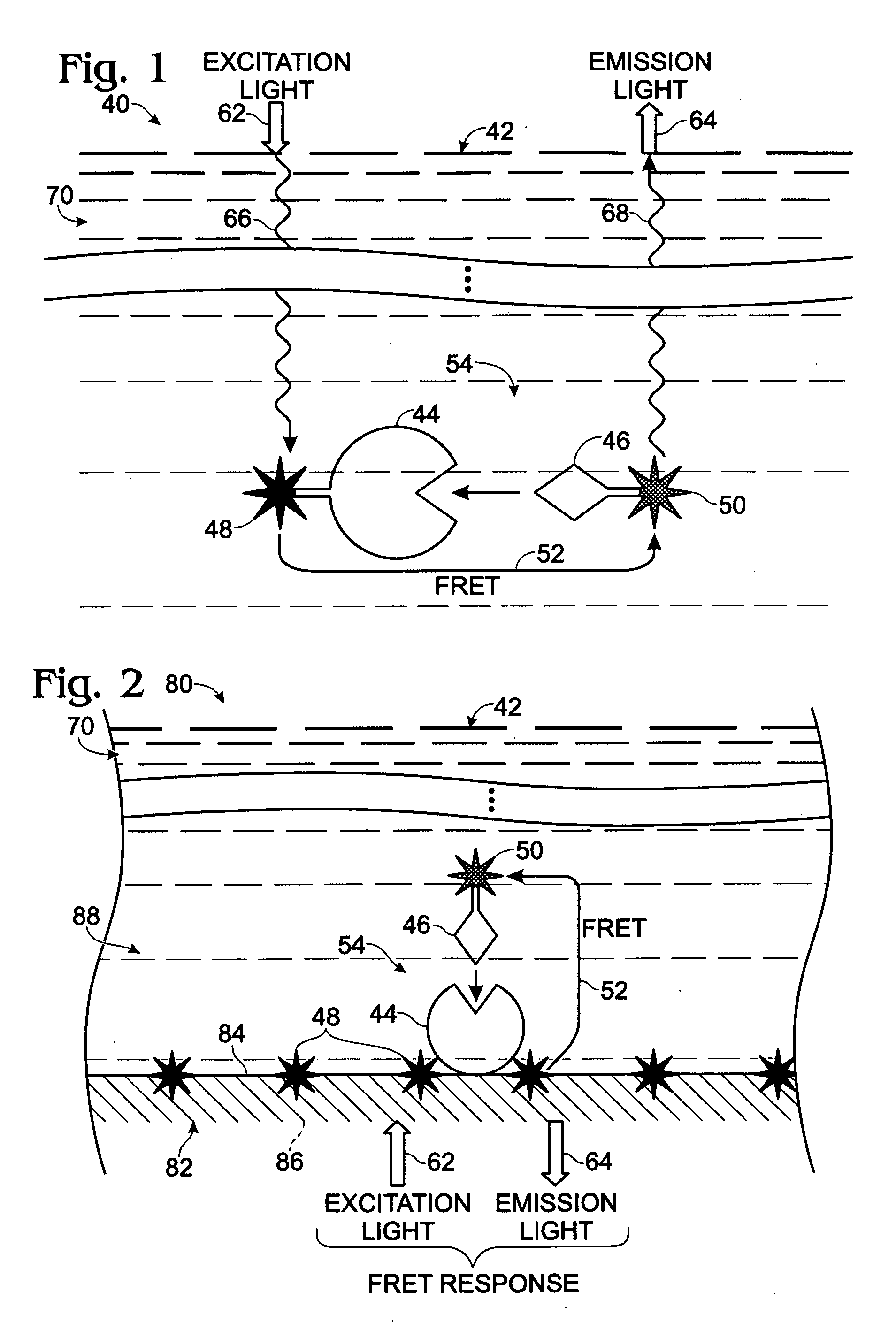
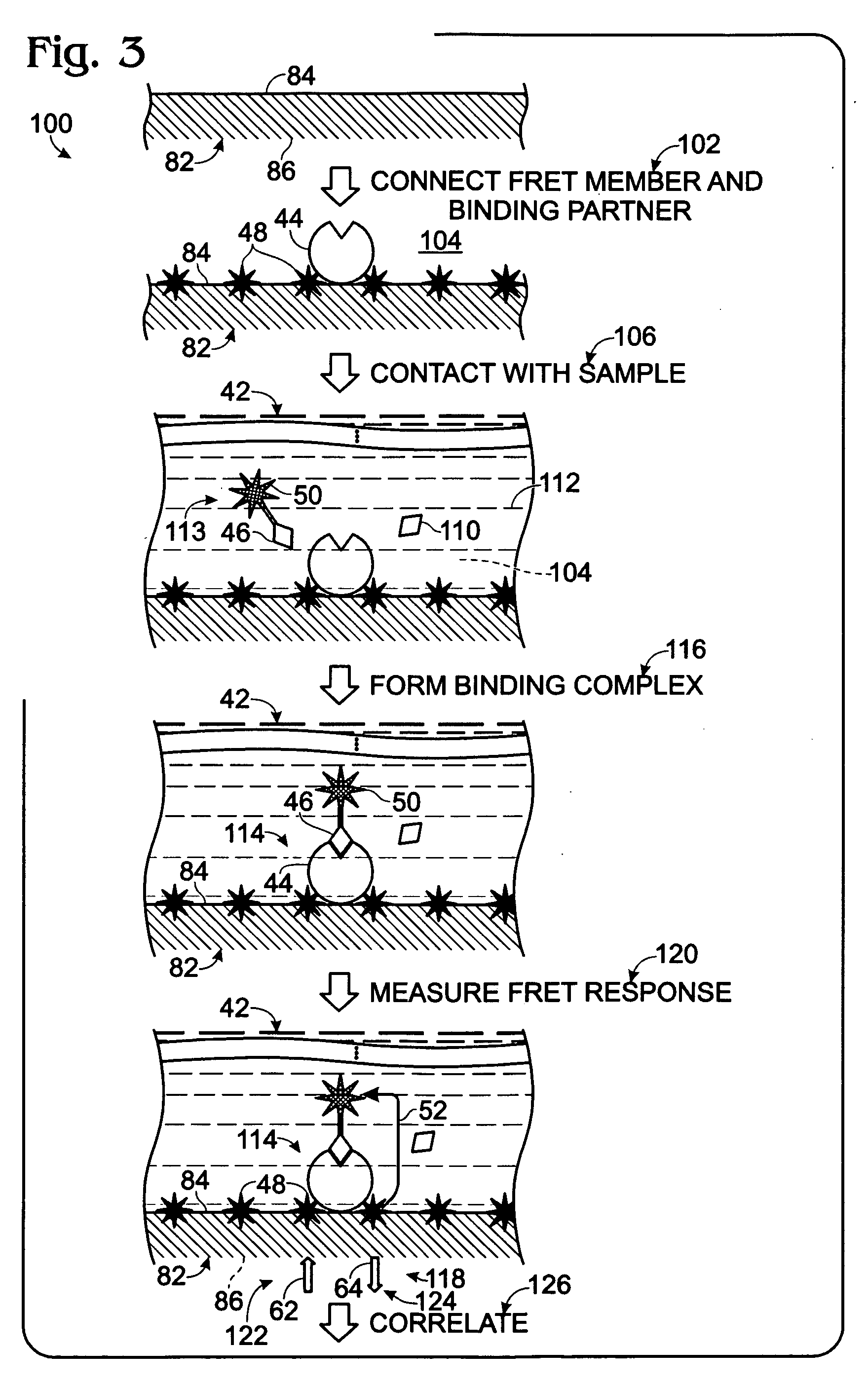
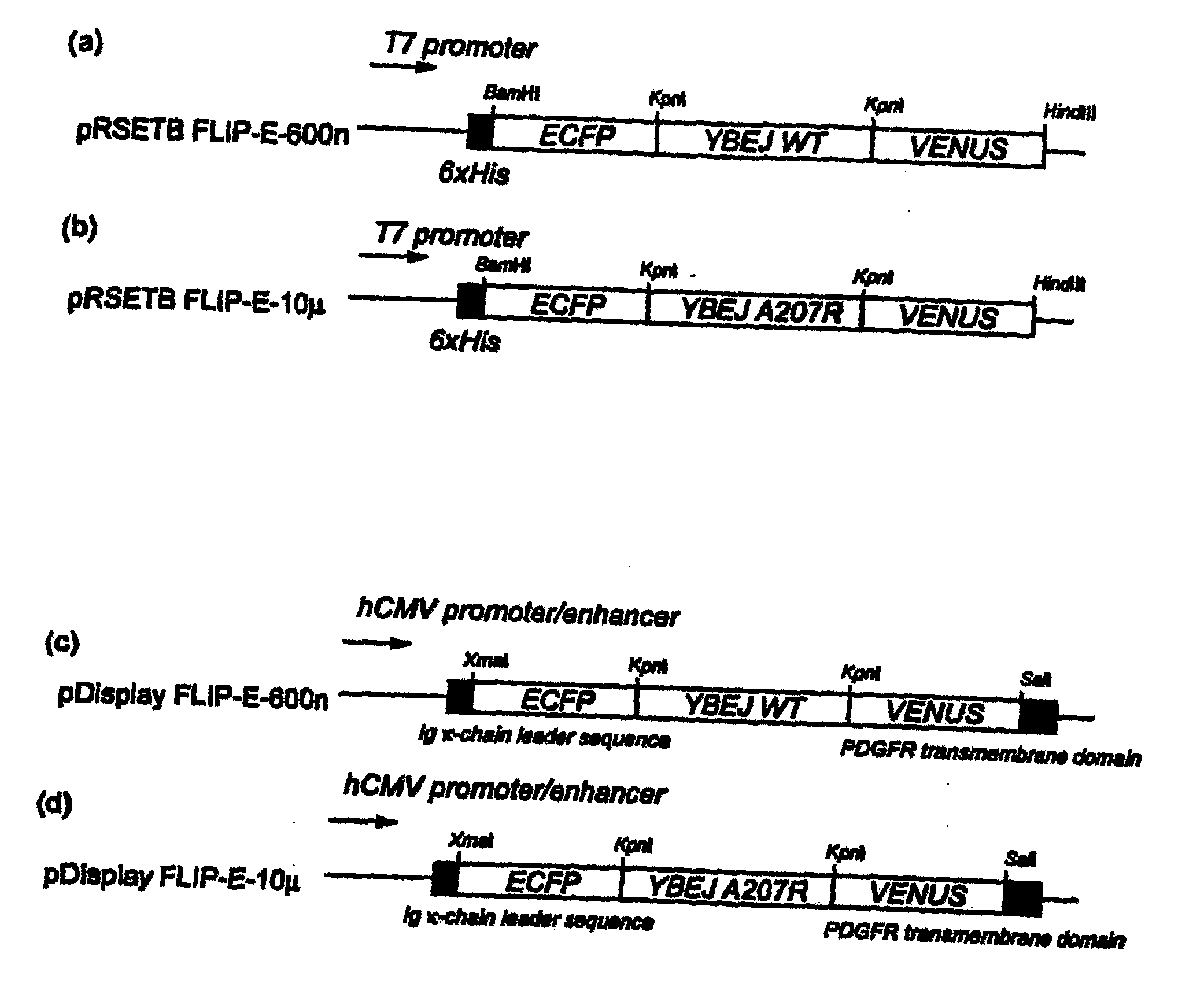
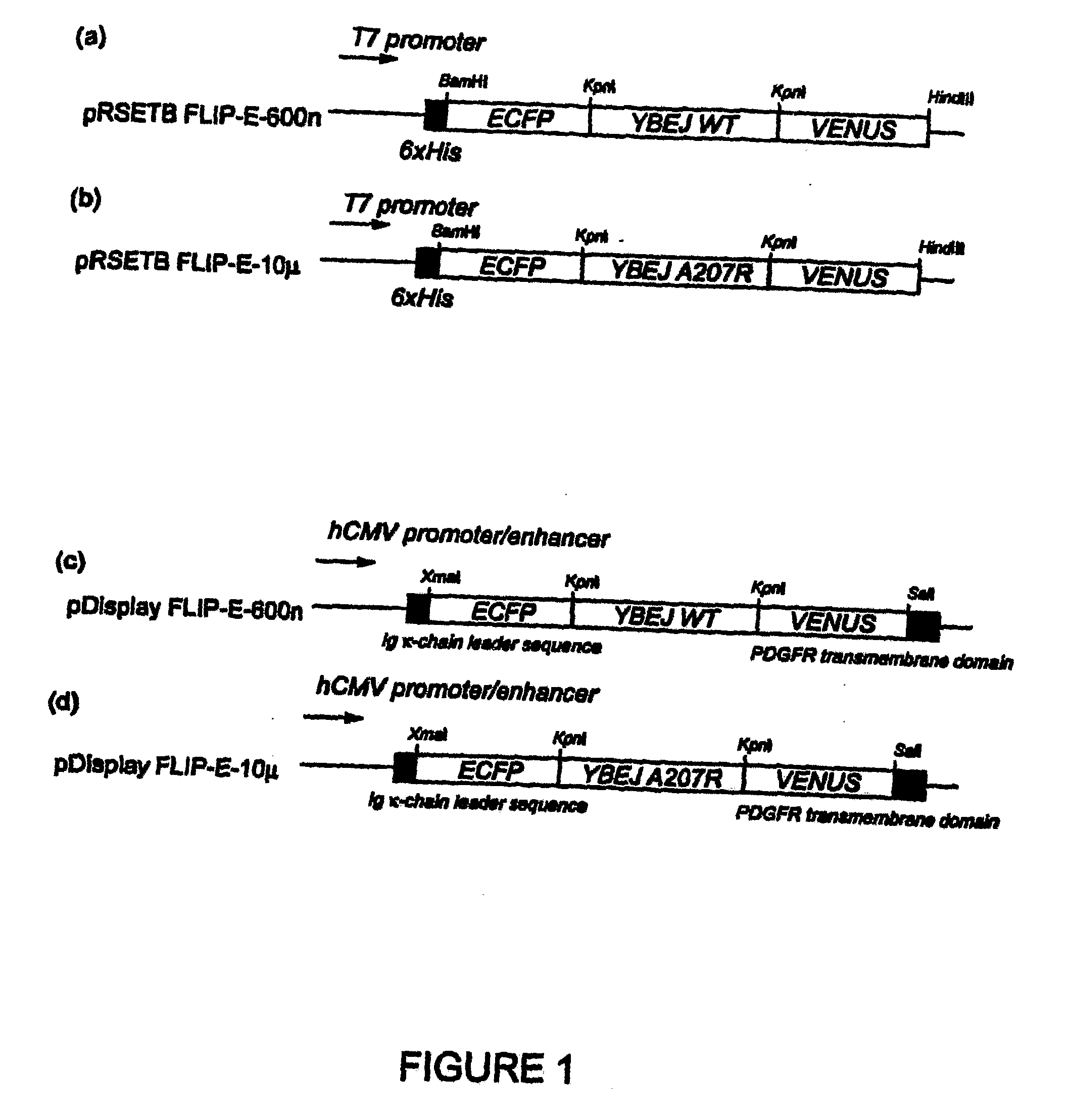
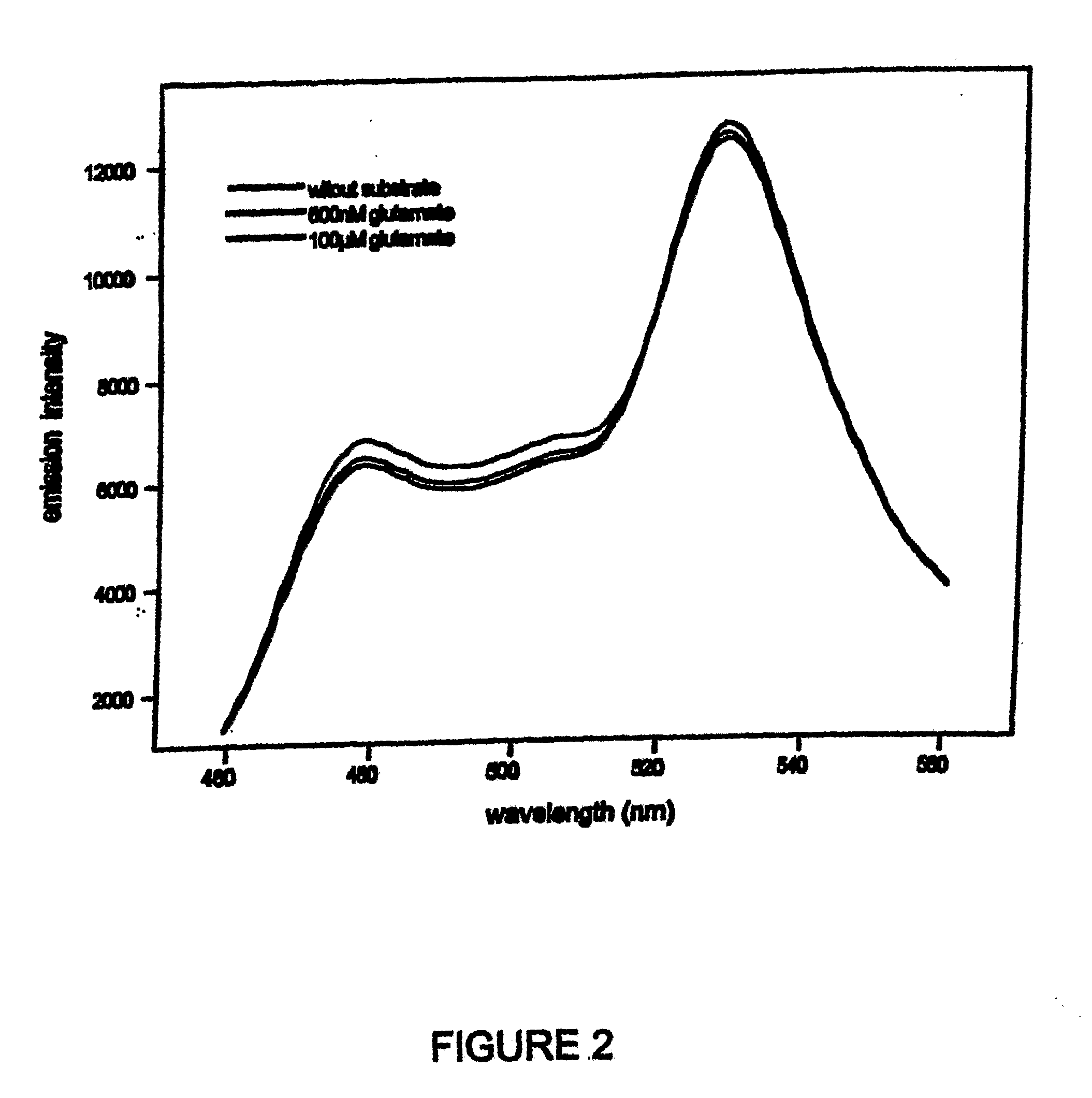
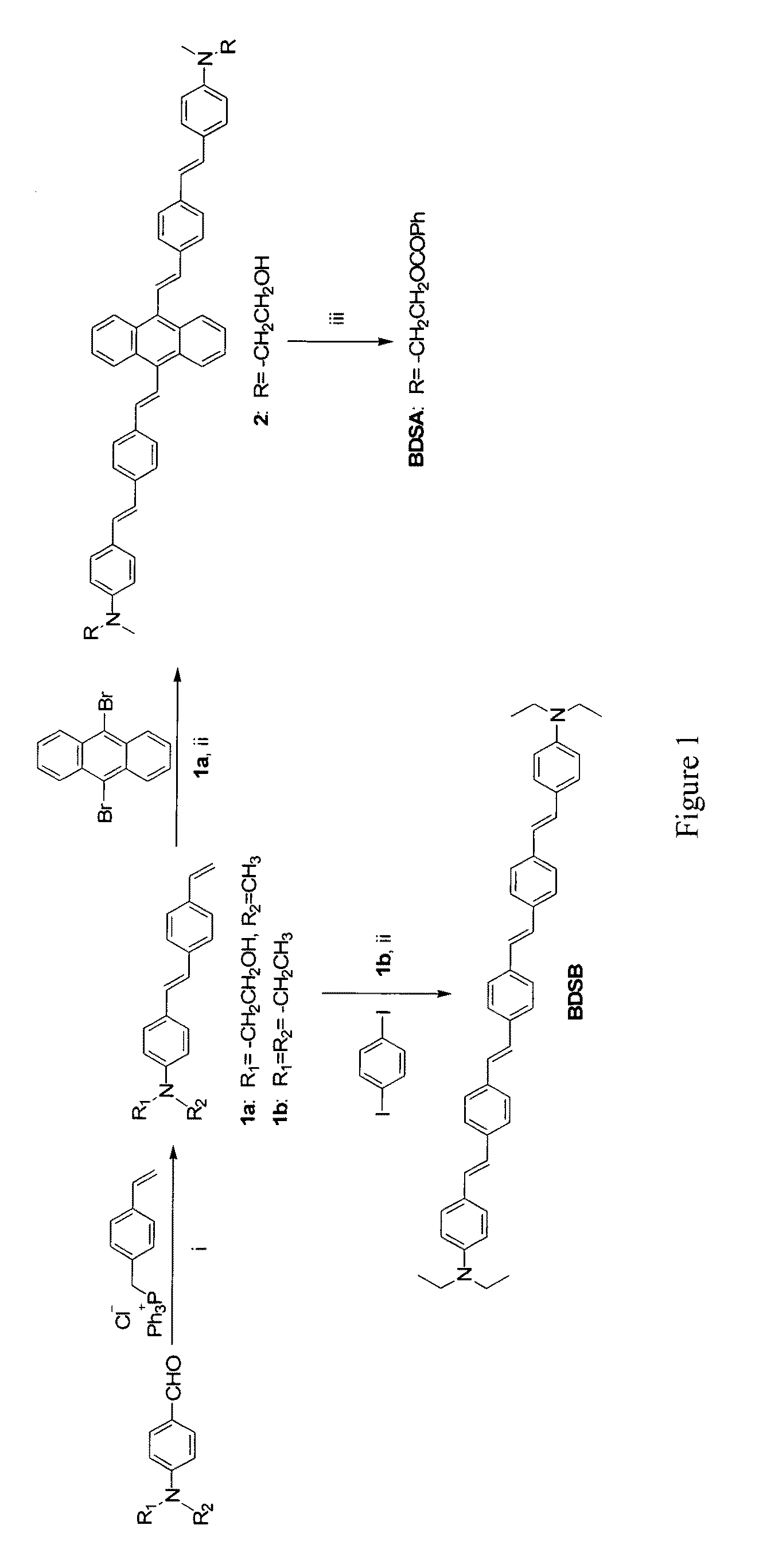
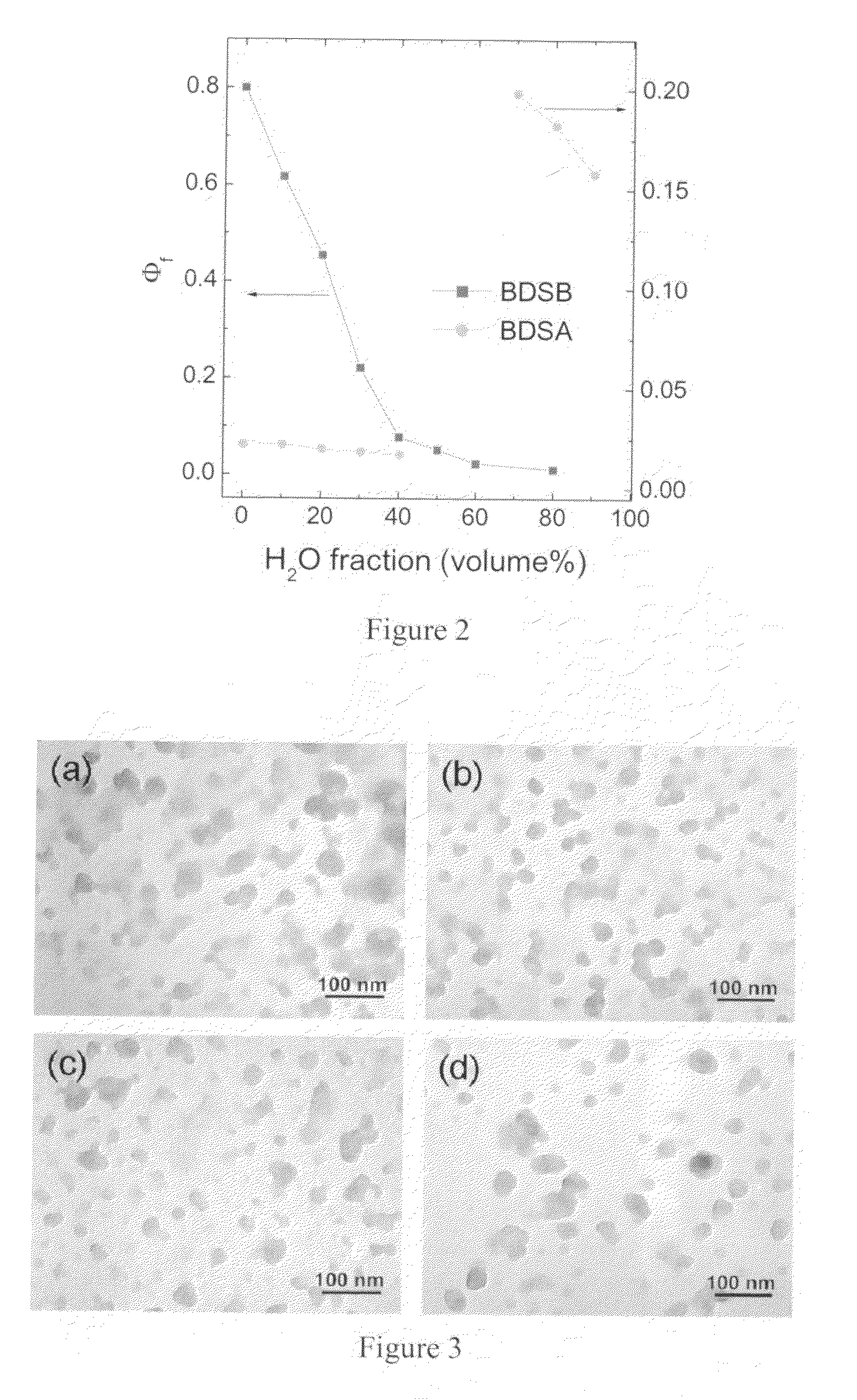
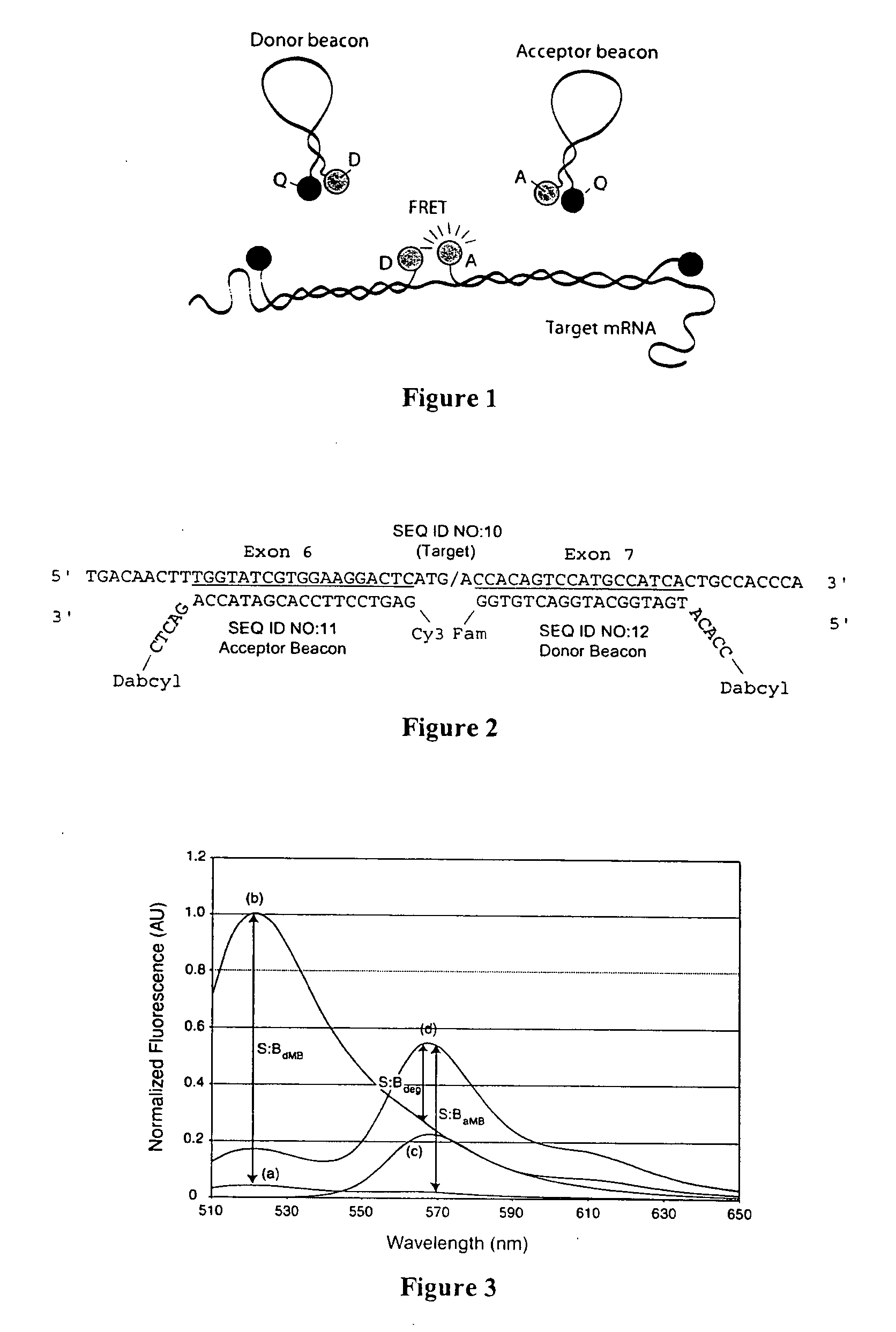
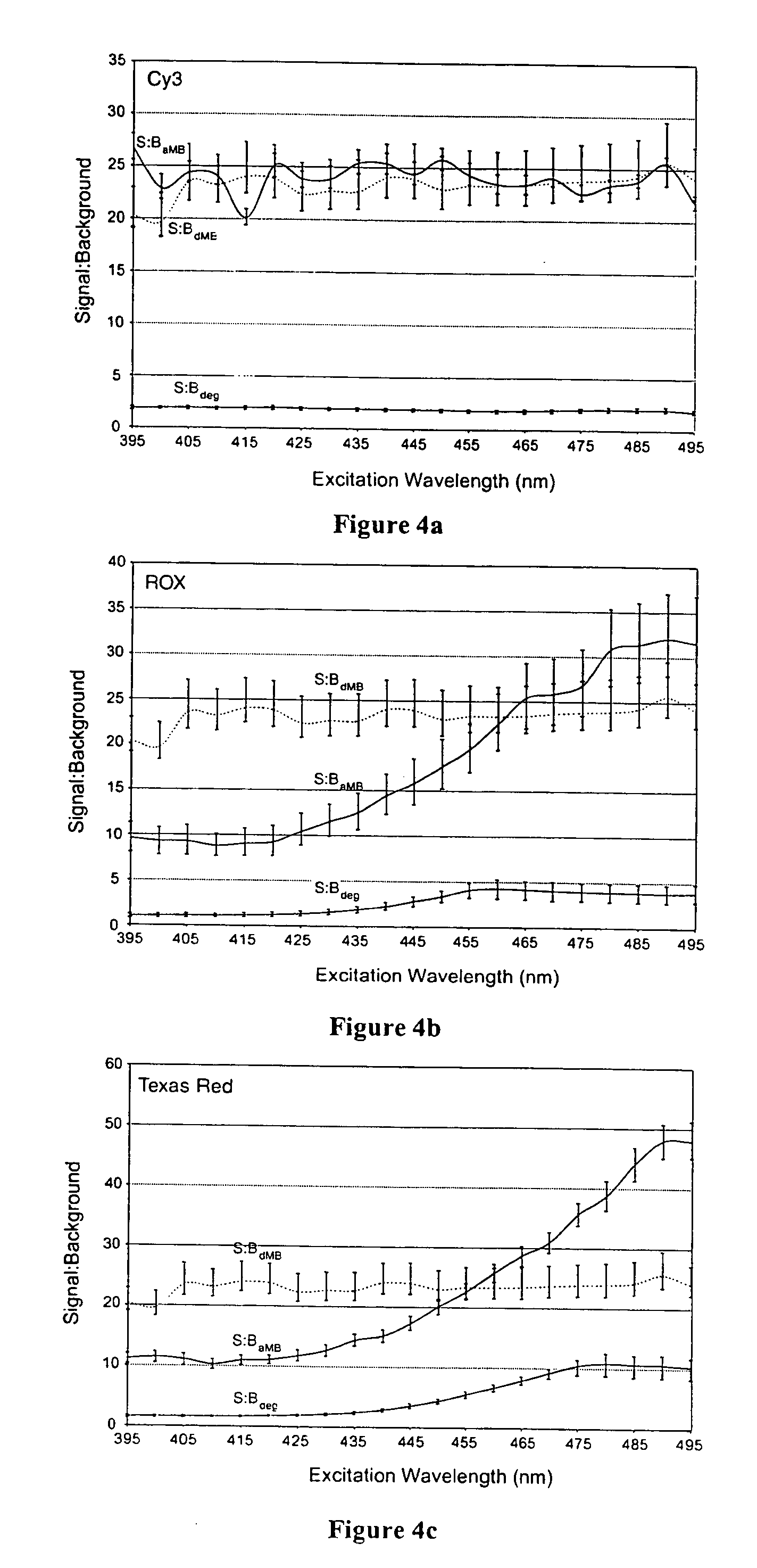
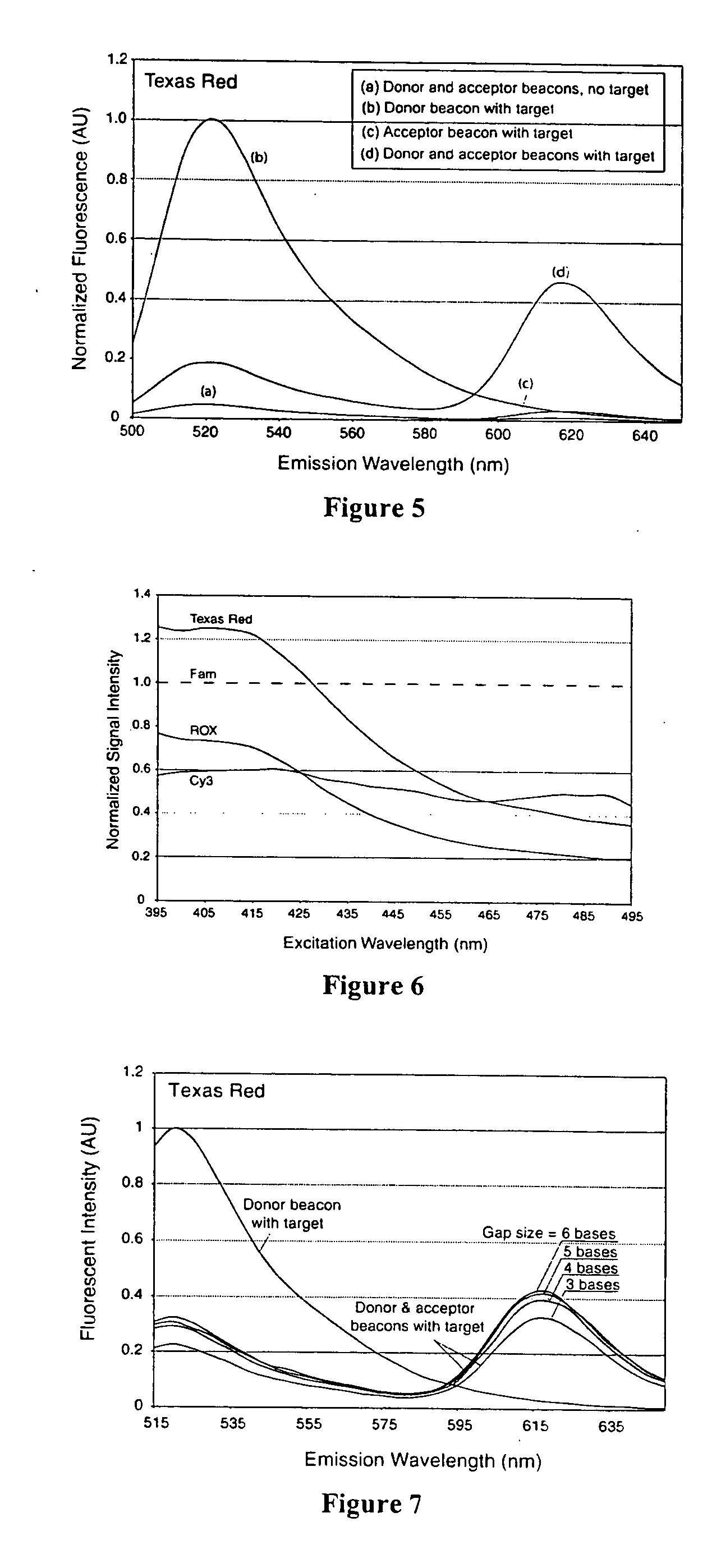
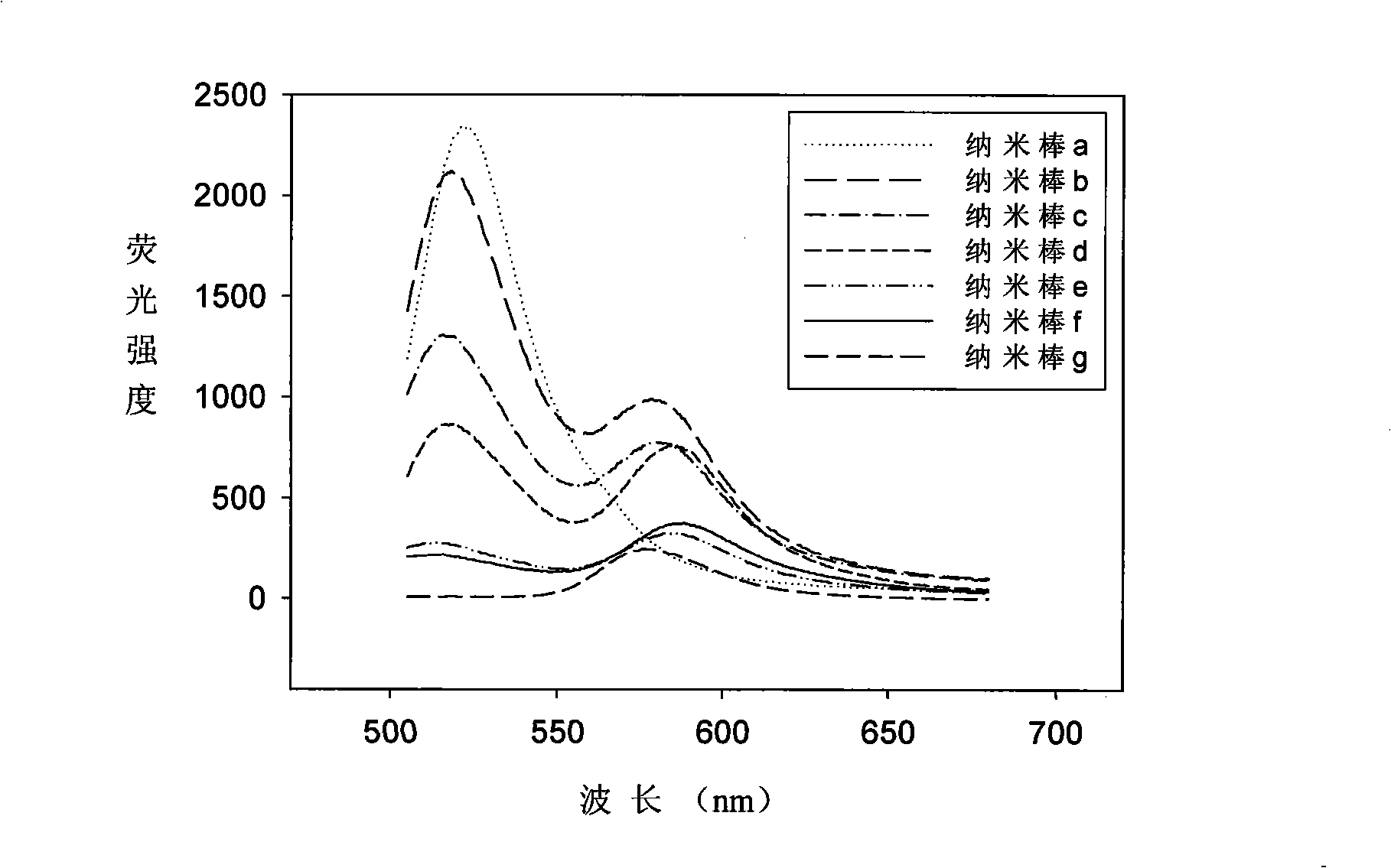
Patents
Literature
360 results about "Förster resonance energy transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
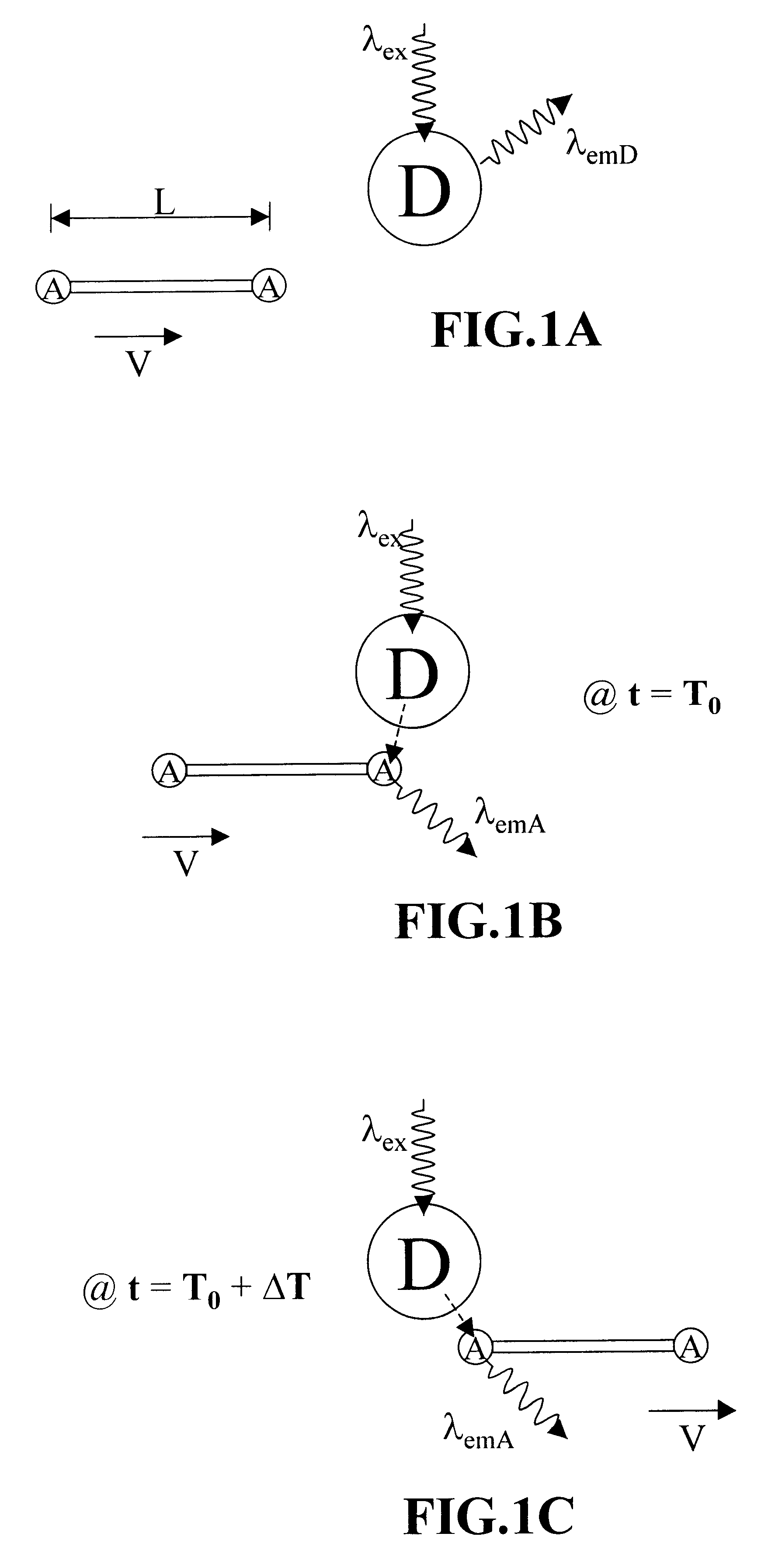
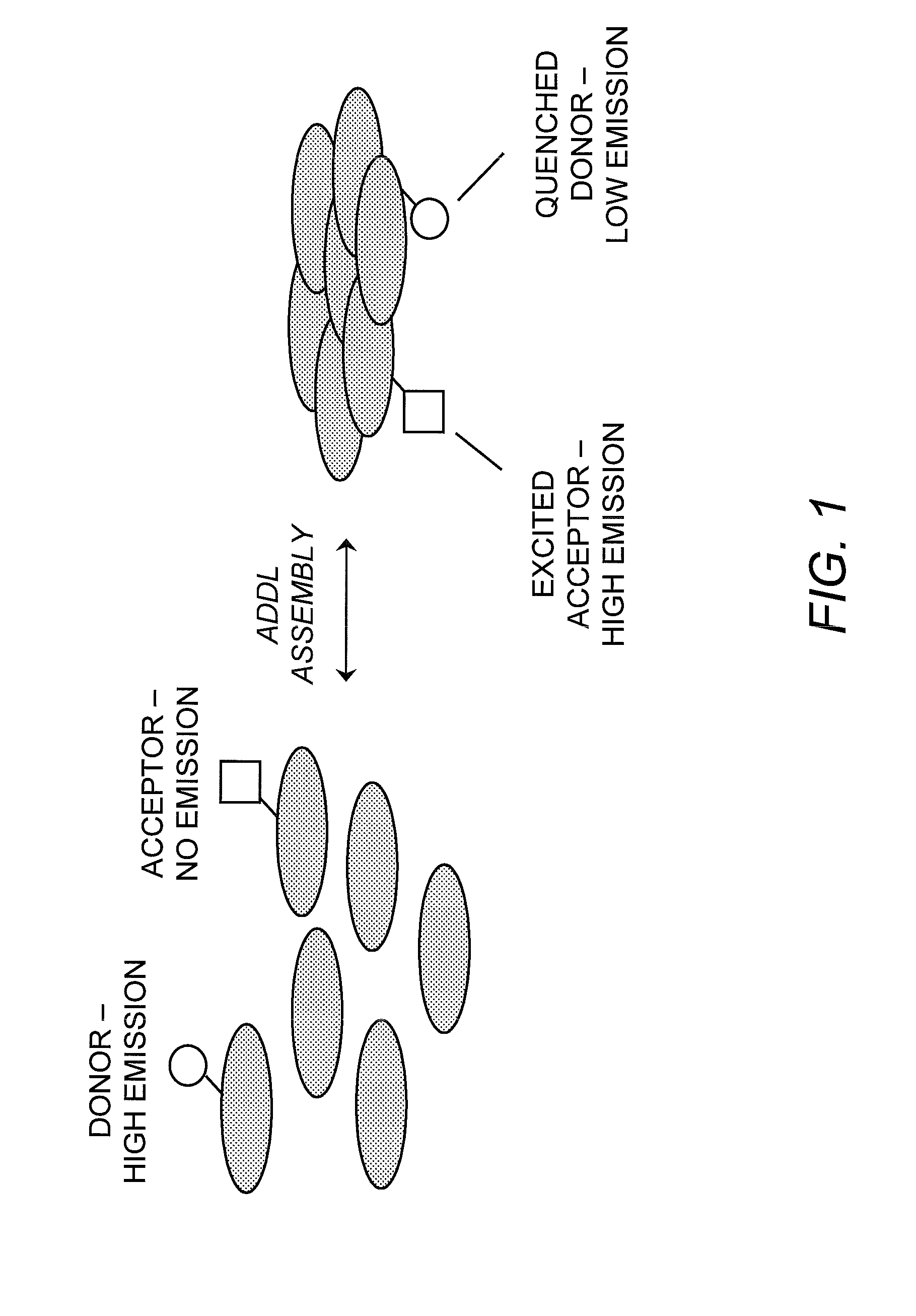
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance.
Methods of analyzing polymers using a spatial network of fluorophores and fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveUS6263286B1Easy to analyze and useMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEnergy transferResonance
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for analyzing molecules, particularly polymers, and molecular complexes with extended or rod-like conformations. In particular, the methods and apparatuses are used to identify repetitive information in molecules or molecular ensembles, which is interpreted using an autocorrelation function in order to determine structural information about the molecules. The methods and apparatuses of the invention are used for, inter alia, determining the sequence of a nucleic acid, determining the degree of identity of two polymers, determining the spatial separation of specific sites within a polymer, determining the length of a polymer, and determining the velocity with which a molecule penetrates a biological membrane.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Fluorescence polarization assay system and method
An instrument is disclosed for fluorescence assays which is capable of reading many independent samples at the same time. This instrument provides enhanced throughput relative to single-sample instruments, and is well-suited to use in general fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, multi-band fluorescence, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and fluorescence polarization. This invention is beneficial in applications such as high-throughput drug screening, and automated clinical testing. Also disclosed are means and methods for a fluorescence polarization measurement which is highly sensitive, inherently self-calibrated, and unaffected by lamp flicker or photobleaching. This fluorescence polarization invention can be practiced on a variety of fluorescence instruments, including prior-art equipment such as microscopes and multi-well plate readers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS7081336B2Quick checkEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Quantitative methylation detection in DNA samples
InactiveUS6960436B2Quick fixFast and cost-effective and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LGenomic DNA
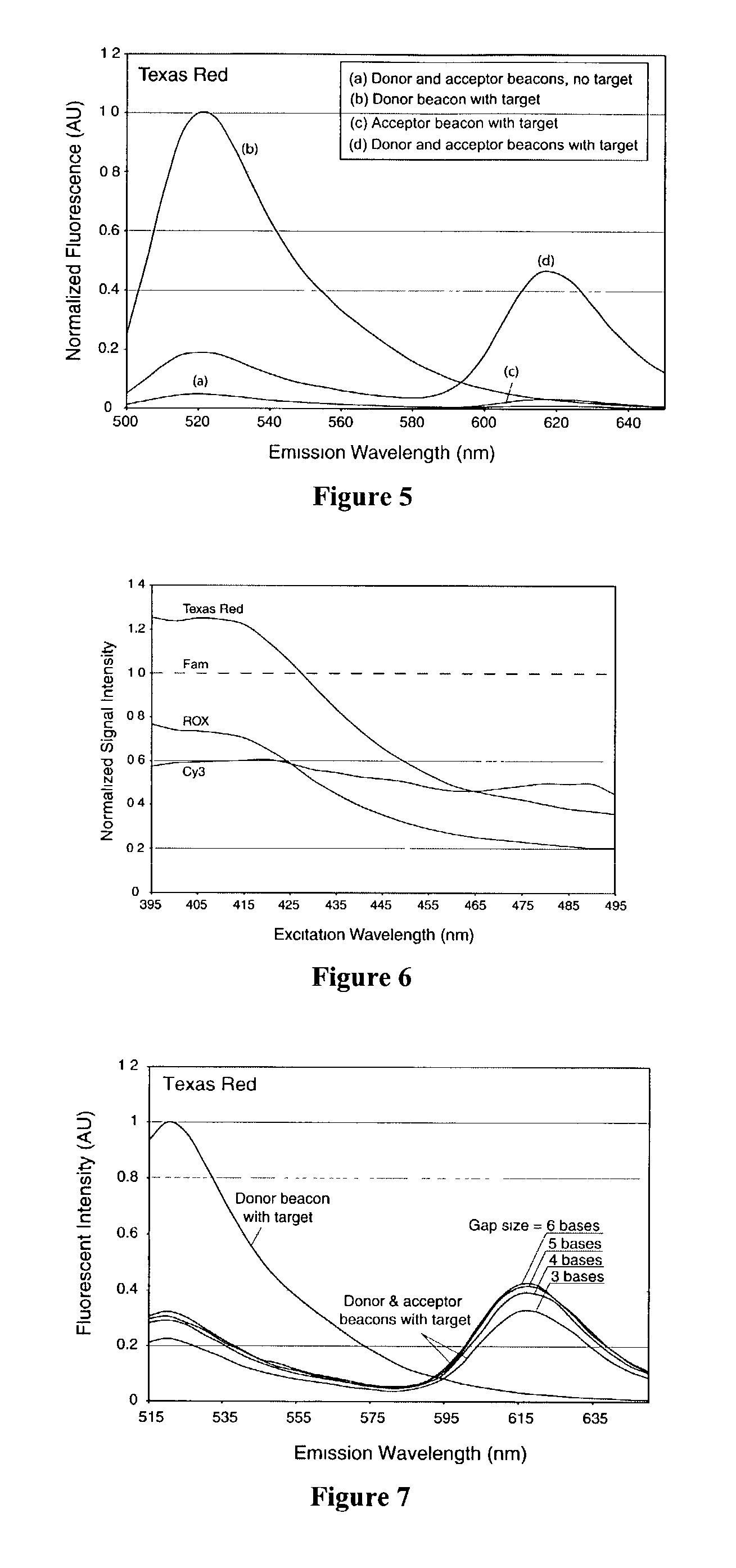
Described is a method for methylation detection in a DNA sample. An isolated genomic DNA sample is treated in a manner capable of distinguishing methylated from unmethylated cytosine bases. The pretreated DNA is amplified using at least one oligonucleotide primer, a polymerase and a set of nucleotides of which at least one is labeled with a first type of label. A sequence-specific oligonucleotide probe, marked with a second type of label, hybridizes to the amplification product and a FRET reaction occurs if a labeled oligonucleotide is present in close proximity in the amplification product. The method determines the level of methylation of a sample by measuring the extent of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the donor and acceptor fluorophore.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Single molecule detection and sequencing using fluorescence lifetime imaging
InactiveUS20110236983A1Avoid detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by electrical excitationEnergy transferNucleic acid detection
A nucleic acid detection system and method are provided, in which excitation energy is transmitted from a pulsed excitation source to a reaction site including a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based dye system to generate a fluorescent signal at the reaction site, the fluorescent signal is detected by a detector from the reaction site, and detection of the fluorescent signal is respectively blocked and permitted at the detector by a detector gate this is timed based on an emission start time of the transmitted excitation energy.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Tandem fluorescent protein constructs
This invention provides tandem fluorescent protein construct including a donor fluorescent protein moiety, an acceptor fluorescent protein moiety and a linker moiety that couples the donor and acceptor moieties. The donor and acceptor moieties exhibit fluorescence resonance energy transfer which is eliminated upon cleavage. The constructs are useful in enzymatic assays.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA SAN DIEGO LLC +1
Method for detecting upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using carbon nanomaterial as receptor
InactiveCN103487418ACarbon source is easy to getEasy to prepareFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSurface markerQuenching
The invention discloses a method for detecting fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using a water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial as a fluorescence donor and using a carbon nanomaterial as a fluorescence receptor. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preparing the water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial and performing surface marker to obtain a fluorescence donor solution; (2) preparing the carbon nanomaterial to obtain a fluorescence receptor solution; (3) mixing the fluorescence donor solution and the fluorescence receptor solution for incubation and measuring the fluorescence intensity to obtain a fluorescence quenching curve; (4) mixing certain-concentration fluorescence donor solution and certain-concentration fluorescence receptor solution for incubation, adding a target object with different concentrations for continuous incubation, measuring the fluorescence intensity and drawing a standard curve; (5) calculating the concentration of the target object in an actual sample according to the standard curve. According to the method, interference of the background fluorescence of a biological sample can be avoided, detection to serum or the target object in a whole blood sample can be directly realized, the washing and separation processes are not needed, the detection speed is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Fluorescent protein sensors for detection of analytes
InactiveUS7060869B2Reduce sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEnergy transferAnalyte
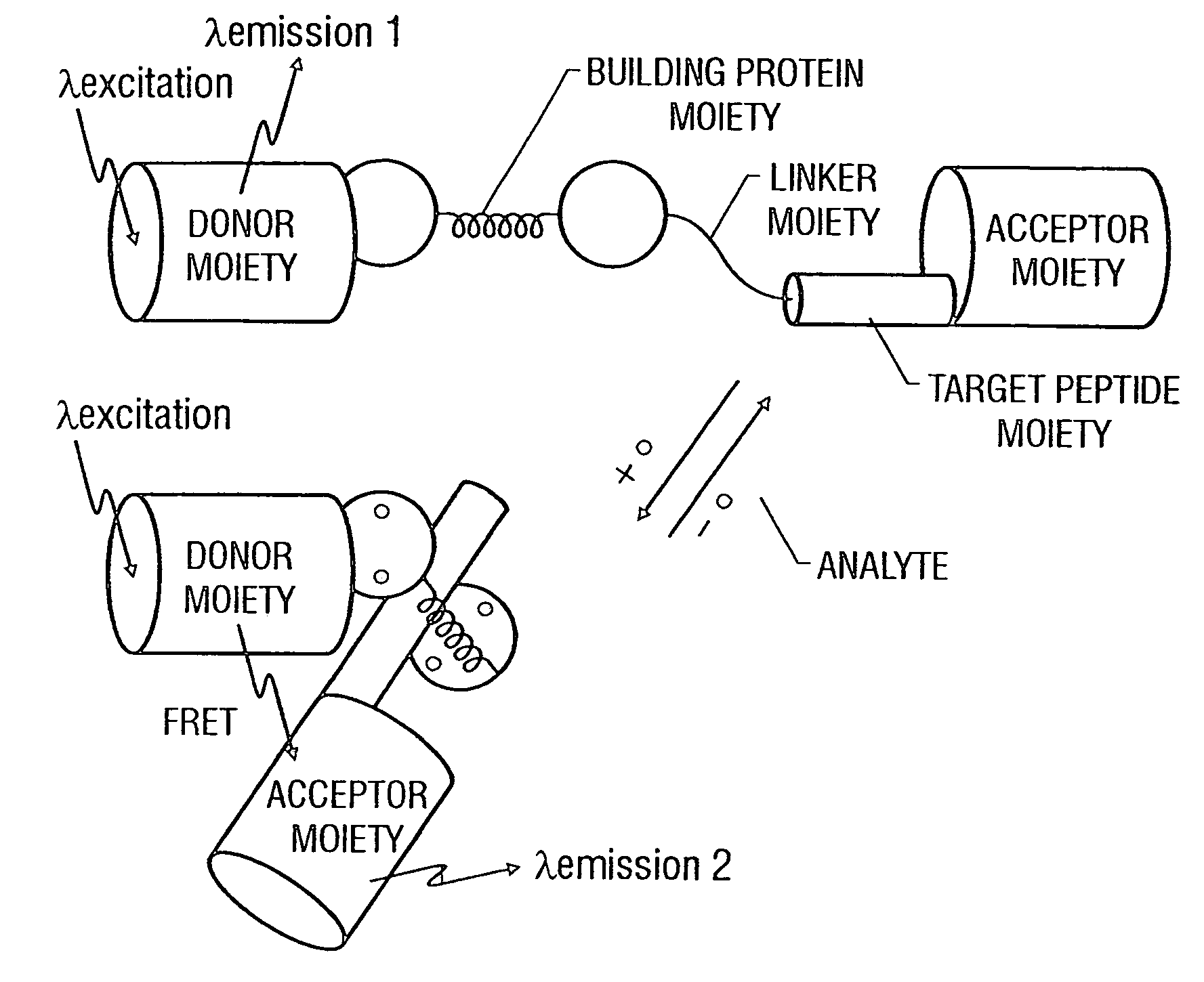
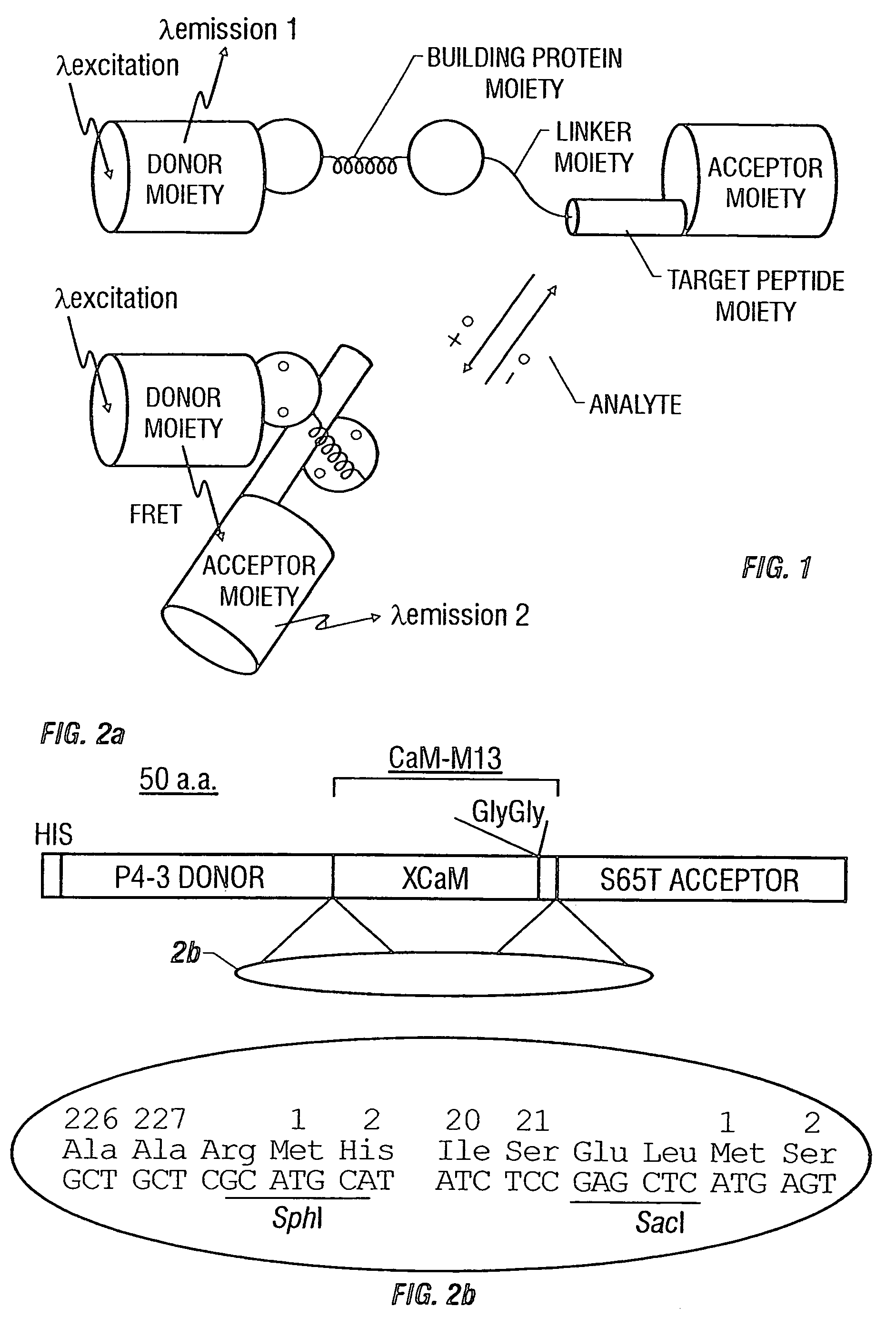
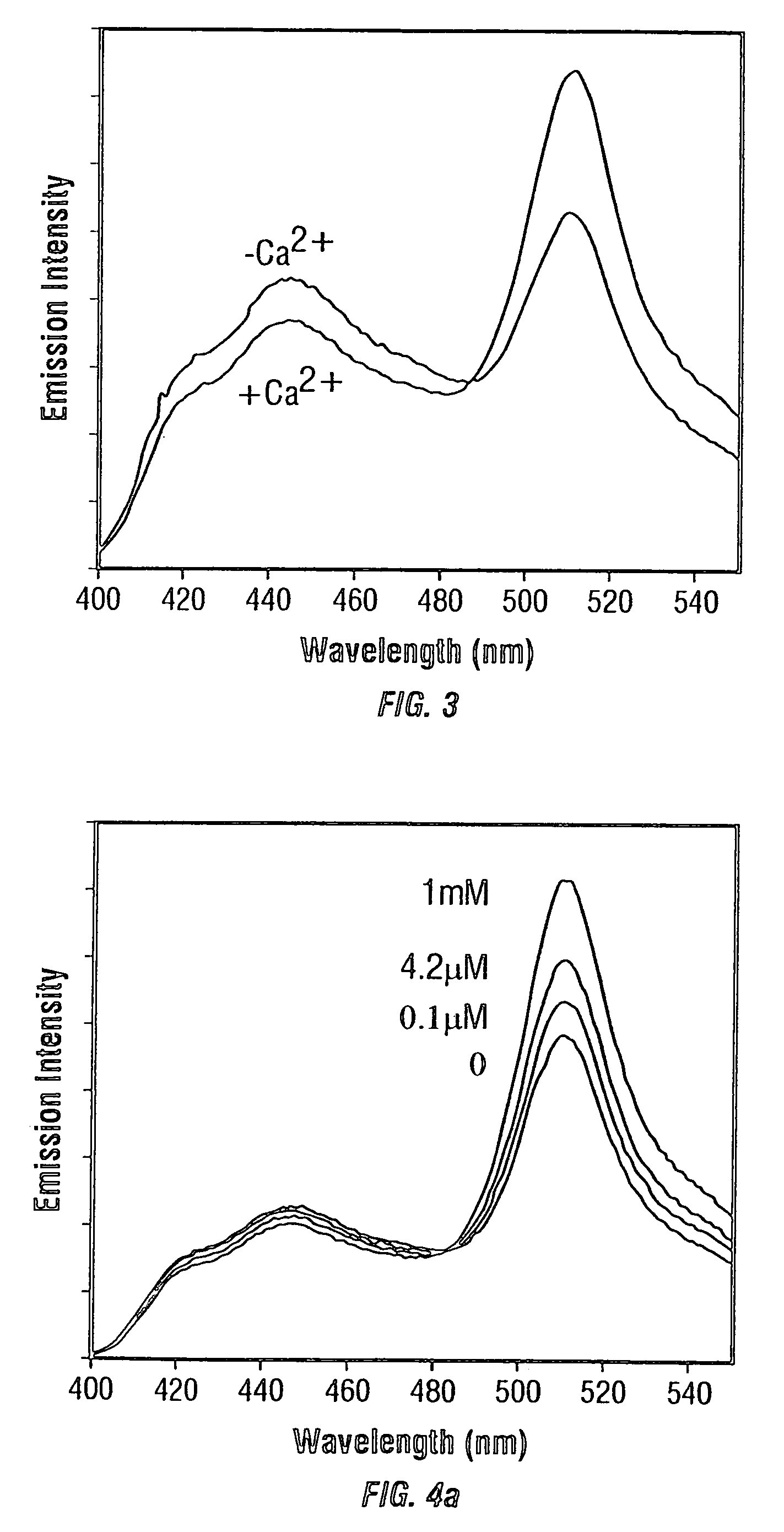
Fluorescent indicators including a binding protein moiety, a donor fluorescent protein moiety, and an acceptor fluorescent protein moiety are described. The binding protein moiety has an analyte-binding region which binds an analyte and causes the indicator to change conformation upon exposure to the analyte. The donor moiety and the acceptor moiety change position relative to each other when the analyte binds to the analyte-binding region. The donor moiety and the acceptor moiety exhibit fluorescence resonance energy transfer when the donor moiety is excited and the distance between the donor moiety and the acceptor moiety is small. The indicators can be used to measure analyte concentrations in samples, such as calcium ion concentrations in cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of FXR ligands
The present invention includes nuclear receptor heterodimer and nuclear receptor-coactivator peptide assays for identifying ligands for nuclear receptors, utilizing scintillation proximity and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and methods of using identified ligands.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Universatl fluorescent sensors
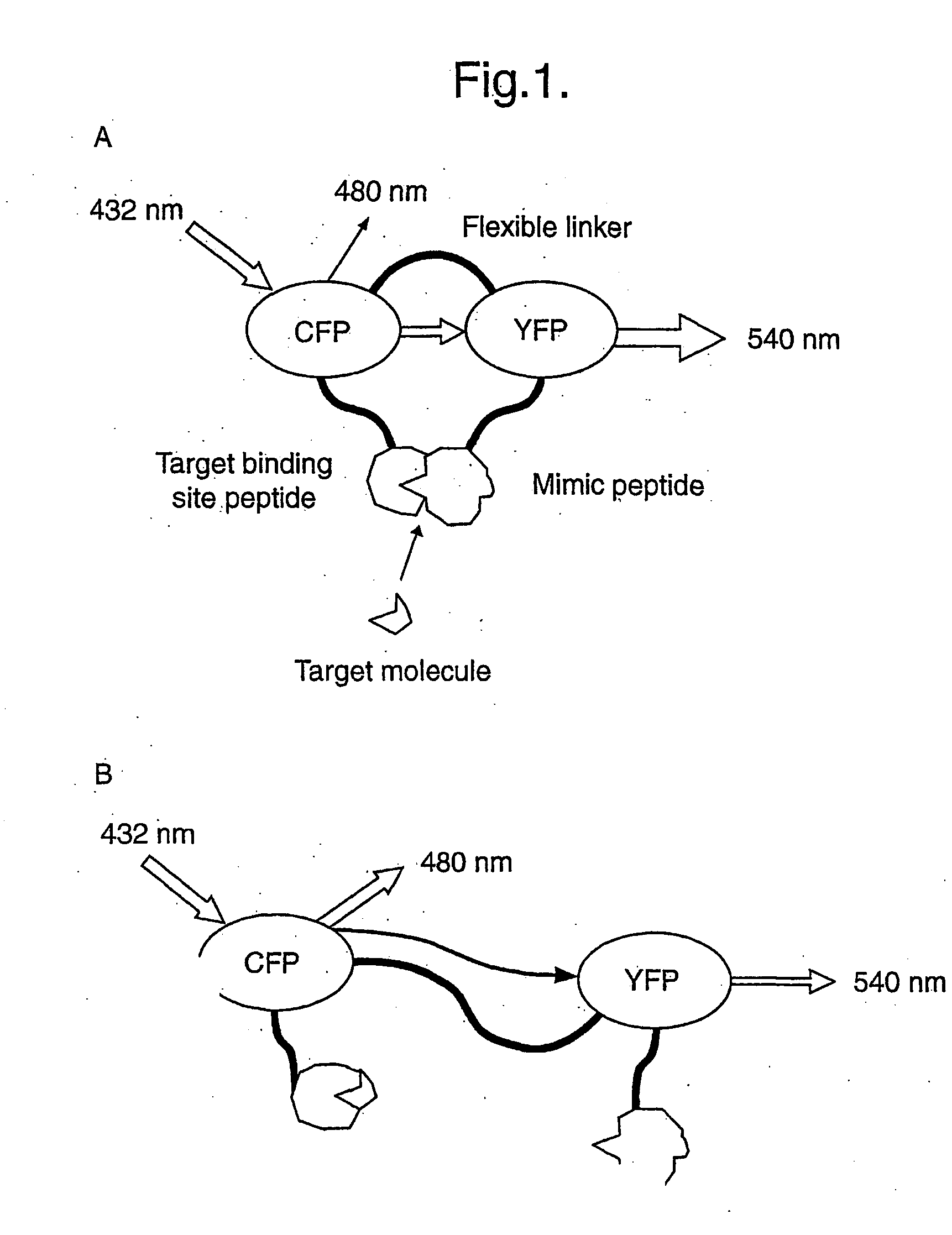
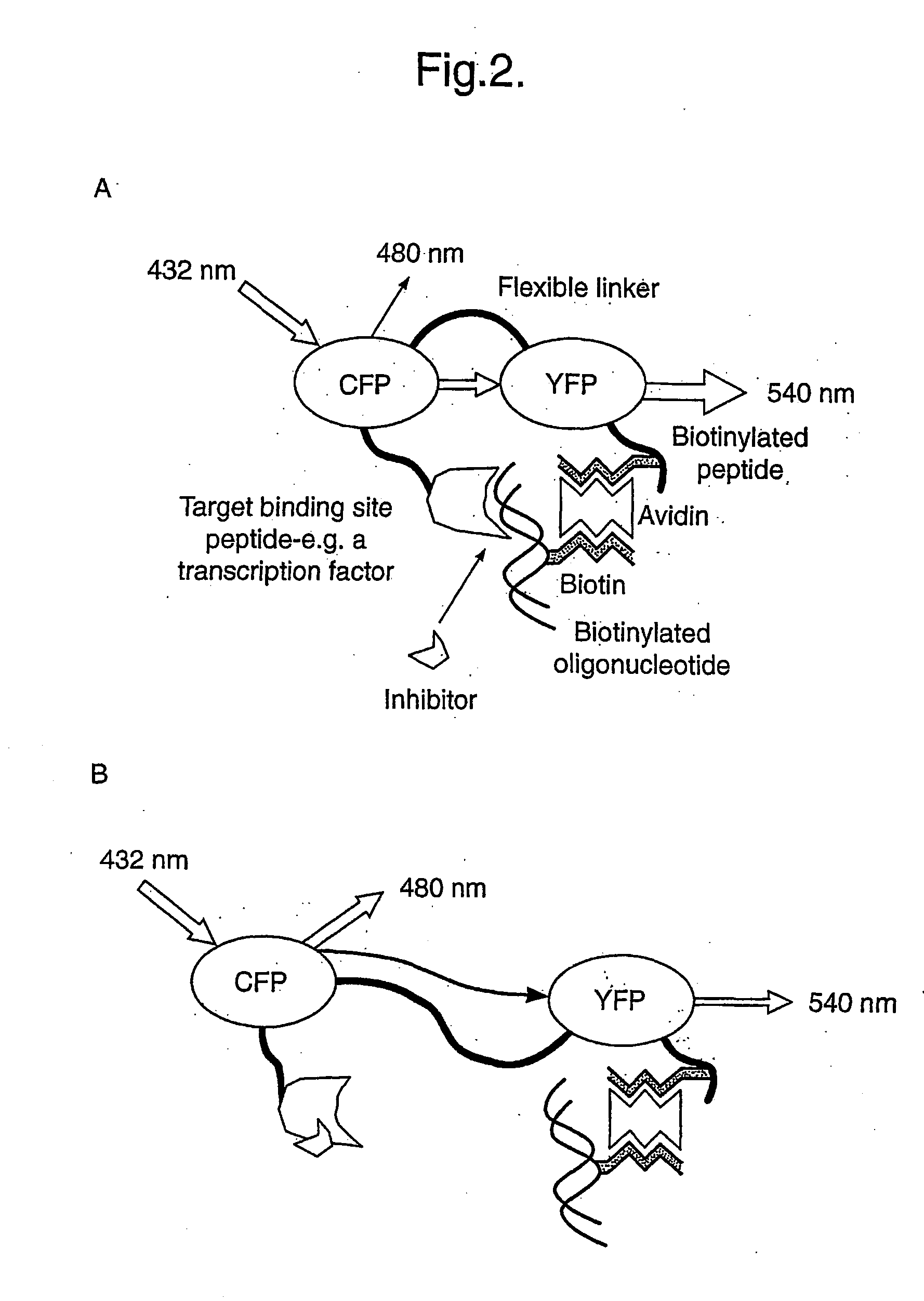
A probe comprises: (1) a target binding site moiety which is attached to a first fluorescent polypeptide; (ii) a mimic moiety which is capable of binding to the target binding site moiety and is attached to a second fluorescent polypeptide; and (iii) a linker which connects the two fluorescent polypeptides and which allows the distance between said fluorescent polypeptides to vary, said fluorescent polypeptides being so as to display fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between them, wherein the linker comprises one or more of: (1) a sequence capable of being recognised and bound by an immobilized component; (2) a protease cleavage site; (3) a non-analyte binding site; (4) two or more copies of the sequence (SerGly3); or (5) one or more copies of a rod domain from a structural protein. Probes of the invention are used, for example, in the detection of a wide range of substances or in the identification of inhibitors of the interaction between two substances which, in the absence of an inhibitor, interact with each other.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Quantitative methylation detection in DNA samples
InactiveUS20030148290A1Quick fixFast and cost-effective and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPolymerase LGenomic DNA
Described is a method for methylation detection in a DNA sample. An isolated genomic DNA sample is treated in a manner capable of distinguishing methylated from unmethylated cytosine bases. The pretreated DNA is amplified using at least one oligonucleotide primer, a polymerase and a set of nucleotides of which at least one is labeled with a first type of label. A sequence-specific oligonucleotide probe, marked with a second type of label, hybridizes to the amplification product and a FRET reaction occurs if a labeled oligonucleotide is present in close proximity in the amplification product. The method determines the level of methylation of a sample by measuring the extent of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between the donor and acceptor fluorophore.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Nucleic acid analyzing method based on cascade HCR (hybridization chain reaction)
ActiveCN107574227AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferImaging analysis
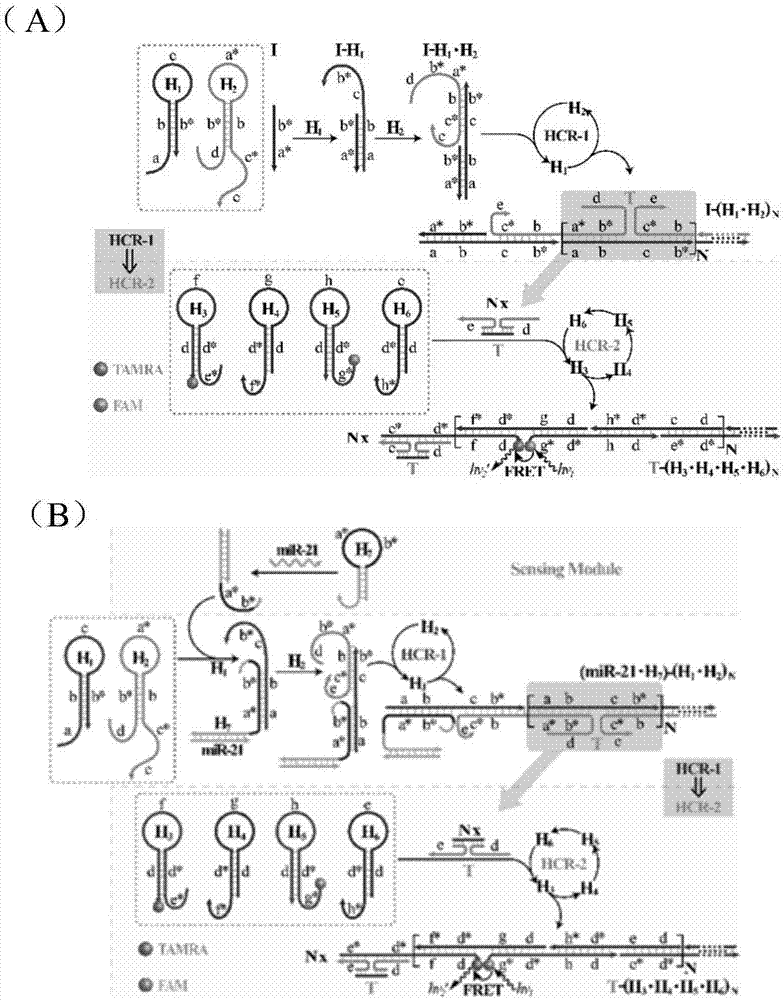
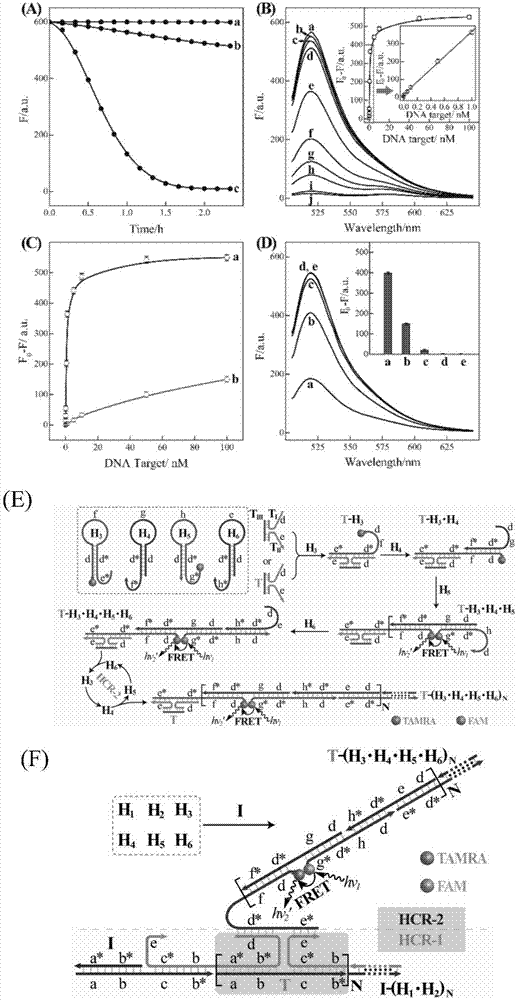
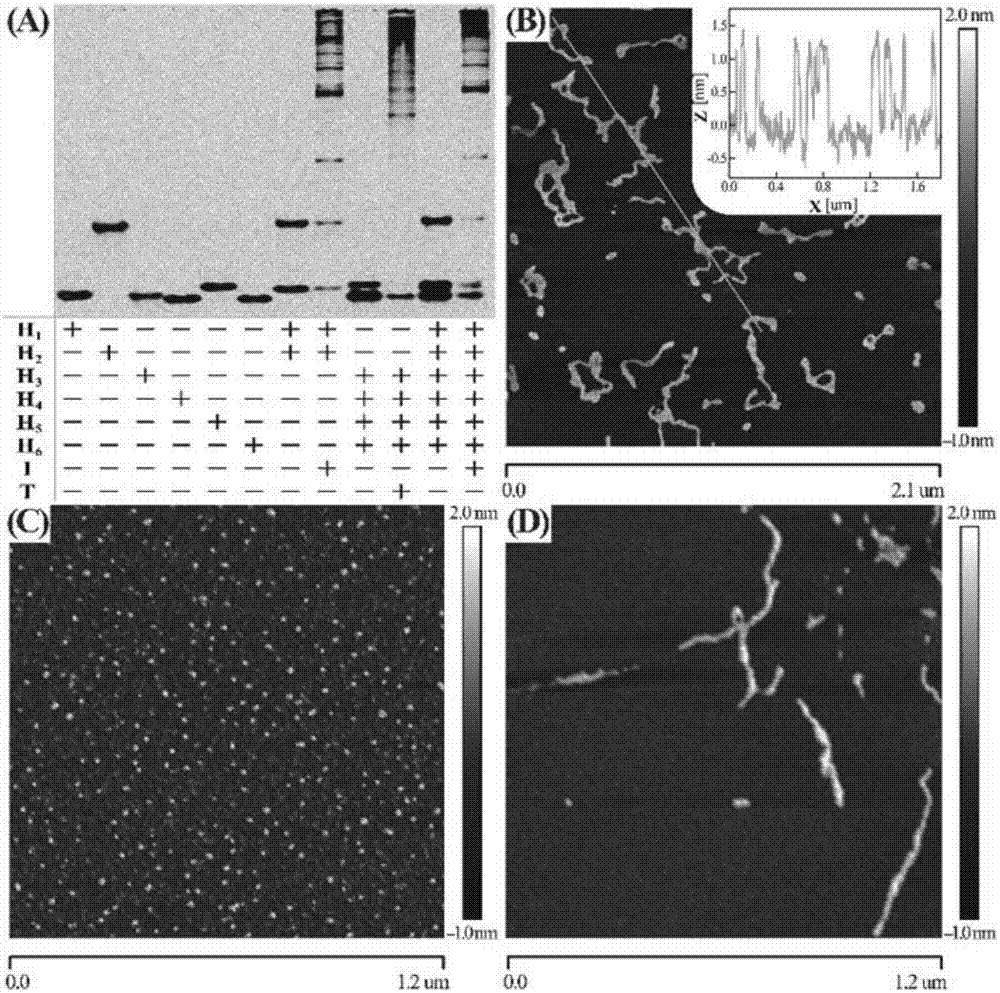
The invention discloses a nucleic acid analyzing method based on cascade HCR (hybridization chain reaction), and belongs to the field of molecule detection. The nucleic acid analyzing method is characterized in that on the basis of single HCR, two stages of HCR reaction are designed, and the signals can be further amplified on the basis of single HCR; the hairpin nucleic acid probes marked with multiple different fluorescent dyes can be alternatively hybridized by a final target product, so as to form a branched DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nanometer structure; the signal output is provided bythe fluorescent resonance energy transfer, and the concentration of the target nucleic acid can be judged according to the change value of the fluorescence intensity of fluorophore. The nucleic acid analyzing method has the advantages that the nucleic acid analyzing method can be used for in-vitro detection of DNA and miRNA (miniature ribonucleic acid), the specificity is good, and the sensitivityis high; the nucleic acid analyzing method can be used for the imaging analysis of miRNA in cells, and be favorable for the early diagnosis on cancers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Flourescence polarization assay system and method
An instrument is disclosed for fluorescence assays which is capable of reading many independent samples at the same time. This instrument provides enhanced throughput relative to single-sample instruments, and is well-suited to use in general fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, multi-band fluorescence, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and fluorescence polarization. This invention is beneficial in applications such as high-throughput drug screening, and automated clinical testing. Also disclosed are means and methods for a fluorescence polarization measurement which is highly sensitive, inherently self-calibrated, and unaffected by lamp flicker or photobleaching. This fluorescence polarization invention can be practiced on a variety of fluorescence instruments, including prior-art equipment such as microscopes and multi-well plate readers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
Fluorescent test strip based on resonance energy transfer, and preparation method and application for fluorescent test strip
ActiveCN102890155ANo pollution in the processOperational securityBiological testingEnergy transferResonance
The invention discloses a fluorescent test strip based on resonance energy transfer, and a preparation method and application for the fluorescent test strip. The fluorescent test strip comprises a bottom liner, a sample absorption mat, a combining mat, a chromatography membrane and a water-absorbent mat, wherein the sample absorption mat, the combining mat, the chromatography membrane and the water-absorbent mat are sequentially connected with one another closely and are attached to the bottom liner; antibodies marked by fluorescent receptors are attached to the combining mat; a detection line and a calibration line are arranged on the chromatography membrane; the detection line is close to the combining mat; the calibration line is close to the water-absorbent mat; antigens marked by fluorescent substances are attached to the detection line; proteins marked by fluorescent substances are attached to the calibration line; the antigens marked by the fluorescent substances and the antibodies marked by the fluorescent receptors can be combined by specificity of antigen and antibody reaction; and the proteins marked by the fluorescent substances do not react with the antibodies marked by the fluorescent receptors. The fluorescent test strip has the advantages of safety in operation, simplicity, convenience, sensitivity, low cost, speediness and the like, is wide in application range, and can be used for single-item detection or quick detection items such as multiple-item detection.
Owner:广州健尔圣医药科技有限公司
Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Assay Based on Modified Solid Surface
System, including methods, apparatus, and kits, for fluorescence resonance transfer (FRET) binding assays that are surface-based.
Owner:WEI HUANG
Development of sensitive fret sensors and methods of using the same
Intramolecular biosensors are disclosed, including PBP-based biosensors, comprising a ligand binding domain fused to donor and fluorescent moieties that permit detection and measurement of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer upon binding ligand. At least one of the donor and fluorescent moieties may be internally fused to the biosensor such that both ends of the internally fused fluorophore are fixed. In addition, methods of improving the sensitivity of terminally fused biosensors are provided. The biosensors of the invention are useful for the detection and quantification of ligands in vivo and in culture.
Owner:CARNEGIE INSTITUTION OF WASHINGTON
Nanoparticles for two-photon activated photodynamic therapy and imaging
InactiveUS20090035576A1Improve behaviorPowder deliveryPhotodynamic therapySinglet oxygenSilicon dioxide
The present invention provides organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) nanoparticles into which have been incorporated two-photon absorption dye molecules. The two photon absorption dye displays a unique aggregation induced fluorescence enhancement behavior. As a result ORMOSIL nanoparticles with high amounts of the dye can be prepared. These particles can be used for imaging. In one embodiment, the nanoparticles can additionally have incorporated therein a photosensitizer. The photosensitzer can be activated by intraparticle fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) from the dye aggregates resulting in enhanced fluorescence and singlet oxygen generation from photosensitizer under two-photon excitation conditions. Such nanoparticles can be used for photodynamic therapy applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Method of detecting adenosine with fluorescent sensor on the basis of aptamer
InactiveCN106950206AEffective quenchingHigh absorption coefficientFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transferAnalysis data
The invention discloses a method of detecting adenosine with a fluorescent sensor on the basis of an aptamer. In the method, gold nano particles modified with the aptamer are used as a recognition probe and an energy acceptor, and carbon dots modified with an aptamer complementary chain are used as a fluorescent probe and an energy donor; through a hybridization reaction, fluorescence resonance energy transfer is carried out between the gold nano particles and the carbon dots, and fluorescence of the detection system is quenched. After addition of adenosine, the adenosine and the aptamer complementary chain are competitively combined with the aptamer, so that energy transfer efficiency between the gold nano particles and the carbon dots is weakened; and the fluorescence of the detection system is recovered, so that based on the change of the fluorescence signal, the method achieves quantitative detection of the adenosine. The method has strong specificity and simple operation, is low in required quantity of a sample, is high in sensitivity, can be used for detecting the adenosine in a blood sample and supplies useful analysis data for clinical diagnosis on diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
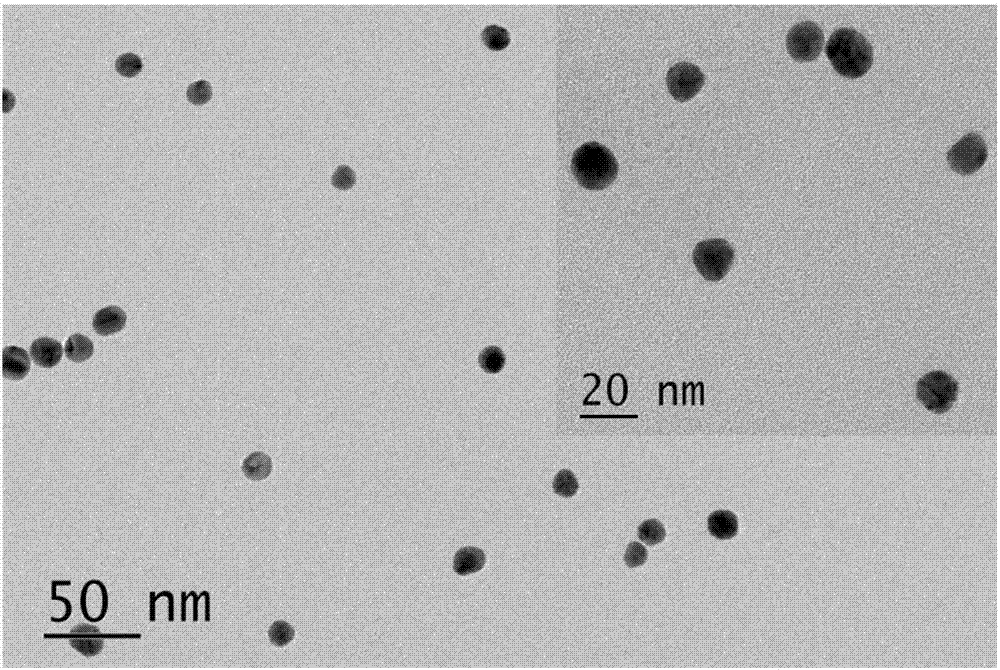
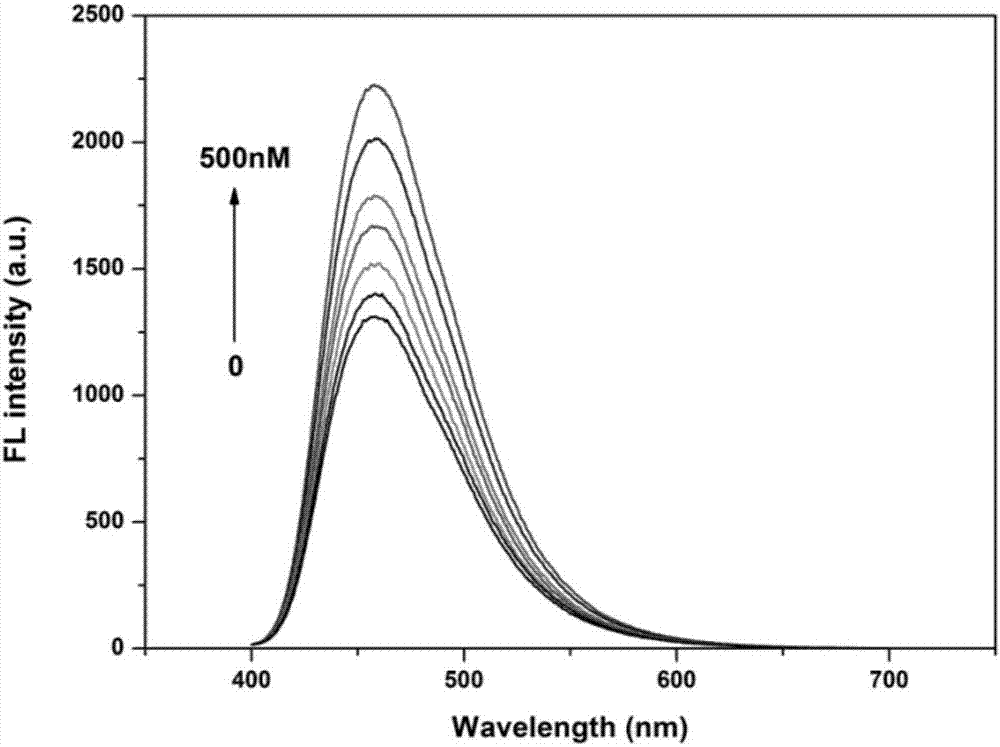
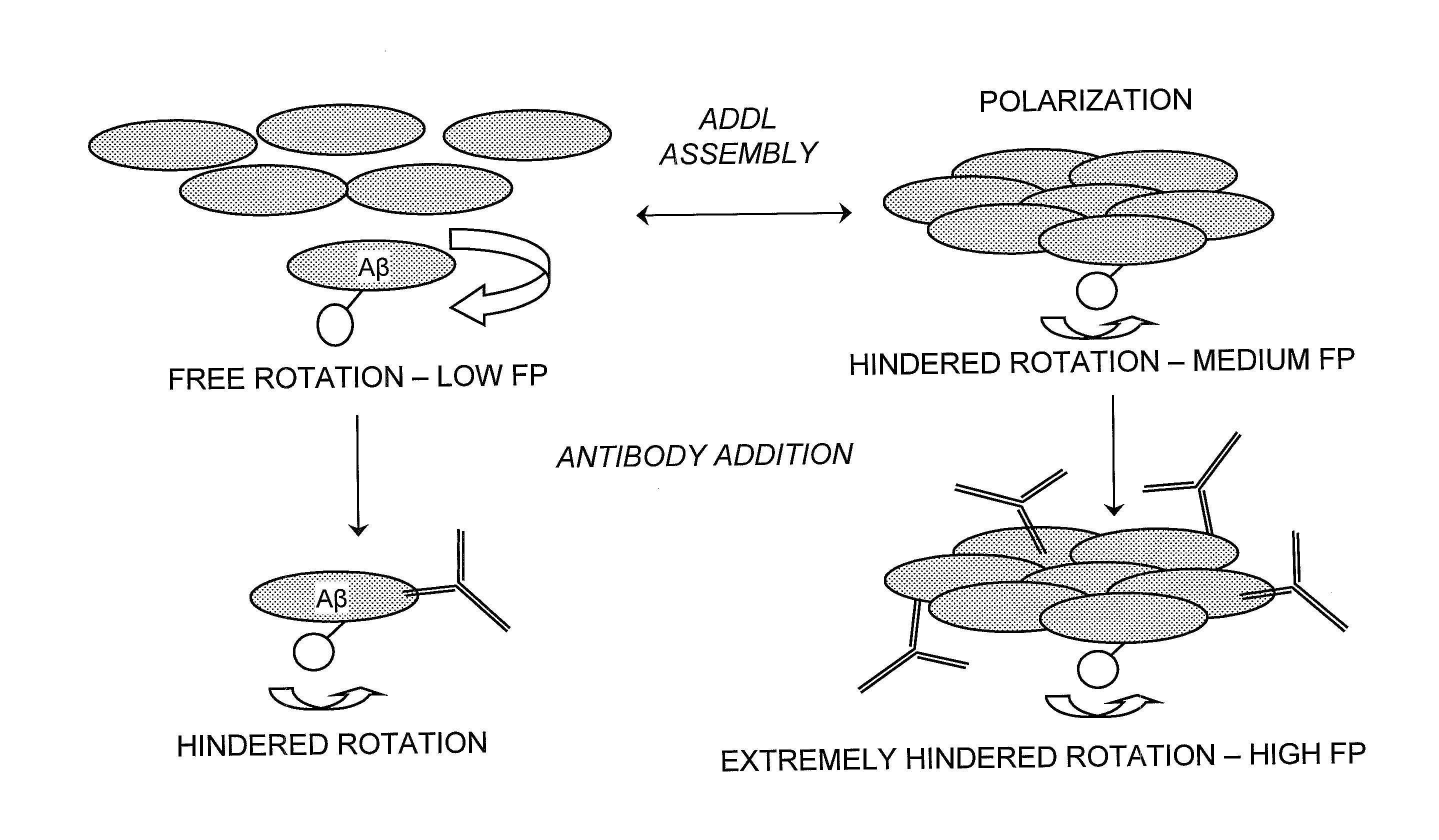
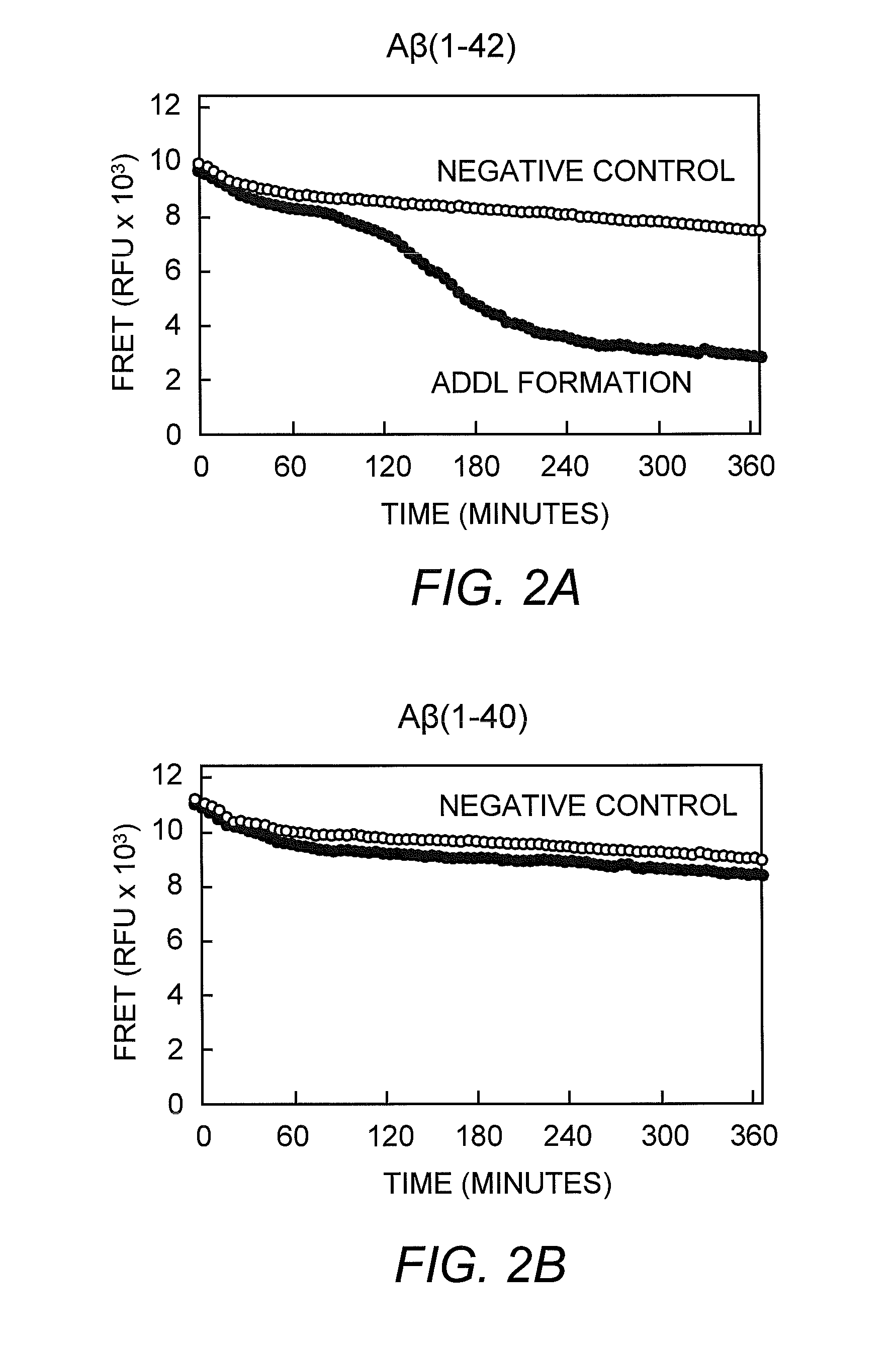
Method for detecting oligermization of soluble amyloid beta oligomers
The present invention relates to the assay, analysis, and characterization of soluble amyloid beta oligomers, as well as the characterization of inhibitors of soluble amyloid beta oligomer assembly. In particular, the present invention is a method for detecting assembly of soluble amyloid beta oligomers via a combination of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) or time-resolved FRET and fluorescence polarization (FP).
Owner:ACUMEN PHARMA
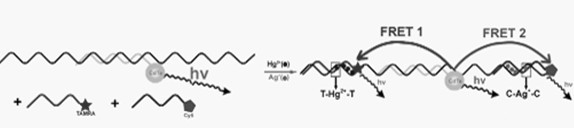
Method for simultaneously detecting mercury ion and/or silver ion in water solution based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting a divalent mercury ion and a silver ion in water solution based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer, belonging to the field of heavy metal ion detecting technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a detecting probe, comprising following steps: (1), preparing a cadmium telluride (CdTe) quantum dot which is encapsulated by mercaptopropionic acid (MPA); (2), designing and composing a nucleic acid probe for detection; (3), preparing a fluorescent probe CdTe-DNA of quantum dots and nucleic acid; and secondly, detecting heavy metal ion Ag+ and / or Hg2+. The method provided by the invention can detect two ions simultaneously, the workload is low, the cost is low and the process is not complex.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
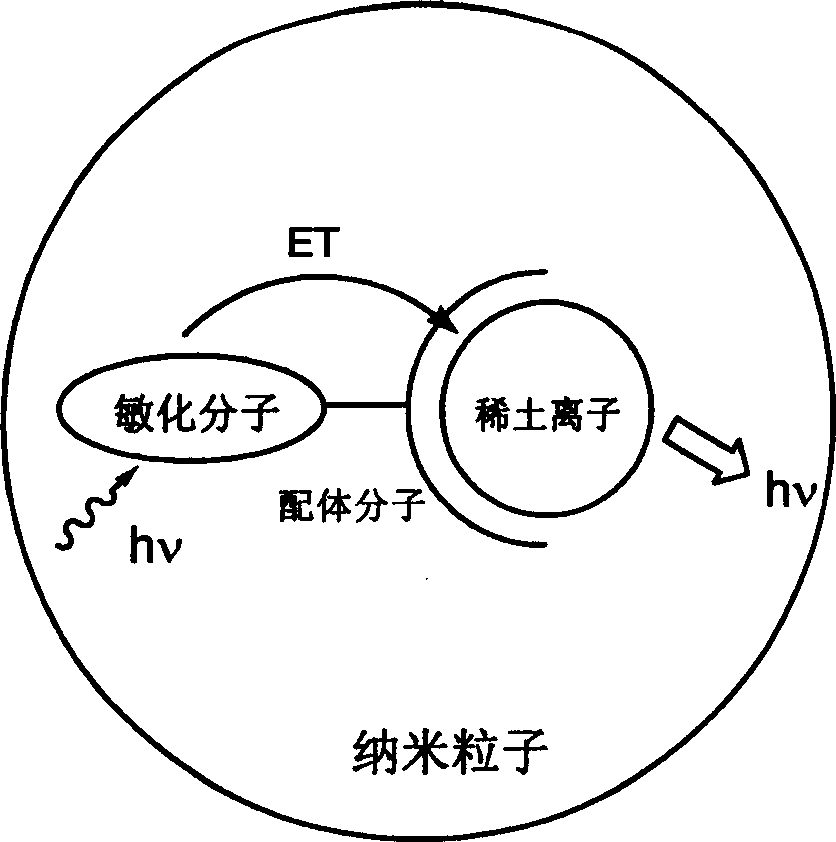
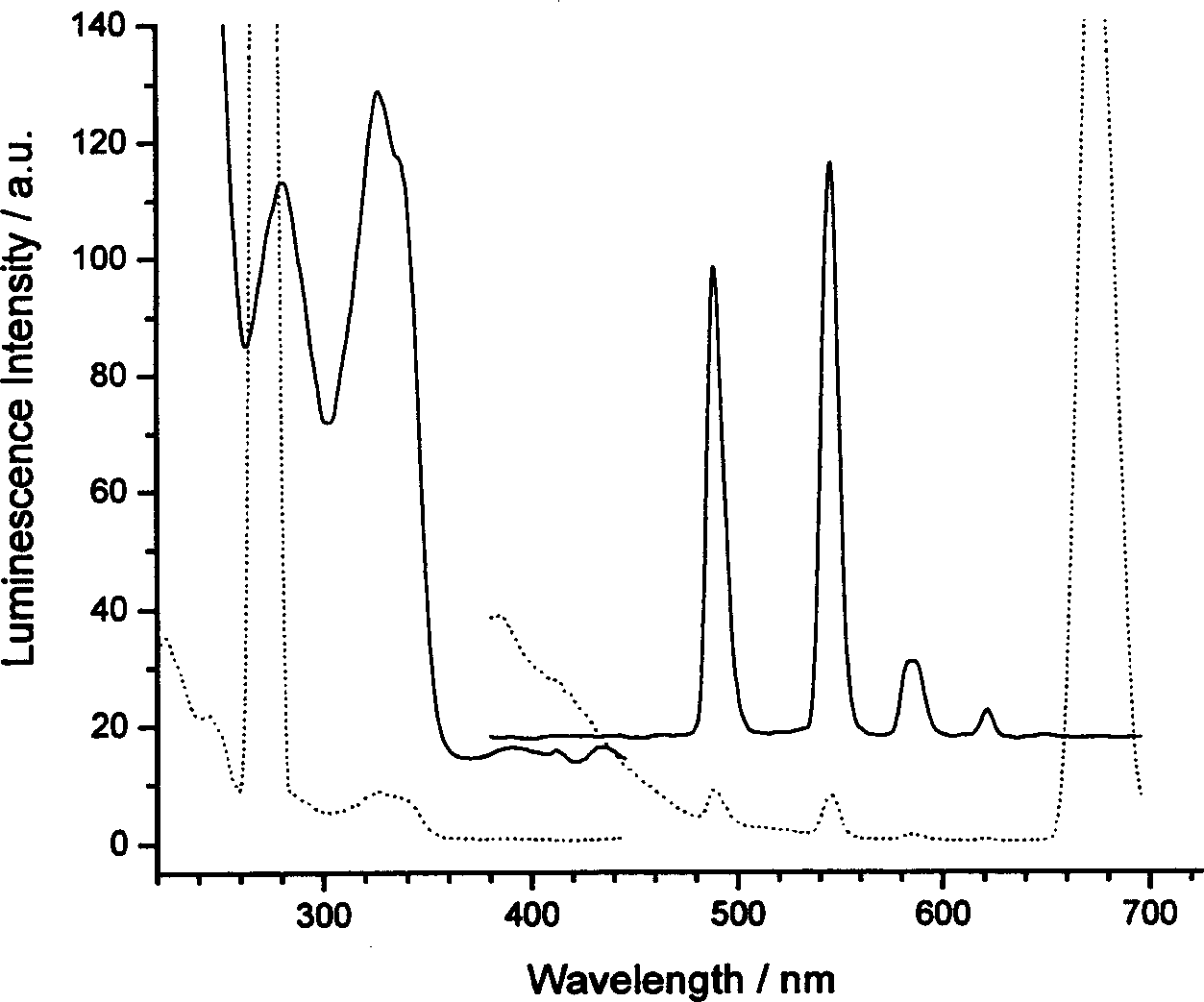
Rare-earth nano luninous particle based on fluorescent energy transfer principle and its preparing method
InactiveCN1775898AHigh luminous intensityGood luminous stabilityLuminescent compositionsSolubilityEnergy transfer
The invention relates to emitting rare earth nm particle based on fluorescence energy transferring principle and the method to manufacture, and new style rare earth nm particle manufacturing and the surface decorating used for testing biology molecule mark and tracing. The rare earth nm particle is made up from emitting rare earth complexes as the core and covering SiO2. The rare earth complex is made up from organic ligand joining with a sensitization molecule and rare earth ion. The rare earth nm particle marker has good water solubility and long fluorescence lifetime. The surface of the particle could covalence joining plural probe molecule that could be used to testing or tracing the biology molecule.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
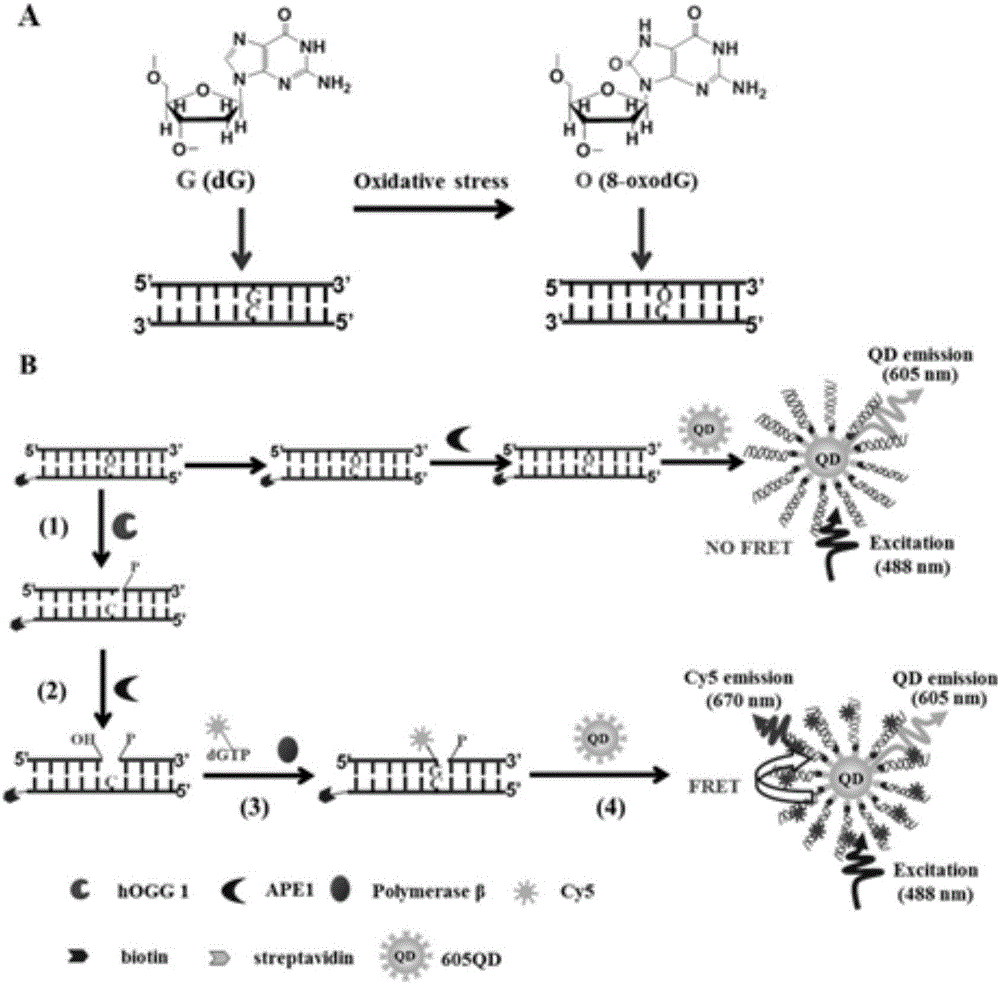
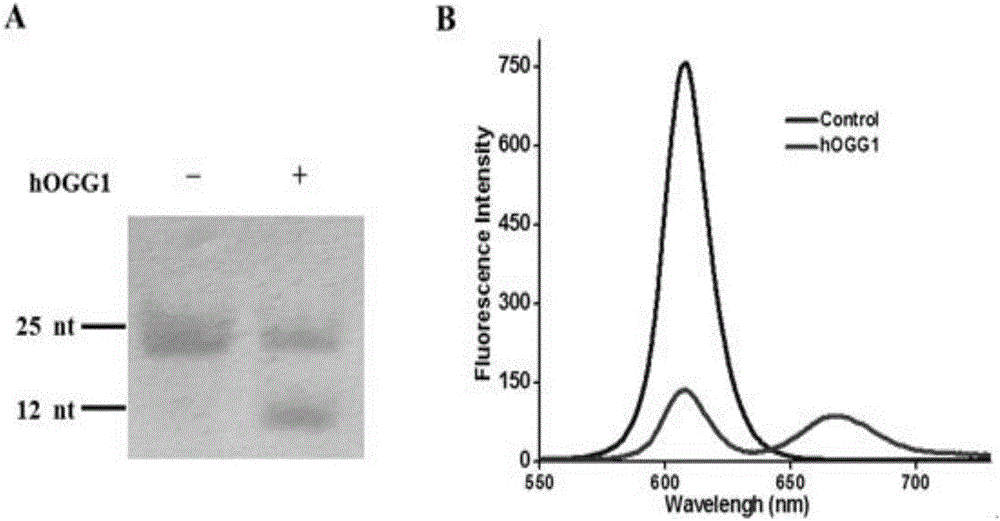
Method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylase activity on basis of single quantum dot level
ActiveCN105755101AStrong specificityLow specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFörster resonance energy transferAPURINIC ENDONUCLEASE
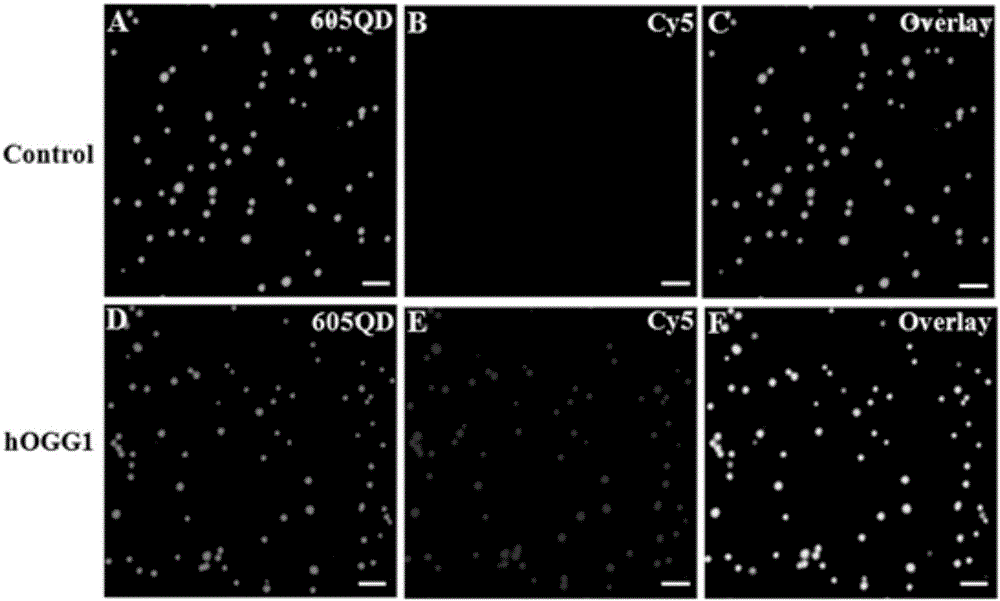
The invention discloses a method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylase activity on basis of single quantum dot level.In detection, DNA glycosylase hOGG1 specifically recognizes and excises damaged guanine to leave an abasic site, apurinic endonuclease-1 further excises the abasic site to leave a nucleotide gap, and DNA polymerase beta polymerizes Cy5-dGTP at the gap to generate a double-tagging double-strand nucleotide substrate; by specific reaction between biotin and streptavidin, the DNA substrate is combined to the surface, covered with the streptavidin, of quantum dots to form a QD-DNA-Cy5 compound; due to reduction of spatial distance, fluorescence resonance energy transfer occurs between the quantum dots and Cy5, and Cy5 fluorescence signals can be observed in the unimolecular level.The method has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and sensitivity, and the lower limit of detection can reach 1.8*10<-6>U / microliter.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Methods and compounds for increasing sensitivity of botulinum assays
ActiveUS9303285B2Promote degradationReduce sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorophoreCell
Apparatus, systems and methods can provide improved detection of botulinum neurotoxins. In one aspect an isoquinolynyl compound can be used to enhance the sensitivity of both Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and non-FRET cell-based assays. In another aspect, non-FRET assays and constructs utilize a reporter that is not coupled with the second fluorophore in a manner that produces significant FRET. In that subject matter an environment cell can include an enzyme that facilitates degradation of the reporter significantly faster after the cleavage than before the cleavage, and presence of the Botulinum toxin correlates with reduction of the signal from a baseline signal. Where the environment is a cell, the cell can advantageously express both the construct that includes the reporter, and an enzyme that facilitates the degradation.
Owner:BIOMADISON
Quantum dot-cyanine dye-folic acid biological probe and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a quantum dot-cyanine dye-folic acid biological probe. The probe structure comprises a probe which is formed by the quantum dot is bonded with the cyanine dye, and the cyanine dye is bonded with the folic acid. The invention further provides a preparation method of the quantum dot-cyanine dye-folic acid biological probe. The invention has the advantages of convenient preparation method and easy inducing quantum dot of the dye. The biological probe has the characteristics of targeted identifying tumor tissue and transferring fluorescence resonance energy, thereby not being capable of targeted identifying cancer cell and being capable of identifying the space location and the space structure of the cancer cell by the characteristic of transferring fluorescence resonance energy. The biological probe has the dual advantages of the quantum dot and the cyanine dye probe, and has simple preparation method, thereby being high-stability and high-efficiency targeted fluorescence mark. The probe has high sensitivity and less usage amount.
Owner:TIANJIN URBAN CONSTR COLLEGE
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS20060127940A1Rapid and specific and sensitive hybridization detectionEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Dual nucleic acid probes with resonance energy transfer moieties are provided. In particular, fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties are provided on hairpin stem-loop molecular beacon probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid, e.g. mRNA, to generate an observable interaction. The invention also provides lanthanide chelate luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties on linear and stem-loop probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid to generate an observable interaction. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific and sensitive hybridization determination in vivo. The probes are used in methods of detection of nucleic acid target hybridization for the identification and quantification of tissue and cell-specific gene expression levels, including response to external stimuli, such as drug candidates, and genetic variations associated with disease, such as cancer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Multi-color optic-encoding siliceous skin nano-rods and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101333436AGood package efficiencyImprove packaging efficiencyBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transferResonance
The invention discloses a multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell. The multi-color optical encoding nano-rod takes the shape of a core shell, the shell is made of silicon dioxide and the kernel is fluorescence-encoded polylysine which contains fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B; the fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B are a fluorescence resonance energy transfer supplier-receptor pair. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell, which includes the steps of enabling the fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B to react with the polylysine to prepare fluorescence-encoded polylysine, and wrapping the fluorescence-encoded polylysine, used as kernel material, in a silicon dioxide substrate through reverse microemulsion method; in this way, the multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell can be prepared. The multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell has the advantages of strong fluorescence intensity, good biological compatibility, good hydrophilicity, little leakage of dye and stable property.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
High-throughput, high-precision methods for detecting protein structural changes in living cells
ActiveUS20150204847A1Highly parallel biological researchQuick analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein targetProtein structure
Methods for identifying a compound that alters fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) of a protein. The methods include use of a genetically engineered cell that includes a target protein. The target protein includes one or more heterologous domains. In one embodiment, a target protein includes two heterologous domains, and in another embodiment, the target protein includes a heterologous domain and the cell further includes a second protein that includes a heterologous domain. A heterologous domain may include a chromophore or an amino acid to which a fluorescent dye attaches. The fluorescence lifetime of one or more chromophore, one or more fluorescent dye, or the combination thereof, is measured after contacting the cell with a compound A difference between the fluorescence lifetime in the presence of the test compound and the fluorescence lifetime in the absence of the test compound indicates that the test compound alters the FRET of the target protein.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO +1
Synthesis of Alloyed Nanocrystals in Aqueous or Water-Soluble Solvents
InactiveUS20090220792A1Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthQuantum yieldCelsius Degree
The present invention relates to nanocrystals and methods for making the same; in particular, the invention relates to ternary or higher alloyed nanocrystals and methods for making such structures in aqueous or water-soluble solvents. In certain embodiments of the invention, methods of preparing ternary or higher alloyed nanocrystals involve providing at least first, second, and third nanocrystal precursors (e.g., NaHSe, ZnCl2, and CdCl2) and forming nanocrystal structures in an aqueous or water-soluble solvent. In some cases, nanocrystal precursor solutions may also include a water-soluble ligand (e.g., glutathione, GSH). As such, ternary or higher alloyed nanocrystals (e.g., ZnxCd)—xSe) comprising the at least first, second, and third nanocrystal precursors may be formed, and the water-soluble ligand may coat at least a portion of the surface of the ternary or higher alloyed nanocrystal. Advantageously, methods for forming nanocrystals described herein can be performed at low temperatures (e.g., less than 100 degrees Celsius), and, in some embodiments, do not require the use of organic solvents. The present inventors have applied these methods to prepare blue-emitting nanocrystals with emissions that are tunable between 400-500 nm, and with quantum yields of greater than 25% in aqueous solution. These nanocrystals may be highly water soluble and can be used in a variety of applications, including those involving cell culture, sensing applications, fluorescence resonance energy transfer, and in light-emitting devices.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
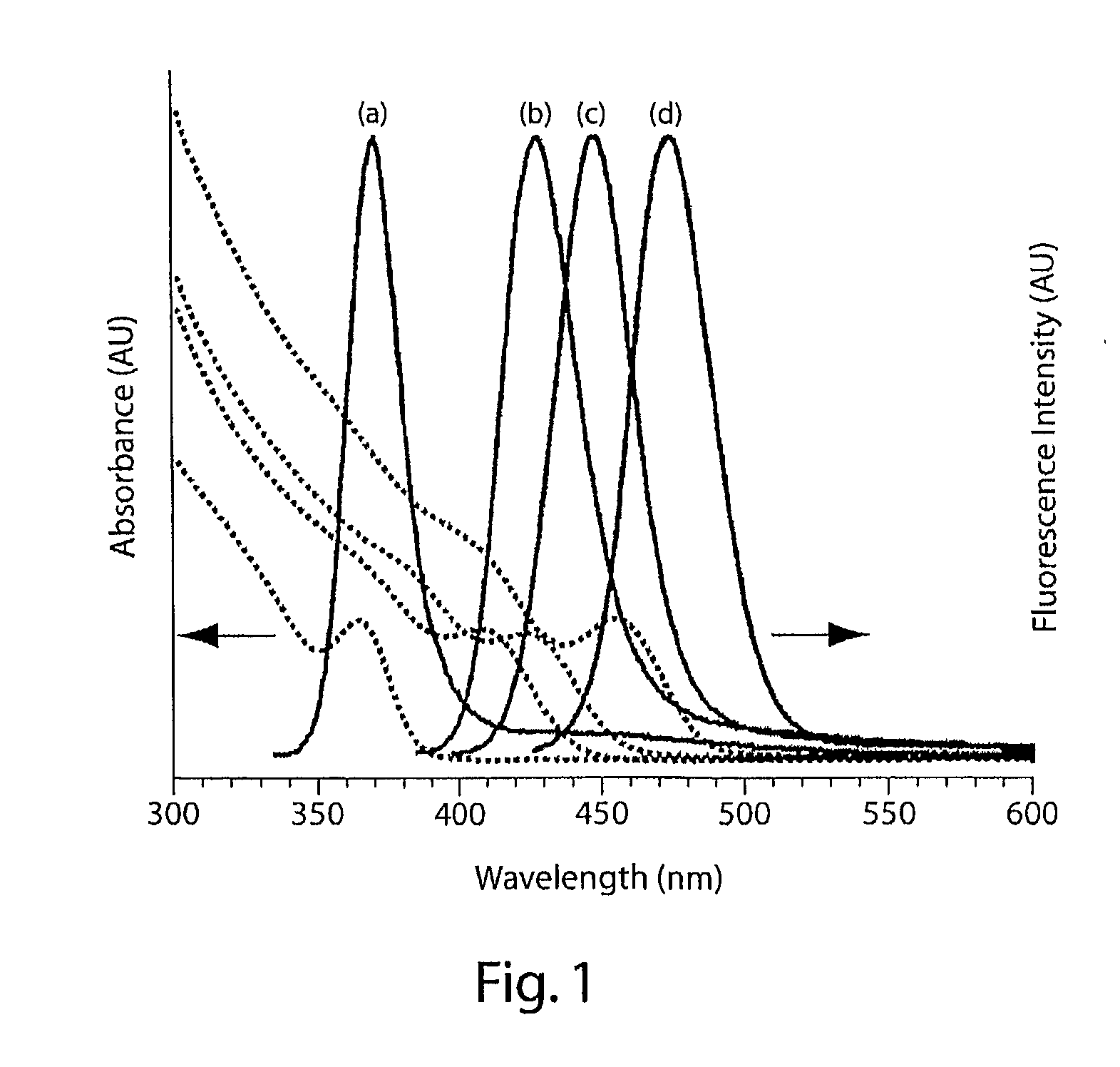
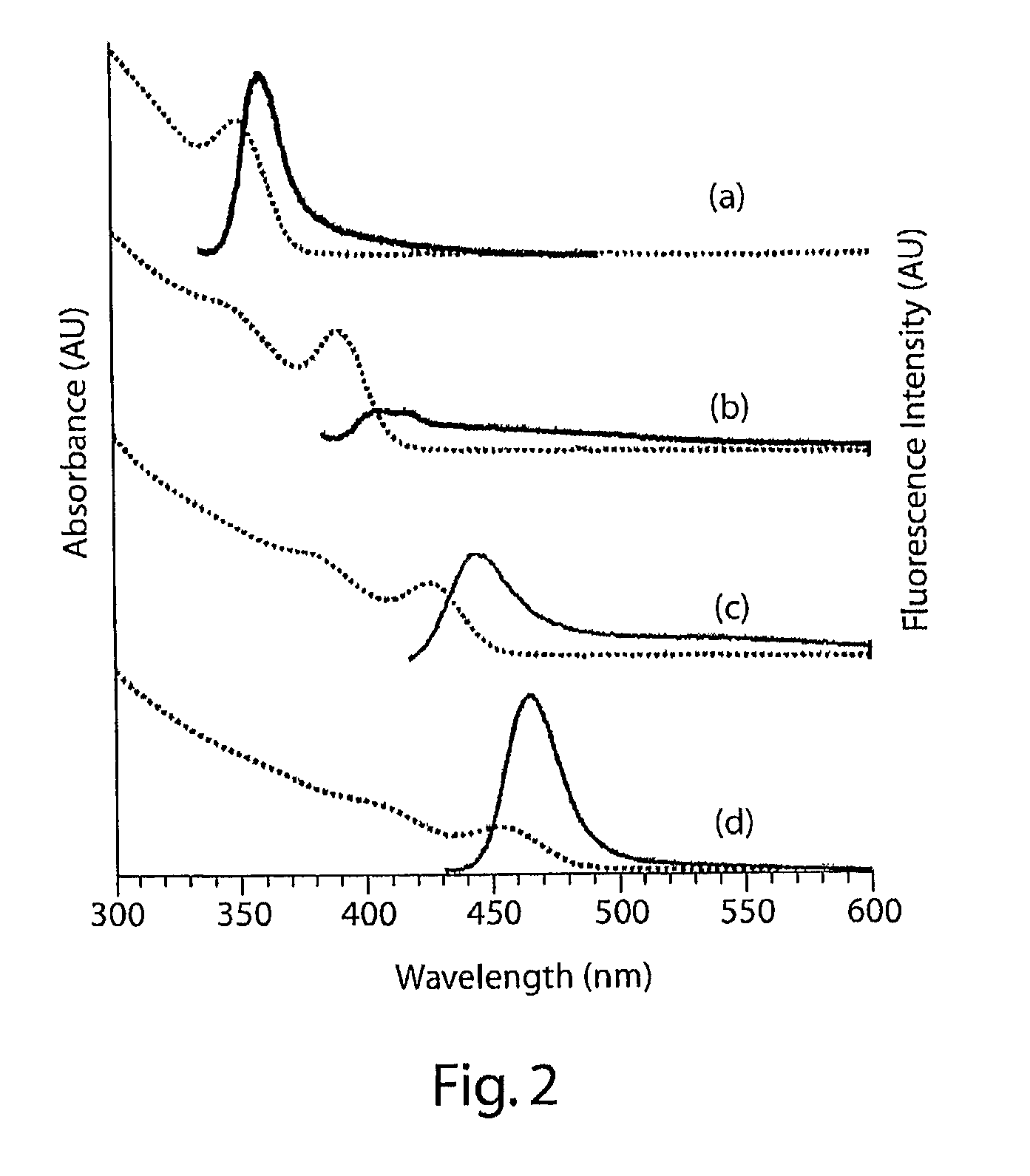
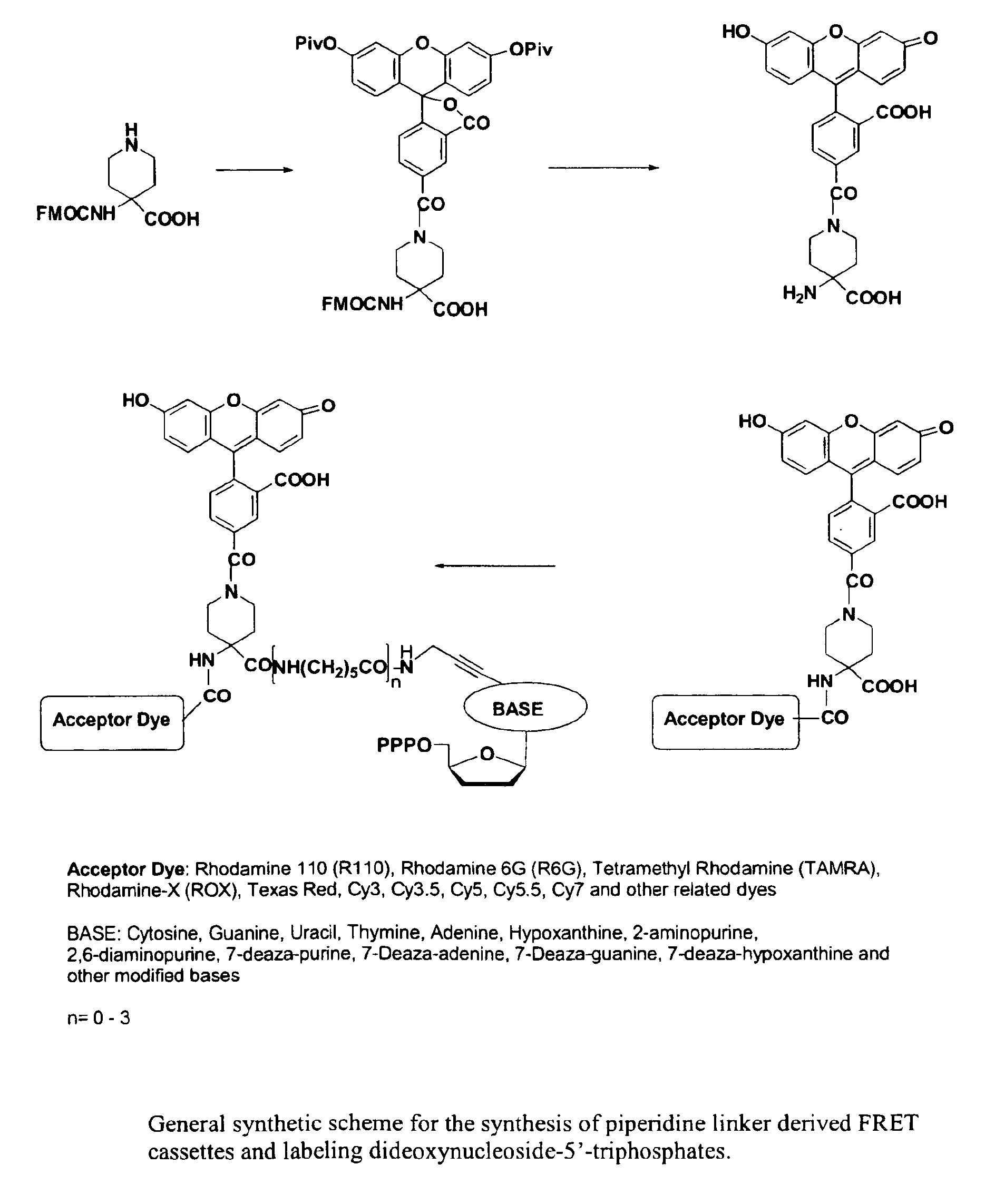
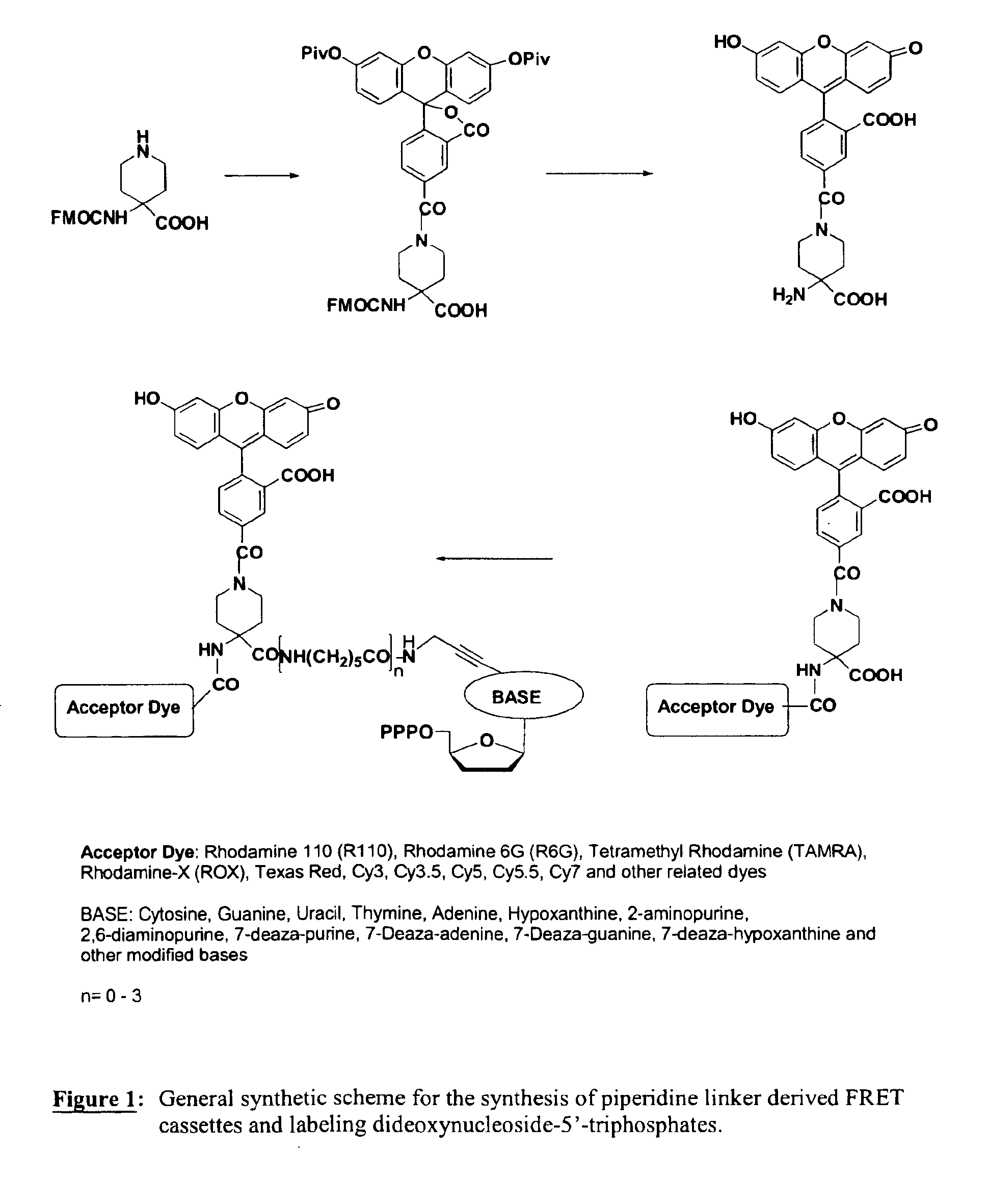
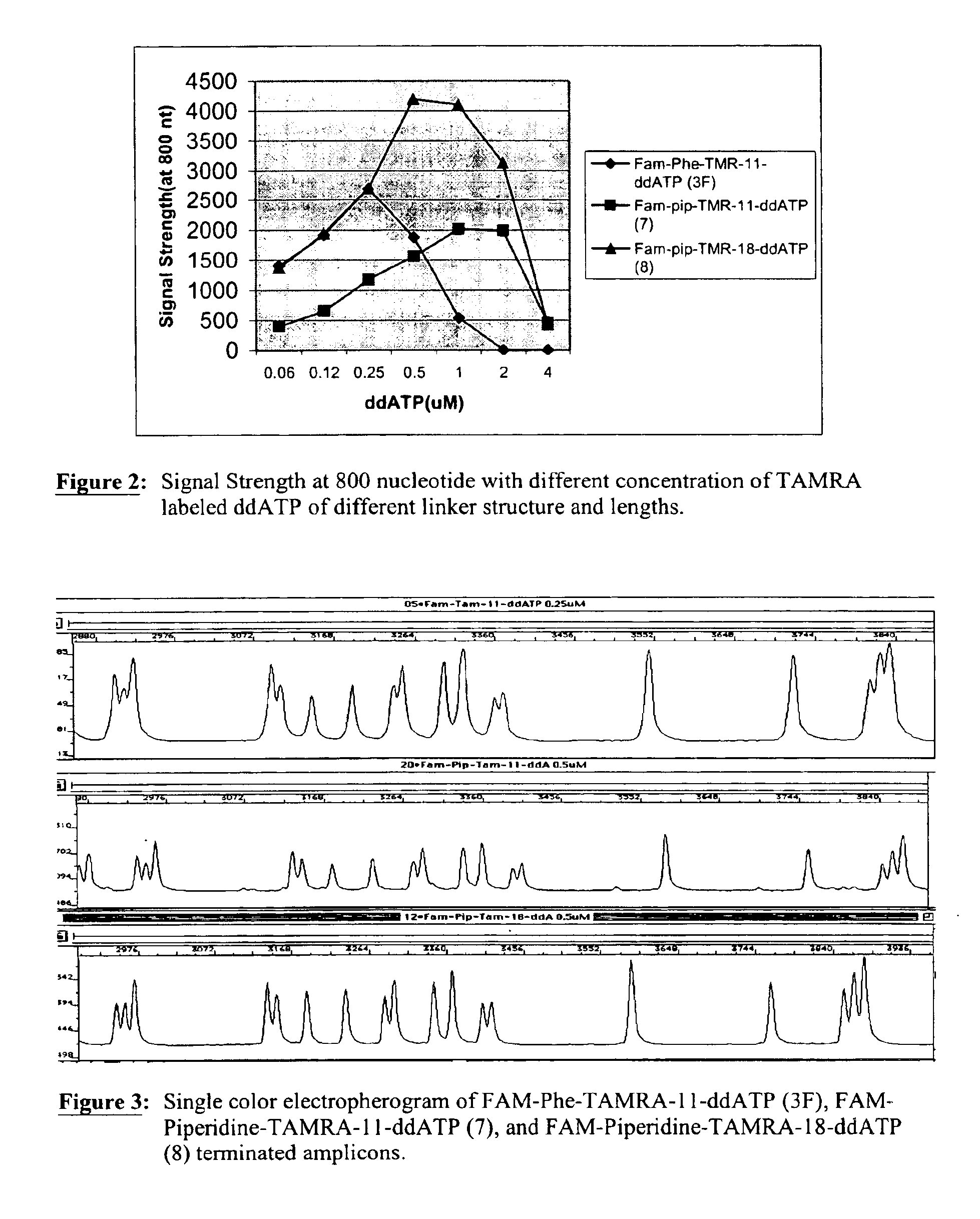
Heterocyclic FRETdye cassettes for labeling biological molecules and their use in DNA sequencing
InactiveUS6855503B2Methine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesEnergy transferDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
Exploitation of suitably functionalized heterocyclic molecules, in the design and synthesis of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) cassettes and their corresponding dideoxynucleotide terminators culminated into efficient reagents for DNA sequencing. Additionally, these FRET cassettes / terminators, of the present invention, derived from different classes of heterocyclic systems have high potential to be used for general labelling of biological molecules to generate highly sensitized signals. Their preparation, energy transfer efficiency, and use as labels, specifically, in DNA sequencing reactions is disclosed.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
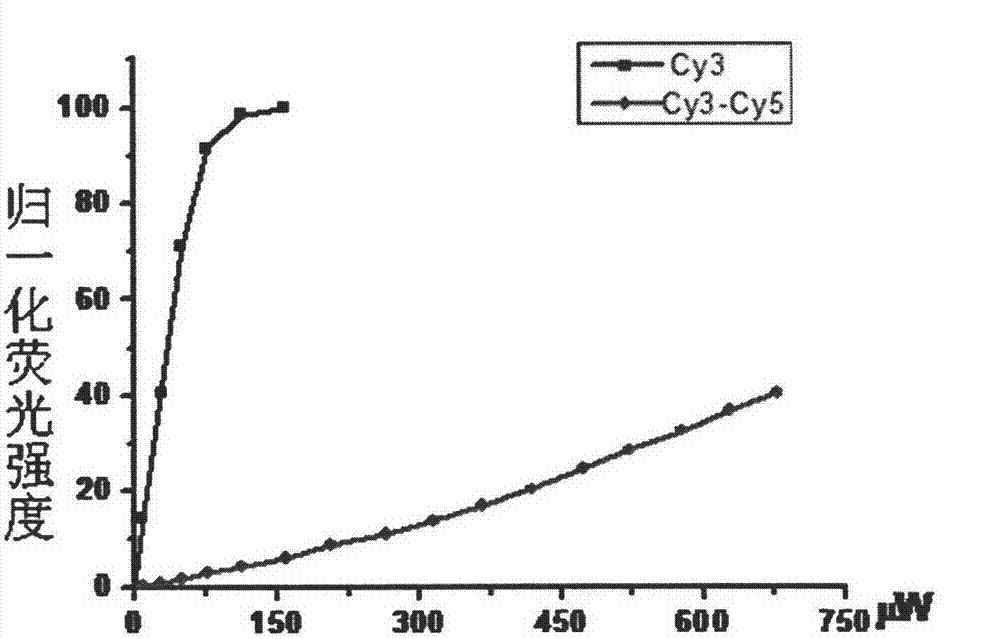
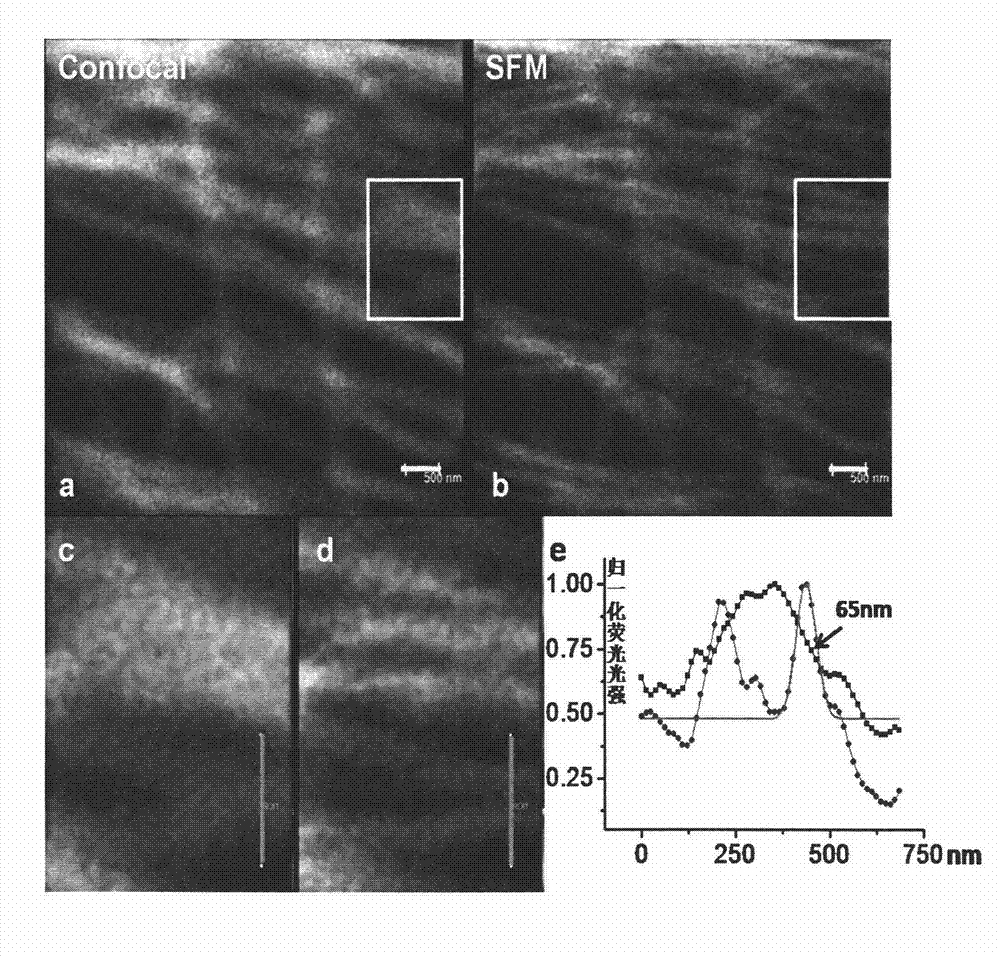
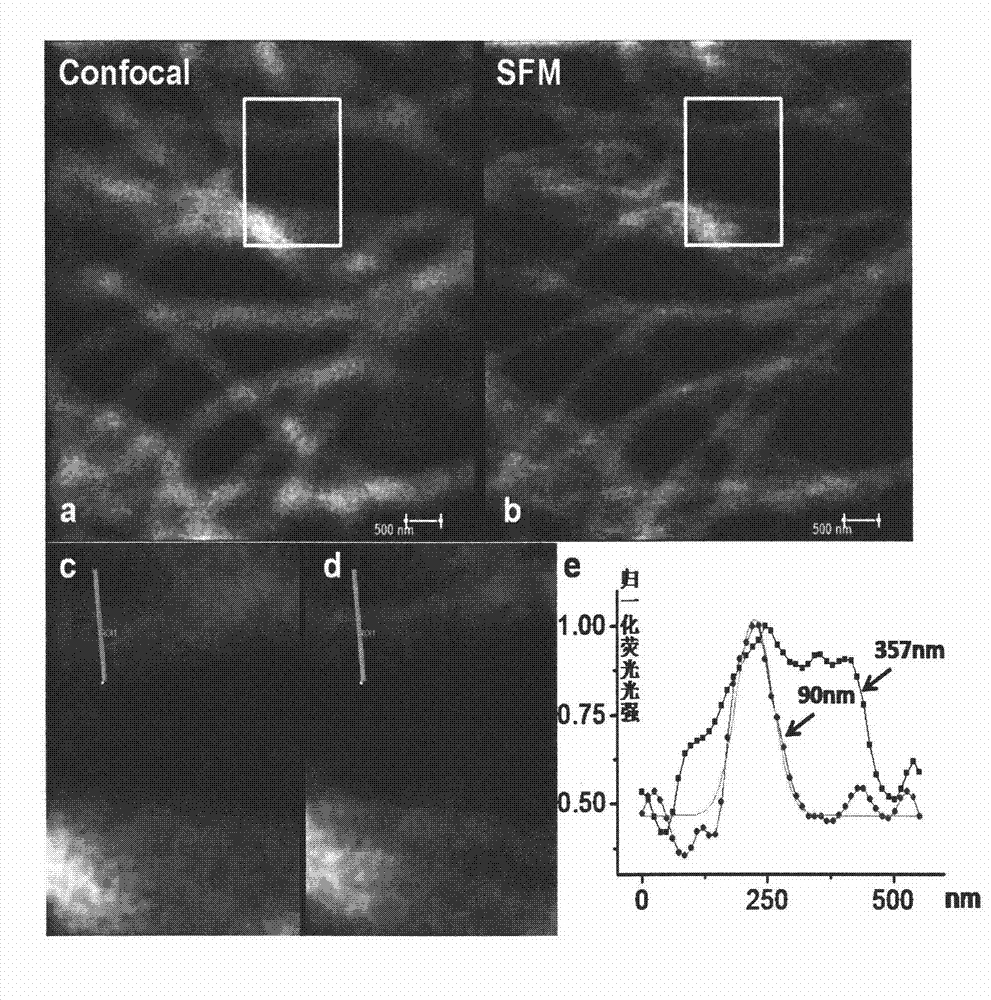
Super-resolution imaging method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
ActiveCN102830101ASuper-resolution imaging methods are fastSuper-resolution imaging method is simpleMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminous intensityLaser scanning
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). The super-resolution imaging method comprises the following steps: 1) marking a sample to be detected with a fluorescent probe having high FRET efficiency, wherein the fluorescent probe having high FRET efficiency has a marked FRET molecule pair, the FRET molecule pair includes a first fluorophore (a donor) and a second fluorophore (a receptor), and the first fluorophore can exert FRET on the second fluorophore; and 2) carrying out laser scanning confocal microscope imaging at an excitation light threshold with an excitation light intensity capable of allowing the FRET molecule pair in the step 1) to generate FRET. A super resolution technology based on saturated FRET in the invention can realize super resolution imaging of a biological sample on an ordinary laser confocal microscope, and the method provided by the invention has high resolution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com